I DONT KNOW SHIT
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What is this
What is the precursor
How is it converted to this
What is it converted to after
Is it a five or a 4 steroid
What is its function
Where is it
cholesterol (C27)
Acetyl-CoA
through HMG-reductase
progestenone (C21)
five
dkfljd
in the mitochondria
what are the parts of the steroidgenesis pathway
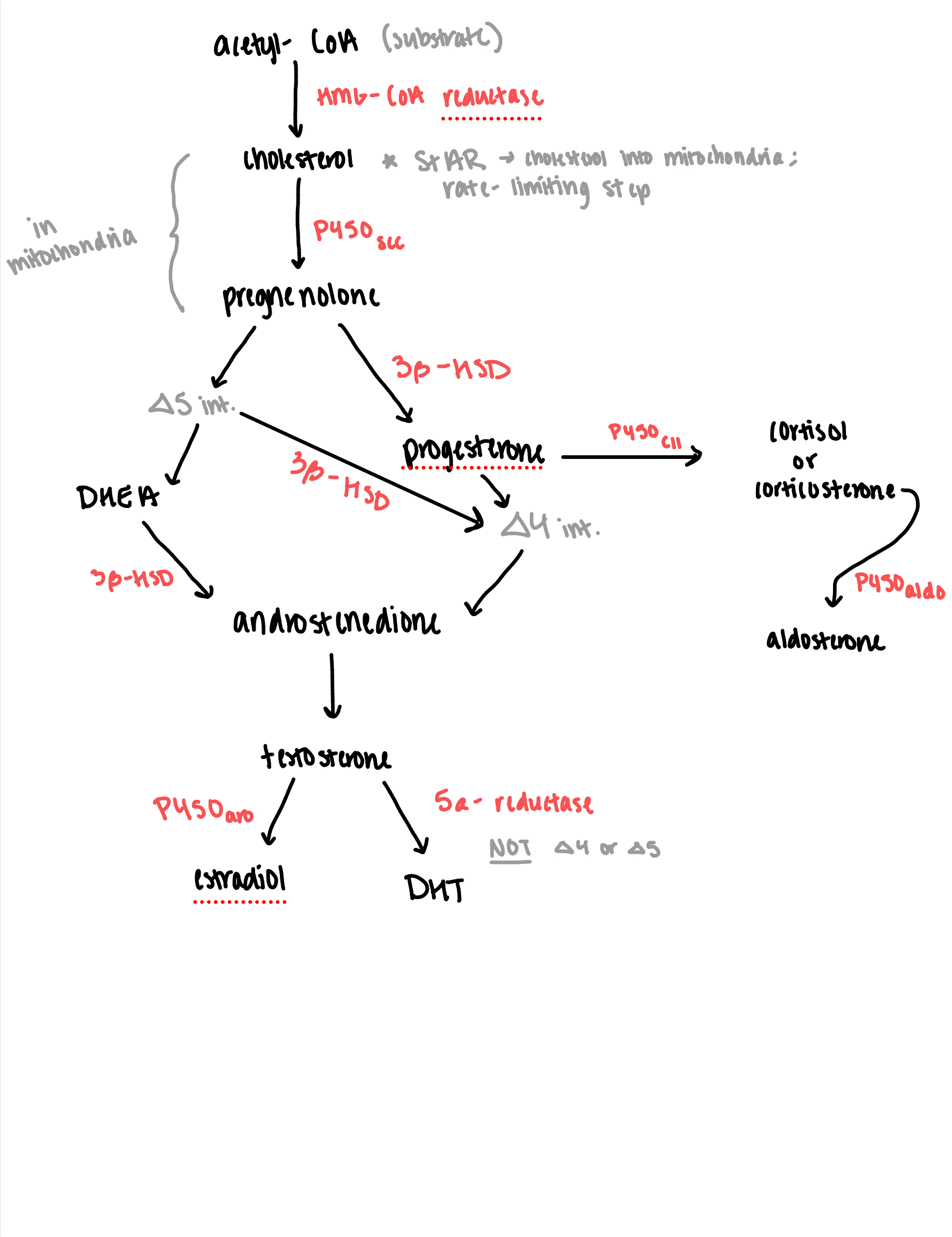
What is this
What is the precursor
How is it converted to this
What is it converted to after
Is it a five or a 4 steroid
Pregnenolone (C21)
It’s precursor is cholesterol (C27)
It is converted by P450scc
if it is going the 4 pathway, it is converted to progesterone. If it’s going the 5 pathway, it is going to DHEA (C19)
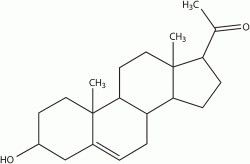
What is this
What is the precursor
How is it converted to this
What is it converted to after
Is it a five or a 4 steroid
This is DHEA
The precursor is pregnenolone
It is converted to this by an intermediate
It is converted to androstenedione
It is a five steroid
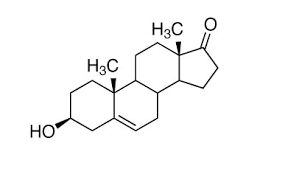
What is this
What is the precursor
How is it converted to this
What is it converted to after
This is androstendione
The precursor is DHEA on the 5 side and progesterone on tIte 4 side
It is converted to this on both sides by 3B-HSD
It is converted to testosterone after
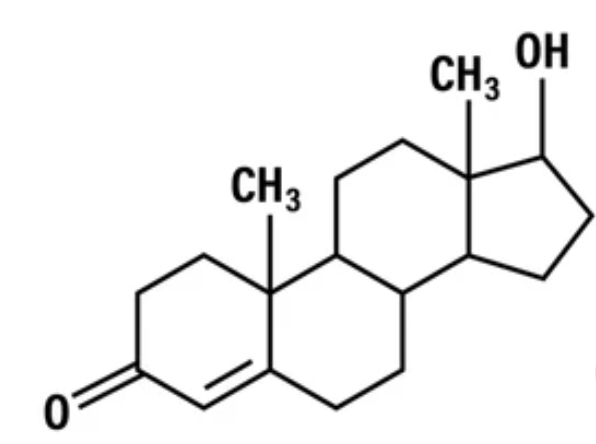
What is this
What is the precursor
How is it converted to this
What is it converted to after
Is it a five or a 4 steroid
This is testosterone
The precursor is androstenedione
It is converted to two potential things. It could be estriol by the 450aroscc. It could be converted to DHT by 5a-reductase
It is neither
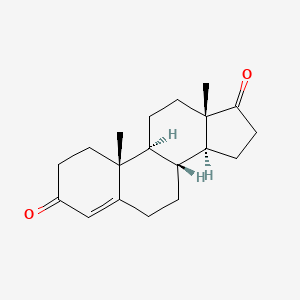
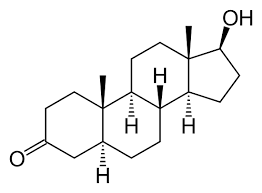
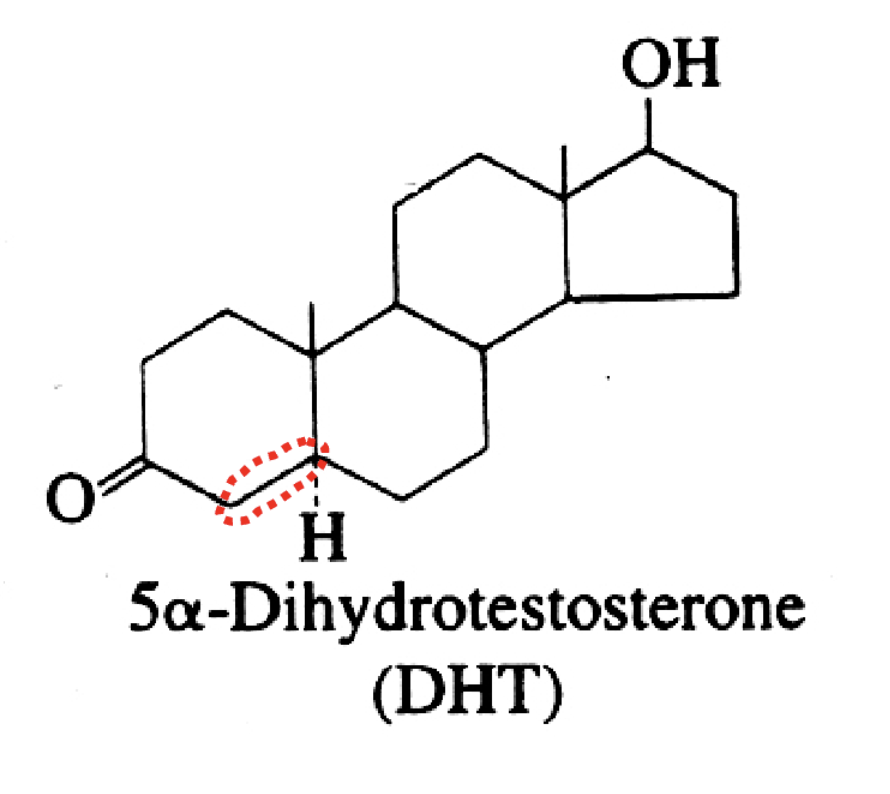
What is the structure of DHT
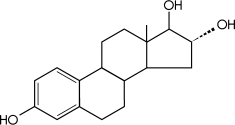
What is the structure of Estriol
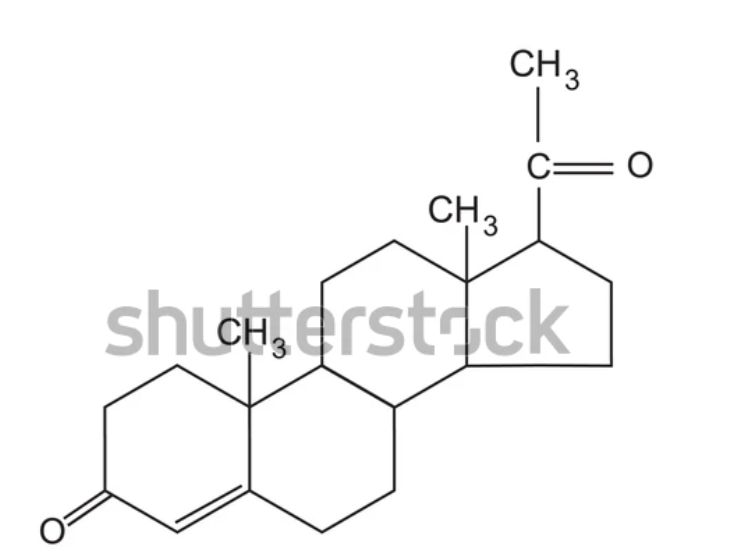
What is this
What is the precursor
How is it converted to this
What is it converted to after
Is iit a five or a 4 steroid
It is a progesterone
The precursor is pregnenolone
It is converted to this by 3B-HSD
It can be converted to two things, depending on the intermediate: aldosterone if the intermediate is P50aldo or an unknown intermediate leads to androstendione
It is a 4 steroid
what defines corticosteroids
have an OH on the C21
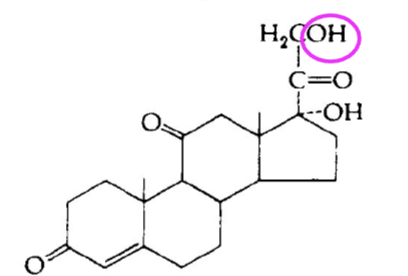
difference between mineralcorticoids and glucocordicoids structurally
mineralcorticoids focus on ion channels
glucocordicoids focus on glucose
what is the biologically active form of vitamin D3 synthesis
1,25 DHC
what are the key characteristics of stAR
-takes place in mitochondria
-limiting step for cholesterol into the membrane
-not an enzyme
synthesis of cholesterol characteristics
-rate limiting enzyme is HMG-CoA reductase
substrate is acetyl-coa reductase
how to make progestogens
catabolic process cholesterol (C27) —> progestogens(C21)
transgenic mouse
genetically engineer mice with inserted foreign gene or remove endogenous gene. It is used to observe how the presence or absence of certain
A bioregulator, enzyme, or receptor affects your endocrine system.
RIA (radioimmunoassay)
measure the concentration of a hormone in a sample
mass spectrometry
Purpose: identify an unknown compound by
measuring mass to charge ratio of components
• Typically used after HPLC has been used to
separate compound out of a mixture
HPLC high performance lipid chromatography
Purpose: separate
components in a
heterogeneous mixture
Each molecule has unique size,
hydrophobicity, and charge that allows them to travel through the column at a
different rate.
Immunohistochemistry
Purpose: to visualize location of the hormone
secreting cells or enzymes necessary for
hormone synthesis
how is catecholamine different from catecol
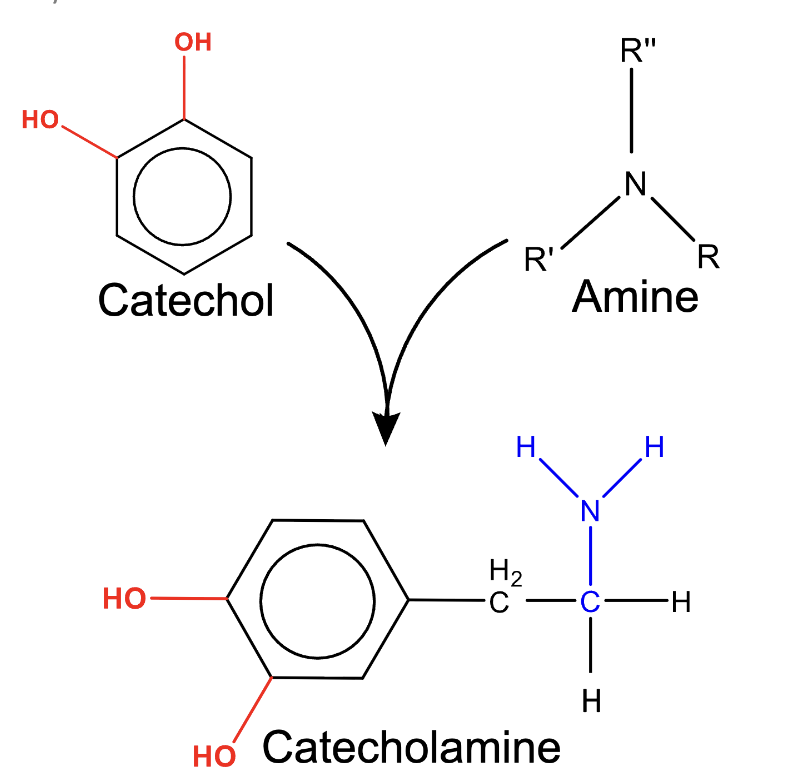
catecholamine synthesis
DOPA is 1st catechol
DA 1st catecholamine
structure for DHT and what is distinct
no double bond (not a 4 or 5)
organs involved in vitamin d3 synthesis + role
skin, kidney and liver
-calcium homeostasis
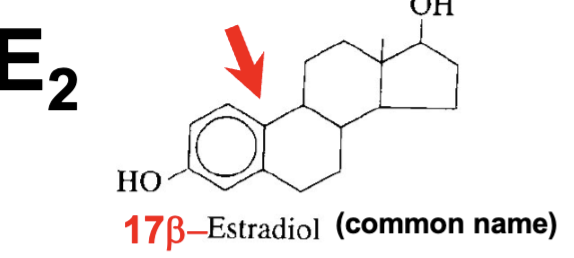
what structure does estradiol have
only have OH on 17th carbon
how do we use metabolism for removal of bioregulators
By enzymatic degradation
Proteins, peptides —> AAs
By enzymatic inactivation Biogenic amines. etc
By conjugation
Steroids, Thyroid hormones
What are SERMs
a class of drugs that act as either estrogen agonists (mimicking estrogen) or antagonists (blocking estrogen), depending on the specific tissue in the body
What are SPRMs
drugs that bind to the progesterone receptor (PR) to exert either blocking (antagonistic) or promoting (agonistic) effects on progesterone-regulated pathways
autocrines vs paracrines
paracrines affect other cells
autocrines affect itself
pheromones vs allemones
Pheromones affect the same species
Allemones affect different species
what can metabolism do
-make the hormone more or less deactivated
-alter structure
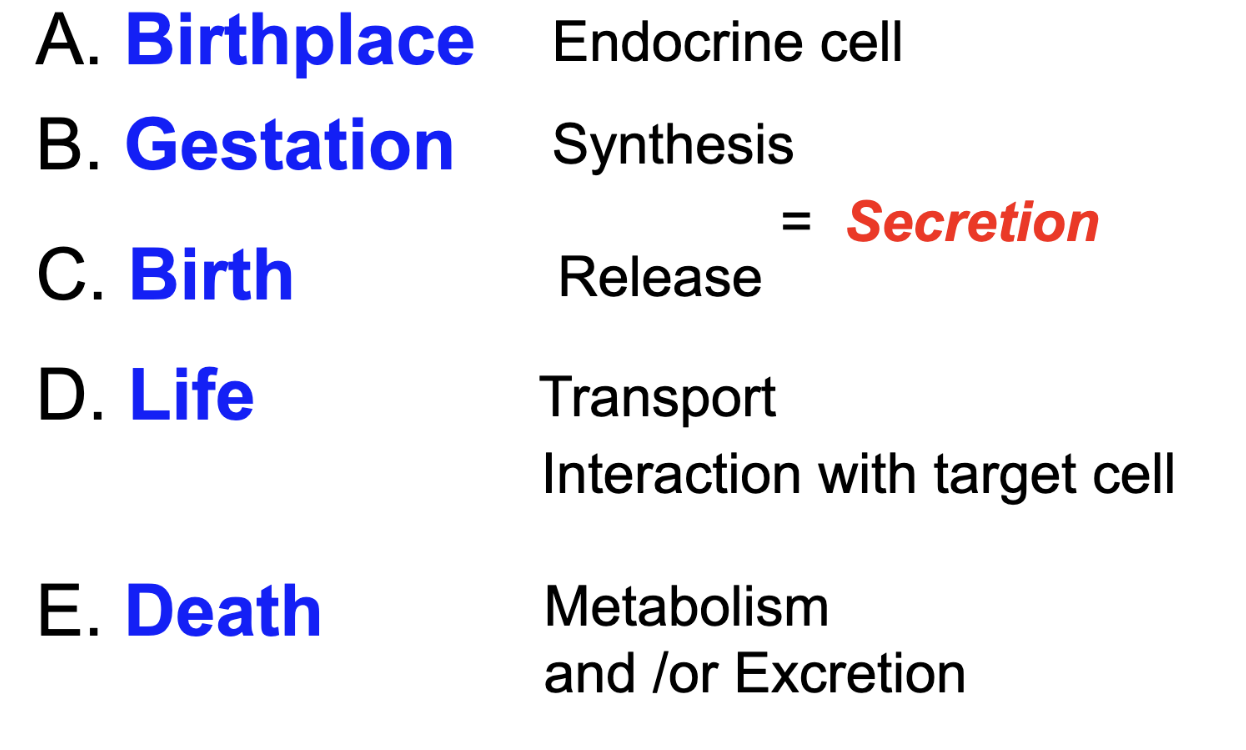
what are the steps of a bioregulators life
what are the steps for synthesis of proteins
amino acid
synthesis (DNA—→ polypeptide)
proteins(FSH, LH), peptides (vasopressin)
stored
released
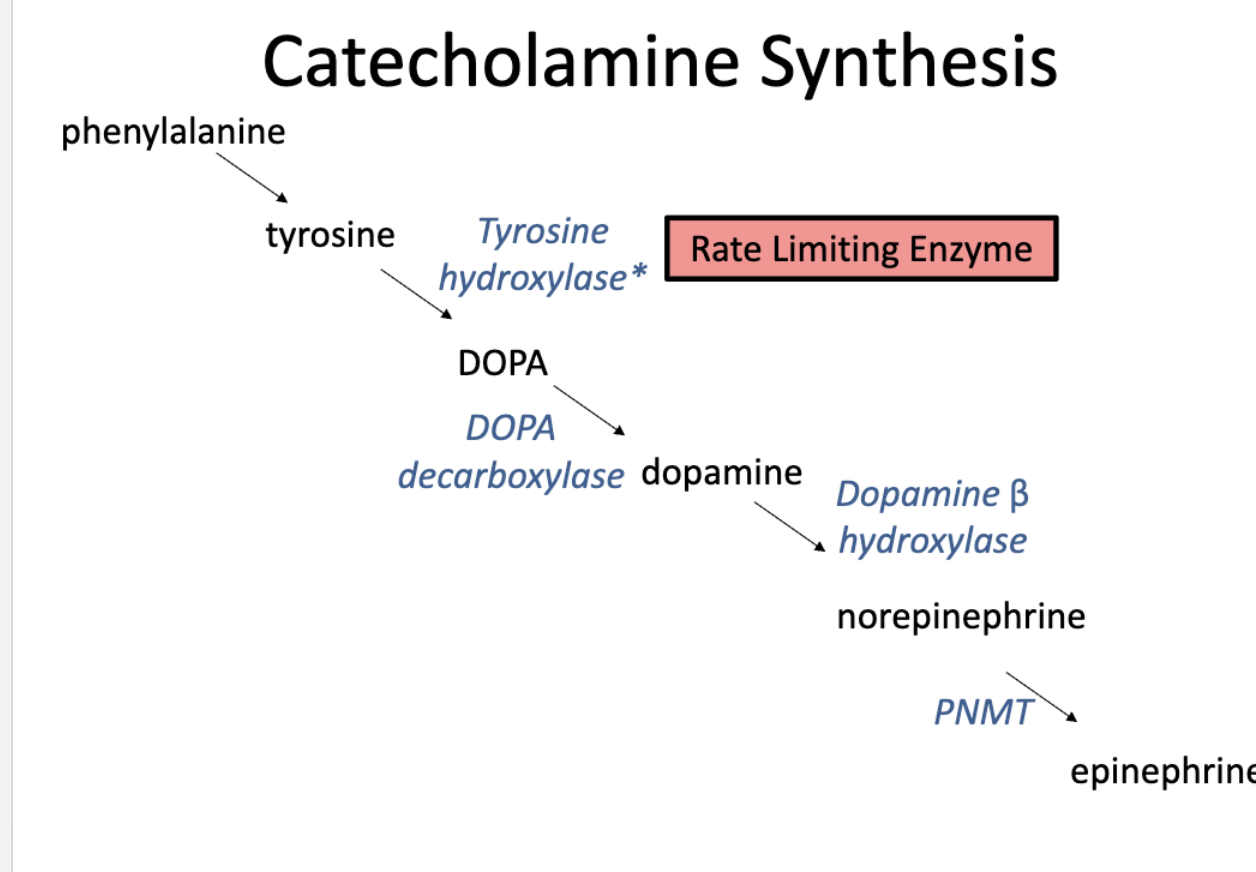
synthesis for biogenic amines
amino acids —tyrosine and tryptophan
synthesis (decarboxylase)
makes catecholamine (ex NE) , and indolamine (ex: melatonin)
Storage
Release
synthesis for thyroid hormones
amino acid (tyrosine)
synthesis
thyroid hormones (T3 and T4)
storage
release
synthesis for steroids
cholesterol
synthesis
steroids —androgens, estrogens, glucorticoids, mineralcorticoids, progestogens
release
synthesis for eicosanoids
arachidonic acid
eicosanids (prostaglandins)
release
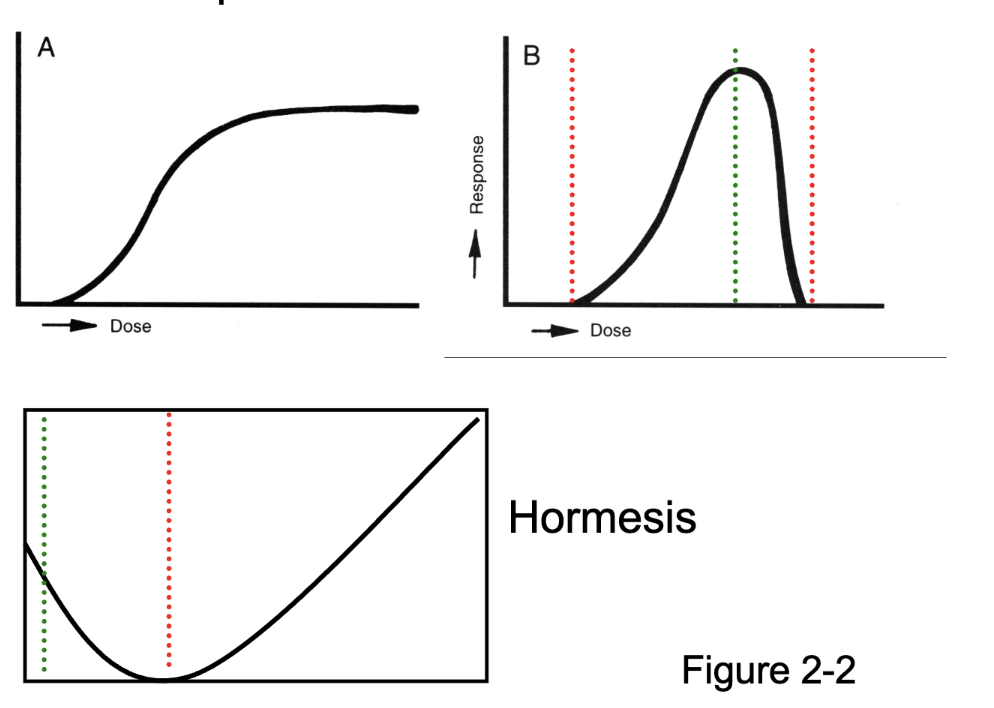
dose response curve
for the first curve, when receptors are saturated, it lvls out
for the second curve, it shows how a pharmacological dose can lead to toxicity if in too high of a dose
hormesis is a two-phased dose-response relationship to an environmental agent whereby low-dose amounts have a beneficial effect and high-dose amounts are either inhibitory to function or toxic
what is unique about neuromodulators
it doesn’t generate an action potential but it still affects other neurons
what are cytocrines secreted from
all cells, and to local messengers in the ECF(NOT SYNAPSE)
who secretes intracrines
all cells
who secretes semiochemicals
organisms
who do phermones affect
SECRETED by the same species
who do allemones affect
a different species (must be secreted)
intracrine
SECRETED inside cell