Integration of systems: Anatomy and Physiology
1/11
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Draw and label the structures of the heart
Be able to draw and identify veins, arteries and capillaries in a cross section. Describe and compare similarities.
Which blood vessels contain valves and why?
veins to prevent backflow of blood due to lack of pressure that is in arteries.
Describe the tissues in each vessel type.
Artery - Outer layer, smooth muscle, elastic layer, inner layer
Vein - outer layer, smooth muscle, inner layer (valves)
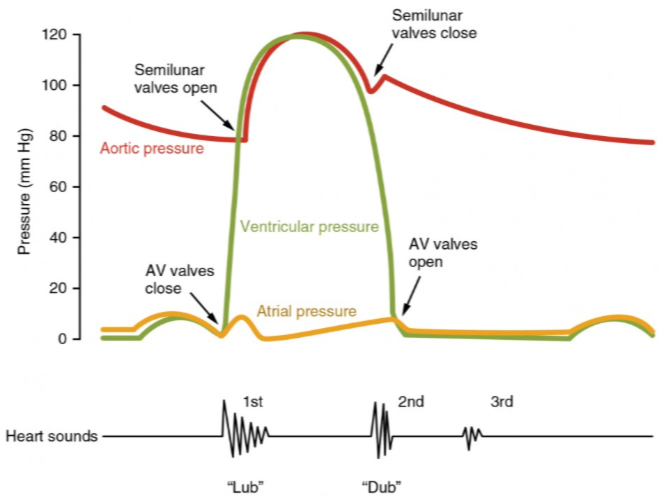
What is a diastole and systole?
Diastole - ventricular filling with blood
Systole - ventricular contraction/ expelling of blood
State the location and function of sinoatrial node and atriventricular node
SA node - creates signals
AV node - conducts signals to heart to cause contractions
both in right atrium walls
How is blood pressure measured?
sphygmomanometer; a device comprised of an inflatable cuff connected to a pressure gauge (generally a column of mercury). inflates to match pressure of arm
What are the 2 types of circuits that blood travels through in the body?
Pulmonary circuit - short, from heart to lung to heart
Systemic circulation - heart to rest of body
What is the cause and consequence of coronary occlusion?
Cause - CHloesteral deposits/plaque
Consequence - blockage leads to chest pain, shortness of breath, even heart attacks
What is the effect of epinephrine on the heart? Where is it produced/secreted? When is it released?
Effect - increased heart rate
Location of production/secretion - Adenal gland
Released when: Stress/ amygdala hyjack
What are some factors that stimulate the heart rate to increase? Decrease? What is the control mechanism of heart rate in the brain?
Increase - Stress, caffeine, meds, lack of sleep
Decrease - Hypothroidsim, meds, heart condtions
Control - SNS and PNS
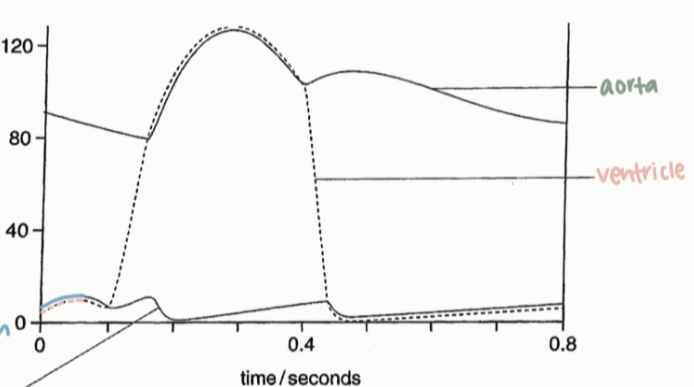
Read a graph of the cardiac cycle. Identify atrial contraction, opening of AV valves, closing of AV valves, ventricular contraction opening of semi lunar valves, closing of semi-liner valves