PCL 2 Exam 2
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
In a 1:4 mixture of urea and Eucerin, what is the percent concentration of urea?
1/(1+4) = 1 part urea/5 total parts = 20% urea
In a 1:2 mixture of Lidocaine 1% and Sodium Bicarbonate 8.4%, what is the concentration of Lidocaine?
1 part lidocaine/3 total parts x 1% (strength of lidocaine) = 1/3 or 0.33% lidocaine
Mannitol is available as 25% concentration. A mannitol 10% drip (500mL) is needed. How much 25% mannitol will need to be added to D5W?
(10% mannitol needed)(500mL needed) = (25%10% available)(x mL)
x = 200 mL mannitol 25%
Added to 300 mL D5W (mannitol 0%) for a total concentration of 500mL 10% mannitol
D5W/0.33% NaCl is ordered (1 liter). How much 23.4% NaCl will need to be added to D5W?
(0.33% NaCl)(1000ml) = (23.4% NaCl)(X ml)
X = 14.1 mL of 23.4% NaCl needed
Added to 885.9 ml of D5W for a total volume of 1000 mL
A patient receives 50mL of Lidocaine 0.5% infiltration during an emergency C-section, they are now experiencing an arrythmia. How many mg's did they receive?
250 mg lidocaine
0.5% = 0.5g/100 ml
50ml x 0.5g/100ml x 1000mg/g = 250 mg
Epinephrine is available as 1:1000 strength, what percent strength is this?
What is the concentration in mg/mL?
1/1000 = 0.001 x 100% = 0.1% strength
5mL of 7% NaCl for inhalation is needed. How much 10% NaCl and 3% NaCl must be combined?
2.86 mL of 10% NaCl and 2.14 mL of 3% NaCl
10 (7-3) = 4 4 parts 10%; 5ml x 4/7 = 2.86ml
7
3 (10-7) = 3 3 parts 3%; 5ml x 3/7 = 2.14 ml
The package insert of ceftriaxone 2 gram vial says to add 19.3 mL of diluent to achieve a concentration of 100 mg/mL. How much diluent must be added to obtain a concentration of 200mg/mL?
9.2 ml of diluent should be added
200mg/vial x 1ml/100mg (resultant conc.) = 20ml/vial
20ml - 19.2 ml = 0.8ml (displacement powder vol.)
200mg/vial x 1ml/200mg (desired conc.) = 10ml/vial
10ml - 0.8ml (powder vol.) = 9.2ml of diluent
Azithromycin 5mg/kg daily for 4 days is ordered, the patient weighs 38 pounds. What is the correct dose?
86 mg/day
38lb x 1kg/2.2 lb = 17.3 kg x 5mg/kg = 86.36mg (round to whole number)
Vancomycin 1500mg in 250mL NS should be run over 90 min. The IV set delivers 10 drops/mL. How many drops per minute should be used?
28 drops/min
250ml/90 min x 10 drops/ml = 28 drops/min
Dopamine is available as 400 mg/250 ml solution. The patient weights 70 kg. The physician orders 5 mcg/kg/minute. What is the rate the nurse should program into the pump in ml/hour?
13 ml/hour
70kg x 5mcg/(kgxmin) x 1mg/1000mcg x 250ml/400mg x 60 min/hour = 13.13 ml/hr (round to 13)
What is the equation for Ideal Body Weight (IBW)?
Males: 50kg + 2.3kg for each inch over 60 in
Females: 45.5kg + 2.3 kg for each inch over 60in
What is the equation for adjusted body weight? When is adjusted body weight used?
AdjBW = IBW + 0.4(ABW- IBW)
Adjusted body weight is used when the patient is >20% above IBW
Calculate the ideal body weight and adjusted body weight of a male who is 6 feet tall and weighs 350 lbs.
6ft = 72 in
IBW = 50 + (2.3 x 12in) = 77.6 kg
350lb x 1kg/2.2lb = 159.09kg
AdjBW = 77.6kg + 0.4(159.09 - 77.6) = 110.2 kg
What is the equation for body surface area (BSA)?
Sqrt( (height(in) x weight (lb)) / 3101)

The oncologist orders cisplatin 75mg/m^2. The patient is 72 inches tall and weighs 180 pounds. What is the appropriate dose?
152 mg dose
BSA = sqrt( (72in x 180lb)/3131) = 2.03 m^2
2.03 m^2 x 75mg/m^2 = 152.6mg (round to 152)
What is the equation used to calculate creatinine clearance? How do you know what weight to use?
Use adjustedBW for obese patients (20% or more above IBW)
If the patient is not obese, use IBW
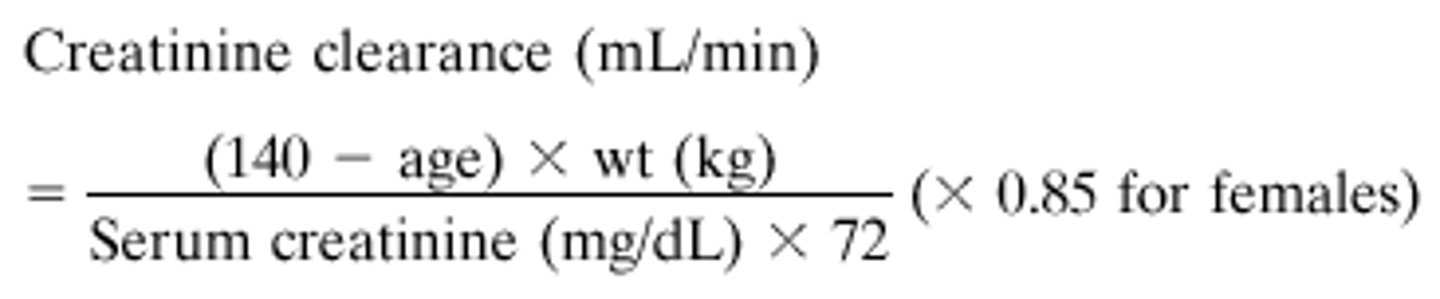
XW is an 88-year-old female who is 62 inches tall and weighs 57kg and has a serum creatinine level of 1.4 mg/dl. What is her calculated creatinine clearance?
CrCl = 25 ml/min
(140-88)x 57kg = 2964/(72 x 1.4 mg/dl) = 29.40 x 0.85 (because the patient is female) = 24.994
What is the equation used to calculate area under the curve dosing?
Total dose(mg) = target AUC x (GFR + 25)
GFR = CrCL
The oncologist orders carboplatin AUC 5. The patient is a 44-year-old male who weighs 75 kg and is 70 inches tall. The patient's serum creatinine is 1.6 mg/dl. What is the appropriate dose of carboplatin?
430 mg
CrCl = (140-44)(73)/(72x1.6) = 7008/115.2 = 60.83 ml/min (round to 61 ml/min)
Total dose (mg) = 5 x (61 + 25) = 430 mg
How do you calculate corrected calcium?
Corrected calcium = serum calcium + 0.8(4 - serum albumin)
A patient has a serum calcium level of 9.6 mg/dl (8-10 mg/dl) and a serum albumin level of 2.5 g/dl. What is this patient's corrected calcium level?
Corrected calcium = 10.8
9.6 mg/dl + 0.8(4 - 2.5 g/dl) = 10.8
How do you calculate corrected Phenytoin?
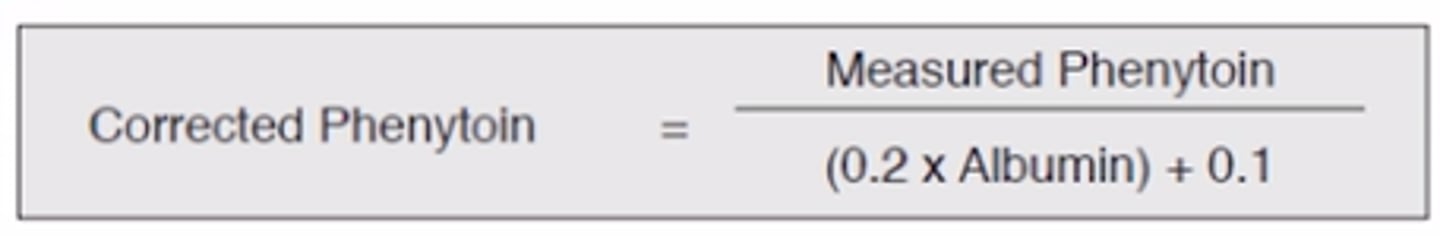
A patient has a measured phenytoin level of 19 mcg/ml (10-20 mcg/ml) (toxic = 30+mcg/ml) and an albumin level of 2.4 g/dl. What is the corrected phenytoin level?
Corrected phenytoin = 32.8
19/((0.2 x 2.4 g/dl) + 0.1) = 32.8
Aseptic technique applies to which routes of administration?
All parenteral compounds.
Includes drugs administered intravenous, intramuscular, intradermal, subcutaneous, intrathecal, epidural, intra-arterial, intra-articular, intracardiac, intraocular, and intraperitoneal.
What is the main disadvantage of parenteral products?
risk of infection
What checks should be done to verify a CSP (at a minimum)?
- Incompatibility and/or particulate matter is not present in the CSP
- All calculations involved in preparation of the CSP were performed correctly
- The right drug was used
- The right volume was used
- The right diluent was used
- The right volume of diluent was used
- The expiration date of the drug(s) used are in-date
- The expiration date of diluent(s) used are in-date
- Auxiliary labels are included and are appropriate
- Instructions for administration are correct
- The correct Beyond-Use-Date (BUD) is assigned
What is first air?
Also referred to as "clean air", it is the air that exits the HEPA filter.
It is important that manipulations are consistently exposed to first air to prevent contamination.
How long must horizontal laminar flow hoods be run before they can be used?
HLFW must run at least 30 minutes prior to use if turned off.
How should horizontal laminar flow hoods be cleaned?
They are cleaned perpendicular to air flow, so in HLFW the cleaning motion is up and down.
The surfaces of the HLFW must be cleaned in the following order: upper surface (top), pole and hooks, sides, workbench
What is a biological safety cabinet (BSC)?
- vertical laminar airflow
- provides product, environmental, and operator protection
- inward flow of air through front opening
- often exhausts air to outside
- should run for at least 4 minutes if turned off
- should be used when preparing hazardous agents
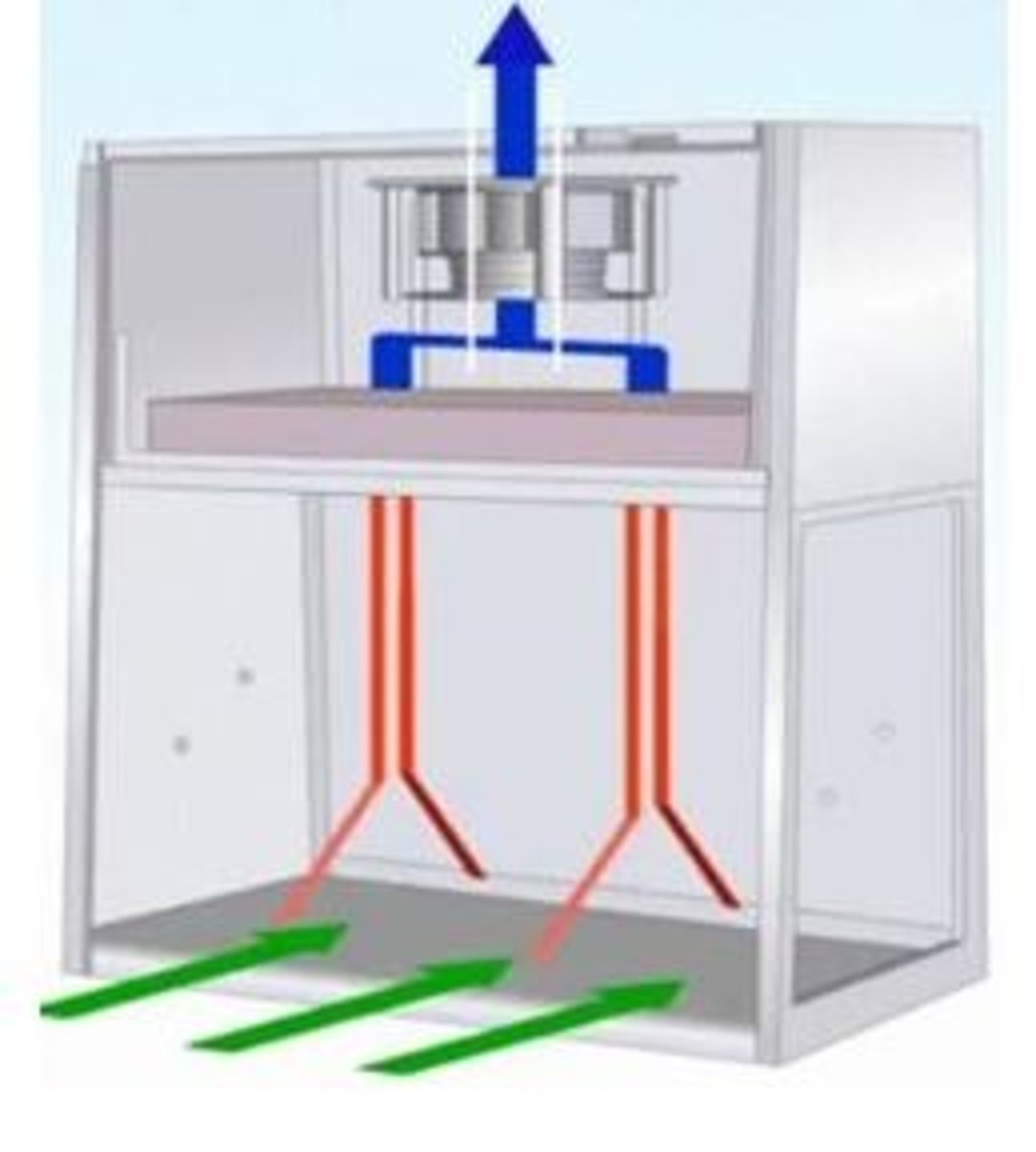
How should biological safety cabinets and vertical laminar flow hoods be cleaned?
We clean perpendicular to airflow, so in VLFW the movement is side to side.
The surfaces of the VLFW should be cleaned in the following order: pole and hooks, back, sides, sash, workbench
When should flow hoods be cleaned?
- beginning of each shift
- prior to each batch preparation
- after spills
- when known or suspected to be contaminated
- every 30 minutes for extended preparations
- soiling can be first cleaned with sterile water then disinfected as usual
- a sporicidal agent must be used at least monthly (IPA is NOT sporicidal)
What are RABS?
Restricted Access Barrier Systems (aka compounding isolators, aka "glove boxes")
These the include aseptic isolator and the containment isolator
What is the advantage of using RABS?
You can start compounding faster than in a flow hood.
RABS can be fired up in 2 minutes as long as it has not been turned off for more than 24 hours (have to wait 10 minutes if off for more than 24 hours)
Can hazardous compounding and nonhazardous compounding take places in the same PEC?
NO
Equipment used for hazardous substances should be completely separate from equipment used for nonhazardous substances.
When should PECs be certified?
- at initial installation
- if device or room is moved
- following a major repair
- if there is major service to the facility
- non-viable and viable air sampling (conducted by a third party)
- Surface sampling (can be conducted "in house")
What is non-viable and viable air sampling?
Non-viable air sampling - all dust bunnies will be captured and measured to determine a classification for how clean the air is (non viable particulate includes dust, dirt, etc.)
Viable air sampling - whatever is captured is plated, if nothing grows then there is no viable particulate, but if there is growth viable particulate is present (viable particulate includes viruses, bacteria, etc.)
What is the role of secondary engineering controls?
Secondary engineering controls are direct compounding areas (clean rooms)
Areas surrounding PECs must be controlled to prevent contamination. SECs work adjunct to PECs to maintain environmental quality.
What is a buffer area? What is the minimum ISO classification for buffer areas?
Buffer areas must be ISO class 7 at minimum
Buffer areas are where PECs are located. Items brought into this area should be limited, and should be cleaned prior to entering the space.
What is an ante area? What is the minimum ISO classification for ante areas?
Ante areas are located just outside of the buffer area. They exist for activities such as handwashing, garbing, staging, order entry, and labeling. All outer garments, cosmetics, and jewelry (except wedding bands with no stones) should be removed in ante-area before entering the buffer area.
Ante areas should be, at minimum, be ISO class 8 for non-hazardous compounding and ISO class 7 for hazardous compounding.
What kind of air pressure should be used for ante rooms? For buffer rooms?
Ante rooms have to have positive pressure (when the door is open to the uncontrolled space, air will flow out not in). This makes it difficult for any particulate to get into the ante room.
In the non-hazardous compounding room, there should be positive pressure relative to the ante-room (so air flows out of the buffer room into the ante room).
For hazardous compounding, the buffer room should have negative pressure (so any hazardous vapors cannot get out into the hospital). This puts you at a disadvantage for contamination because it could potentially draw in particulate matter (which is why the ante room must have less particulate when attached to a hazardous compounding room)
What is the line of demarcation?
A visible line on the floor used to separate the "clean" and "dirty" side of the ante room.
Garbing should take place on the dirty side. Once fully garbed, personnel would be allowed to cross the line to the clean side.
What factors influence sterility of compounded sterile preparations?
- environmental quality
- proper hand washing
- proper hand hygiene
- use of personal protective equipment
- primary and secondary engineering controls
- maintenance of equipment and environment
- aseptic technique
How long should hands be washed before sterile compounding?
Hand washing is an essential and critical step in preventing contamination of CSP. It needs to be a full 30 seconds to the elbow.
What is transient hand flora? How is it removed?
Transient hand flora is 15% of all flora on the hands. This kind of flora is removed with hand washing.
What is resident hand flora?
Resident hand flora is 85% of all flora on the hands. This kind of flora is not removed by hand washing.
How are spores removed from the hands?
- spores require physical removal with hand washing
- they cannot be removed with hand sanitizers or alcohol
When should critical sites be in contact with first air?
ALL critical sites must be in contact with first air AT ALL TIMES during compounding
What are considered critical sites?
- hub of the needle
- tip of the needle
- shaft of the needle
- tip of the syringe
- ribs of the plunger
- rubber closure of the vial (when penetrated)
- opening of an ampule
- additive/injection port of an IV bag
What are the steps of aseptic technique?
1) gather supplies
2) disinfect vials, ampules, and injection port
3) prepare syringe and needle
4) enter vial
5) withdraw contents
6) inject into diluent/solution
7) mix and check final admixture
8) cover and label admixture
At what angle should a needle enter the vial?
When entering a vial, the needle should enter with bevel up at a 45 degree angle. This is done to prevent coring.
How is positive pressure created in a vial?
If air added exceeds volume of solution withdrawn, then positive pressure is created. This results in spraying or dripping of solution from the vial.
Positive pressure should be AVOIDED if at all possible.
How is negative pressure created in a vial?
If the amount of air removed exceeds volume of solution removed, negative pressure within the vial will result. This results in difficulty removing volume needed from the vial.
What is the purpose of the United States Pharmacopeia (USP)?
- provides definitions, descriptions, and requirements for multiple pharmaceutical settings
- publishes standards for: identity, quality, strength, purity, packaging, and labeling
What information is in USP chapter 797?
Relates requirements for all persons to transport, store, and prepare compounded sterile products (CSPs).
It was first published in 2004, became official in 2008, and a new revision will be enforceable on November 1st of 2023 (supposedly).
What chapters of USP are considered enforceable?
Chapters <1> to <999> are considered enforceable.
Information in chapter 1000 and above is NOT considered enforceable (it is simply for guidance).
What other USP chapters relate to sterile compounding?
- Chapter 71: sterility tests
- chapter 85: bacterial endotoxin tests
- chapter 788: particulate matter in injections
- chapter 1075: good compounding practices
- chapter 800: hazardous preparations
Are state regulators of sterile compounding allowed to deviate from standards in USP chapter 797?
Yes,! However, they generally do not.
State regulators may require different education and training requirements, and may require stricter environmental controls, quality assurance, and quality control.
Are compounded preparations approved by the FDA?
No
Compounded preparations are not approved by the FDA, but are exempted from certain requirements. Compounding may fall under 503A or 503B.
What is 503A?
"traditional compounding"
- must comply with current good manufacturing practices (cGMP)
- must be labeled with adequate directions for use
- must be patient specific
- does not need to register with the FDA
What is 503B?
"outsourcing facilities"
- may compound without a prescription
- must register with the FDA and is subject to routine inspections by the FDA
These facilities look more like manufacturers than hospitals. They make compounds for use in different facilities.
What is quality control?
Processes that can be measured as the compounded sterile preparation (CSP) is being produced.
Measures are done daily and include:
- air quality testing
- testing of routine disinfection processes
- donning of personal protective equipment (PPE)
- review of orders and packages of ingredients for identity and accuracy
- inspection of CSPs for absence of particulate atter and leakages
- inspection of CSPs for thoroughness of labeling
What is quality assurance?
Involves the evaluation of the final preparation and the facility in which it is compounded.
It looks at the overarching qualities and culture of safety throughout the facility in which sterile compounds are made.
What are the required characteristics of QA programs?
- formal and written
- considers all aspects of preparation and dispensing (including environmental testing and verification)
- description of activities for monitoring and evaluation
- description of reporting and evaluation of monitoring
- includes thresholds for evaluations and follow-up
- includes training requirements
Who does the expectations for education and training defined in USP 797 apply to?
applies to EVERYONE who compounds sterile preps
Training should not be limited to compounding staff, but should include everyone handling CSPs and maintaining the engineering controls (housekeeping)
What are the three major components in evaluating quality?
Facilities, personnel, and monitoring.
All three components contribute to quality system.
What are the three facets to maintaining control of a facility?
- design of sterile compounding area (PEC and SEC)
- daily monitoring of facilities required by pharmacy personnel
- periodic certification
What is a primary engineering control (PEC)?
ISO class 5 environment
Examples include: laminar flow hoods, vertical flow hoods, compounding isolators, etc.
What is a secondary engineering control (SEC)?
ISO class 7 environment
Refers to the room in which a PEC resides, and the ante room
What are the temperature requirements for facilities according to USP 797?
Temperature of the ante-area and buffer area SHOULD be less than 20 degrees C (but if it is 21 degrees C for a few minutes you would not have to throw everything away)
Humidity should be 60% or below
How much growth is allowed on an ISO class 5, ISO class 7, and ISO class 8 surface?
A little bit of growth is allowed, but the facility should be doing something to negate that.
- ISO Class 5 surfaces can have no more than 3 cfu/swab
- ISO class 7 surfaces can have no more than 5 cfu/swab
- ISO class 8 surfaces can have no more than 50 cfu/swab
How often do PECs and SECs need to be recertified?
Every 6 months.
The certification is conducted by trained, professional certifiers.
What are the required certifications for PECs?
- HEPA filter integrity (every 6 months)
- Airflow patterns (every 6 months)
- particle counts (every 6 months)
- surface sampling (monthly) (can be conducted by pharmacy staff)
What are the required certifications for SECs?
- Air sampling for viable particulate (every 6 months)
- surface sampling for viable particulate (monthly, can be conducted by pharmacy staff)
- HEPA filter integrity (for total particulate count, every 6 months)
- Airflow patterns (every 6 months)
- air exchanges per hour (every 6 months)
What type of training is required for CSP staff?
- a rigorous orientation and initial training (done 1 time before compounding for patients)
- ongoing training (less intense, done at least annually)
- ongoing competence
How often must ongoing competence for Media Fill be completed?
Media fill competence simulates the most complex preparation that personnel would be expected to compound.
It must be done every 6 months for category 1 and category 2 (every 3 months for category 3)
How often must a gloved fingertip test be conducted for compounding personnel?
The gloved fingertip test demonstrates that personnel can garb and compound without contamination.
It must occur in a PEC every 6 months for category 1 and 2 (every 3 months for category 3)
How does USP define category 1 risk level?
PEC (ISO 5) located in an unclassified space known as segregated compounding area
Compounding conducted outside of a clean room space
How does USP define a category 2 risk level?
PEC 9ISO 5) located in an ISO 7 buffer room with an ISO 8 ante room (ante room must be ISO 7 for hazardous medications)
How does USP define a category 3 risk level?
PEC (ISO 5) located in an ISO 7 buffer room with an ISO 8 ante room (ante room must be ISO 7 for hazardous meds)
This category has enhanced cleaning, monitoring requirements, and preparations must undergo sterility and endotoxin testing.
What are the BUDs for category 1 facilities outlined in USP 797?
12 hours at room temperature
24 hours refrigerated
What are the BUDs for category 2 facilities outlined in USP?
4 days at room temperature
10 days in the refrigerator
45 days in the freezer
What is immediate use prevision?
USP 797 provides an immediate-use provision for emergent situations.
These compounds must be made from 3 or less sterile products, administration must be started within 4 hours, and they must be appropriately labeled with names of amounts of ingredients, name of preparer, and exact 4 hour time unless the CSP is administered by the preparer.
What are some exceptions to the USP 797 BUD guidelines?
- proprietary bag and vial system (addEASE, ADD-Vantage, Mini Bag Plus)
- if CSP is prepared from nonsterile ingredients, shorter BUDs must be assigned
- if end-product testing is performed, BUD's can be extended
For what preparations are master formulation records required?
Master formulation records are detailed instructions about how a CSP is to be prepared. They must be created for CSPs that are prepared for more than 1 patient (batches, and for CSPS prepared from nonsterile ingredients (rare in hospitals)
For which preparations are compounding records required?
Compounding records must be created for EVERY CSP/
A medication label or order may serve as a compounding record, but it must be stored and easily retrievable (i.e, no handwritten BUDs on labels)
What must be included in a compounding record?
Compounding records must contain at least the following information:
- name, strength or activity, and dosage form of the CSP
- date and time of preparation of the CSP
- assigned internal identification number (e.g., prescription, order, or lot number)
- a method to identify the individual involved in the compounding process and verifying the final CSP
- name of each component
- vendor, lot number, and expiration date for each component for CSPs prepared for more than 1 patient and for CSPs prepared form nonsterile ingredients
- weight or volume of each component
- strength or activity of each component
- total quantity compounded
- assigned BUD and storing requirements
- results of QC procedures (e.g., visual inspection, filler integrity testing, pH testing)
- if applicable, the compounding record must also include: master formulation record reference for the CSP
- calculations made to determine and verify quantities and/or concentrations of components
How long may single dose containers be used?
Single dose containers may be used for up to 12 hours if kept continuously in a category 2 or category 3 space
What is an informatics pharmacist?
A new and evolving job title managing the use of health-system technology.
ASHP definition of pharmacy informatics: "the use and integration of data, information, knowledge, technology, and automation in the medication-use process for the purpose of improving health outcome"
What is an electronic health record (EHR)?
An electronic record that connects all of the systems inside a health care system. It includes information from hospitals, physicians, clinicians, insurers, laboratory data, vital signs, and regulatory reports.
They can cost anywhere from 0 -50 million+ dollars. (there are EHR systems that are 'free', but they take a percentage of the money earned from claims
What are the elements of an effective EHR?
- bar code capable
- customizable
- logical
- user friendly
-dependable
What are health information exchanges (HIEs)?
Networks that allow the community pharmacist to be able to access an EHR. Michigan health information network (MiHIN) services West Michigan.
These are free (a federally funded program). To access data, data must be shared.
What is the difference between an EHR and a HIE?
EHRs are located INSIDE the health system.
HIEs are located OUTSIDE the health system
Smart pumps
- wifi
- guardrails
- libraries
- integrated to EHR
- bar code capable
- cost $1500-3500 per pump
Syringe pumps
- used mostly in pediatrics
- allows for a slow infusion of a small volume
- cost $1500-3500 per pump
Patient controlled analgesia pump
- used for pain management
- ideally bar code capable
- must program manually if not integrated
What are WOWs and COWs?
WOW = workstation on wheels
COW = computer on wheels
- integrated to EHR
- locks patients' meds in drawer
- should be biometric
- bra code capable
- long battery life
- cost $5000-10000 per cart
Automatic dispensing cabinets (ADCs)
- omnicell, Pyxis, etc.
- should be biometric
- should be integrated with EHR
- bar code capable
- customizable
- ability prevent and detect diversion
- cartless model (pharmacy fills ADC instead of patient drawer, nurse will obtain a patient's meds from the ADC, nurse should be able to pull multiple patients on a single transaction)
- cost $30,000-200,000 per cabinet
What are filling robots?
Robots that fill patient specific medication drawers daily.
These are too expensive for small health systems (need to be filling a LOT of meds for these to make sense)
- integrated with the EHR
- uses bar code technology
- only as good as the re-packager
- allows for central fill
- costs $500k - 2.5 million