Biology I Chapters 1-3 Exam
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Cohesion
The tendency of molecules of the same kind to stick together.
Adhesion
The tendency of two separate kinds of molecules to stick together.
Acid
A substance that donates hydrogen atoms to a solution, has a lower pH
Base
A substance that reduces the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution.
Aqueous Solution
A solution in which water is the solvent.
Solvent
The dissolving agent (ex. water).
Salt
A synonym for an ionic compound, often exists as crystals.
Hypothesis
Evidence based inquiry used to investigate the natural world, can be tested by humans.
Non polar
A molecule that doesn’t have a distinct positive or negative end, the charge is evenly distributed. Electrons are shared equally.
Transcription
DNA is transcribed into RNA, the RNA is a copy of the DNA as that doesn’t leave the nucleus, it’s called messenger RNA (mRNA).
Starch
A storage polysaccharide, a long chain of sugar units.
Translation
Translates RNA into an amino acid chain, which makes a protein, the mRNA is read by rRNA which is located in the ribosomes.
Trans Fat
Unsaturated fats that have been converted to saturated fats by adding hydrogen, associated with health risks.
Collagen
Primary building block for skin, muscles, bones, tendons and ligaments. Proteins that are composed of the amino acids proline, glycine and hydroxypoline.
Polypeptide
Amino acids that are linked by a dehydration reaction, creating a peptide bond and forming a chain.
Saturated Fat
Have no double bonds and have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom.
Chitin
a component of insect exoskeletons and fungal cell walls, it’s a polysaccharide which is a long chain of sugar units.
Hydrophilic
“Water loving”, a molecule or substance that has a strong affinity for water, readily dissolving or interacting with it due to its polar nature. Contains charges/partial charges that allow it to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Polar
A molecule where one end has a slightly positive charge and the other end has a slightly negative charge. Electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom.
Hydrophopic
A property of molecules that don’t mix with water, lipids are hydrophobic
What are the 3 domains of life?
Bacteria, archaea and eukarya.
Bacteria
Very common and can be found on many surfaces, prokaryotic.
Archaea
Found in hot springs, hard to find, produces proteins, prokaryote.
Eukarya
Includes the kingdoms fungi, plantae and animalia, made up of eukaryotes.
What are the 7 characteristics of life?
Reproduction, growth and development, response to stimuli, order, energy processing, regulation and evolutionary adaptation.
Levels of organization in organisms from simplest to most complex
Atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems, biosphere.
Taxonomic Hierarchy (broad-specific)
Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species.
Evolution
Process of change that transforms life on earth, the cause for unity and diversity of the living world (determined by what gets passed on).
Producer
Takes sunlight and converts it into chemical energy.
Consumer
Consumes producers to gain energy, the energy exits the consumer as heat.
Independent Variable
The factor that is manipulated, it isn’t changed by the other variables being measured.
Dependent Variable
Measure used to judge the outcome of an experiment, depends on the manipulated variable.
Control Group
A group or condition that remains unchanged and serves as a baseline for comparison. Demonstrates the effect of a single variable.
Primary Structure
The sequence of amino acids in its polypeptide chain.
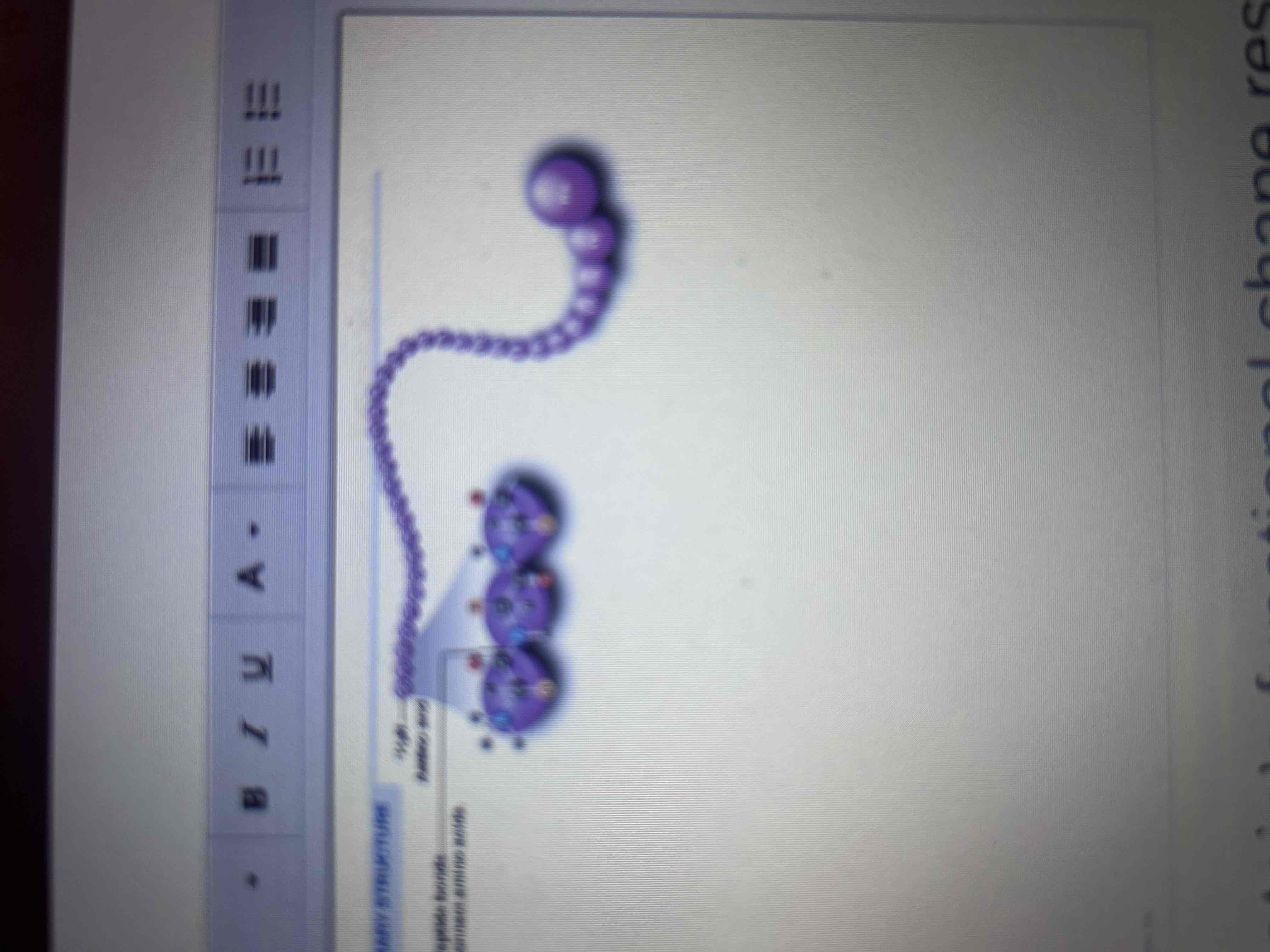
Secondary Structure
The coiling or folding of the chain, stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
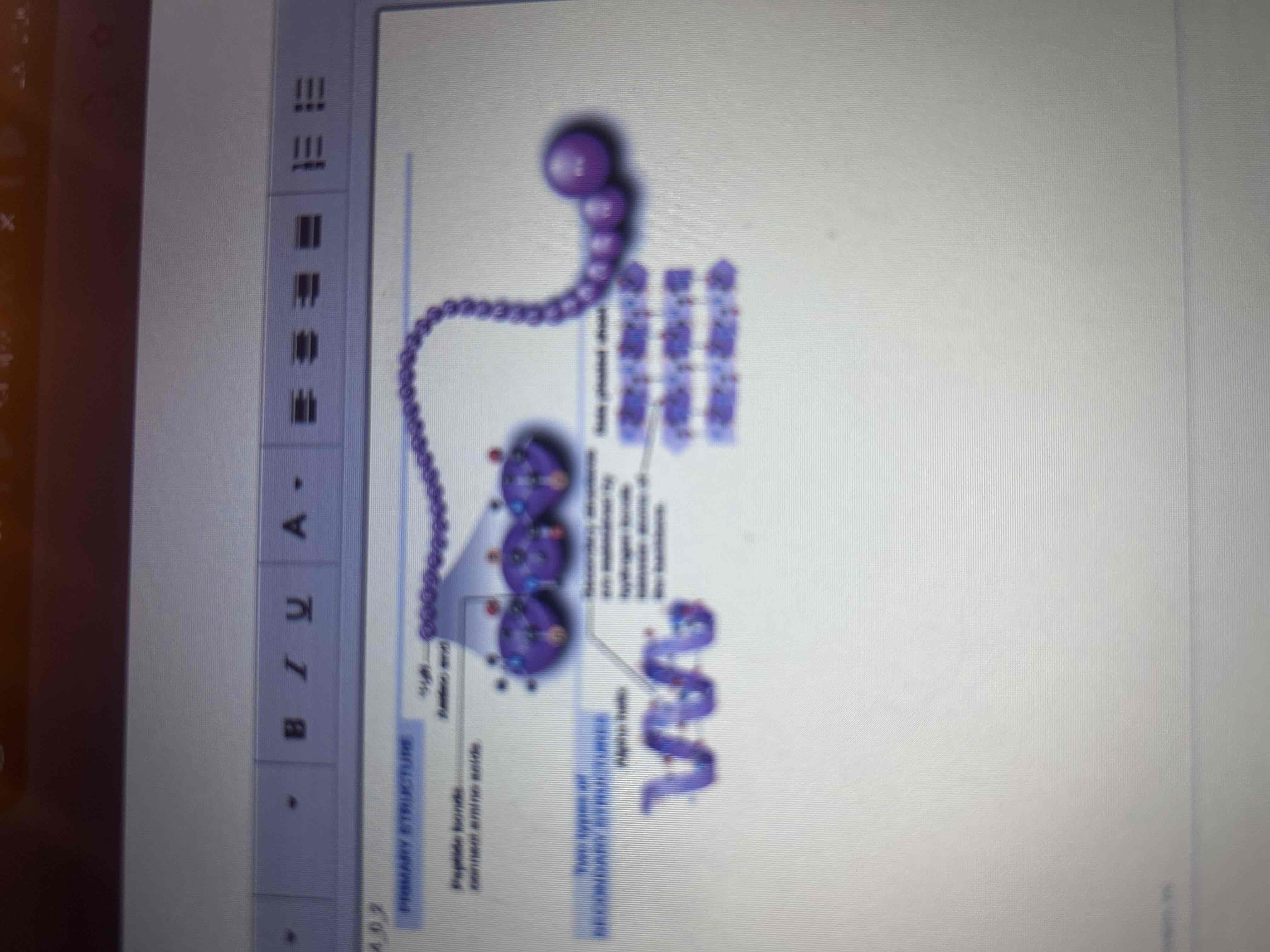
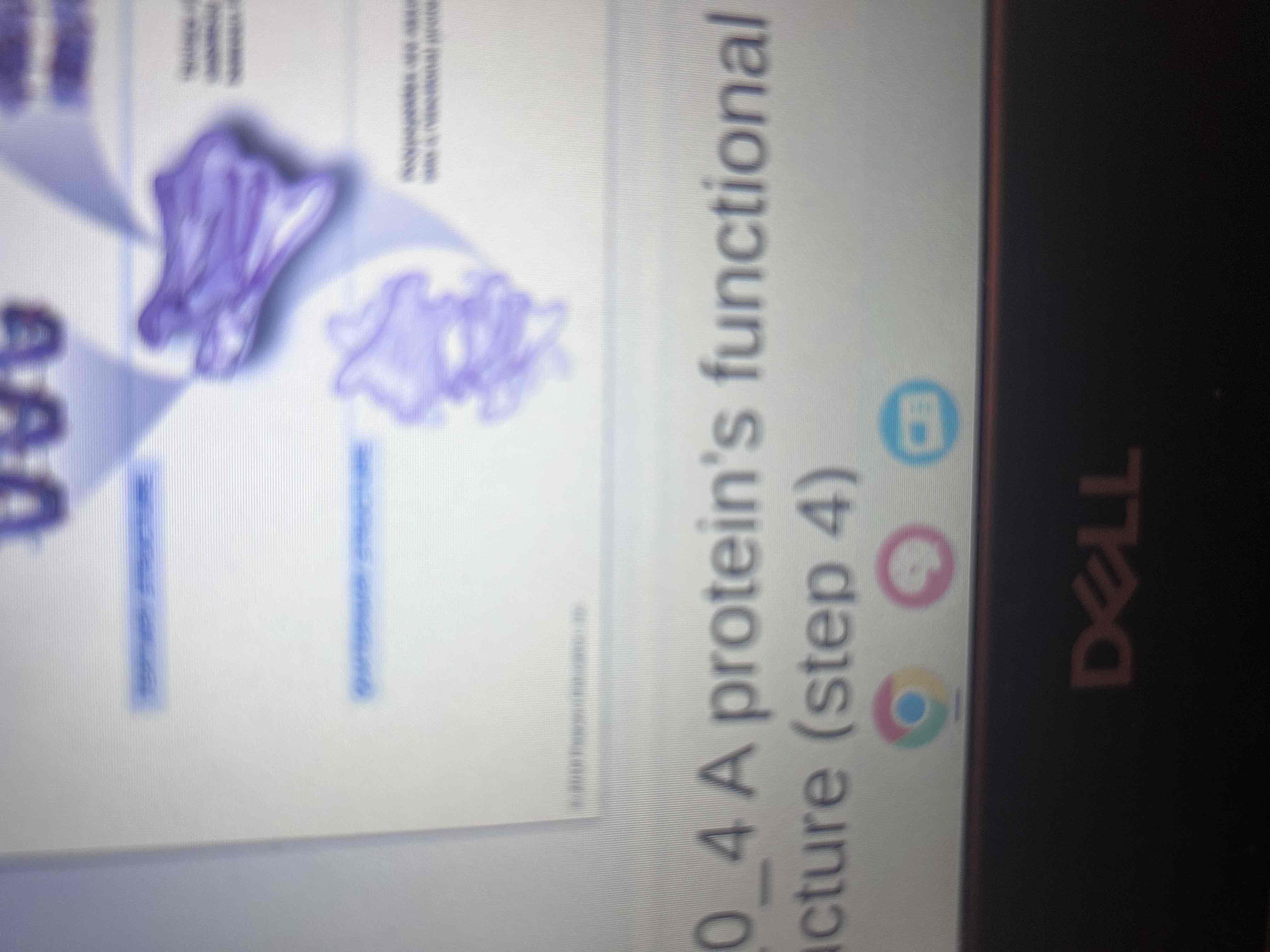
Tertiary Structure
The overall three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide, resulting from interactions among R groups.

Quaternary Structure
Proteins made of more than one polypeptide.
Specific Heat
The specific heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of substance 1 degree Celsius.
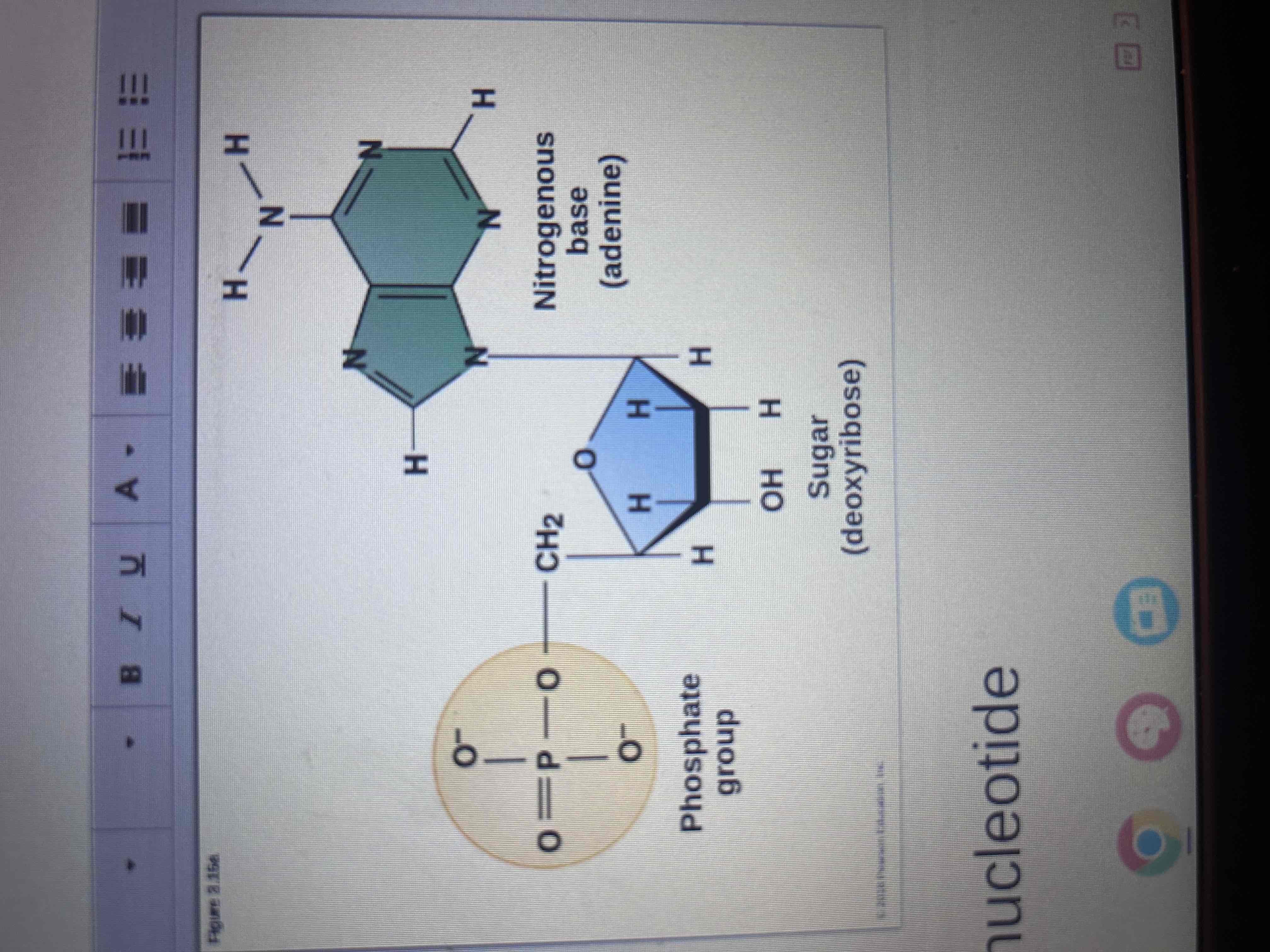
Parts of a nucleotide
Phosphate group, sugar and nitrogenous base.
Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
Lipids
Glycerol and fatty acids
Proteins
Amino acids
Nucleic Acids
Nucleotides
Dehydration Synthesis
Removes a molecule of water as two molecules become bonded together, cells linking monomers together to form polymers.
Covalent Bond
Atoms share electrons.
Ionic Bond
The attraction of two opposite charges holds ions together.
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak bond that holds water together.
Ion
Atom or molecule with an electrical charge resulting from the gain/loss of one or more electron.
Isotope
Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
Where are carbohydrates found?
Small sugar molecules, examples are starch, glycogen, cellulose (plant cell walls) and chitin (insect exoskeletons and fungal cell walls).
Where are lipids found?
Phospholipids (cell membrane), steroids (cholesterol), cholesterol (animal membranes and sex hormones).
Where are amino acids found?
DNA and RNA.
Dogma of biology
Genetic information flows in one direction, from DNA to RNA to protein.
Arm
Supports the body tube and lenses. Use it to carry microscope.
Base
Supports the entire microscope. Broad and heavy, the base give the instrument stability.
Ocular Lens/Eyepiece
In the upper part of the microscope, monocular microscopes have one, binocular microscopes have two.
Body Tube
Holds the ocular at one end and the nosepiece at the other, a prism reflects light to the naked eye.
Reviving Nose Piece/Turret
Located at lower end of body tube, revolving device that holds objectives.