2.3.2 Causes of climate change
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What are the natural causes of climate change?
variations in heat from the Sun (sun spots)
volcanic activity
changes in the Earth’s orbit
What are the human causes of climate change?
burning of fossil fuels
deforestation
waste disposal
Changes in the Earth’s orbit.
The Milankovitch cycles are cyclical time periods that relate to the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Scientists believe that these cyles affect the timings and seasonality of the Earth’s climate.
What are the 3 Milankovitch cycles?
Eccentricity
Precession
Axial tilt
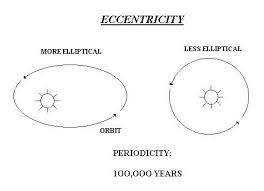
Eccentricity
This describes the path of the Earth as it orbits the Sun. The Earth’s orbit is not fixed and it changes over time from almost circular to being mildly elliptical.
A complete cycle from circular to elliptical to circular occurs every 100 years.
It appears that more circular = colder periods
more elliptical = warmer periods
Precession
This describes a natural ‘wobble’ that occurs with the Earth rather like a spinning top. [Essentially that the Earth itself spins at an axis]
A complete wobble takes about 26,000 years.
The Earth’s wobble accounts for some regions of the world experiencing very long days and very long nights at certain times of the year, e.g. northern Norway.
![<p>This describes a natural ‘wobble’ that occurs with the Earth rather like a spinning top. [Essentially that the Earth itself spins at an axis]</p><p>A complete wobble takes about 26,000 years.</p><p>The Earth’s wobble accounts for some regions of the world experiencing very long days and very long nights at certain times of the year, e.g. northern Norway.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/980f348e-72c2-4206-a268-bb313e11599e.jpg)
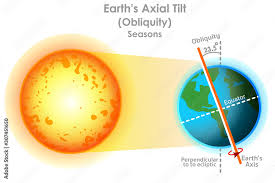
Axial tilt
The Earth spins on its axis, causing day and night.
The Earth’s axis is currently tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees.
However, over a period of about 41,000 years, the Earth moves back and forth between two extremes: 21.5 and 24.5.
A greater axial tilt means a higher average temperature
Volcanic activity
Violent volcanic eruptions blast huge quantities of ash, gases and liquids into the atmosphere.
This leads to a volcanic winter where fine particles of ash can block out the Sun, leading to a reduction in surface temperatures.
Ash can be carried by winds across the globe, transferring these cooling conditions to many regions surrounding.
Ash does not usually stay in the atmosphere for more than a few weeks so is unlikely to have a long-term impact.
However, the conversion of sulfur dioxide [from volcanic eruption] to sulfuric acid have a longer impact. The fine aerosols act like tiny mirrors reflecting radiation from the Sun. These usually last about to 3 years.
![<p>Violent volcanic eruptions blast huge quantities of ash, gases and liquids into the atmosphere. </p><p>This leads to a volcanic winter where fine particles of ash can block out the Sun, leading to a reduction in surface temperatures. </p><p>Ash can be carried by winds across the globe, transferring these cooling conditions to many regions surrounding.</p><p>Ash does not usually stay in the atmosphere for more than a few weeks so is unlikely to have a long-term impact. </p><p>However, the conversion of sulfur dioxide [from volcanic eruption] to sulfuric acid have a longer impact. The fine aerosols act like tiny mirrors reflecting radiation from the Sun. These usually last about to 3 years.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/dd15303b-95b3-4f1f-887b-62ef9381267e.jpg)
Variations in energy from the Sun
A sunspot is a spot or dark patch that appears from time to time on the surface of the sun.
They are very small and hard to detect; however, they do have an effect on the climate.
The number of sunspots increases from a minimum to maximum to minimum over a period of 11 years.
The idea is that they are darker spots because they give off more heat radiation and so causes the Earth’s temp. to rise.
Very few sunspots were observed between 1645 and 1715, a period known as the Maunder Minimum. This coincides with the coldest period during the Little Ice Age.

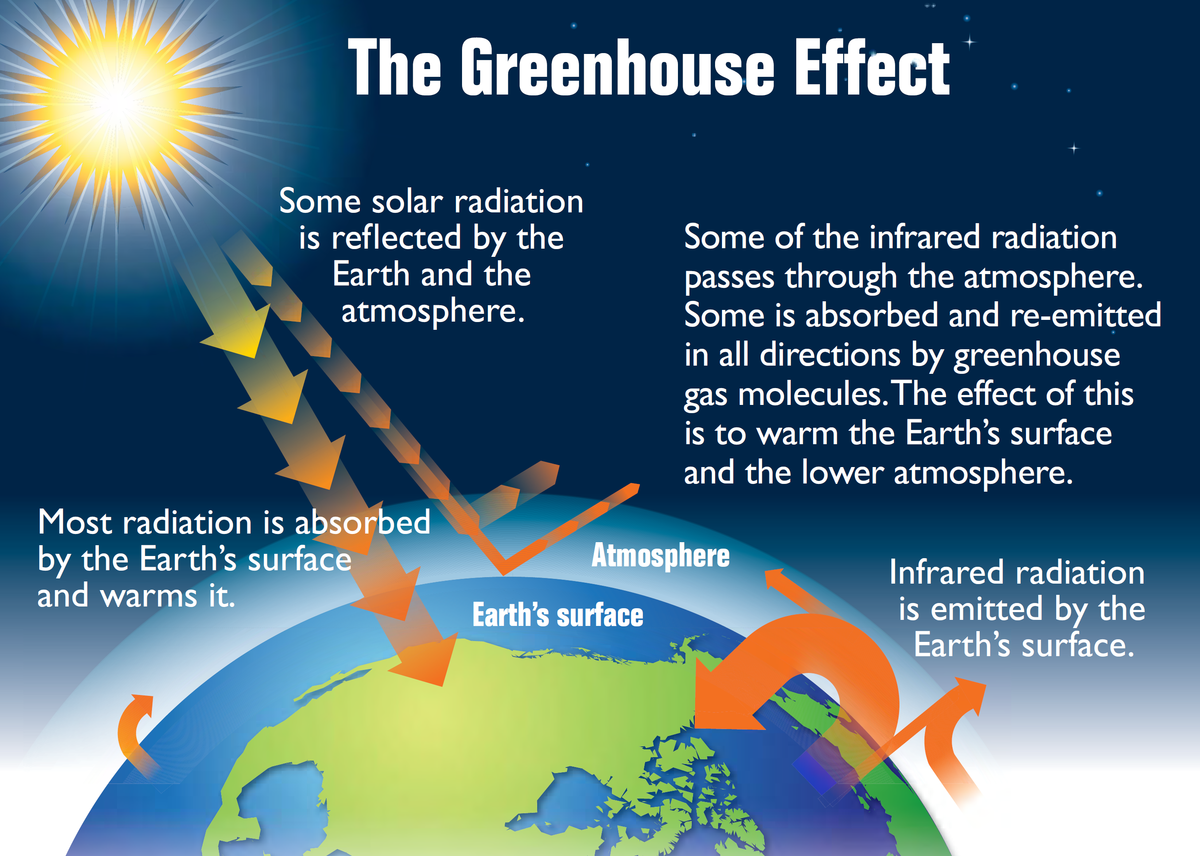
The natural greenhouse effect.
Heat travels in the form of short-wave radiation to reach the Earth’s outer atmosphere
Some radiation is absorbed and reflected in the form of long-wave infrared radiation into space
Some is absorbed by liquids and greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and so the atmosphere acts like a blanket over Earth, allowing life to exist
The enhanced greenhouse effect.
In recent years, the natural greenhouse effect has become more effective at retaining heat given off from the Earth.
The main reason is due to human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, cattle farming, etc.