Dunham Sports Medicine Terminology
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Abduction
the movement of a limb or other part away from the body
Active Range of Motion
how much a joint can move due to muscle use without any outside assistance
Adduction
The movement of a limb or other part towards the body
Dorsiflexion
the backward movement or upward bending of the foot at the ankle, where the toes and the top of the foot move towards the shin
Eversion
the act of turning inside out
Flexion
the action of bending or the condition of being bent, especially the bending of a limb or joint
Inversion
turning in towards the midline of the body
Passive Range of Motion
a method of moving a joint through its available range of motion using an external force, such as a physical therapist, a machine, or gravity, while the person remains completely relaxed and does not use their own muscles for movement
Mobility
the ability to move or be moved freely and easily
Resistive Range of Motion
a clinical assessment where a person moves a joint against an external force or resistance provided by another person (like a physical therapist) or an object
Range of Motion
the full degree of movement possible at a joint, extending from full flexion (bending) to full extension (straightening)
Plantar Flexion
a movement of the foot that involves bending the ankle joint up and down
Pronation
the rotational movement of the hand and forearm so the palm faces downward or backward, and a similar inward rotation of the foot
Proprioception
perception or awareness of the position and movement of the body
Aerobic Exercise
rhythmic and continuous physical activity that uses large muscle groups, increases heart rate and breathing, and relies on oxygen to meet energy demands
Anaerobic Exercise
high-intensity activity involving short, powerful bursts of movement that doesn't require oxygen for energy
Treatment
anything that alleviates pain, helps with injury or sickness
Rehabilitation
the action of restoring someone to health or normal life through training and therapy after imprisonment, addiction, or illness
Strength
the quality or state of being physically strong
Cryotherapy
the use of extreme cold in surgery or other medical treatment
Anterior
the front part of the body or a structure positioned toward the fron
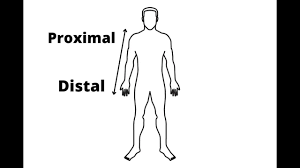
Distal
a body part that is farther from the center of the body or the point of attachment of a limb or appendage
Dorsal
a position towards the back or spinal column of the body, or the upper surface of an animal or part
Medial
closer to the body's midline
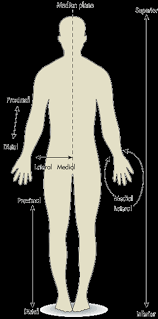
Inferior
a body part is located below another part of the body, or toward the feet

Proximal
closer to the center of the body or point of attachment
Lateral
a position or structure located to the side of the body, away from the midline
Posterior
the back or rear part of the body or an anatomical structure
Superior
a position that is above or higher than another part of the body

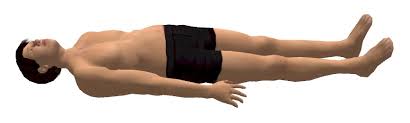
Supine
when a person or animal lies flat on their back, with their face turned upwards
Hypertrophy
the enlargement of an organ or tissue from the increase in size of its cells
Inflammation
The body's response to an injury(swelling)
Irritation
inflammation or other discomfort in a body part caused by reaction to an irritant substance
Isometric Muscle Contraction
when a muscle generates force and increases tension without changing its length or causing movement at the joint
Ligament
a strong band of connective tissue that connects the bones
Muscle
a band or bundle of fibrous tissue in a human or animal body that has the ability to contract, producing movement in or maintaining the position of parts of the body
Nerve
(in the body) a whitish fiber or bundle of fibers that transmits impulses of sensation to the brain or spinal cord, and impulses from these to the muscles and organs
Plantar
the sole or the bottom of the foot
Tendon
a flexible but inelastic cord of strong fibrous collagen tissue attaching a muscle to a bone
Vein
a blood vessel that carries blood back to the heart
Artery
any of the muscular-walled tubes forming part of the circulation system by which blood is conveyed from the heart to all parts of the body
Biomechanics
the study of the mechanical laws relating to the movement or structure of living organisms
Kinesiology
the study of the mechanics of body movements
Physiology
the branch of biology that deals with the normal functions of living organisms and their parts
Eccentric Muscle Contraction
a type of isotonic contraction where the muscle lengthens under tension, acting as a "brake" or controlling force to resist an external load
Extension
a part that is added to something to enlarge or prolong it; a continuation
Symptoms
a physical or mental feature which is regarded as indicating a condition of disease, particularly such a feature that is apparent to the patient
Sprain
a soft tissue injury that occurs when a ligament is stretched or torn
Grade 1 Sprain / Strain
the mildest form of an injury to ligaments (sprain) or muscles/tendons (strain), characterized by overstretching with minimal or no tissue tearing, resulting in mild pain, slight swelling, and usually the joint or limb remaining stable and functional
Grade 1 Sprain
Takes 1-3 Weeks to heal
Grade 2 Sprain / Strain
involves a partial tear of ligaments, tendons, or muscle fibers, causing moderate pain, swelling, bruising, and some joint instability or weakness
Grade 2 Sprain
Takes 3-6 Weeks to heal
Grade 3 Sprain / Strain
involves a complete tear of a ligament, tendon, or muscle, leading to severe pain, significant swelling, bruising, and instability
Grade 3 Sprain
Takes 6-12 weeks to heal
Contusion
An area with ruptured blood capillaries; a bruise
Concussion
a mild traumatic brain injury caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head or body that makes the brain move rapidly inside the skull, leading to chemical changes and stretching/damage to brain cells
Tendonitis
the inflammation or irritation of a tendon, which is the fibrous cord that connects a muscle to the bone
Laceration
a tear or ragged cut in skin or flesh
Sprain
a soft tissue injury that occurs when a ligament is stretched or torn
Strain
excessive pressure or physical injury to muscles or tendons
Superficial
existing or occurring at or on the surface
Supination
the rotation of the forearm or leg such that the palm or sole faces upward or forward and outward
Puncture
Make a hole in something
Abrasion
The process of scraping or wearing something away
Atrophy
waste away, especially as a result of the degeneration of cells, or become vestigial during evolution
Concentric Muscle Contraction
occurs when a muscle shortens as it generates force, typically to overcome external resistance and cause joint movement
Eccentric Muscle Contraction
a type of isotonic contraction where the muscle lengthens under tension, acting as a "brake" or controlling force to resist an external load