4th Six-Weeks, Unit I: Wold War II
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
dictatorship
A form of government in which the leader has absolute power and authority.

appeasement
Accepting demands in order to avoid conflict

Neutrality Acts
Originally designed to avoid American involvement in World War II by preventing loans to those countries taking part in the conflict; they were later modified in 1939 to allow aid to Great Britain and other Allied nations.
Cash and Carry
countries such as Britain and France would have to pay for American goods in cash and provide transportation for them. This would keep US ships out of the war zone and eliminate the need for war loans

Lend Lease
Approve by Congress in March 1941; The act allowed America to sell, lend or lease arms or other supplies to nations considered "vital to the defense of the United States." Replaced Cash and Carry.

conventional weapons
Soldiers, small arms, artillery, tanks, war planes, and ships (as opposed to chemical, biological, and nuclear weapons).

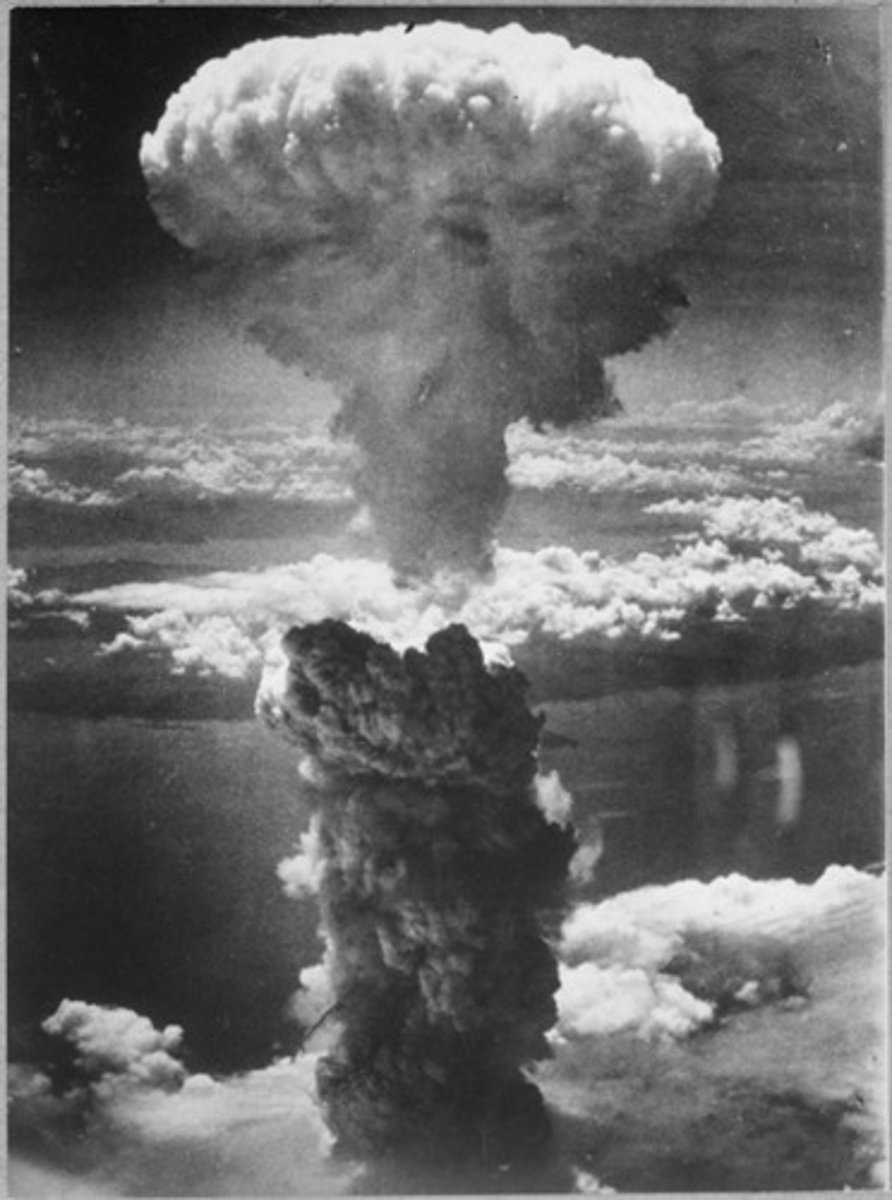
atomic weapons
weapons of mass destruction that cause radiation and physical damage - developed by U.S. in 1945, used on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Developed in 1949 by the U.S.S.R. (The Soviet Union).

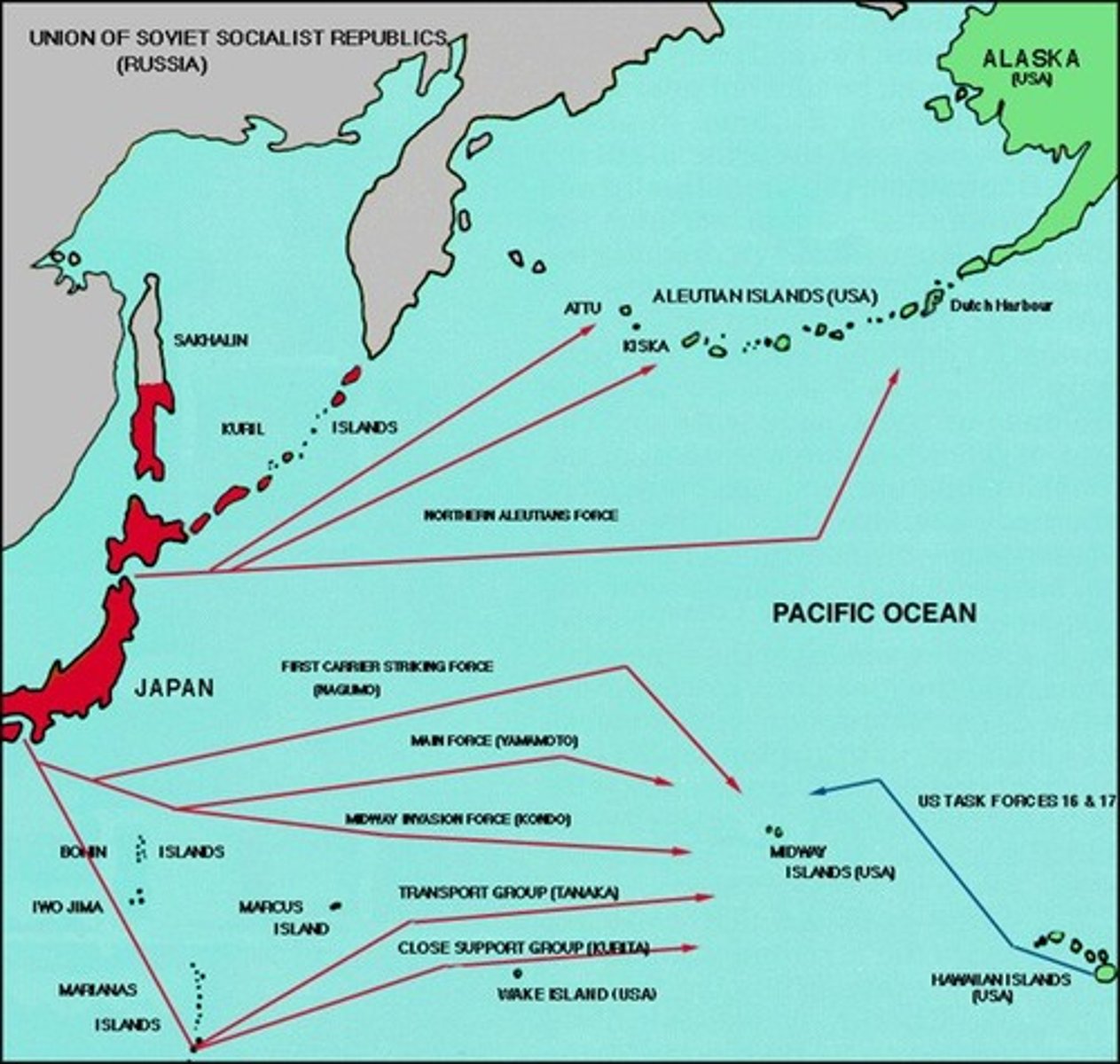
Battle of Midway
1942 World War II battle between the United States and Japan, a turning point in the war in the Pacific
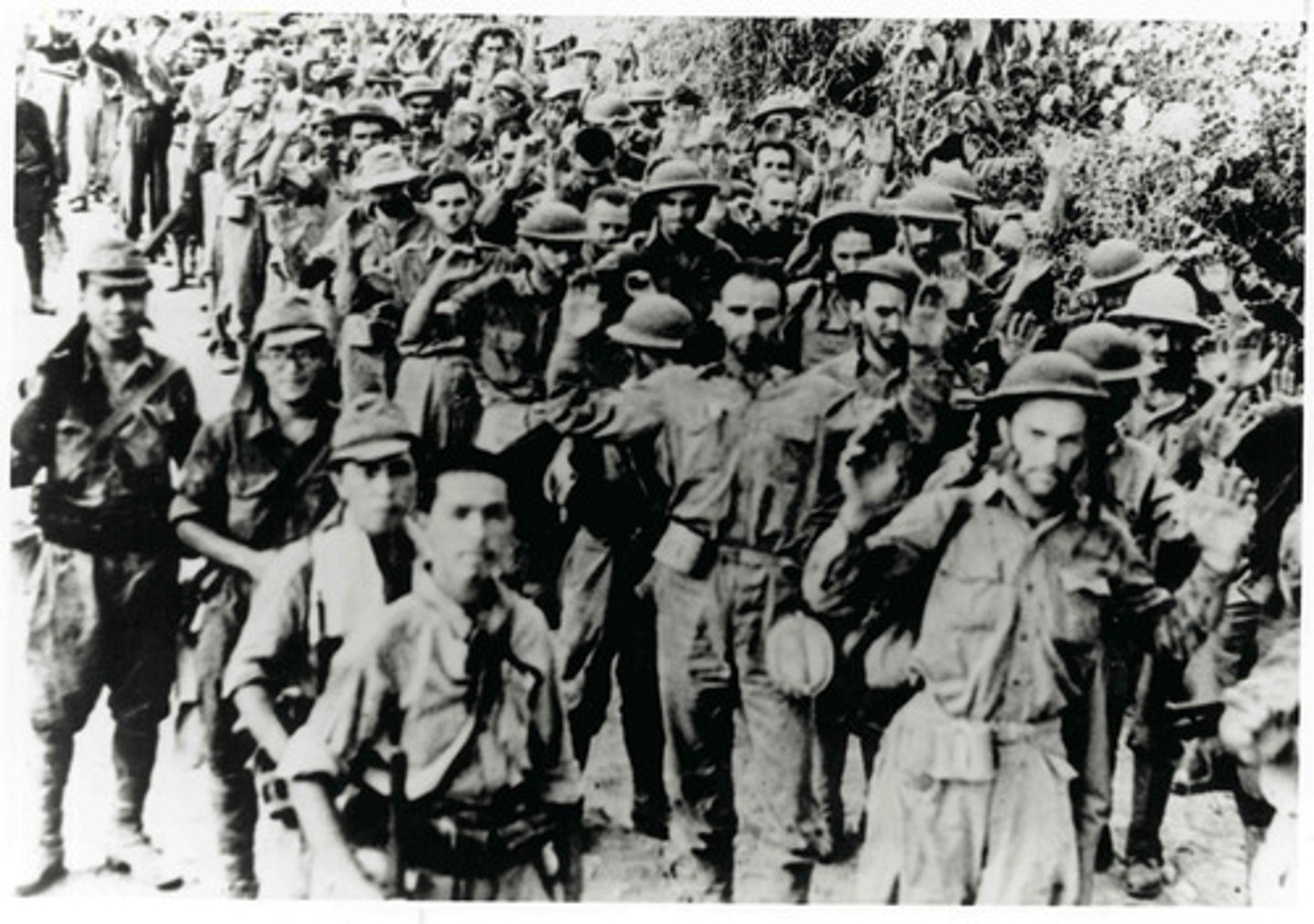
Bataan Death March
A long trek across the Philippines that American and Filipino prisoners of war were forced to make by the Japanese in 1942. The Japanese forced 75,000 American and Filipino prisoners too march 65 miles w/ little food or water. About 100,000 prisoners died or were killed.

Invasion of Normandy
1944; "D-Day"; Eisenhower directed an assault on a beach in France; Established the second front through France, only one of three successful invasions across the English Channel. Also called Operation Overlord.

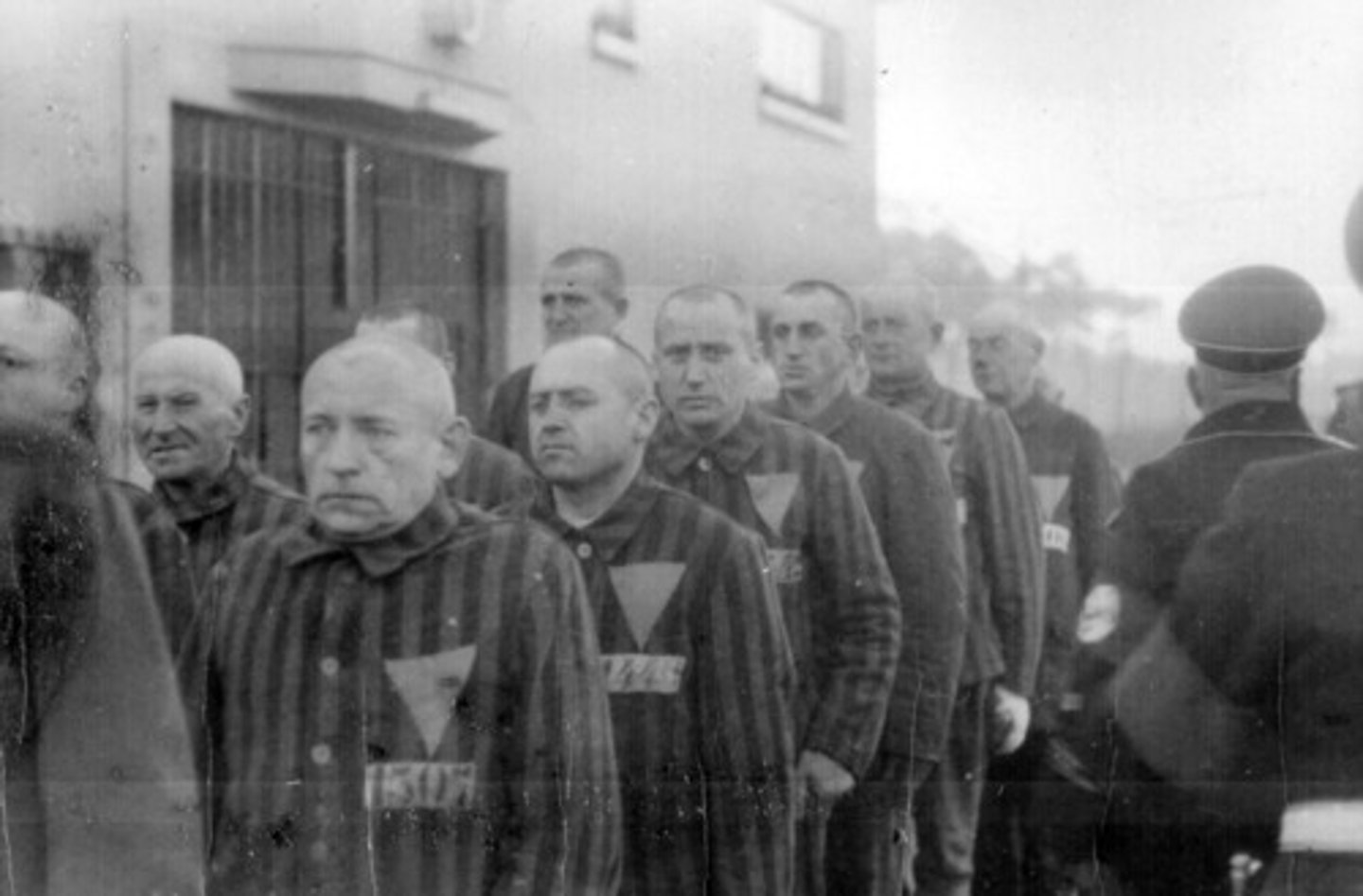
concentration camps
Camps used by Nazis to imprison "undesirable" members of society (Hitler's enemies, the Jewish population, intellectuals, homosexuals, etc.) Conditions were inhuman, and prisoners were generally starved or worked to death, or killed immediately.

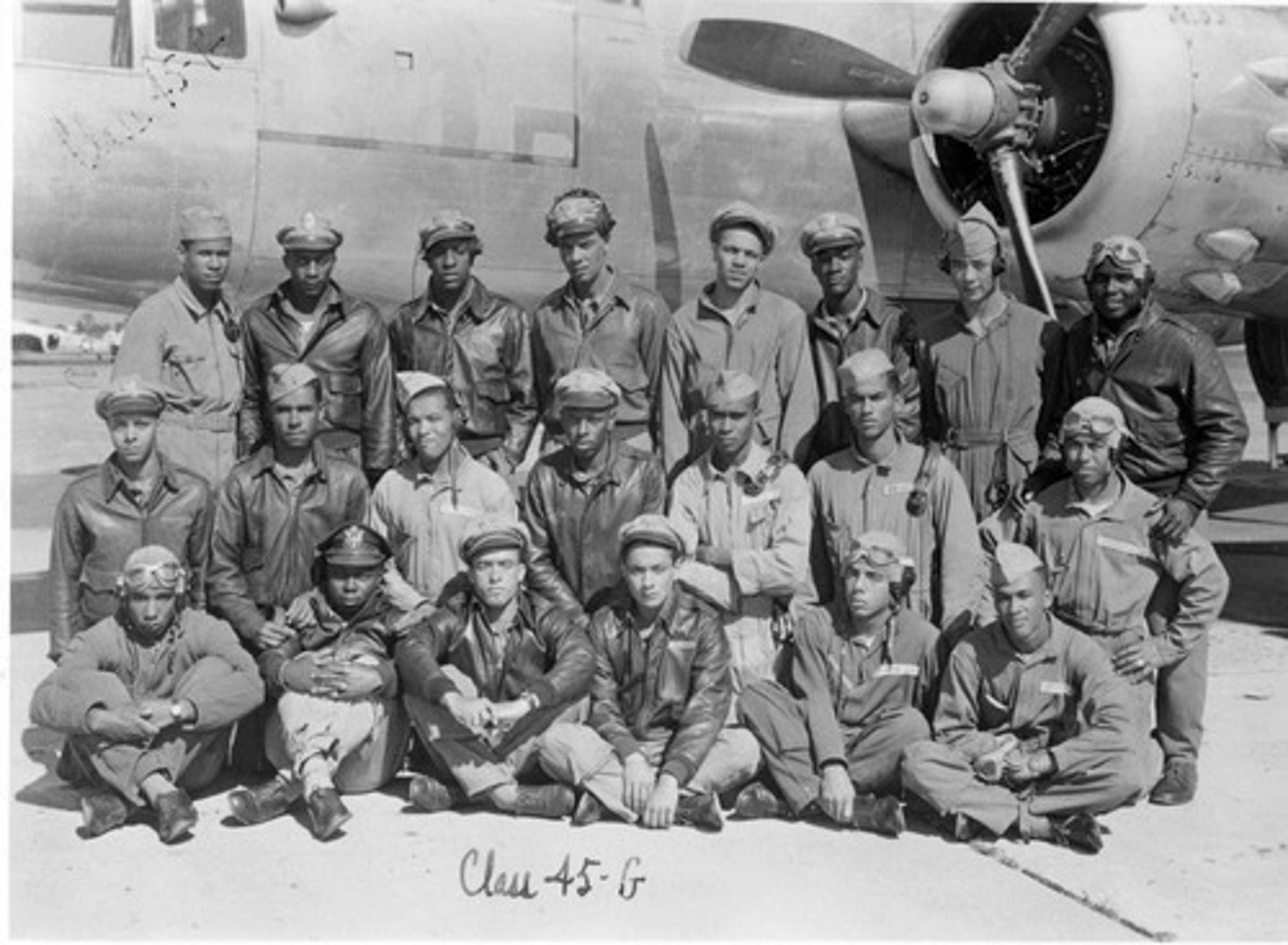
Tuskegee Airmen
332 Fighter Group; African American group of fighter pilots; famous for shooting down over 200 enemy planes. Won many awards for bravery and never lost a single pilot.

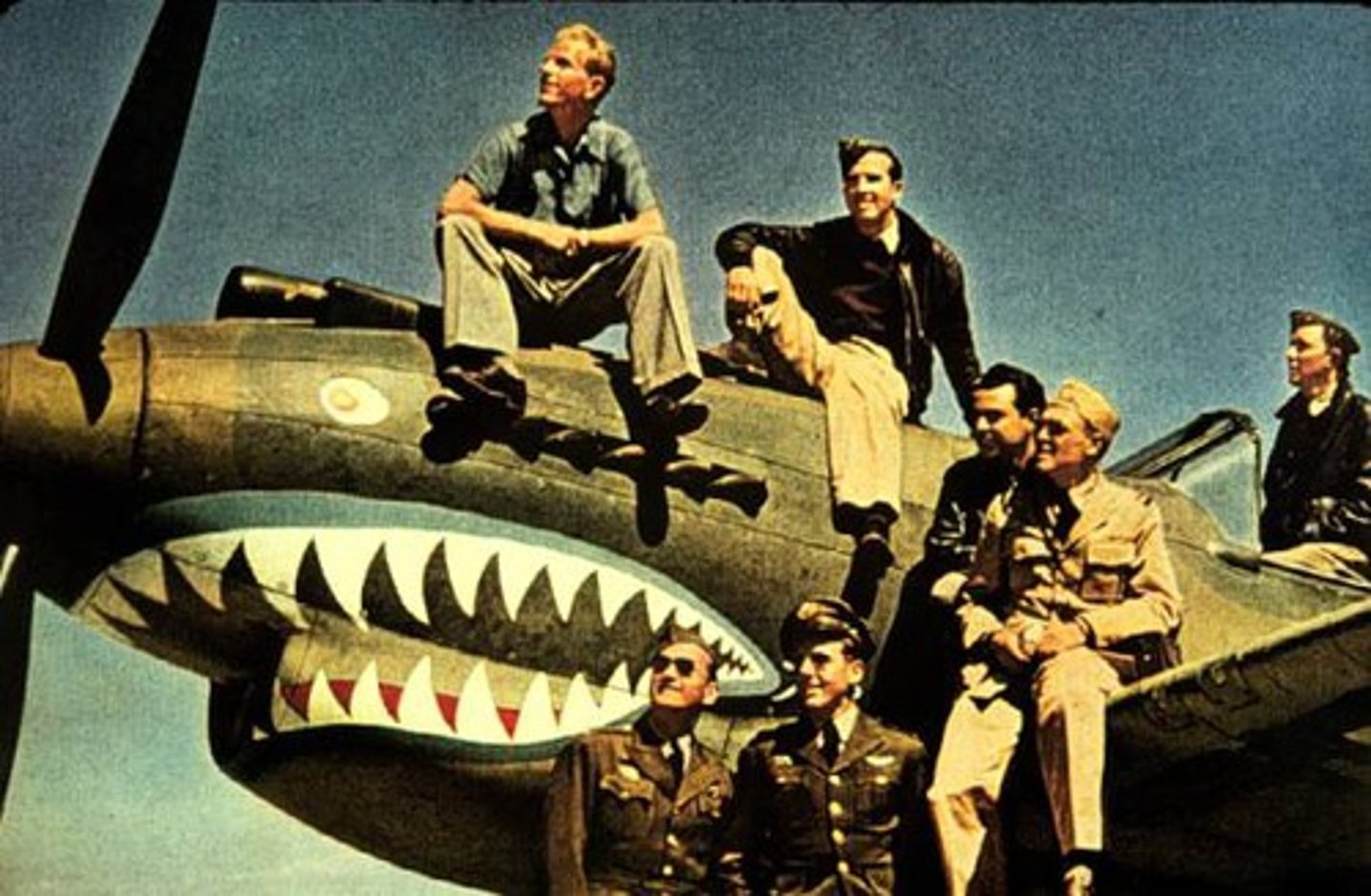
Flying Tigers
American Volunteers that flew P-40 Tomahawks in China and Burma to defend Chinese and Allied troops; slowed Japanese invasion and stopped Japanese from bombing China

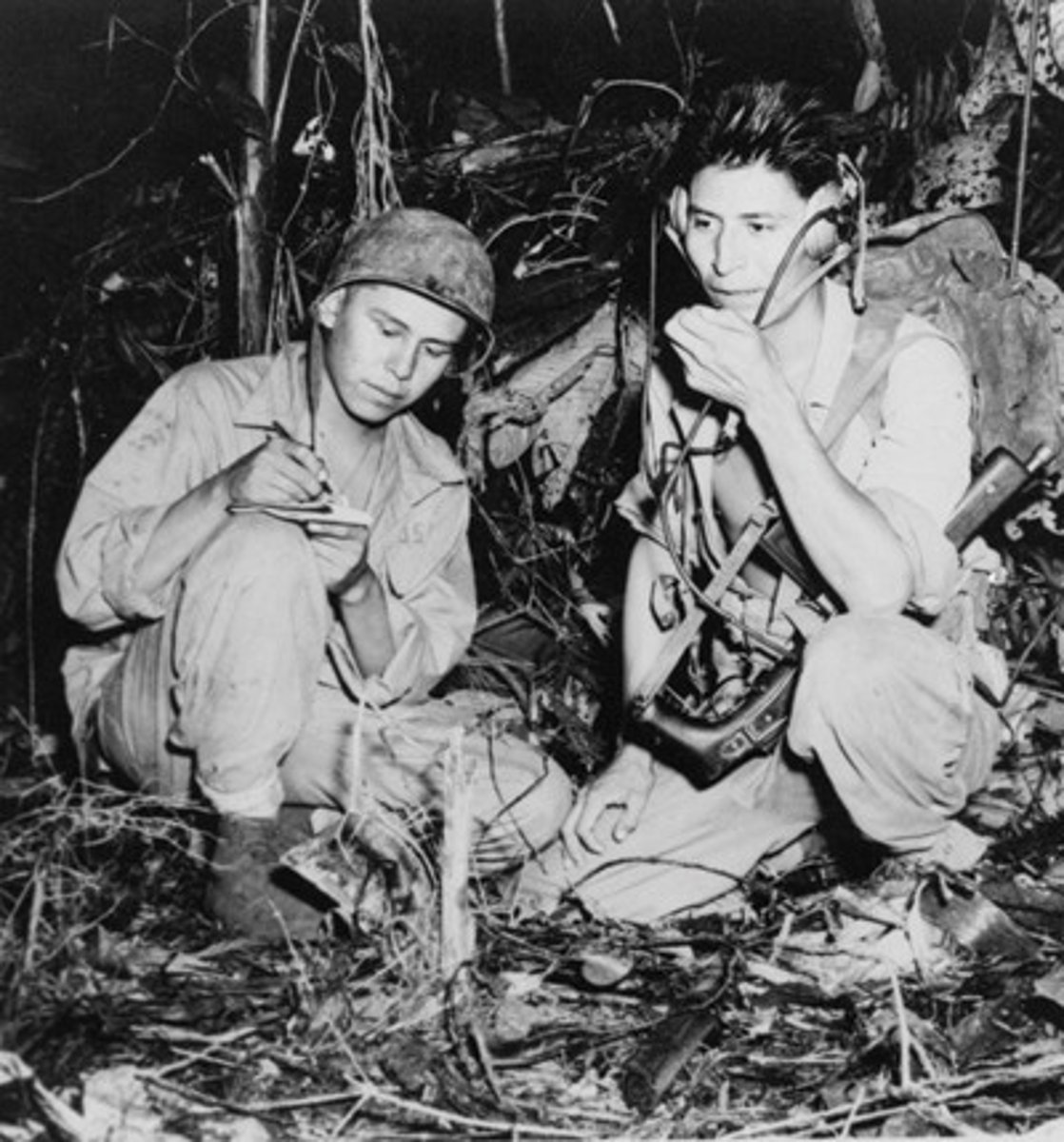
Navajo Code Talkers
Native American men who served in the military by transmitting radio messages in their native language, which was undecipherable by German and Japanese spies.

mobilization
Act of assembling and putting into readiness for war or other emergency: "mobilization of the troops"

Executive Order 9066
1942. Issued by FDR and applied by Stimson, it allowed for the internment of Japanese-American citizens and residents. 112,000 Japanese-Americans forced into camps, causing loss of homes & businesses.

war bonds
An effort by the US Government to raise 300 billion for the war effort. Americans loaned the government money (bonds) with a promise of a repayment plus interest at a later date. 50 billion was raised.

Victory Gardens
Gardens that citizens planted to raise their own vegetables, so that food could be sent to the troops.

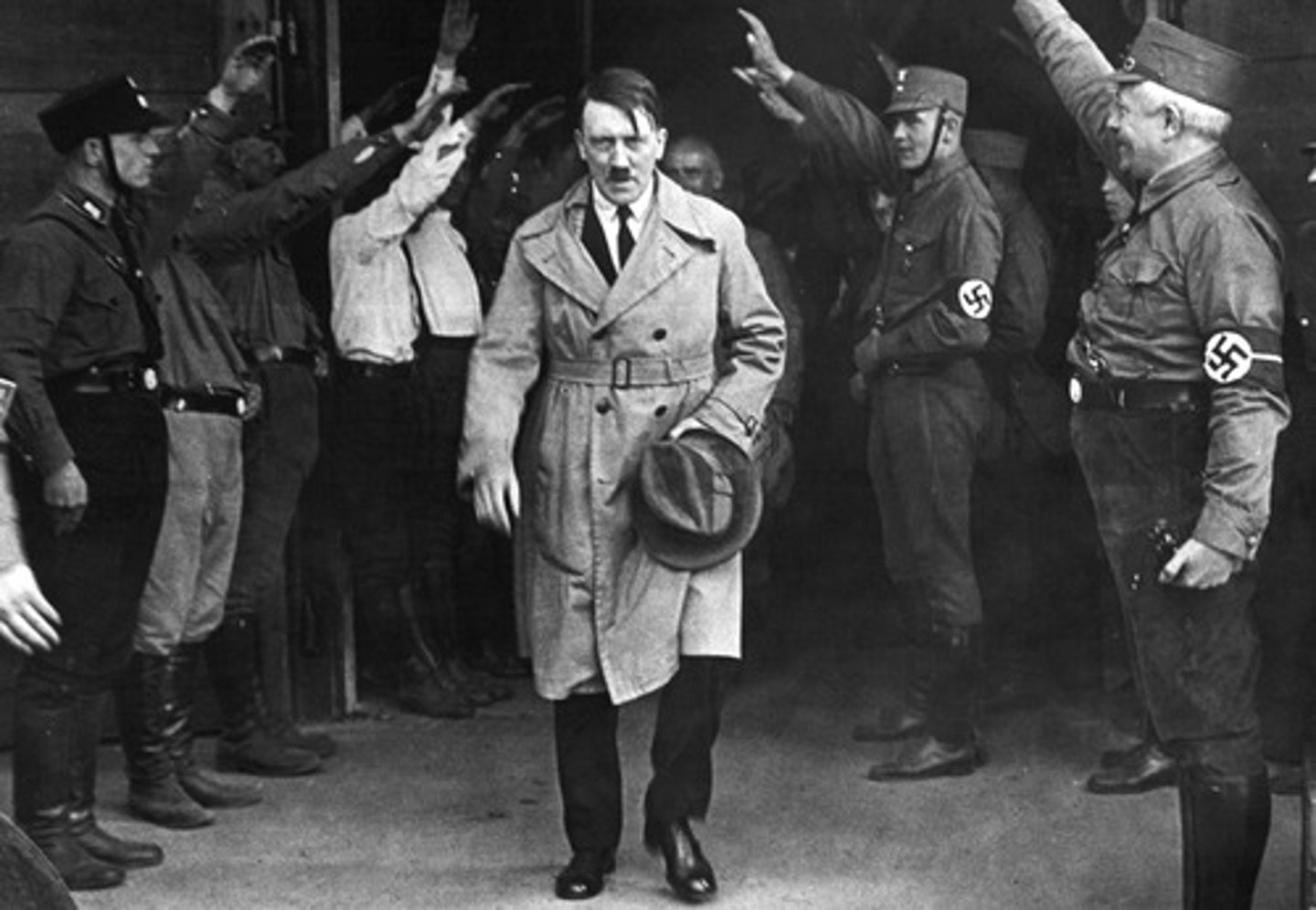
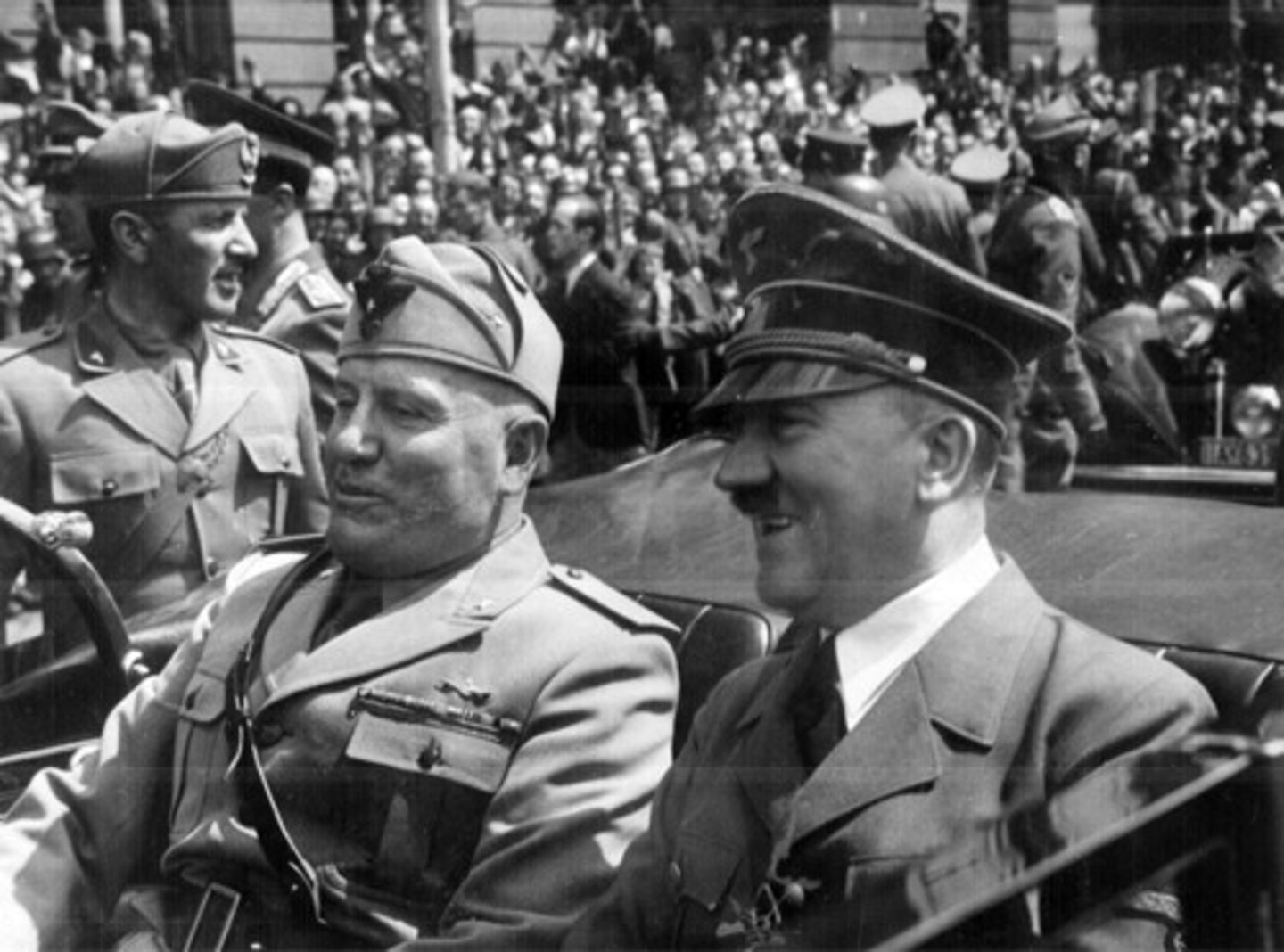
Adolf Hitler
Austrian-born founder of the German Nazi Party and chancellor of the Third Reich (1933-1945). His fascist philosophy, embodied in Mein Kampf (1925-1927), attracted widespread support, and after 1934 he ruled as an absolute dictator. Hitler's pursuit of aggressive nationalist policies resulted in the invasion of Poland (1939) and the subsequent outbreak of World War II. His regime was infamous for the extermination of millions of people, especially European Jews.

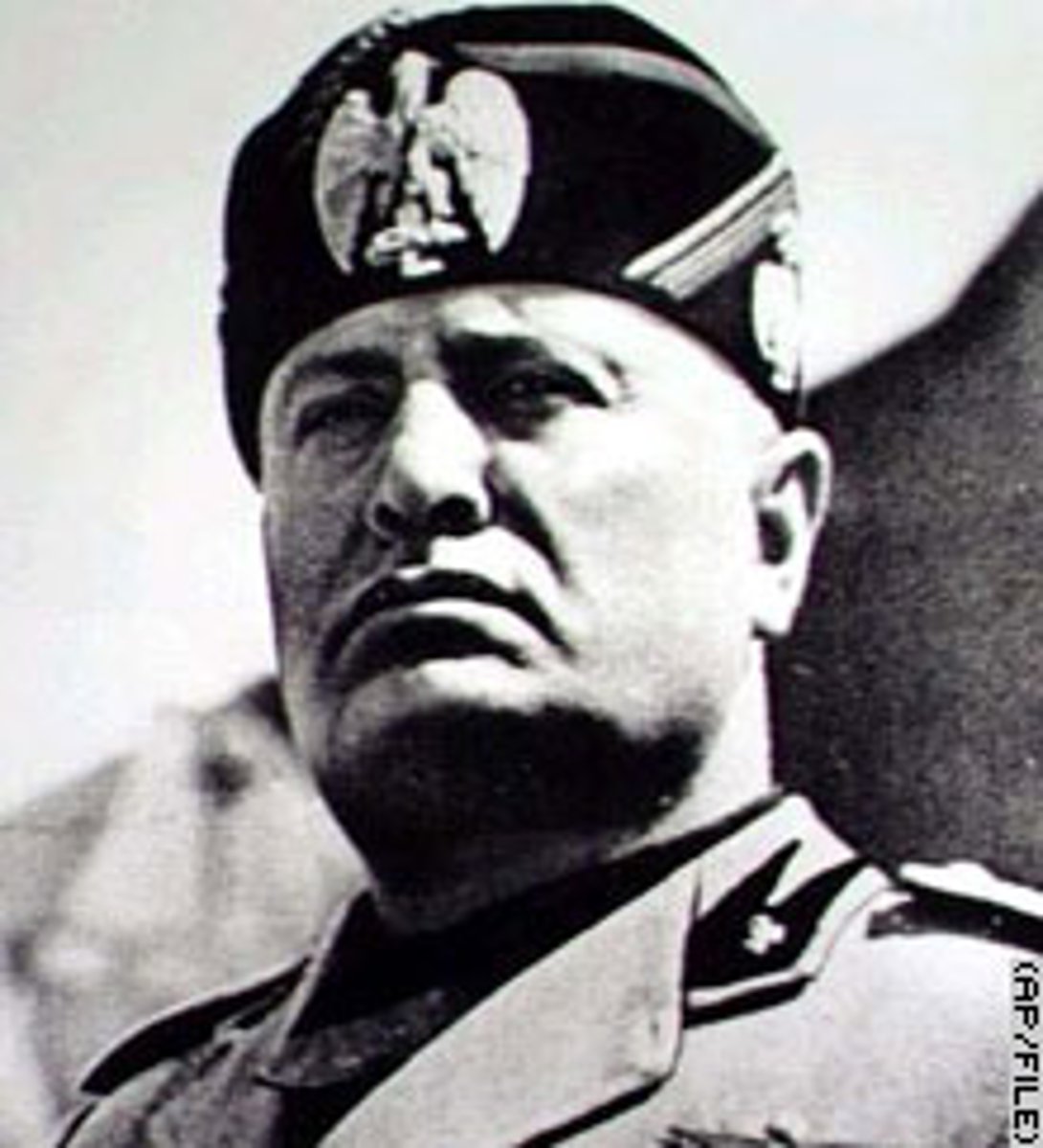
Benito Mussolini
Fascist dictator of Italy (1922-1943). He led Italy to conquer Ethiopia (1935), joined Germany in the Axis pact (1936), and allied Italy with Germany in World War II. He was overthrown in 1943 when the Allies invaded Italy. (p. 786)

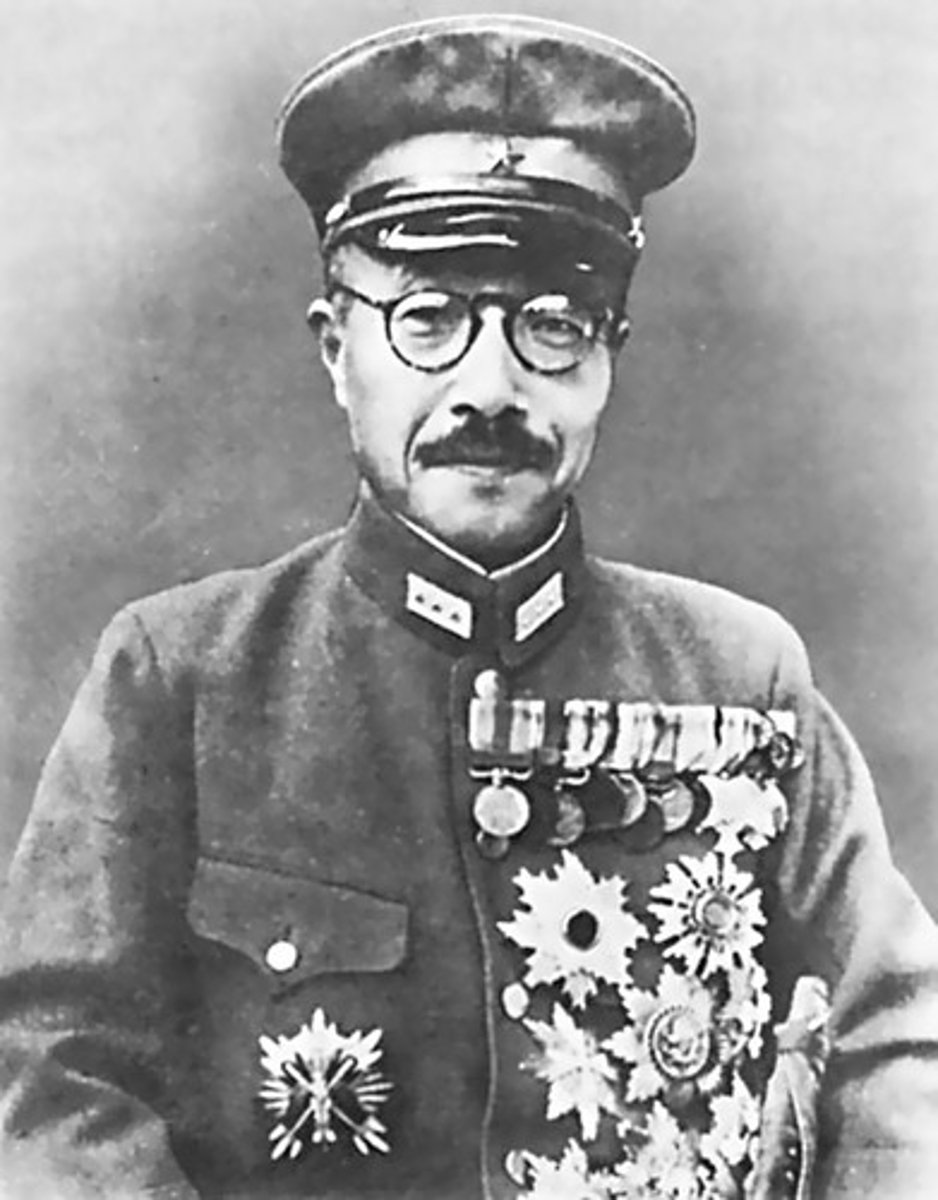
Hideki Tojo
Japanese army officer who initiated the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor and who assumed dictatorial control of Japan during World War II

Franklin Delano Roosevelt
the 32nd president of the United States, and the only president to serve more than two terms; from 1933 to 1945. Engineered the New Deal, which did much to halt the damages of the Depression, and led the country during World War II until his death in 1945.

Harry S. Truman
(1945-1949) and (1949-1953), Succeeded Franklin D. Roosevelt upon his death. Led the country through the last few months of World War II, and made the controversial decision to use two atomic bombs against Japan in August 1945. After the war, Truman was crucial in the implementation of the Marshall Plan, which greatly accelerated Western Europe's economic recovery. Created the CIA.

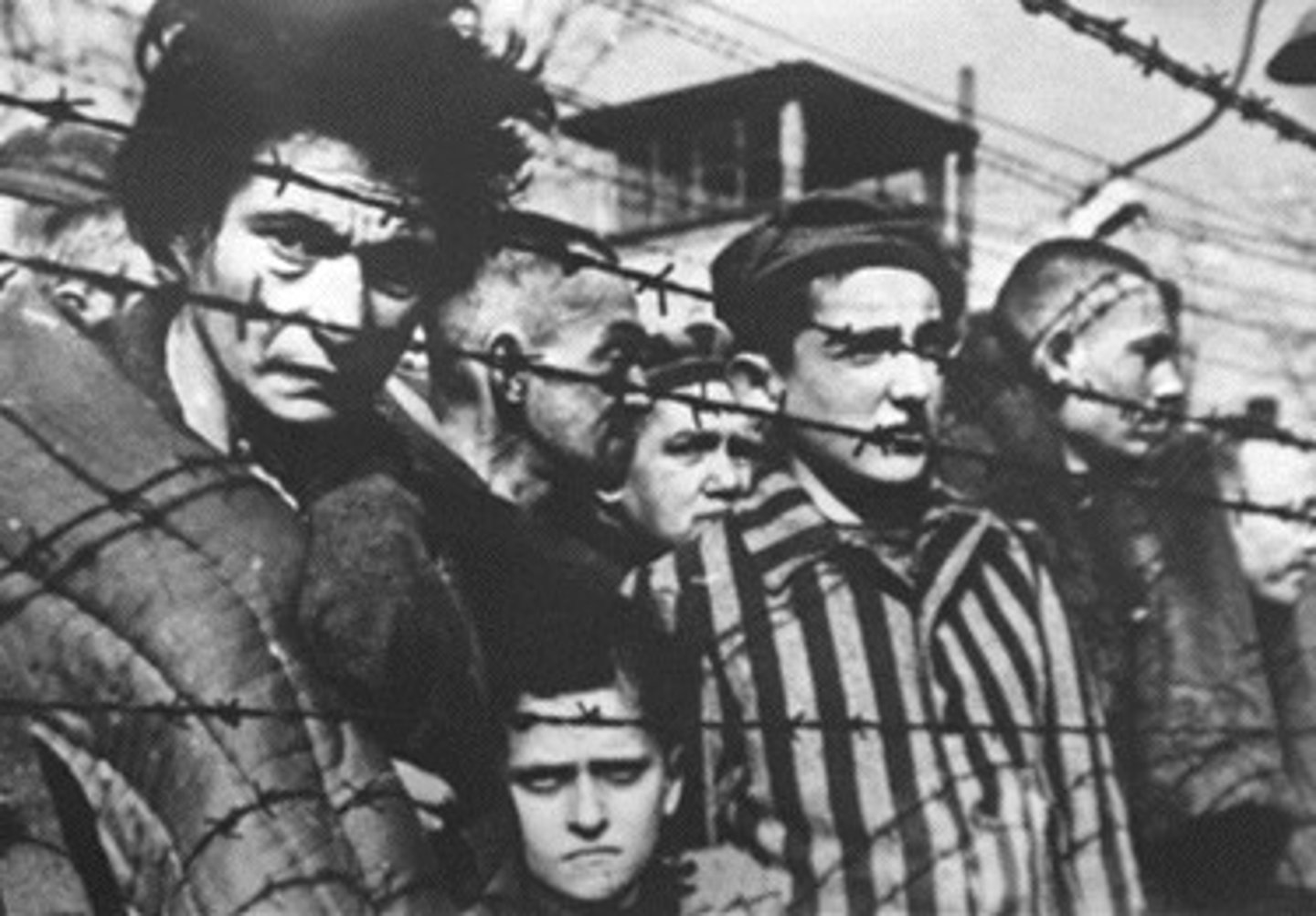
Holocaust
A methodical plan orchestrated by the Nazi party to ensure German supremacy. It called for the elimination of Jews, non-conformists, homosexuals, non-Aryans, and mentally and physically disabled. Also known as "Shoah" in Hebrew.

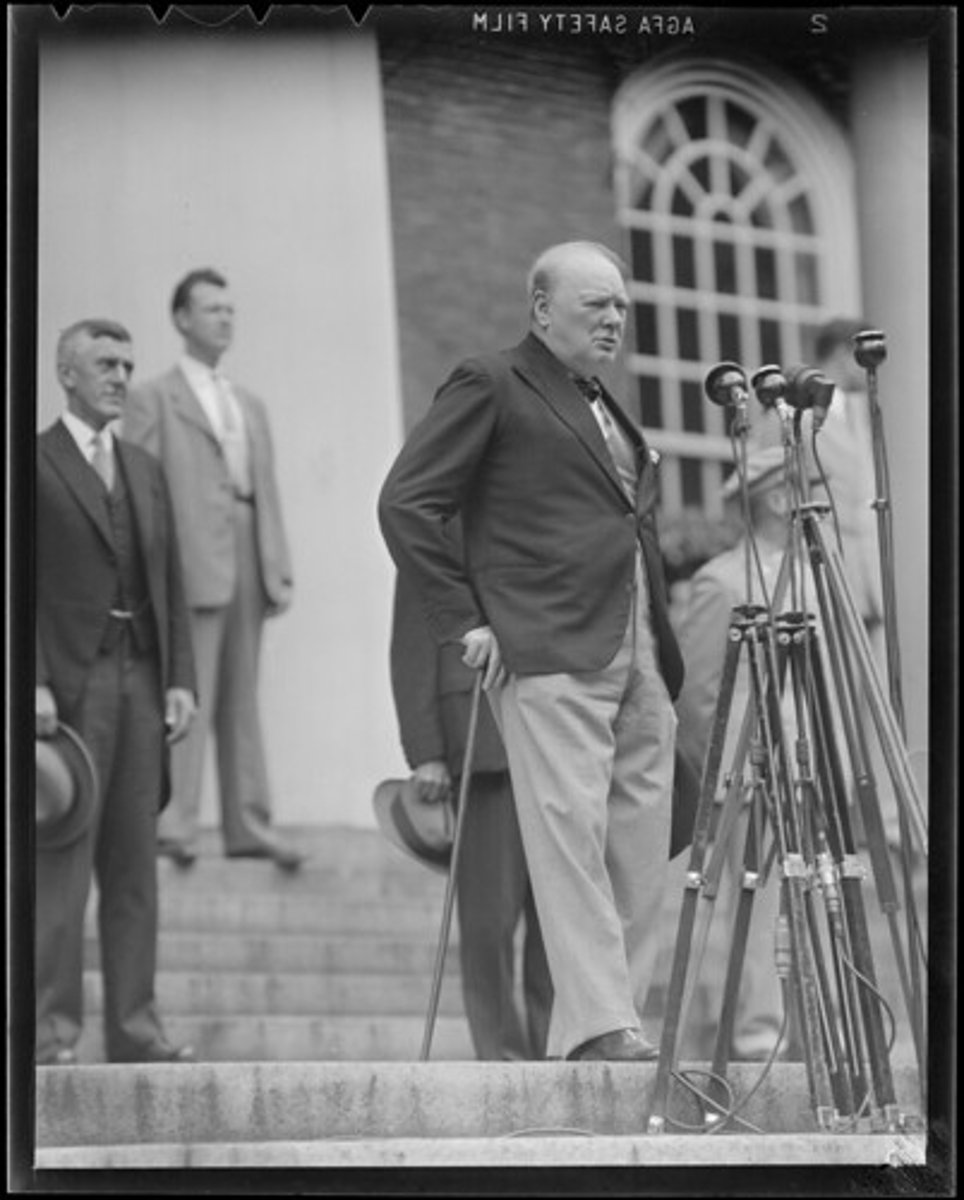
Winston Churchill
British statesman who led throughout most of World War II and, along with Roosevelt, planned many Allied campaigns. He predicted an Iron Curtain that would separate Communist Europe from the rest of the West.

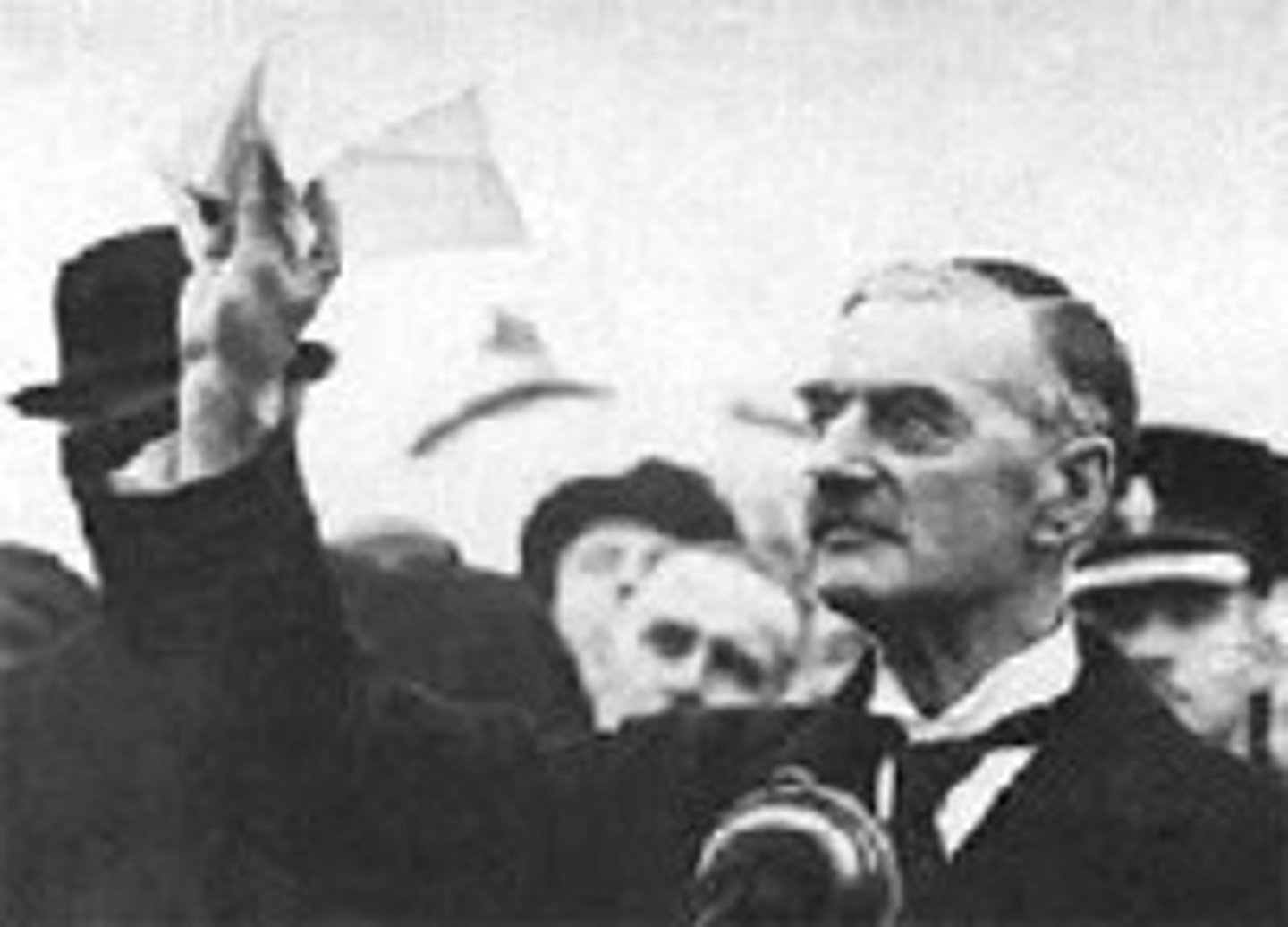
Neville Chamberlian
British Prime minister who, in Munich, agreed to appease Hitler by not opposing Hitler's move against the Sudetenland in 1938, famously saying "There will be peace in out time."

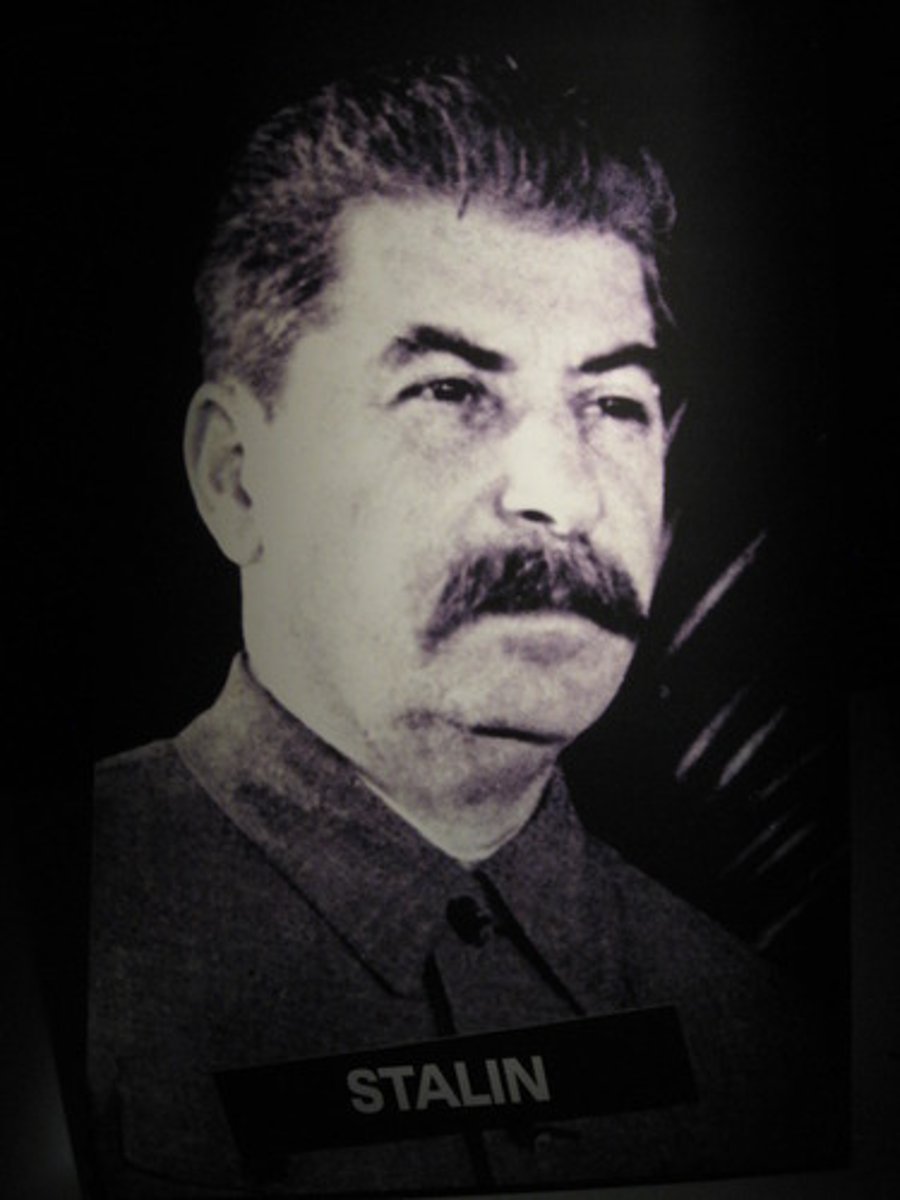
Joseph Stalin
Bolshevik revolutionary, head of the Soviet Communist Party after 1924, and dictator of the Soviet Union from 1928 to 1953. He led the Soviet Union with an iron fist, using Five-Year Plans to increase industrial production and terror to crush all opposition.

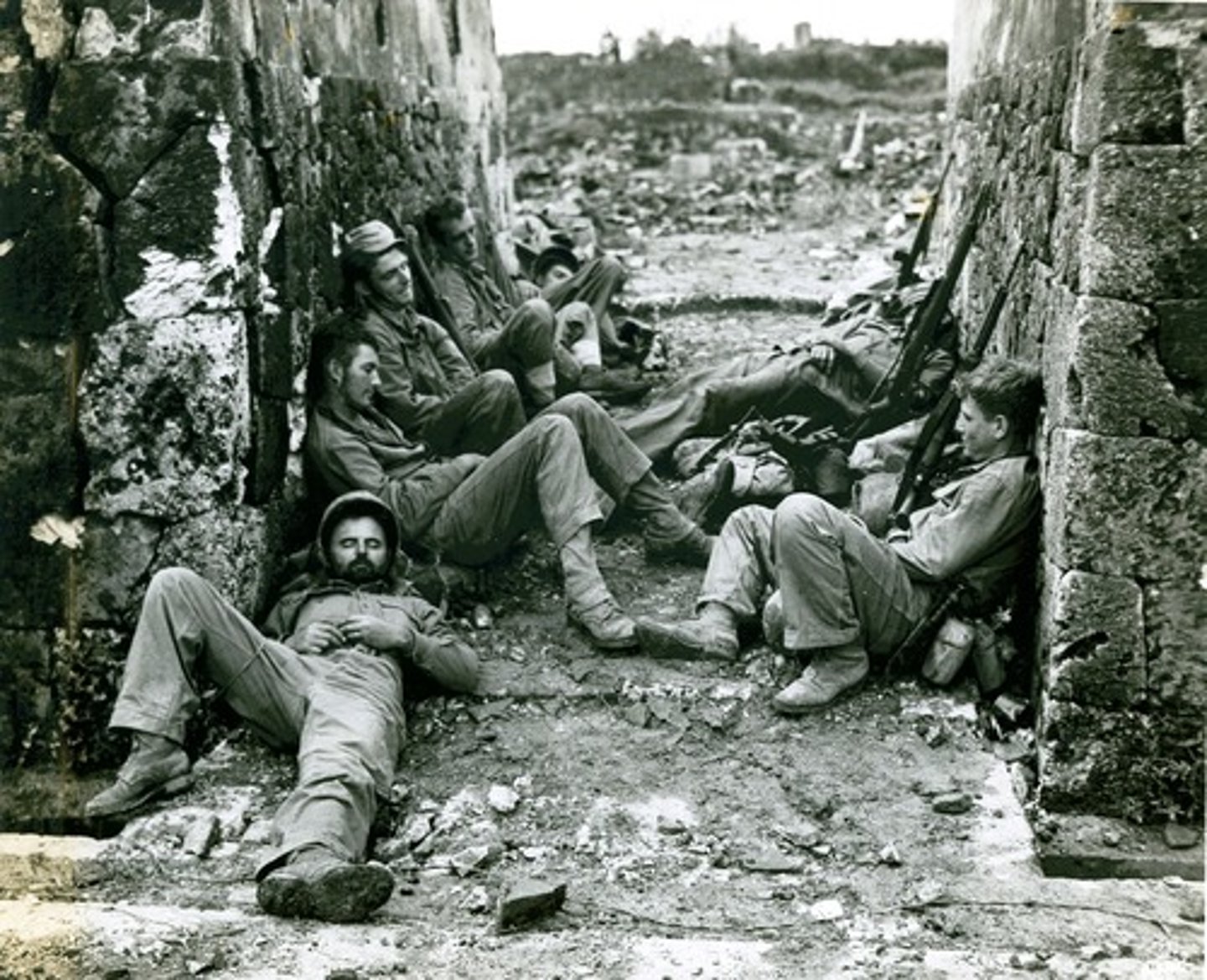
Okinawa
Last major battle of WWII on an island only 300 miles from the Japanese mainland. Horrific fighting in which the Japanese lost 110,000 soldiers (killed) and the US lost 50,000 (casualties).

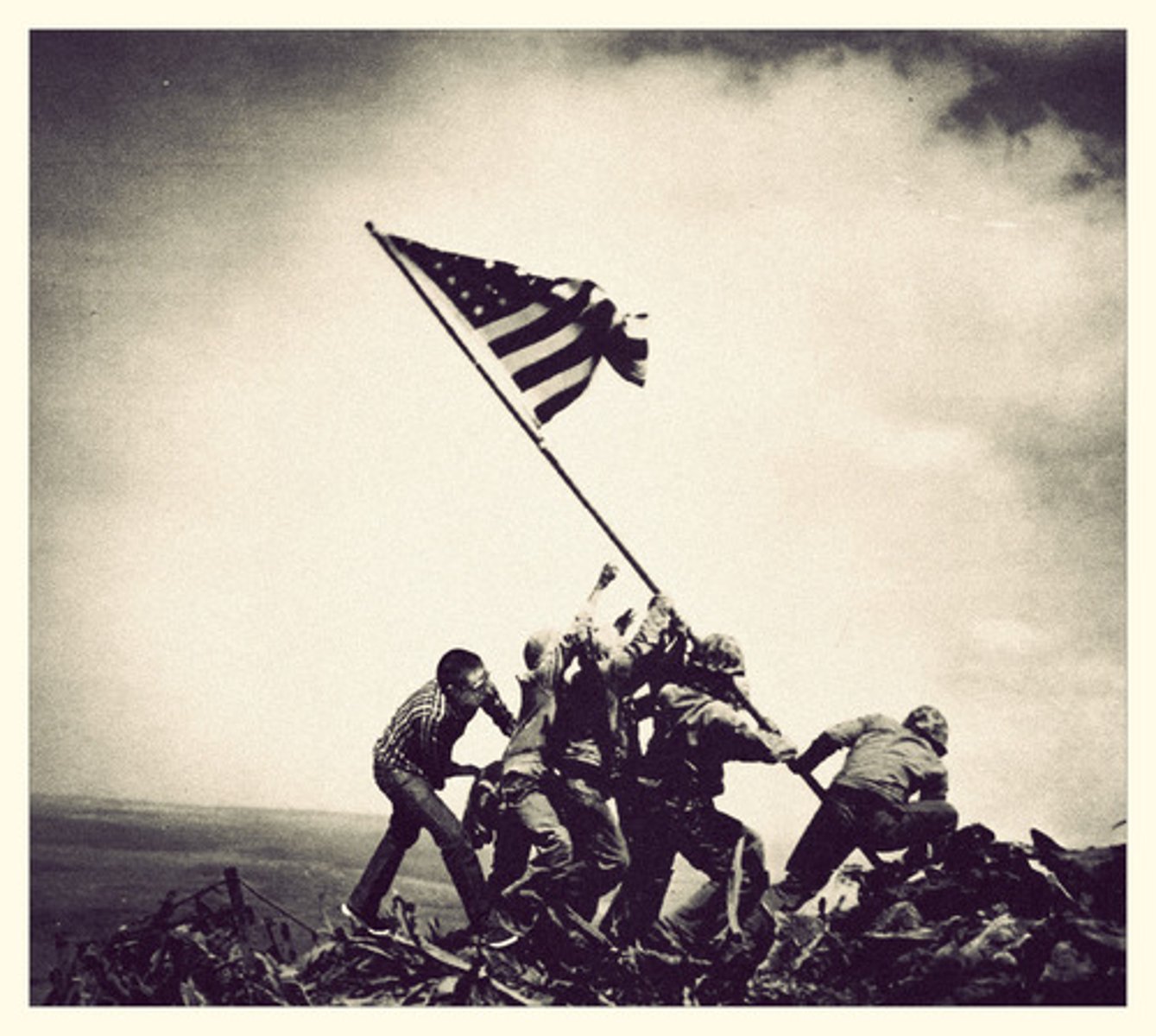
Iwo Jima
450 miles from Japan, possible a good Allied base from which to attack Japan. There were 21,000 Japanese killed (of 22,000 defending) and the Americans suffered casualties (17,000 wounded; 6000 killed).

Leapfrogging
Allied strategy in the Pacific to focus on less heavily defended islands

Great Depression
(1929-1939) The dramatic decline in the world's economy due to the United State's stock market crash of 1929. Results in millions of people losing their jobs as banks and businesses closed around the world. Many people were reduced to homelessness, and had to rely on government sponsored soup kitchens to eat. World trade also declined as many countries imposed protective tariffs in an attempt to restore their economies.
Manhattan Project
Code name for the U.S. effort during World War II to produce the atomic bomb.

lebensraum
(German for "habitat" or literally "living space") served as a major motivation for Nazi Germany's territorial aggression. In his book Mein Kampf, Adolf Hitler detailed his belief that the German people needed ____________ (for land and raw materials), and that it should be taken in the East.

Treaty of Versailles
the treaty imposed on Germany by the Allied powers in 1920 after the end of World War I. The German were forced to pay large war debts to the victors and the treaty restricted Germany's military development. Anger over this treaty helped the Nazi Party rise to power.

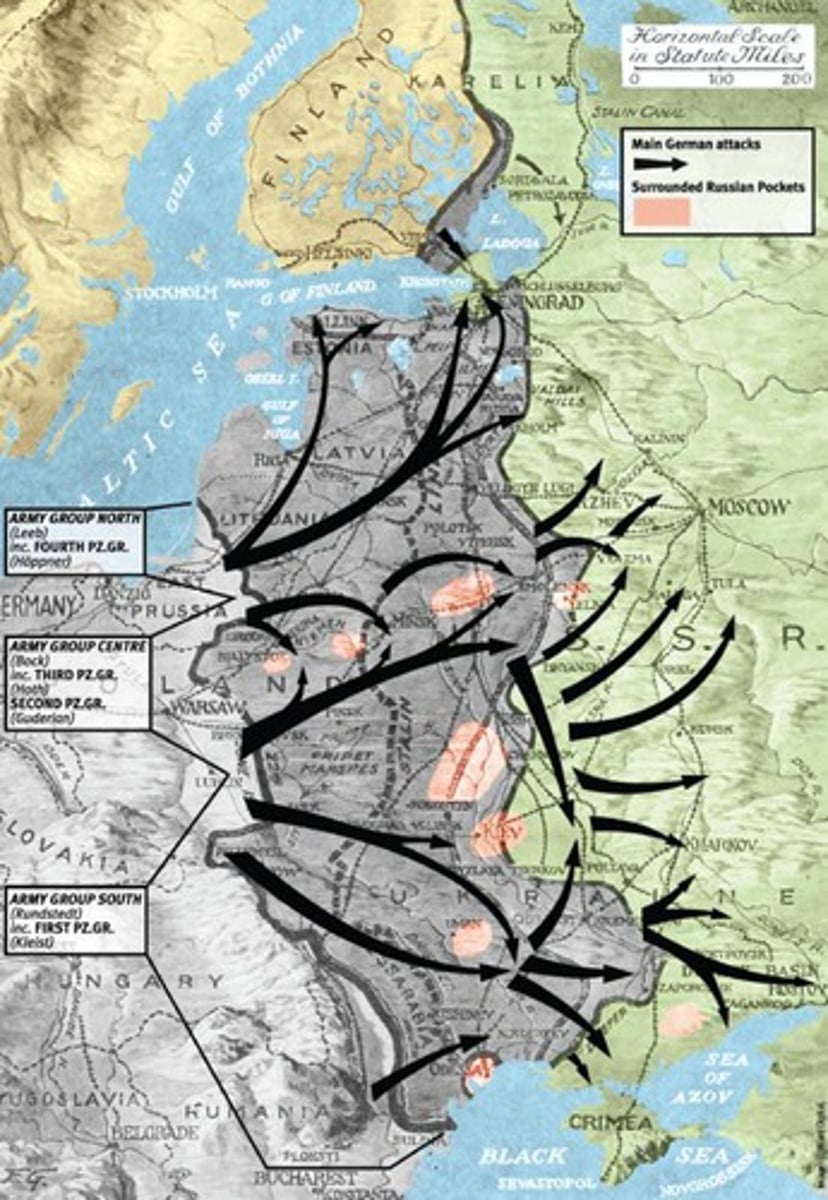
Operation Barbarossa
Codename for Nazi Germany's invasion of the Soviet Union during World War II.
Dresden Bombing
(Feb, 1945) Extremely deadly bombing carried out by the US in Dresden, Germany. One of the final bombings of WWII in which many German civilians died.

Nanjing Massacre
(the Rape of Nanjing) a six-week period following the Japanese capture of the Chinese city of Nanjing. During this period, hundreds of thousands of civilians were murdered and 20,000-80,000 women were raped by soldiers of the Imperial Japanese Army.

fascism
A political movement that promotes an extreme form of nationalism, a denial of individual rights, and a dictatorial one-party rule.

Allied Powers
Alliance of Great Britain, Soviet Union, United States, and France during World War II.
Axis Powers
Alliance of Germany, Italy, and Japan during World War II.
