Stars and Nebulas
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
white dwarfs.
Stars that have masses similar to the S7n’s, and size similar to the Earth are:
DNA
Which of the following has NOT yet been observed in space?
10 billions years
What is the typical main sequence lifetime of a G-type star?
starlight scattered by dust particles.
A reflection nebula is caused by:
A trillion years.
What is the typical main sequence lifetime of an M-type star?
Nebula.
A “fuzzy” dark or light patch in the sky is called a:
90% hydrogen, 9% helium by weight.
Interstellar gas is composed of:
stars in that region are hidden by dark dust particles.
Some regions along the plane of the Milky Way appear dark because:
primarily in dense dust clouds.
Complex molecules in the interstellar medium are found:
this indicates where a star will spend the majority of its life.
What does it mean when a star is in the Main Sequence?
Luminosity and surface temperature
What are the two most important intrinsic properties used to classify stars?
blue-white-yellow-orange-red
What is the correct order of color of light emitted by stars from hottest to coolest?
.01 to 100 masses
In what range of masses are most stars found?
Stars.
The spectra of interstellar gas clouds show that they have the same basic composition as
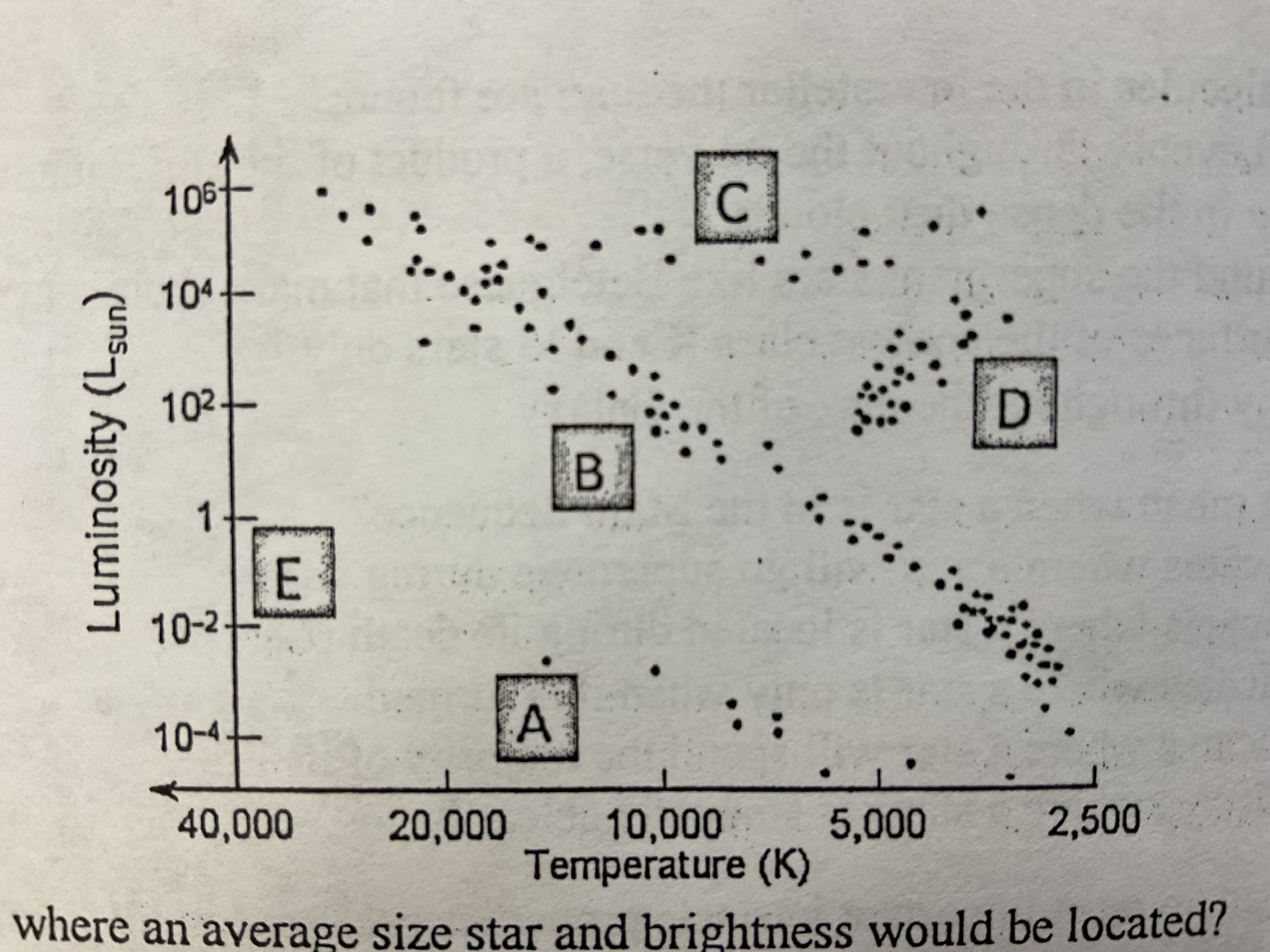
B
Which location shows where an average size stars and brightness would be located?
White dwarf
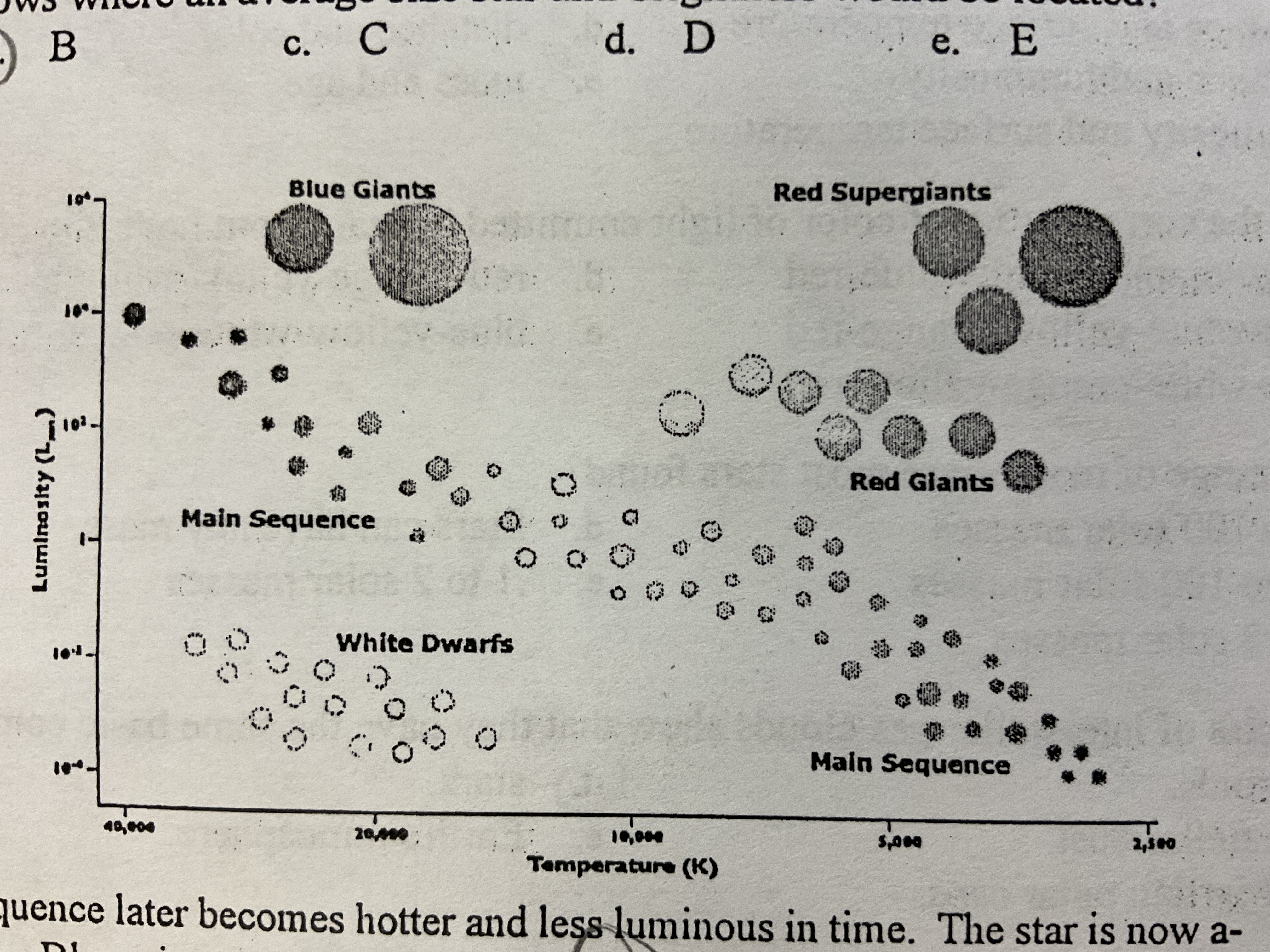
A star in the main sequence later becomes hotter and less luminous in time. The star is now a-
A magnetar
A type of neutron star with immense magnetic fields is known as-
Clear
Which of the following is not a type of nebula?
between the Red Giant and White Dwarf phase.
At what point in the star life cycle is the Planetary Nebula found?
Failed stars that are unable to fuse Hydrogen are-
Brown dwarfs.