SSD dose calculations week 5
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Why is it important to understand the factors that affect radiation treatment delivery?
• Wrong settings = Too much or too little radiation → Bad for the patient!
factors include field size, beam energy, and things in the beam’s path (like trays, wedges, and compensators).
• Tiny mistakes = Big dose changes
Using the right dose rate, scatter factors, and absorption factors keeps treatment safe and accurate.
how tissue absorbs radiation
Dose delivery type: photon beam radiotherapy is carried out under two set up conventions
Constnce source surface distance- SSD
Or isocentric source axis distance- SAD
Non isocentric
Not established at axis of the beam
SSD = Source-to-Skin Distance
You keep the distance from the machine to the patient’s skin the same for every beam.
This means:
The patient may need to be moved for different beam angles.
The isocenter is placed on the skin, not inside the body.
You still deliver dose to a certain depth—just calculated differently.
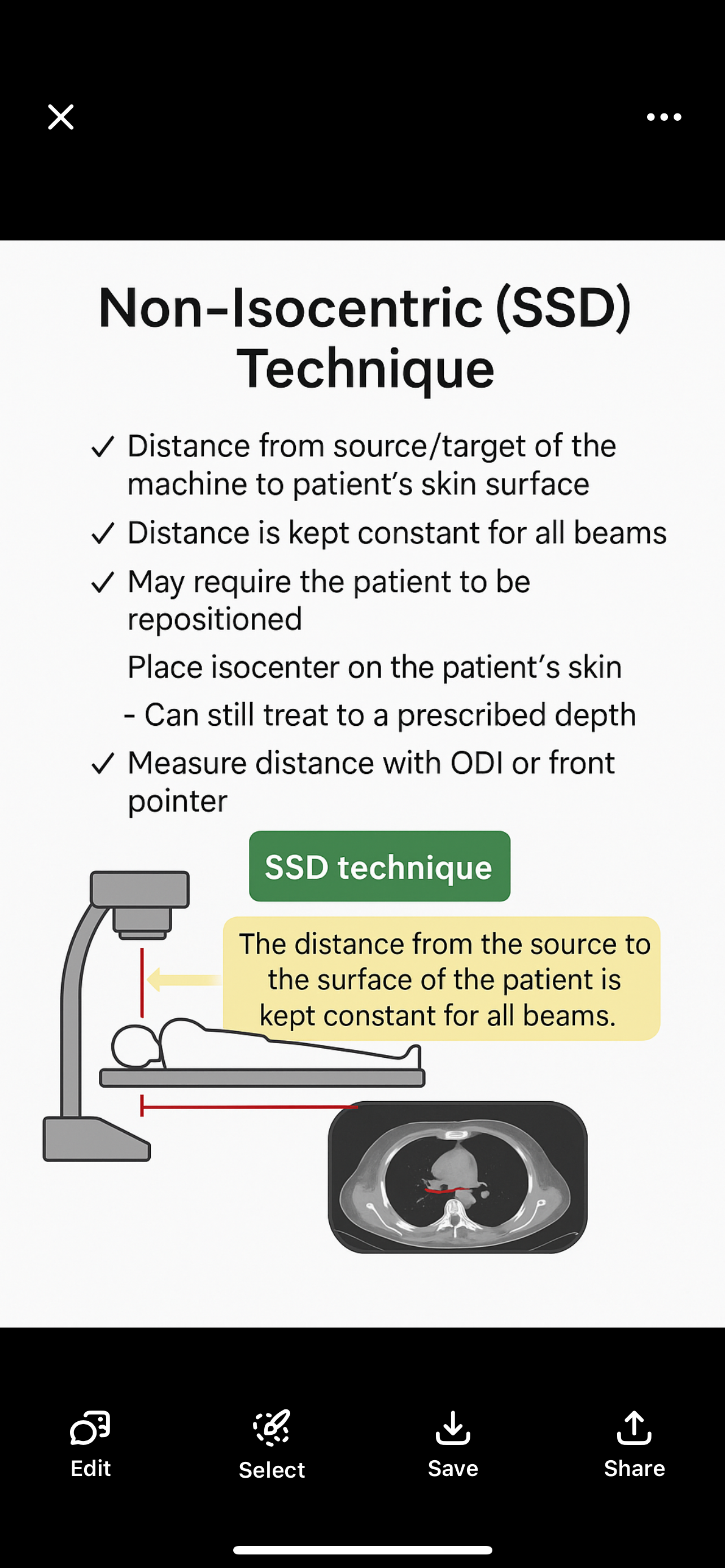
SSD (Non-Isocentric) Technique – When to Use It
Use SSD setup for:
Electrons – always use SSD.
Shallow tumors (superficial treatments).
Emergencies – faster setup.
Single beams (like AP chest field).
When distance needs to be longer (extended SSD). designed around surface distance, not an internal point (like SAD/isocenter techniques).
What do Mus represent
like a gas pump for radiation therapy!
⏺ MUs = The setting on a linear accelerator.
⏺ They control how much radiation is given.
⏺ Ensure the correct dose reaches the patient.
⏺ Adjust for dose rate and treatment conditions.
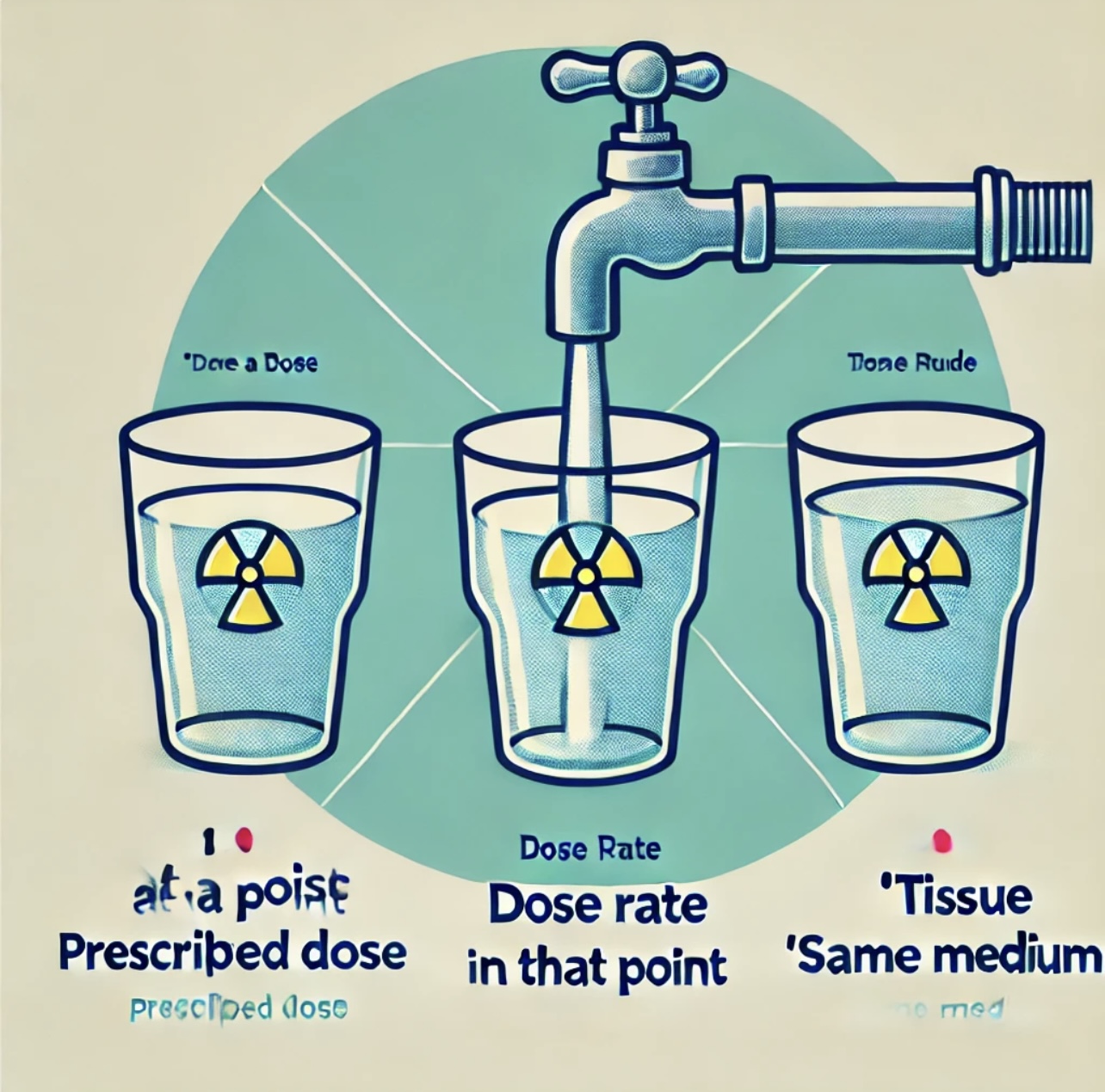
State the three points that are needed for a treatment (dose) calculation.
Think of it like filling a glass of water:
1. Dose at a Point – How much water you need (prescribed radiation dose).
2. Dose Rate at That Point – How fast the faucet flows (rate of radiation delivery).
3. Same Medium – Make sure it’s the right glass (dose and dose rate must be in tissue).
Describe a SSD/Nonisocentric treatment
• Fixed Distance: 80 cm (Cobalt-60), 100 cm (Linac)
• Non-Isocentric: Beam stops at skin, not deep inside.
• Field Size: Measured on the skin, not internally.
• Uses PDD (Percent Depth Dose) for dose calculation.
• Good for superficial tumors & skin treatments.
From a calculation standpoint, what is a disadvantage to SSD treatments?
1. Distance Changes? Extra Math!
• If SSD isn’t exactly 100 cm, PDD must be recalculated.
2. Needs More Corrections!
• Mayneord Factor adjusts PDD for different SSDs.
• Inverse Square Correction adjusts for dose rate changes.
3. More Calculations = More Work!
• SSD treatments require extra steps if the setup isn’t perfect.
When is Extended Distance Treatment Needed?
For Large Fields – Covers a bigger treatment area.
✔ When You Can’t Get Close – Physical obstacles in the way.
✔ Useful for Whole-Body or Large Tumor Treatments.
Tissue Absorption Factors – What You Use Depends on the Setup
If you’re using SSD (Non-Isocentric):
Use PDD (Percent Depth Dose)
Based on distance from the skin.
If you’re using SAD (Isocentric):
Use TAR, TMR, or TPR
Based on distance from a point inside the body (isocenter).
No need to keep SSD constant.