Nervous System
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
brain and spinal cord
spinal and cranial nerves
What does the CNS include? PNS?
posterior longitudinal ligament (anterior prevents excessive extension)
what ligament prevents excessive flexion of the spine
intertransverse
what ligament prevents excessive lateral flexion and rotation
brain and spinal cord
what does the meninges surround
dura
arachnoid
pia
superficial to deep: meninges
dura mater in subdural space
where would an epidural get inserted
cerebrospinal fluid
what is inside the subarachnoid space in the arachnoid mater
more roots that go off to limbs
why is it called the cervical and lumbar enlargement
lumbar
the conus medullaris tapers the spinal cord in start of what region
cauda equina
“horse tail”
filum terminale
secures cauda to the coccyx and is an extension of the pia mater that anchors the spine in place
denticulate ligaments
extensions of pia mater that secure the spinal cord to the dura mater
nuclei
1
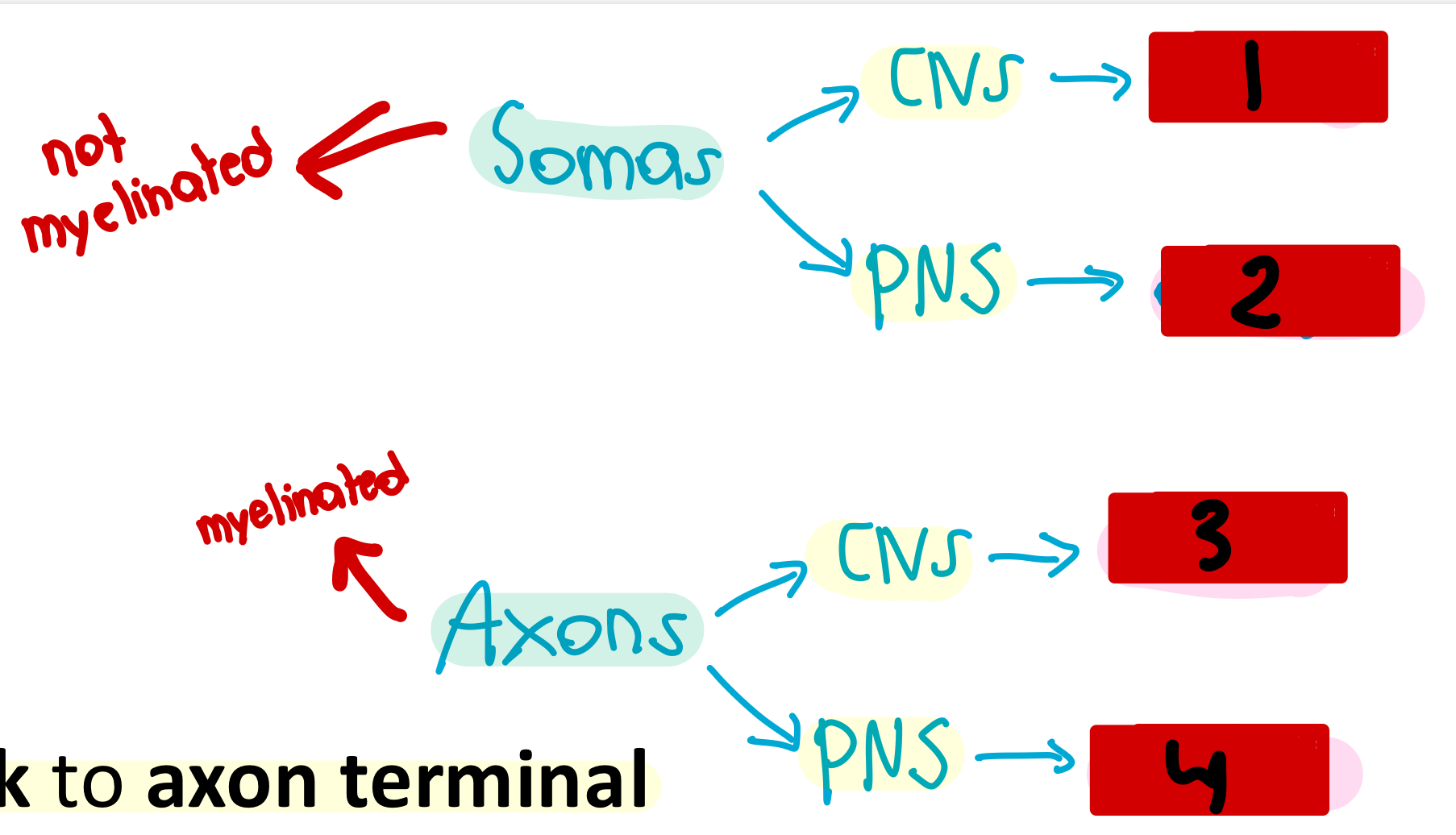
ganglia
2
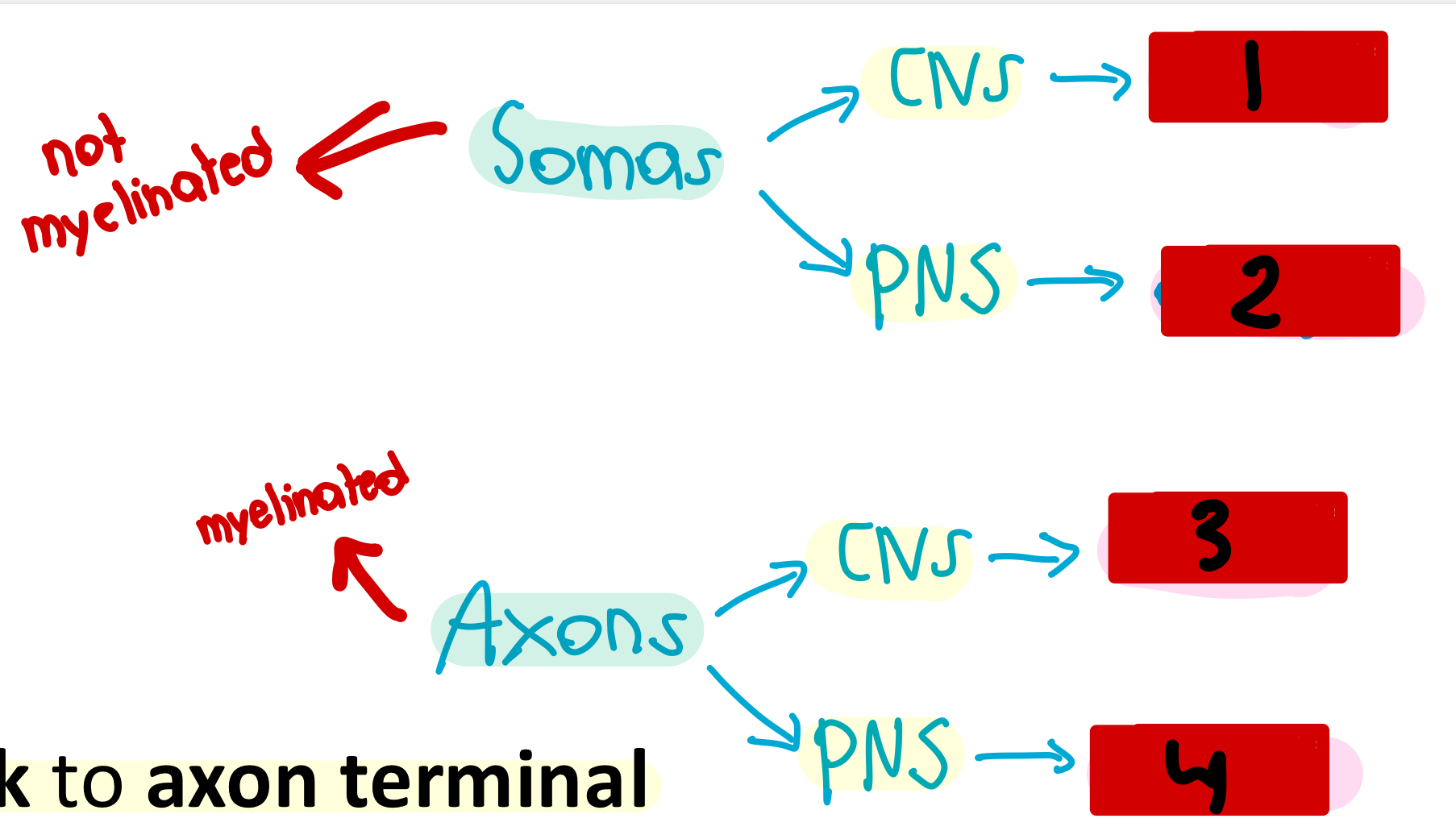
tracts
3
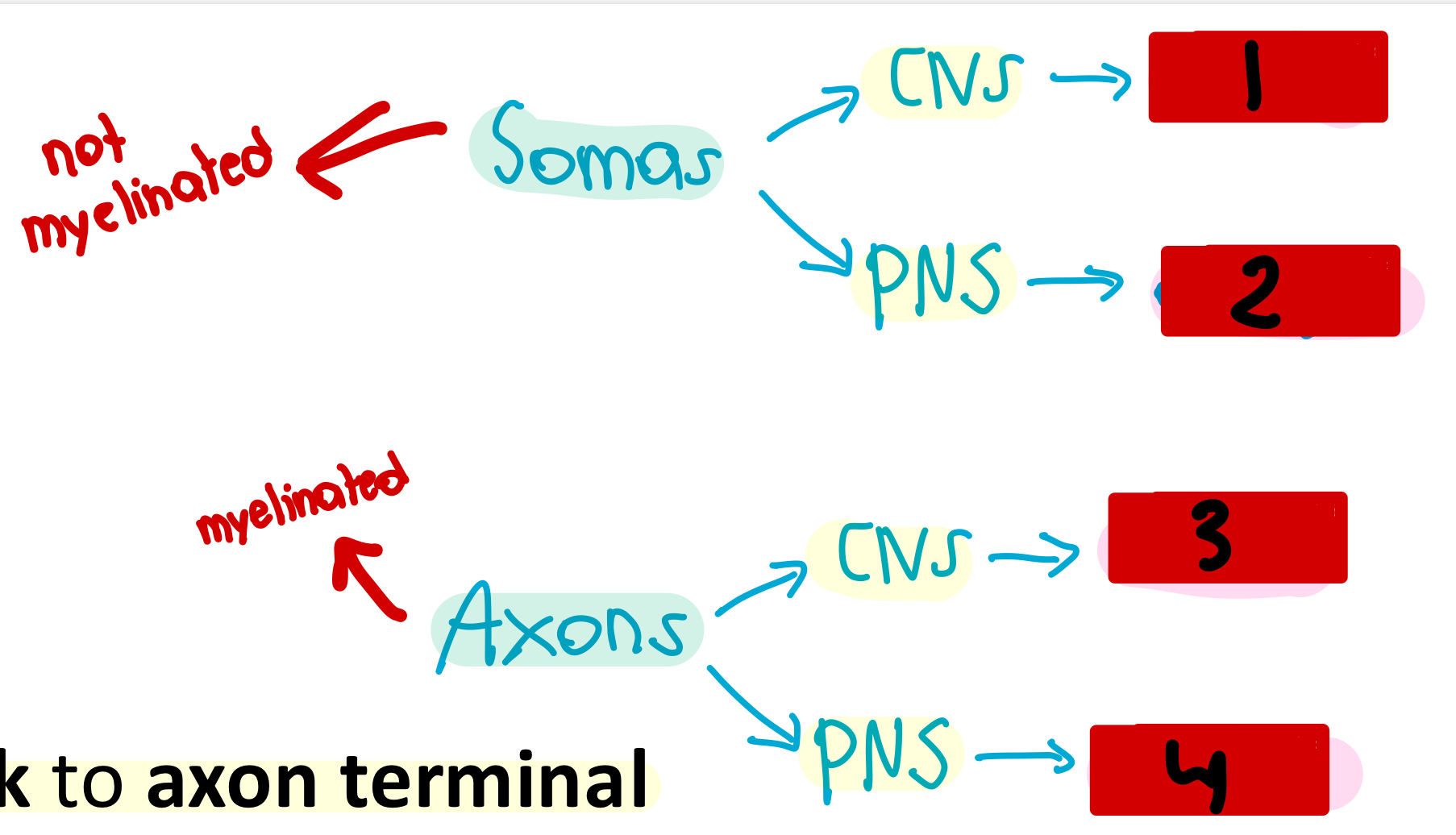
nerves
4
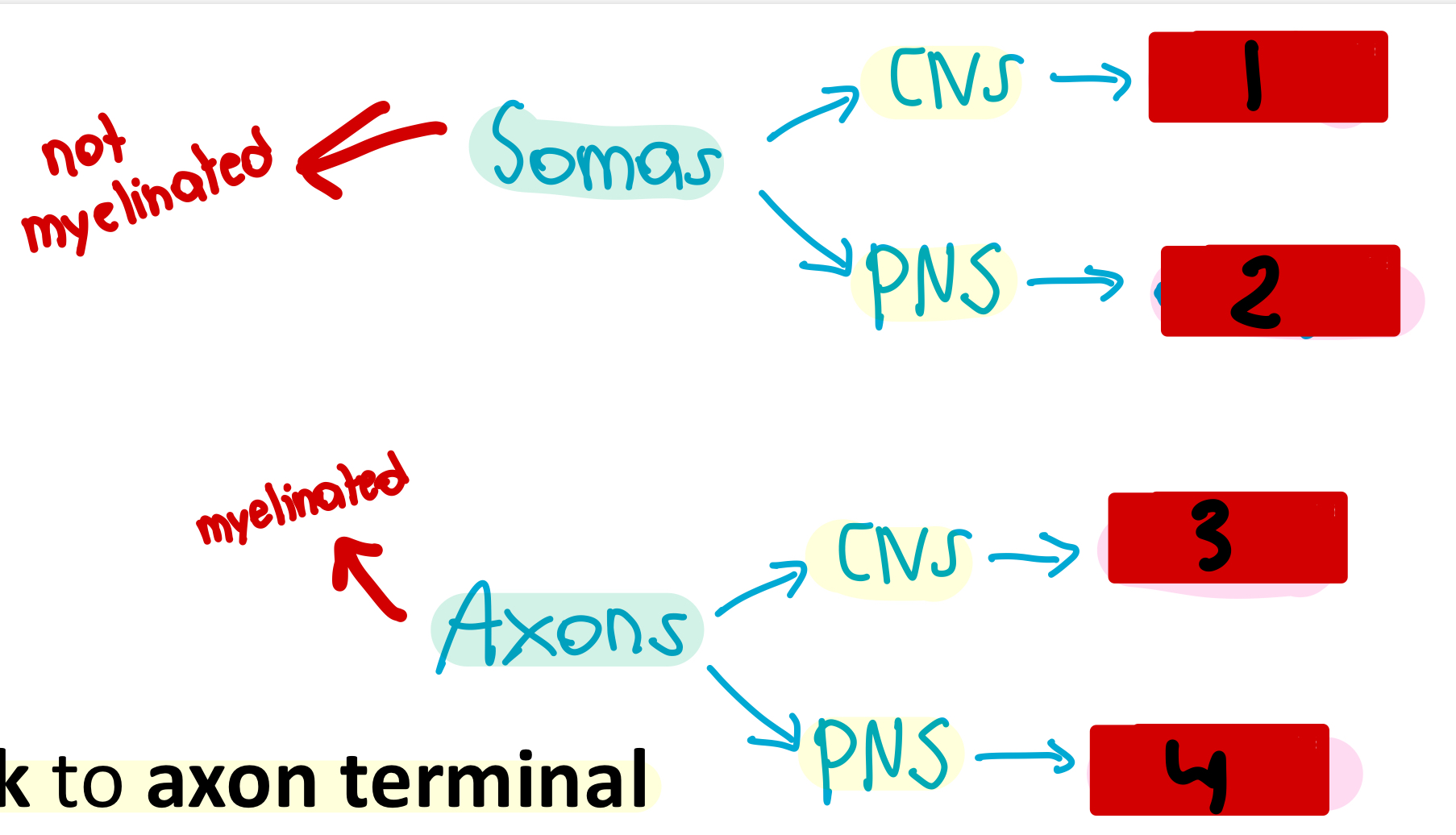
used for integration and act as a control center
What is the function of the CNS?
back to the CNS (brain and spinal cord)
where does sensory input send information to
out to the PNS (brain to a muscle for voluntary contraction…somatic nervous system)
when the brain interrogates information, it will then send that info…
communication lines between the CNS and the rest of the body
What is the function of the PNS?
1. Sensory (afferent) division
2. Motor (efferent) division
What are the subdivisions of the PNS?
1. Sensory input
2. Integration
3. Motor output
What are the functional divisions of the nervous system?
Somatic sensory fibers and Visceral sensory fibers
What are the two types of fibers that would be found in the sensory division of the peripheral nervous system?
sensory, afferent, dorsalmotor, ventral, efferent
SAD MOVE acronym
Nervous Tissue
what is highly cellular with little extracellular space in the nervous system
1. neurons
2. neuroglia
What are the 2 principal cell types found in nervous tissue?
neurons
excitable cells that transmit/communicate electrical signals
neuroglia
small cells that surround and wrap delicate neurons
protect the neurons and make sure they survive (neurons do not heal well or reproduce quickly)
What is the function of neuroglia?
impulses
longevity
metabolic rate
neurons
- structural units of nervous system
- large highly specialized cells that conduct _____
- extreme _______
- high _________
- all have cell body and one or more processes
dendrites
What part of the neuron receives signals?
Cell body/soma
- biosynthetic center of the neuron
- synthesizes proteins, membranes, and other chemicals
axon
What part of the neuron sends signals?
Myelin Sheath
- protects and electrically insulates axon
- increases speed of nerve impulse transmission
axon hillock
the start of the axon where the incoming action potentials combine
Axon Terminal
end of neuron where neurotransmitters are secreted to another neuron or next function begins
nuclei
What would you call a collection of somas in the CNS?
ganglia
What would you call a collection of somas in the PNS?
tracts
What would you call a collection of axons in the CNS?
nerves
What would you call a collection of axons in the PNS?
1. Astrocytes
2. Microglial cells
3. Ependymal cells
4. Oligodendrocytes
5. Satellite cells
6. Schwann cells
6 glial cells
start- foramen magnum
end- L1 or L2 vertebrae
Where does the spinal cord start and end?
- provides two-way communication to and from brain and body
- major reflex center: reflexes are initiated and completed at the spinal cord
What are the functions of the spinal cord?
dura mater
thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding the spinal cord
subdural space
space between dura mater and arachnoid mater
arachnoid
web-like middle layer of the meninges
subarachnoid space
space between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater that contains the cerebrospinal fluid
pia mater
Thin, innermost layer of the meninges
conus medullaris
What marks the end of the spinal cord?
Cauda Equina of the spinal cord
collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord that go into the sacral canal
Filum Terminale
_____ of the spinal cord
anchors spinal cord to coccyx and protects cauda equina
Dentriculate Ligaments
extensions of pia mater that secure cord to the dura mater
thoracic
the lateral horn is only found in which vertebrae
vertebral foramen
spinal nerves pass through the ________ in the spinal cord
sensory
dorsal horns receive ___________ input
motor
ventral horns receive ____________ input
towards the brain/sensory inputs
white matter that runs ascending goes...
away from the brain/to lower cord levels (motor inputs)
white matter that runs descending goes...
side to side
white matter that runs transverse goes...
1
Somatic Spinal Nerve has ___ motor neuron(s)
2
Autonomic Spinal Nerve has ___ motor neuron(s)
epineurium
outermost layer of connective tissue that covers bundles of fascicles (entire nerve)
perineurium
connective tissue line that covers 1 fascicle (collections of axons)
endoneurium
innermost connective tissue layer that covers a single axon
only in thoracic and superior lumbar region of the spine
where are lateral horns located
motor
the anterior (ventral) nerve root contains __________ fibers from ventral horn motor neurons that innervate skeletal muscles
sensory (afferent)
the posterior (dorsal) nerve root contains _____ fibers from sensory neurons in dorsal root ganglia that conduct impulses from peripheral receptors
deep muscles
skin
the posterior ramus is the smaller of the two main branches in the rami and innervates the ______ of the back and the ______ of the back
trunk
upper and lower limbs
the anterior ramus is the larger of the two main branches in the rami and innervates _____ and the ______
meningal branch (with spinal nerves)
tiny branch that re-enters vertebral canal to innervate meninges and IV discs
rami communicates
contain autonomic nerve fibers that join ventral rami in thoracic region
dermatome
area of skin innervated by cutaneous branches of single spinal nerve (sensory)
myotome
Area of muscle innervated by motor fibers
dermatomes
Extent of spinal cord injuries ascertained by affected....
nerve plexuses
All ventral rami except T2-T12 form interlacing nerve networks called ...
T2-T12
All ventral rami except ______ form interlacing nerve networks called nerve plexuses
central canal
what part of the cross section of the spinal cord does cerebrospinal fluid run through
ventral dorsal and lateral columns
what parts of the cross section of the spinal cord include all white matter/myelinated
ventral dorsal and lateral horns
what parts of the cross section of the spinal cord contain gray matter
gray commissure
what part of the cross section of the spinal cord communicates from left to right
gray matter
where are nuclei located in the cross section of the spinal cord
white matter
where are tracts located in the cross section of the spinal cord
dorsal root ganglion
where are ganglia located in the cross section of the spinal cord
roots
where are nerves located in the cross section of the spinal cord
false
t or f: cell bodies are located in the white matter
endoneurim
what connective tissue lining surrounds 1 axon
perineurium
what connective tissue lining surrounds 1 fascicle of axons
epineurium
what connective tissue lining is a nerve (fascicles together)
dorsal roots
ventral roots
what roots have sensory fibers? motor fibers?