Conservation of mass and energy
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What does the law of conservation of mass state about physical and chemical changes?
The law of conservation of mass states that matter is never created or destroyed in ordinary physical and chemicalchanges.
In a physical change, such as water freezing into ice, the substance retains its identity, even though its physical properties change.
In a chemical change, the original substances transform into new substances with different identities, but the total amount of matter remains the same.
No matter how substances change, the mass before and after the reaction remains equal.
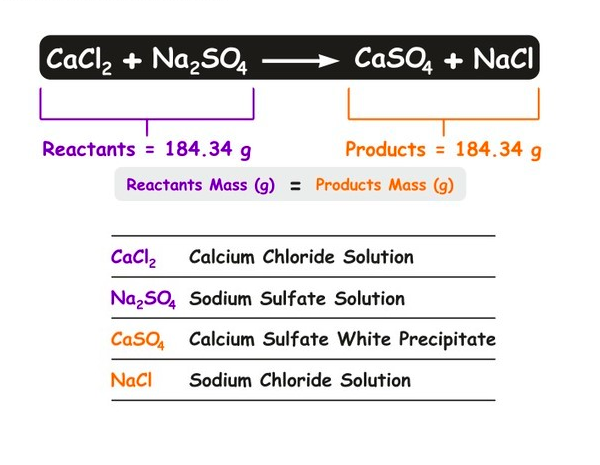
How do chemists describe a chemical change?
Chemists use a chemical equation to describe a chemical change.
Chemical formulas and atomic symbols represent the substances involved.
An arrow (→) separates the reactants (substances before the reaction) from the products (substances formed after the reaction).
Example:
When hydrogen gas (H₂) burns in oxygen (O₂), water (H₂O) is formed:
H₂ + O₂ → H₂O
Reactants: Hydrogen (H₂) and Oxygen (O₂) (left side of the equation)
Product: Water (H₂O) (right side of the equation)
Why is it important to balance a chemical equation, and how is it done?
To balance an equation:
Adjust the coefficients (the numbers in front of the elements or compounds).
Ensure the number of each type of atom is equal on both sides.
For example, the unbalanced equation for water formation:
H₂ + O₂ → H₂O
Balanced equation:
2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
Now, both sides have:
4 hydrogen atoms
2 oxygen atoms
The ___ states that energy is never created or destroyed in ordinary chemical and physical processes.
law of conservation of energy
__ is the energy of motion. The faster an object moves, the more kinetic energy it has. For example, a fast-rolling bowling ball has more kinetic energy than a slow-rolling one.
Additionally, atoms and molecules have kinetic energy as they constantly move. The temperature of a substance measures the average kinetic energy of its particles.
Kinetic energy
The formula to calculate kinetic energy (KE) is:
KE = ½ mv²
Where:
m = mass of the object (kg)
v = velocity of the object (m/s)
The unit of kinetic energy is __, which is equivalent to kg•m²/s².
joules (J)
____ have kinetic energy as they constantly move. The temperature of a substance measures the average kinetic energy of its particles.
atoms and molecules
___ is the energy of motion. It depends on an object's mass and velocity. For example, a moving car or a rolling ball has kinetic energy. The formula for kinetic energy is:
KE=1/2 mv²
Kinetic energy
___ is stored energy due to an object’s position or condition. For example, a stretched rubber band, a book on a shelf, or a raised weight all have potential energy. The formula for gravitational potential energy is:
PE=mgh
where m = mass, g = gravity (9.8 m/s²), and h = height above the ground.
Potential energy
In a chemical reaction, ___ stored in the bonds of molecules is converted when bonds break and new bonds form.
chemical energy (potential energy)
When bonds break, some of the stored chemical energy is released, often as ___. This increases the kinetic energy of the particles, making them move faster and raising the temperature.
heat
When new bonds form, energy is either ___, depending on the reaction.
absorbed or released
___ reactions release heat energy, increasing kinetic energy.
Exothermic
___ reactions absorb heat energy, converting it into stored chemical energy.
Endothermic