CompSci - Communication and Networking
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Define Symbol.
Particular pattern of bits represented by a signal.
Define Baud Rate
Number of signal changes in the medium per second.
Define Bit Rate.
Number of bits transmitted over medium per second, measured in bps *bits per second
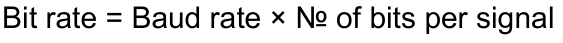
Define Bandwidth
Bandwidth is the range of frequencies that can be transmitted through the medium.
Direct relationship between Bandwidth and Bit rate.
Latency? Increases with?
Difference in time between an action being initiated and an event taking notice, often measured in ms.
Latency usually increases with distance.
What is a protocol?
Set of rules for communication between devices.
Usally set internationally so that all devices can communicate around the world.
How can computers transmit their data?
Serially, or parallel.
What is S____ Data Transmission?
Data sent one bit at a time
usually over metal wire or optical fibre/wireless channel
medium → long distances (e.g. keyboard → mouse)
What is P______ Data Transmission? What is important to remember about this?
Numerous parallel communication lines that send multiple bits of data simultaneously.
The different comm lines can have different electrical properties which means signals travel through them at different speeds, causing SKEW.
Skew can worsen over longer distances and bits can overlap.
Cross talk (when lines are packed together, signals can leak into another line)
ALL these issues causes corruption of data
Short Distances. (e.g. between components of processor and within RAM)
T or F: Serial Transmission is less expensive than Parallel
T
Advantages of Serial Over parallel?
Doesn’t suffer from skew or crosstalk. → More reliable especially over long distances.
Use just one line → Cheaper + The reason for why it doesn’t suffer issues above.
Synchronous VS Asynchronous
Synchronous:
→ Clock signals
→ Data sent at frequent intervals
→ Useful for Real-Time Systems
→ Used in busses with in FED Cycle
Asynchronous:
→ Start and Stop Bits = Indicate duration of Transmission
→ Start and stop bits are either 0 or 1 and are always opposites of each other
→ Sender and receiver must use same Baud Rate and synchronise clocks for duration of transmission
What is Physical Topology?
Actual architecture of network.
Two Types
→ Star
→ Bus
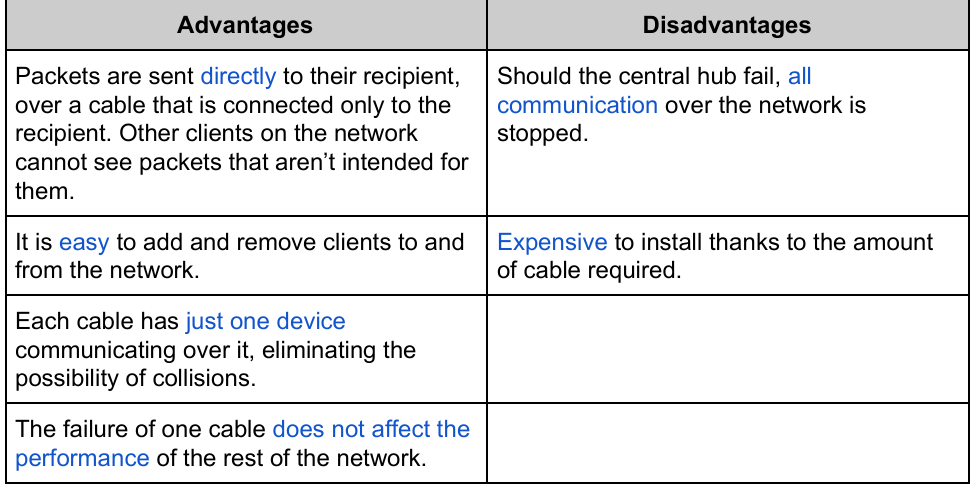
Describe Physical Star network Topology
→ Each client has own connection
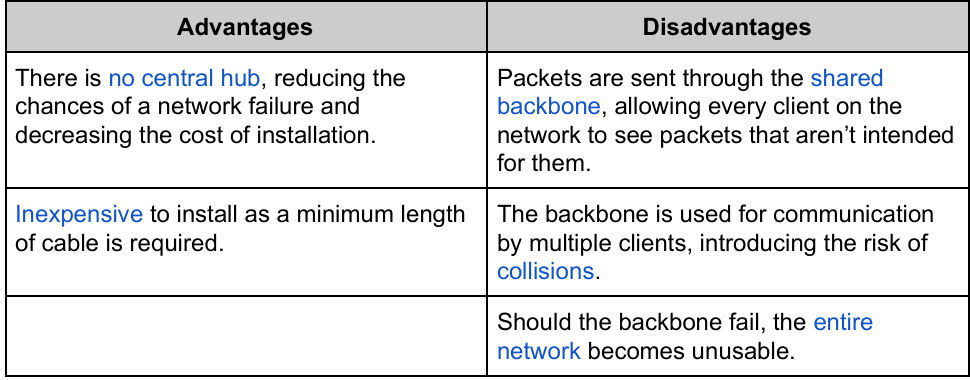
Describe Physical Bus Network Topology.
Connects clients to single cable, called backbone.
Device placed at either end, called terminator.
Thus, no need for a central hub.
What is a logical network topology?
Refers to flow of data packets in a network.
Logical star topology?
Delivers data packets only to recipient.
Logical Bus network.
Delivers data packets to all clients.
What is a host?
Device that provides services: printer sharing, file storage, internet access, e.t.c.
often a server but can be clients themselves.
What can physical topologies do?
They can have a different logical topology.
Explain a client server network. WHat is it used for?
One or more central servers provide services to clients.
Servers are often more powerful machines than clients.
Enables central management → more security BUT requires expertise.
Explain peer-to-peer networking.
Services provided by clients themselves.
All clients providing services MUST be running for network to be operational.
PROS:
Cheaper
Easier to set up
No need for powerful server
What are wireless networks? What does it require?
Allow clients to communicate without being physically connected to network.
Requires:
→ Wireless access point
→ Wireless network adapter
Wifi? How is it secure?
Wireless local area network, based on international standards.
Encrypted by three ways:
WPA (password)
Disabling SSID Broadcast (Stops displaying availability)
MAC address filter (Whitelisted to allow access for specific devices | Blacklists are used to block specific devices).
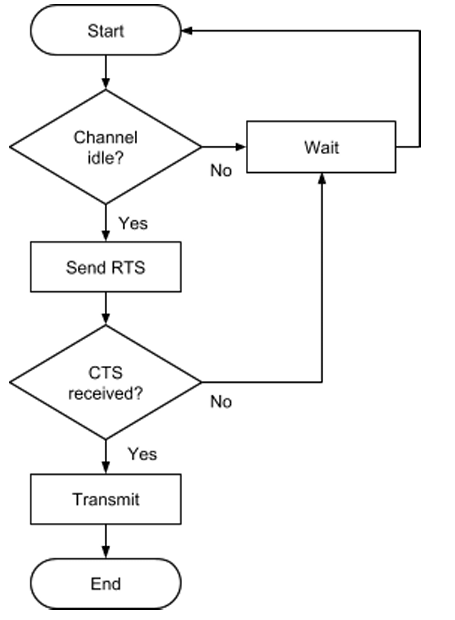
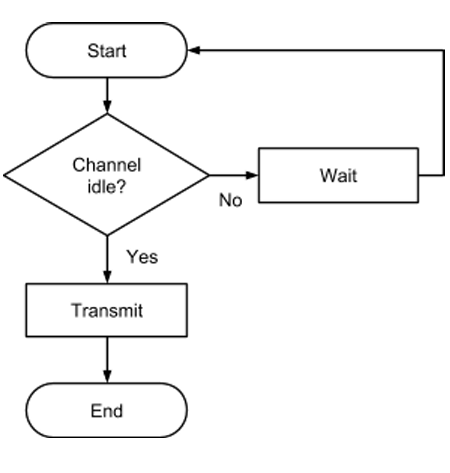
WHat is CSMA/CA? Draw it?
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance
1 - Listens to comms channel to check if it is idel
2 - Can use exponential backoff algorithm to increase waiting time
3 - Stops collisions BUT has HIDDEN NODE problem.
What is an imrpovement to CSMA/CA? Draw it?
RTS/CTS (Request to Send/ Clear to Send)