CHE 2119
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
LECTURE 7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
nitrogen
comprises 78% of the atmosphere
cannot be utilized by plants in atmospheric form
essential for the synthesis of amino acids, proteins, enzymes • a limiting nutrient
nitrogen cycle
the circulation or cyclic movement of nitrogen from the atmosphere to soil and back into the atmosphere
atmosphere
Nitrogen falls from the ______ to the earth by precipitation (e.g. rain or snow).
nitrogen fixation
conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia
carried out by leguminous plants and some bacteria (e.g. azotobacter, clostridium, rhizobium)
nitrification
carried out by nitrifying bacteria (e.g. nitrococcus, nitrosomonas)
ammonia is first converted to nitrites
then nitrites are converted to nitrates (by nitrobacter)
Nitrogen assimilation
the process of absorbing nitrates and ammonia into organic nitrogen
Organic nitrogen is transferred into animals when they consume plants.
ammonification
the process of converting organic nitrogen into ammonia when plants and animals die
carried out by saprophytes like fungi and bacteria
Ammonia is also produced from volcanic eruptions and excretory products of animals.
denitrification
Nitrates are converted into molecular nitrogen through nitric oxide.
carried out by denitrifying bacteria (e.g. thiobacillus denitrificans)
fixed nitrogen
manures
ammonium sulfates (by-product from coking of coal)
ammonia (recovered from coke)
Chile saltpeter (sodium nitrate)
dry distillation of nitrogenous biomaterial waste
decomposition of ammonium salts
Haber (Haber - bosch) process
Fritz Haber and Carl Bosch, 20th century
practical and large-scale synthetic ammonia process
use of abundant and inexpensive elemental H2 and N2 gas
synthetic ammonia
fertilizers (ammonium sulphate, DAP, urea)
nitric acid
explosives
fibers, synthetic rubbers, plastics (nylons and other polyamides)
refrigerants
pharmaceuticals (sulfonamide, vitamins, etc.)
pulp and paper
extractive metallurgy
soda ash
cleaning solutions
air
water
hydrocarbons
raw materials for synthetic ammonia: haber - bosh process
equilibrium
return to ______ with increase in [N2]
pressure
return to ______ upon compression
very slowly
hydrogen and nitrogen react ___________
iron
catalyst: ___ → promoted by the addition of small amounts of oxides of aluminum and potassium
space velocity
_________ → cu. ft. of exit gases in STP (0oC and 760 mmHg) that pass over 1 cu. ft. of catalyst space per hour (usually 20,000 – 40,000)
doubly promoted
13 - 14% ammonia
singly promoted
8 - 9% ammonia
pure iron
3 - 5% ammonia
catalyst promotion
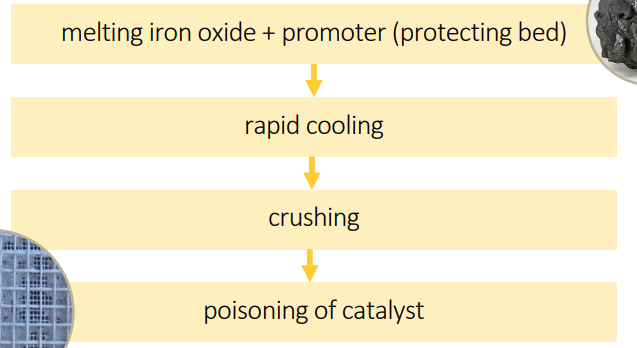
feedstock desulfurization
removal of sulfur oxide and hydrogen sulfide
R-SH + H2 → H2S + RH
H2S + ZnO → ZnS + H2
the sulfur is removed to < 0.1 ppm S in the gas feed
Zinc sulfide remains in the adsorption bed.
manufacture of hydrogen
steam-water gas process
steam-hydrogen (natural gas) process
coke-oven gas process
electrolysis of water
primary (steam) reforming
reformer consists of nickel - based catalyst
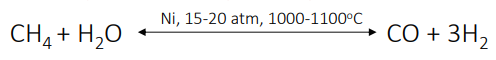
secondary reforming
only 30-40% of the hydrocarbon react
addition of air to convert the unreacted methane molecules

shift conversion
The process gas from the secondary reformer contains 12 – 15% CO.
The gas is passed through a bed of iron oxide/chromium catalyst around 400 – 500 degrees Celsius
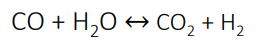
Purification
CO2 Removal
scrubbing with water, amine solutions, or hot potassium carbonate solutions
methanation
CO and Further CO2 Removal
small amounts of CO and CO2 are removed by conversion to CH4 using Ni catalyst
ammonia conversion
Modern NH3 plants use centrifugal compressors for synthesis gas compression.
The synthesis of ammonia takes place on iron catalysts.
reaction is highly exothermic
Only 20 – 30% is reacted per pass in the converter due to unfavorable equilibrium conditions
ammonia
by mechanical refrigeration or adsorption/distillation
ammonia storage
urea (46% nitrogen)
ammonium nitrate (34% nitrogen)
nitric acid
used for the manufacture of ammonium nitrates (fertilizers)
intermediate in polymer industry (polyamides and polyurethanes)
oxidizing acid for the parting of gold and silver, pickling of brass, and photoengraving
nitric acid
Manufacturing Procedure: _____
evaporation of anhydrous ammonia
oxidation of ammonia gas with air (platinum gauze at 920 deg C)
cooling of nitric oxide
oxidation and hydration of nitric oxide
collection of 61 – 65% nitric acid using acid trap
waste gas treatment
evaporation of anhydrous ammonia
• anhydrous ammonia is evaporated using steam
Oxidation of Ammonia Gas with Air
NH3 gas is oxidized with air to nitric oxide by passing through a platinum gauze at 920oC
cooling of nitric oxide
Nitric oxide with excess air is cooled in two heat exchangers and a water cooler
Oxidation and Hydration of Nitric Oxide
Successive oxidations and hydrations of the nitric oxide are carried out with continuous water cooling in a stainless-steel absorption tower
2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
3NO2(g) + H2O(ℓ) → 2HNO3(aq) + NO(g)
Collection of Nitric Acid using Acid Trap
61 – 65% nitric acid
water and nitric acid form an azeotrope
Waste gas treatment
The waste gas from the top of the absorption tower is heated and expanded before being exhausted to the atmosphere