Rheumatology Diagnostics 10/1/25
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards related to key terms and concepts from rheumatology diagnostics lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Histochemistry
A technique used for the differential staining of cells and tissues based on the chemical differences of their parts.
Immunofluorescence
A technique that uses fluorescent dye to identify specific antigens or proteins in a cell or tissue sample.
Ex) ANA testing via indirect immunofluorescence
Acute Phase Reactants
Substances whose levels increase in response to inflammation, associated with infections, trauma, and autoimmune diseases. (acute and chronic inflammatory states)
acute phase reactant labs
ESR, CRP, ferritin
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
Rate at which erythrocytes suspend in plasma fall when placed in a vertical tube.
Units: mm/hr
Nonspecific test
If elevated:
• Systemic and localized inflammatory or infectious disease
• Malignant neoplasms
• Tissue injury/ ischemia
• Trauma
If decreased:
Technical factors: Clotting of sample, Delay in testing > 2hrs, Room temperature
C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
Nonspecific acute phase reactant used to indicate inflammatory illness
Units: mg/dL
More sensitive and rapidly responding indicator than ESR
• Increases first and fastest
• Usually returns to normal quicker
• ↓ when inflammatory process suppressed by anti-inflammatory agents
Elevated
• Acute, noninfectious inflammatory reaction → Rheumatoid arthritis, Reiter syndrome
• Collagen or vascular disease → Vasculitis syndromes, Lupus
• Bacterial infection
• Malignancy
Ferritin
• Can be elevated in conditions not reflecting iron stores
• Elevation occurs 1-2 days after onset of acute illness and level peaks 3-5 days
Units: ng/mL
Elevated
• Juvenile idiopathic rheumatoid arthritis
• Infections
• Lymphoma
• Metastatic disease
schirmer test
tests tear deficiency (how moist is the eye, measures reflex tear production)
Folded sterile filter paper placed over the margin of each lower eyelid (At the junction of the middle and lateral thirds)
→ Patient gently closes eyes and waits 5 minutes
→ Wetting of < 5mm is indicative of aqueous tear deficiency
Positive can help diagnose Sjogrens syndrome
age is limitation (older → drier)
salivary flow study
measures saliva production rate
Patient asked to expectorate once and then collect all saliva into a pre-weighed container
→ After 5-15 minutes, collection vial re-weighed
→ Volume of saliva is calculated
→ Collection of ≤ 0.1mL/min is indicative of abnormal salivary function
Postive can help diagnose sjogrens syndrome
age is limitation (older → drier)
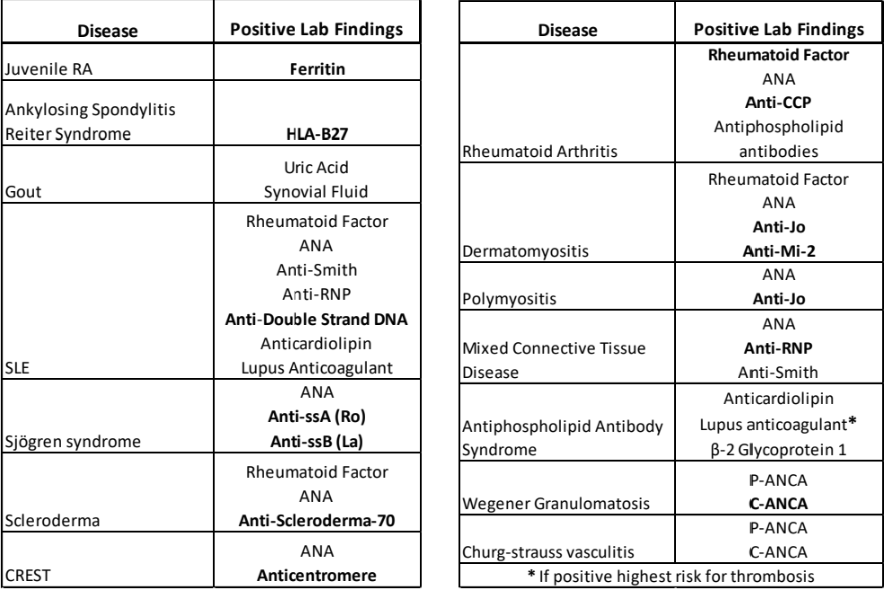
Rheumatologic lab testing options
• ESR
• CRP
• Ferritin
• Uric Acid
• HLA-B27
• Rheumatoid Factor
• ANA
• AnH-CCP anHbodies
• ANCA : Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody
• Antiphospholipid Antibodies : Anticyclic-Citrullinated peptide antibodies
Uric Acid
A serum test that evaluates the level of uric acid in the blood
Units: mg/dL
Elevated (Hyperuricemia)
• Gout
• Serum urate > 6.8mg/dL = Diagnostic
• Above this^^, threshold crystals may deposit in joints and soft tissue
• Therapeutic target range < 6.0mg/dL
Diagnostic serum urate level for gout
> 6.8 mg/dL
Above this, crystals may deposit in joints/tissues
therapeutic target range for serum urate after gout
< 6.0 mg/dL
Human Lymphocyte Antigen (HLA-B27)
A serum test for specific antigens that is associated with certain autoimmune diseases. Should be negative.
Positive: may indicate ankylosing spondylitis (MC), reiter syndrome, anterior uveitis, graves disease
Rheumatoid Factor (RF)
A serum test used in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis, poor specificity.
Units: units/mL
Rheumatoid arthritis: 26-90%
Sjögrens syndrome: 75-95%
Mixed connective tissue disease: 50-60%
Systemic lupus erythematous: 15-35%
Polymyositis or Dermatomyositis: 5-10%
Non rheumatic disease: varies
Anti-CCP Antibodies
Anticyclic-Citrullinated peptide antibodies
Antibodies that indicate rheumatoid arthritis, especially when RF is negative and pt has unexplained joint inflammation.
units: units/mL
Elevated = rheumatoid arthritis
Patients with early RA (30-40%) may have a normal Anti-CCP
associate antiCCP with ___
rheumatoid arthritis
Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)
Antibodies directed against cytoplasmic components of neutrophils
Detected via immunofluorescence staining
2 main patterns:
• P-ANCA
• C-ANCA → 95-99% specific for Wegeners granulamatosis
Indications
• Evaluate for Wegener Granulomatosis
• Follow course of disease
• Monitor response to therapy
Antinuclear Antibody (ANA)
A group of proteins that react against cellular nuclear material, used to diagnose autoimmune diseases.
Reported as dilution, negative at 1:40
Sensitive but not specific
Indications: suspect autoimmune disease
Positive test: Must perform additional antibody testing to corroborate diagnosis
False negative can occur is pt is on steroids
ANA disease percentages
Systemic lupus erythematosus: 95%
Progressive systemic sclerosis (Scleroderma): 70%
Sjögren syndrome: 60%
Rheumatoid arthritis: 30%
Dermatomyositis: 30%
Polyarteritis: 10%
syphilis
causes false positive antiphospholipid antibodies
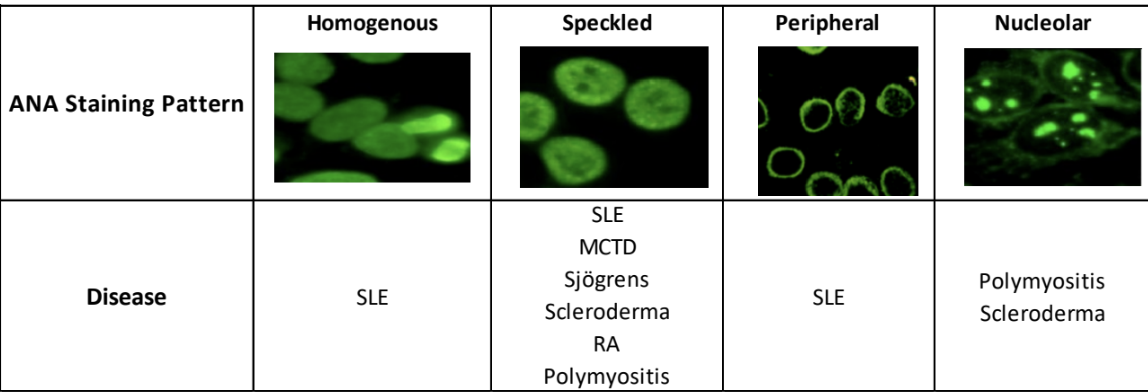
ANA patterns
Homogenous : Lupus
Peripheral : Lupus
Speckled
• Lupus
• Scleroderma
• RA
• Mixed connective tissue
• Sjogren
• Polymyositis
Nucleolar : Scleroderma or Polymyositis
ANA subtypes
• Anti-Smith, AnH-RNP, AnH-Jo
• Anti-ssA(Ro) and AnH-ssB(La)
• Anti-Mi-2
• Anti-scleroderma-70
• Anticentromere
• Anti-Double strand DNA
Anti-Smith, Anti-RNP, Anti-Jo Antibodies
Anti-extractable Nuclear Antigens
Indications
• Assist in diagnosis of SLE and MCTD
• Eliminate other rheumatoid diseases
Results
• Anti-Smith → + 30% pts with SLE
• Anti-RNP → + nearly 100% pts with MCTD
• Anti-Jo → + in autoimmune myositis (polymyositis & dermatomyositis)
Anti-ss A(Ro) and Anti-ss B(La) Antibodies
Anti-extractable nuclear antigens
Indications : Diagnose Sjögrens Syndrome
Produce a speckled immunofluorescent pattern
Anti-ss A(Ro) : 60-70% pts with primary Sjögrens Syndrome
Anti-ss B(La) : 50-60% pts with primary Sjögrens Syndrome
Anti-Mi-2 Antibodies
Produce a speckled ANA staining pattern
Positive
• Dermatomyositis : Typically a more severe form, Increased muscle weakness
Antiphospholipid Antibodies
Antibodies that can indicate antiphospholipid syndrome, associated with thrombotic events.
Subtypes
• Anticardiolipin antibodies
• Anti-beta-2 Glycoprotein 1 antibodies
• Lupus anticoagulant assay
Indications
• 1 or more unexplained venous or arterial thrombotic events
• 1 or more unexplained adverse outcomes in pregnancy
• Patients with lupus
Positive antibodies
• Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
• Lupus at risk
Interfering Factor: Patients who have or had syphilis will have false positive results
Anti-scleroderma-70 Antibodies
Normal = negative
Reported as titer/dilution
Indications
• Suspect Scleroderma
• Monitor therapy effectiveness
Results
• + in 45% of patients with Scleroderma
• Higher titer more likely scleroderma exists and more active disease
• As disease responds to treatment titer should decrease
anticentromere antibodies
Normal = negative
Reported as a dilution above screening titer
Indications
• Concern for CREST syndrome (a Variant of scleroderma)
No correlation between titer and severity of disease
Anti-double strand DNA Antibodies
units: IU/mL
Indications : Diagnosis and follow up of SLE
Results
• Elevated in pts with active Lupus 65-80%
• Titer should ↓ with successful therapy
• Titer should ↑ with exacerbation of SLE
Review table