APES Unit 8-
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
how do people affect aquatic ecosystems?
divert rivers, dam rivers, & introduce substances & diseases → accumulation in oceans & pollution in groundwater
nonpoint source
pollutants enter the environment from many places at once spread out over a large geographic region → difficult to point to one individual source
point source
pollutants that enter environments from an easily identified & confined place → can “point” to it
effects of nutrient pollution
nitrogen & phosphorus increases → eutrophication of surface waters → increased Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) → dissolved oxygen (DO) levels decrease
causes of nutrient pollution
runoff of fertilizers (not pesticides) from farms, golf courses, & residential lawns
sewage lakes/discharge into surface waters
flooded to leaking CAFO manure lakes
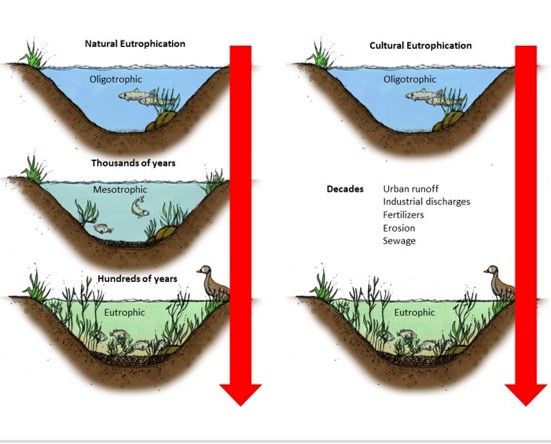
oligotrophic lakes
lakes & ponds with low nutrient (N/P) levels, stable algae populations, & high dissolved oxygen due to lack of nutrient pollution or age of body of water
eutrophic lakes
sediment builds up on the benthic zone (bottom) due to continuous erosion in watershed & deposition into lakes/ponds → shallower benthic environments → increased sunlight reaching these environments → increased growth of rooted aquatic vegetation → more trapped sediment & dissolved nutrients
sediment
eroded material that is carried into rivers & deposited into depositional basins (lakes, bays, river deltas, oceans)— increase turbidity of aquatic ecosystems
common causes of sediment
logging, mining, construction, farming
turbidity
measures depth that light can penetrate from the surface of the water
**increased turbidity reduces NPP of ecosystems & alters entire food webs/chains b.c it affects visual predators’ visibility
thermal pollution
results from any process that changes the ambient water temperature → heat increases respiration rate of aquatic organisms (thermal shock)
dissolved O2 levels based on temperature
hot water has less dissolved O2 since gases diffuse out of solutions more rapidly at higher temperatures → solubility of gases decrease as temperature increases
impact of resevoirs
can change seasonal temperatures of water downstream
impact the timing of migration, spawning, & egg hatching
causes of thermal pollution
nuclear power plants: power plants use cool water from surface/ground water to cool steam produced for turning a turbine back into water (cool) to reuse
cooling towers & holding ponds: require large amounts of cool water to cool stream back to water & discharge it back to the environment
steel mills, paper mills, other manufacturing plants: use cool down machinery → return warm water
urban stormwater drain runoff: causes thermal pollution due to heat from blacktop/asphalt
how does plastic trash get into the ocean?
litter reaches aquatic ecosystems
plastic debris is durable & breaks into microplastics
washes out of watersheds into oceans
areas where circulating currents converge (gyres) bring & trap plastic trash
effects of litter to aquatic ecosystems
marine plastics mistaken as food (plankton or fish eggs)→ ingestion, choking hazard, intestinal blockages → deaths of marine mammals & seabirds
plastics contain harmful substances (Bisphenol A & phthalates) → leech into digestive tracks of organisms + POPs adhere to plastics & increase toxicity
risk of entanglement in plastic → suffocation & exhaustion
impacts of oil spills
organisms may be killed by smothering, injstion, inhaling, or absorbing oil
fish kills become coated → reduces gas exchange
birds loose buoyancy → process to hypothermia
decreased light penetration → reduced photosynthesis & base of marine food chains
chemical dispersants
break down oils into smaller droplets, diluting the concentration & reducing toxicity
others ways to clean up oil spills
microbes that degrade oil
burning oil off the surface of the water
use of skimmers to collect oil on the surface + floating booms to keep it contained
using absorbent material to soak up the oil as it washes ashore
physically cleaning rocks & organisms along short-line
wetlands
area with soil submerged/saturated in water for at least part of the year but shallow enough for emergent plants (adapted to living with roots submerged in standing water—cattails, lilpads, reeds)
ecosystem services of wetlands
supporting: H20 filtration, biodiversity, nutrient cycling
regulating: groundwater recharge, absorb of floodwater, CO2 sequestration
provisioning: habitat for animal & plant foods
cultural: tourism, revenue, fishing licence, camping fees, ed/med research
threats to wetlands
pollutants (nutrients N/P)
sediment
motor soil
pesticides
sea-level rise
development (can be filled in or drained)
water diversion for flood control, agriculture, or drinking water → reduces water flow & dries them up
dam construction
overfishing
mangroves
small trees with unique roots that grow in saline or brackish water throughout the tropics
mangrove ecosystem services
supporting: biodiversity (habitat nursery), H2) filtration, nutrient cycling
regulating: coastal protection, storm buffering, erosion control
provisioning: habitat for juvenile commercial fish species, timber, fuelwood
cultural: tourism, recreation, aesthetics
threats to coasts
same threats as wetlands
sea-level rise
development
pollution
over harvesting aquaculture
mercury
considered most toxic heavy metal in the environment & main contributor is coal combustion, trash incineration, burning medical wastes, & heating limestone for cement production
inorganic mercury (Hg 2+)
has low toxicity, attaches to PM released by combustion → deposited wherever PM settles
methylmercury (CH3Hg+ or MeHg)
Hg2+ depositioned in aquatic ecosystems that converts to a more organic toxic form by phytoplankton & bacteria → is incorporated into lipids found in neurons → inhibits nervous systems function (neurotoxins) as result + lead to miscarriages + birth defects (teratogen) or bioaccumulates in organisms & biomagnifies in ecosystem
arsenic (AS)
naturally occurring element in rocks underground that can dissolve into drinking water & is naturally releases worsens with mining into ground water → coal ash & particulate matter can spread arsenic over large areas
**formally used in pesticides & wood treatments
toxicity of arsenic
carcinogenic (lungs, bladder, kidney)
endocrine disrupting (blocks receptor proteins on cell surfaces from receiving steroidal signal)
lead (Pb)
most abundant heavy metal pollutant (ex. old paint, old water pipes, car batteries, used as glaze in some pottery, PM from vehicle exhaust)
toxicity of lead
neurotoxicant (damages central nervous system)
endocrine disruptor
pathway inhibitors
toxicants that block steps in a biochemical pathway → may inhibit key enzymes (ex. Atrazine inhibits enzymes in Calvin Cycle of photosynthesis, cyanide inhibits electron carrier proteins in ETC of mitochondria, blocking cellular respiration)
endocrine disruptors
pathway inhibitors that interfere with the endocrine (hormonal) systems of animals
hormones stimulate growth, development, sexual maturity, work w/ extremely small concentration
endocrine disrupting chemicals interfere with normal signals → block hormones, preventing signals from working → mimics hormones (sometimes estrogen )
atrazine
endocrine disrupting chemical that binds to receptors, converting estrogen to testosterone in male frogs → higher estrogen/lower testosterene levels → lowers sperm count & causes gender reversal & development of eggs in test or ovary formation
human medications
pass through urine & into sewage or flushed down toilet → common source of endocrine disrupting chemicals
heavy metals
endocrine disruptors such as mercury, lead, arsenic
phthalates
endocrine disrupting compound used to make plastic more flexible & in cosmetic manufacturing (plastic, fragrances)
bisphenol A (BPA)
used to make hard plastics & epoxy → common in food-storage containers
polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAs)
non-stick coating of cookware → enter surface & groundwater through improper disposal of chemical water & landfill leaching
persistent organic pollutants (POP’s)
long-lasting, carbon-based synthetic compounds that do not easily breakdown in the environment, fat-soluble (accumulates & persists in fat instead of passing through body) + endocrine disruptor
travel long distances through wind & water
Ex. DDT, PCB’s, PBDEs, Dioxins, Phthalates (plastics)
sources of POPs
wastewater from industrial processes
pesticide productions
emissions
enter soils/water
assimilated by plants
stores in fatty tissues
eaten by humans
enter humans through drinking water
fat-soluble toxicants
POPs & heavy metals that don’t dissolve easily in water → don’t easily enter blood (not filtered) → stories in fatty acids & buildup
bioaccumulation
process of toxicants building up in biological tissues during a lifetime to greater concentrations than in the environment
biomagnification
process that occurs when concentrations of toxicants become magnified in higher levels of the food chain
eating species from a higher trophic level can pose a risk especially to pregnant women, children, & people with fish diets
ex. bioaccumulation of DDT → near extinction of peregrine falcons & bald eagles due to egg shell thinning
case histories
response of people who have been exposed to a substance in the past (mainly comes from autopsies of those with acute symptoms so little exists for low chronic exposure) → tells us little about risk of being exposed
epidemiological studies
large-scale, long term study of a group who have been exposed to a hazard vs. another group with no exposure → use of statistical methods to look for significant difference
subjects may be exposed to more than one risk factor → confounding effects
required long wait times for results & do not provide information about the toxicology of new substances but do provide accurate predictions of risk associated with exposure
animal studies
performed in the controlled conditions of a laboratory → provide specific data on toxicity of substances
**human responses are often determines from animal studies w/ mice & rats since they share evolutionary history
dose-response analysis
exposes groups of organisms to different concentrations (doses) of a a chemical in order to measure the response (effect) → results are plotted on graph to create dose-response curve to show probability of certain effect
independent variable
concentration of the chemical (added to food, water, air) → LOGARITHMIC SCALE on x-axis
dependent variable
% of population showing a specified response (death or specific impairment)
what is the unit for mass of toxin/unit of body mass?
mg/kg
mg is 1/1000 of kg
what unit is used to measure the mass of toxin/volume of water, air, etc?
mg/L
what are the common units?
ppm (parts of a million)
1 ppm= 1000 ppB
what shape do dose-response curves have?
s-shaped: low morality at low doses → rapid increase in mortality as dose increases (level off near 100% morality at high doses)
LD50
dose or concentration of the chemical that kills 50% of the population being studied
TD50
the dose required to show a specific toxic effect in 50% of the population
ED50
dose required to show a specific, often beneficial, effect on 50% of the population (similar to TD50 & often reported when substance results in desired effect)
threshold dose
minimum dosage where a specified response starts to occur → cells/tissues/organs can metabolize or excrete low doses of a toxicants → impacts start to show at higher doses
precautionary principle
do not proceed with new actions or at least proceed with extreme caution until the ramifications of those actions are well understand— “assume the worst until proven otherwise”
Ex. EPA, FDA, CDC, Europe
for each 3 levels of uncertainty, the experiment determines “safe dosage” concentration diving the results by 10 → results are 1000x lower than animal studies
CONS: may impede pace of technology & hinder economic advance due to higher burden of proof
synergistic effects
interactive impacts that are greater than the sum of their constituent effects
ex. 2+2 = 20
additive effect
mixed toxins that sum up
ex. 2+2 = 4
antagonist effect
mixed toxins that cancel out
ex. 2+2=1
“innocent-until-proven-guilty” approach
assumed a substance is harmless until shown to be harmful → helps technological innovation & economic advancement by limiting initial resting but allows dangerous substances to be widely used before later determination of greater risk
Ex. U.S approach
Toxic Substances Control Act (1976)
directs the EPA to monitor (but not test) thousands of chemicals made in or imported into the US → can ban substances that pose excessive risks but many advocates think its too weak
The Stockholm Convention on POPs
enacted in 2004 & ratified by over 150 nations → set guidelines for phasing out the “dirty dozen”— 12 most dangerous POPs— & encourage the transition to safer alternatives
Delaney Clause (1958) of the food, drug, & cosmetics Act (1938)
bans the use of food additives found to induce cancer in humans or lab animals at any dosage
solid wastes
any discarded material that is not a liquid or gas & is generated in domestic, industrial, business, & agricultural sectors → disposed of in landfills → can contaminate groundwater & release harmful gases if built incorrectly
origins of industrial solid waste (ISW)
mining, farming, construction (demolition)
municipal solid waste (MSW)
waste from home & workplaces other than factories
what are some solid waste migration strategies?
burning waste, restoring habitats as parks, reusing, recycling
sanitary municipal landfill
consists of:
bottom liner (plastic or clay)
storm water collection system
a cap
methane collection system
advantages of sanitary municipal landfills
cheap, efficient, filled land can be used for other purposes, no shortage of space
disadvantages of sanitary municipal landfills
noise, traffic, dust, releases methane & C02 unless being collected, output approach that encourages waste production, eventually leaks & can contaminate groundwater
incineration of solid wastes
waste is burned at high temperatures → releases air pollution (CO, PM, heavy metals) → need for costly scrubbers and electrostatic
The 3R’s: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
Recycling= process by which certain solid waste materials are processed & converted into new products → reduces demand on materials & minerals but process in energy-intensive & can be costly & inconvenient
Reusing= using objects over & over again
Reducing= making less waste
electronic waste/e-waste
composed of discarded electronic devices (TV, phones, computers) → metals can leech into groundwater & sent to other countries
food waste & composting
process of organic materials decomposing & can be used as fertilizer but there is odor & rodents
pathogens
a living organism (virus, bacteria, fungi, parasite, worm) that causes an infectious disease → they adapt & evolve to take advantage of humans for their reproduction
infectious disease
capable of being spread or transmitted (ex. HIV, ebola, COVID)
vector
living organism (rat, mosquito, tick) that carry & transmit infectious pathogens to other organisms
tuberculosis (TB)
bacterial (pathogen) infection that targets the lungs & is transmitted by breathing bacteria from body fluids of an infected person (can linger in air for hours) → causes night sweats, fever, coughing blood, treable with access to powerful antibiotics, & leading cause of disease death in developing world
plague
bacterial (pathogen) infection transmitted by fleas that attach to mice & rats through contact or containated human fluids
malaria
parasite protist (pathogen) infection caused by bite from infected mosquitos (most common in Africa)- symptoms like flue & kills children under 5
west nile
virus (pathogen) caused by bite from infected mosquitos → birds are main host but can be transmitted to humans by mosquitos → brain inflammation
zika virus
virus (pathogen) infection caused by bite from infected mosquitos & sexual contact with infected individuals → causes babies to be born with abnormally small heads & damaged brains
coronavirus
through to have first appeared in bats & spread to other animal hosts → transmitted through touching/inhaling fluids of others → fever, cough, pneumonia, diarrhea, asymptomatic
reservoir species
species humans more commonly come in contact with that the coronavirus can mutate to infect the species & humans
severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARs-CoV)
likely transmitted from palm civets to humans in southern China
middle east respiratory syndrome (MERS)
likely transmitted from humans by dromedary camals in Saudi Arabia
severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARs-Cov-21)
suspected of having been transmitted to humans by unknown vector
dysentery
bacterial infection caused by food/water being contaminated with feces → intestinal swelling, blood in feces, & severe hydration
chlorea
bacterial infection caused by drinking infected water → extremely contagious → vomiting, muscle cramps, diarrhea, severe dehydration
Sewage treatment process
Primary Treatment: physical removal of large debris (TP, leaves, plastic, sediment) with screens or grates
Secondary Treatment: biological breakdown of organic matter by bacteria (aerobic process requiring O2)
Tertiary treatment (optional): chemical treatment to reduce nutrient pollution (nitrate, phosphate, ammonia)
Disinfection: UV light, ozone, or chlorine is used to kill bacteria & pathogens
sludge is disposed in landfills or sent to anaerobic digester → generated methane gas & can be used to generate electricity
Screens & grates filter out large soils → allow sediment to settle out & be removed
oils & grease are skimmed from top & primary is collected & disposed or sent to aerobic digester
O2 bubbles into aeration tank (filled with bacteria that break down organic matter)
Effluent is charge dinto surface water with elevated nitrate & phosphate → eutrophication