2-Chemical Weathering
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What is chemical weathering?

How does chemical weathering consume CO2?
Weathering by carbonic acid. Consumes CO2

What is acid mine drainage?
MINE not rock

What are the factors affecting the kinetic of pyrite oxidation?
advection of oxidants to pyrite surfaces
T of reaction
chemical properties, e.g. pH, Eh
presence or absence of microorganisms
What are the stages of oxidation of pyrite
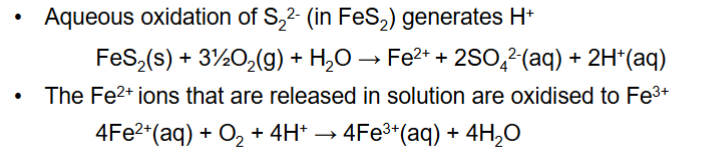
How is pyrite further oxidised by Fe3+

How can oxidation of pyrite occur biotically?
Micro-organisms, groups of bacteria catalyse the oxidation of pyrite by generating Fe3+
What does it mean by natural attenuation of pH?
Downstream the geochemical evolution of AMD is controlled by:
dilution of metal concentrations by mixing with pristine waters
What is sorption?
Precipitation of different metal cations as pH increases.
Sorption of different trace minerals onto the solid surfaces of precipitated metal hydroxides/hydroxysulphates.
pH dependent sequences of precipitation and sorption are very similar and follow order: Fe3+ > Pb > Al > Cu > Zn > Fe2+ > Cd, (precipitate from lower pH (Fe3+) to higher pH (Cd))
Chemical composition of water will also change in response to the mineral precipitation reactions.
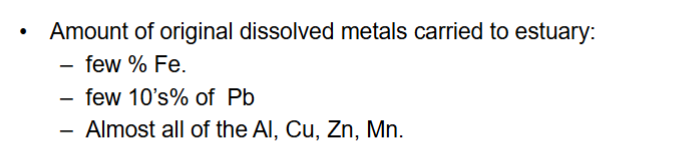
How much of the original dissolved metals are carried to estuary?
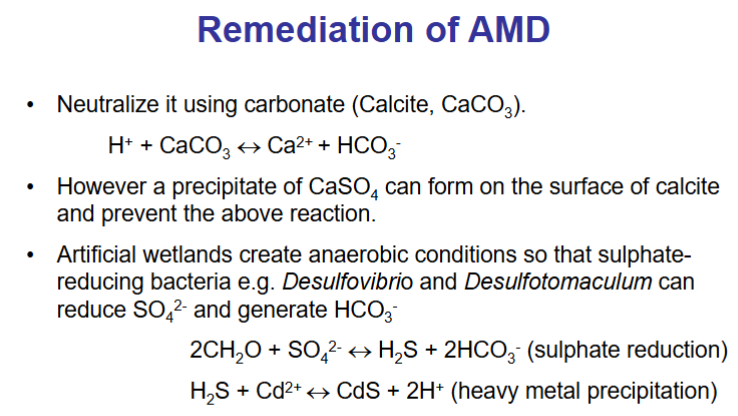
What process are there for the remediation of AMD?
How does mineral temp crystallisation link to stability of mineral?
Minerals that crystallise at higher temperatures will be least stable at the surface.
Means quartz is the most stable mineral in the weathering environment, as its last to crystallise.
Are minerals generally soluble?
Solubility of most minerals in pure water is very low.
Carbonate minerals become more soluble at higher temps
What is the different between congruent dissolution and incongruent dissolution?
Congruent dissolution - mineral dissolves completely, all ions produced go into solution e.g. Mg2+, Ca2+, Na+ are strongly hydrated in solution
Incongruent dissolution - mineral does not dissolve completely
e.g. minerals contain Al incongruent dissolution
Most silicate minerals dissolve incongruently to produce clay minerals, insoluble oxides, and hydroxides.

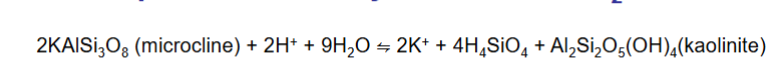
Determine the K equilibrium constant?
Just need to know you can find a straight line equation by rearranging. DONT USE SOLIDS, JUST DISSOLVED THINGS
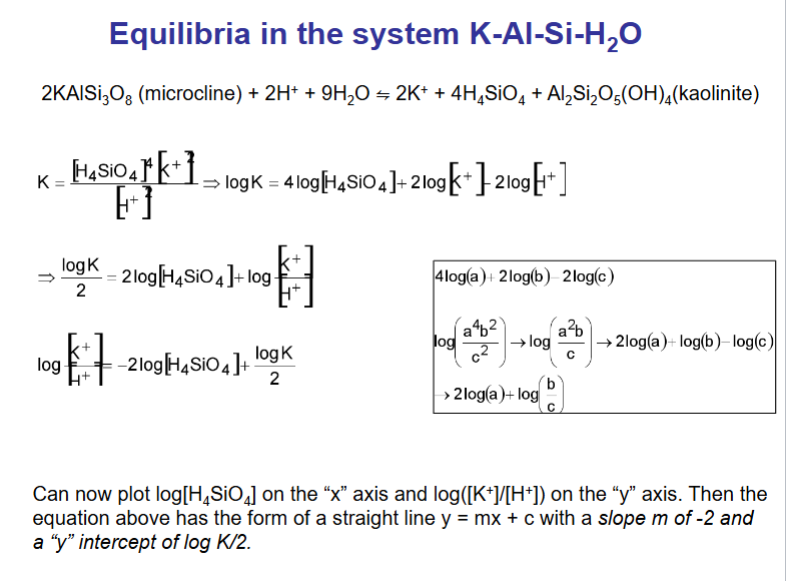
What does a mineral stability diagram show?
A mineral stability diagram shows the conditions (like pH, temperature, pressure, or chemical composition) under which different minerals are stable.
👉 In simple terms:
It’s a map that shows which mineral will form or remain stable in certain environmental conditions
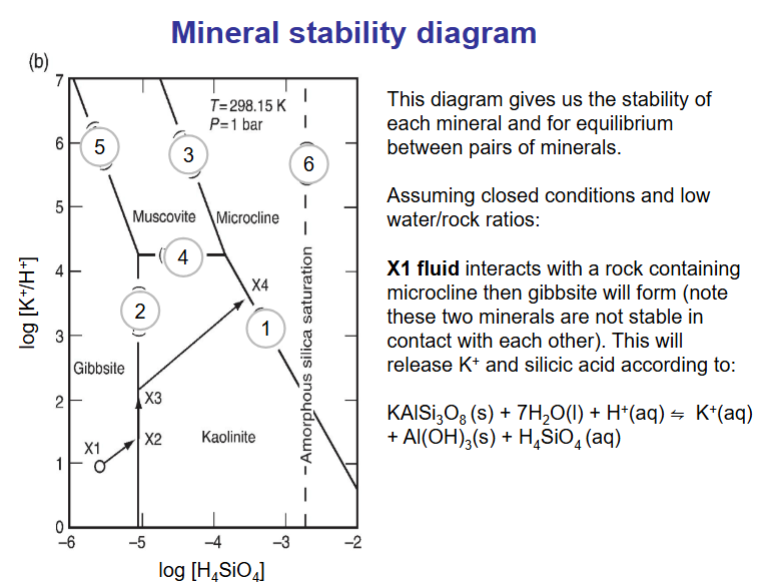
Aluminosilicates formed by incongruent dissolution exist as very small particles <0.002mm, and are part of a group of phases known as ….
clay minerals having sheet structures
What are the properties of clay?
hydrous aluminium silicates, containing minor amounts of impurities such as K, Na, Ca, Mg, or Fe
plasticity soft when wet, shrinks hard when dry
fine particle size, but clumps in saline conditions
compacted clay layers can be lithified to form mudstone rocks
since fine grained they have large surface area, and high potential to exchange material with a solution through adsorption/desorption
What is the clay structure of silicate sheets?
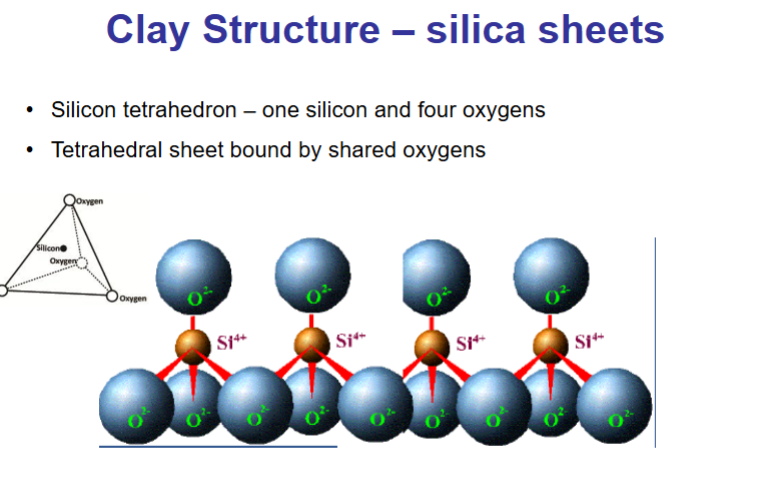
What is the clay structure for alumina sheets?
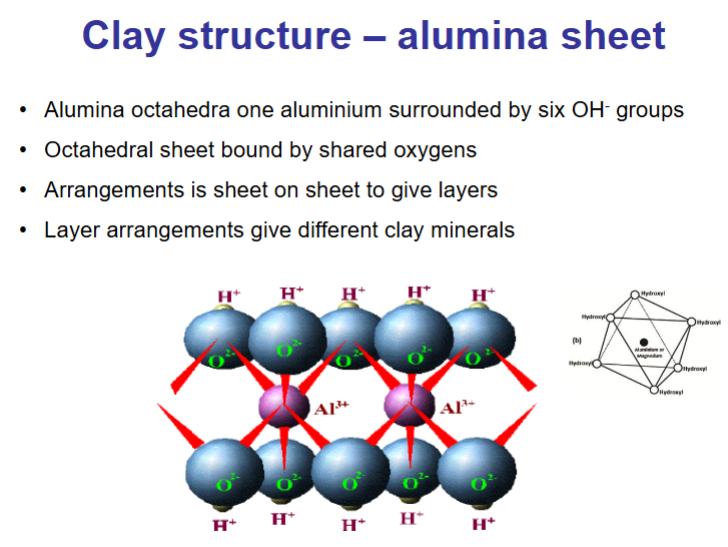
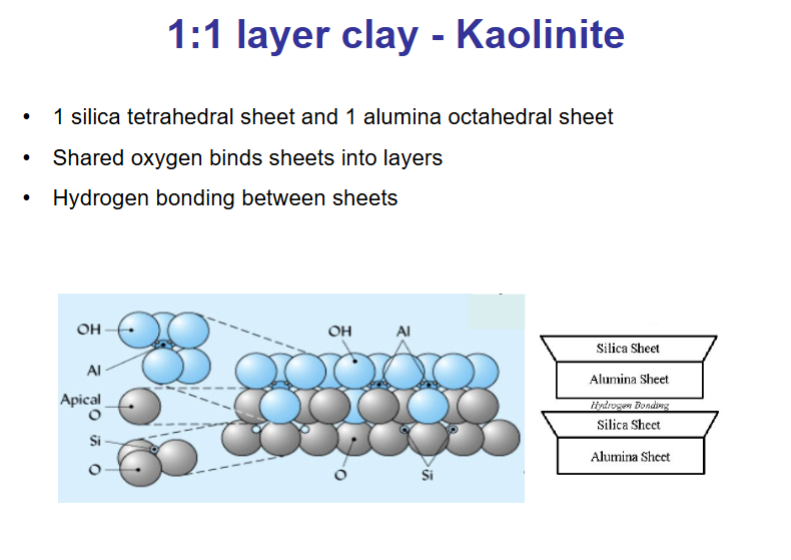
What is the structure of 1:1 layer clay - Kaolinite?
What is the structure of 2:1 clay?
The charge imbalance that results from substitution in the tetrahedral layer (negative charge) is neutralised by loosely bound cations adsorbed into clay mineral surfaces.
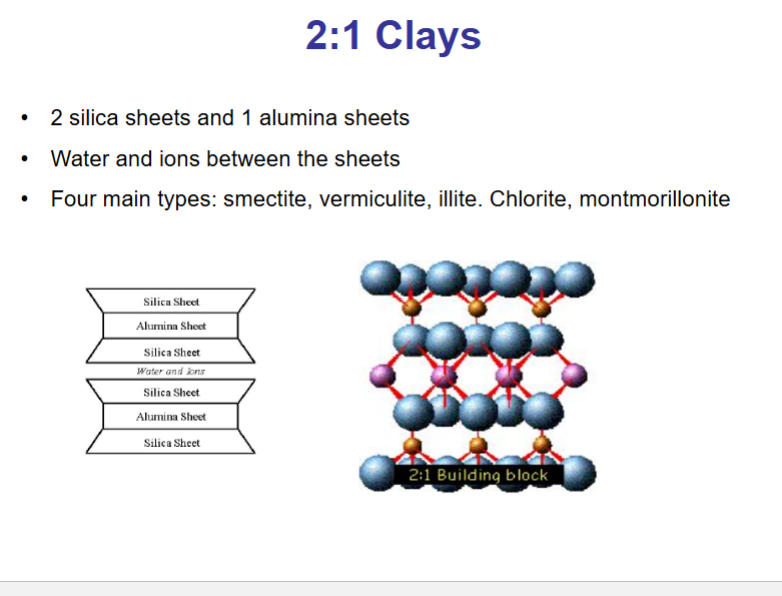
What ions when in clays cause the clay to expand?
Clays with Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ expand as water can fit in the interlayer spacings.
K- bearing clays do not expand in water (K+ fits in silicate rings)