APHG FINAL REALNESS 🌎 🎧 (copy)
1/484
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
485 Terms
what are cities?
hubs for commercial governmental and cultural problems and ideas in a region
what is a food surplus?
agriculture production to support a larger population
what is socioeconomic stratification?
the development/creation of class systems and later job specialization
what are site factors?
factors that people consider in a location when moving there
what are situation factors?
factors that people consider outside a location when moving there
what are the causes of the 1st urban revolution
it caused dramatic social changes(socioeconomic stratification -class systems) and food surpluses also tied closely to the first agricultural revolution
where were settlements during the first urban revolution located?
near water ways
what caused the 2nd urban revolution?
innovation in mining and manufacturing that led to increased urban growth
what are the causes of the 2nd urban revolution?
because of the increase in jobs of manufacturing more people moved to the urban areas which changed social, economic, political, and cultural functions
what factors lead to the creation and expansion of urbanization factors?
transportation(cars), communication(the internet), population growth, migration(rural to urban), and governmental policies
what are the consequences of urbanization?
population density, changes in demographics(smaller families), governmental policies, the strain of infrastructure, competition of jobs and increase of urban sprawl
what is urbanization?
the process by which people live and are employed in a city
what are mega cities?
cities with 10 million or more residents
what are meta cities?
cities with a population with more then 20 million residents
what is happing with urbanization in ldcs
They are experiencing rapid urbanization(urban sprawl) which causes informal settlements
What is happening with urbanization in MDCs?
They are experiencing shifts in urbanization because of technology, technology allows people too not rely on the CBD for resources and jobs this leads to creation of edge cities boomburgs and exurbs
What is a boomburg?
A rapidly growing suburban city that has developed its own unique identity
What is the definition of edge cities?
A settlement that has its own economic district and is located on the outskirts of a city or near a beltway
What is the definition of beltways?
A highway that encircles a urban area
Why do people move to edge cities?
People won’t need to travel as far from suburbs
Prices are lower outside the cbd
Pressure and the amount of time it takes to travel to the cbd from the suburbs
what happens when edge cities form in relation to urban centers?
They take away resources like like
infrastructure
Sewage
Water
Electricity
School/education
Hospitals
Police/fireman
What is the definition of exurbs?
A settlement that exists outside of a suburban area but remains connected to the metro area
How to exurbs form?
They form because technology allows people to not really on living near the CBD for work
What are the characteristics of exurbs?
They have a low population density
Larger home/lot sizes
And less access to goods and services
What is the definition of The core periphery model?
A model that describes how economic, political, and social power is specially distributed between dominant core country’s or areas and the more dependent semi-perifery and periphery country’s or areas
What are the characteristics of the core in the core-periphery model?
Wealthier
Access to healthcare and education
More jobs and businesses
What stage of the demographic transition model is the core of the demographic transition model?
Stage 4
What are the characteristics of the semi-periphery in the core-periphery model?
mid level development
Country’s or areas that were late to become industrial
Low level job opportunity’s
What stage of the demographic transition model is the semi-periphery of the core-periphery model?
Late stage 2 or early stage 3
What are the characteristics of the periphery in the core-periphery model?
low level development
Low standard of living
Labor based jobs
What stage of the demographic transition model is periphery of the core-periphery model?
Stage 2
What is the definition of globalization?
It refers to the interconnection and interdependence of the world
What does globalization cause?
It leds to the increased economic growth (in LDCS and MDCS) it also attracts people to move from rural areas to urban areas which causes urban sprawl
What is urban hierarchy?
A ranking of cities with the largest and most powerful cities on top
What are multinational corporations?
A corporation that owns are contracts the production of goods/services in at least one other country then its home country
What is the definition of world cities?
A city that is connected to other cities around to world through a series of networks
What are the types of connections that connect cities and world cities around the world?
communication
Financial industries
Governmental organization
Entertainment/ fashion industry’s
Manufacturing and trade
Transportation networks
What are examples of world cities?
New York
London
Paris
Tokyo
Hong Kong
What are primate cities?
A city that dominates the social,political, and economic life’s of people in a country
what do you have to have in order to be concindered a primate city?
You must have at least 2 time more residents then the next biggest city in that country/region
What is the rank size rule?
The population of a settlement that is proportional to its rank in urban hierarchy
What is the definition of the gravity model?
A mathematical model that helps indicate how much influence cites have on each other
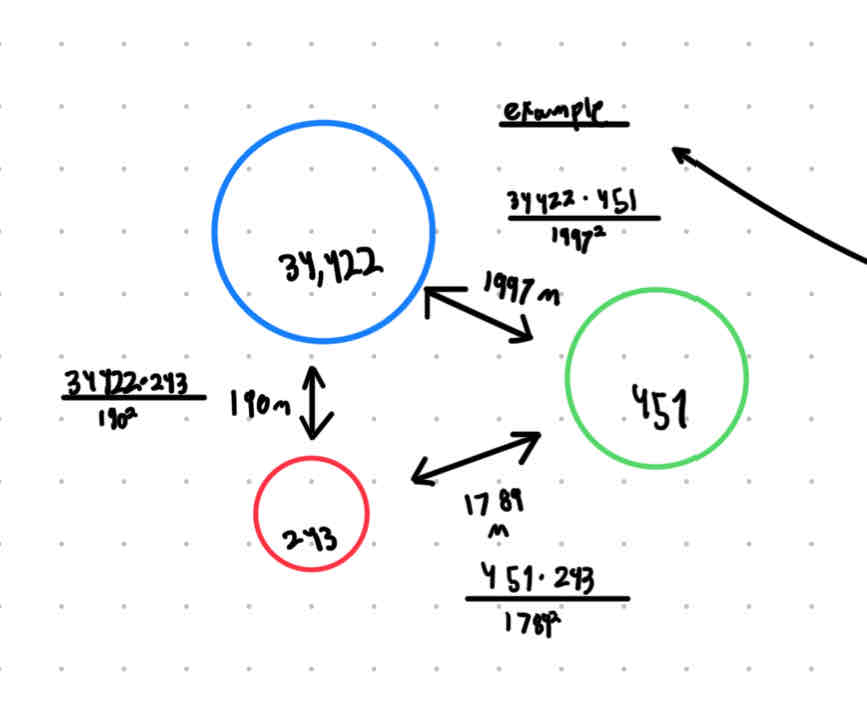
What is the equation of the gravity model?
Population1 x Population2/distance²
LOOK AND THIS EXAMPLE OF THE GRAVITY MODEL
This one
What are the characteristics of the burgess concentric zone model?
The CBD is located in the center with concentric rings around it. Industrial areas are closer to the middle while nicer housing is farther from the CBD. It was created by Ernest burgess in 1923 and is modeled after the city of CHICAGO
What does the burgess consenting zone model look like
What are the characteristics of the hunt sector model?
The CBD is located in the center with specialized sectors coming out from the CBD, the high cost residential areas will grow outward. Was made by homer Hoyt in 1939 and was modeled off the the city of Philadelphia
What does the Hoyt sector model look like?
What are the characteristics of the multiple nuclei model?
It is a model that try’s to account for the change in technology in major cities the model shows multiple CBDs with many diffrent purposes based on the city of Los Angeles and creased by chancey Harris and Edward ullman in 1945
What does the multiple nuclei model look like?
What are the characteristics of galactic city model?
Is based on the multi nuclei model and was designed to model modern metropolitan areas
the industry is located near the beltway
Low income residents are near the city
The model accounts for edge cities
High income residents are further away because they can afford travel costs
Based on Detroit Michigan
Made by chance harris in the 1960s
What does the galactic city model look like?
What are the characteristics of the griffin ford model?
It’s based on Spanish choline’s the CBD is in the center with disamintys(slums) and the high class living in segments that branch out from the CBD
What does the griffin ford model look like?
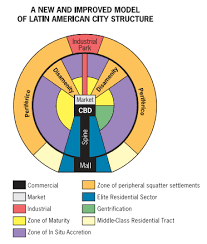
What is the definition of the Southeast Asia city model?
based on islands
Does not have a CBD it has a port that acts as the market
Government, alien commercial zones, and western commercial zones all have access to the port
What is the definition of the port when it pertains to the Southeast Asia city model?
It’s where trade and commerce is located
What does the Southeast Asia city model look like?
What are the characteristics of the sub Saharan Africa city model?
based on sub Sharen Africa
Made by harm de blij in 1935
Slums are on the outskirts
3 CBDs with specialization
What does the sub Saharan African city model look like?
What does the bid rent theory state?
That land/real estate/ rental costs are higher in and around a city’s CBD due to demand
What is the definition of density gradients?
A gradual change in density of a urban area from the center to the periphery
What is the definition of new urbanism?
Is a counter to urban sprawl; an approach to city planning that focuses on fostering European style cities of dense settlements, attractive architecture, and different types of housing and walking distance to goods and services
What is the definition of urban sprawl?
Is unrestricted growth of housing commercial developments and roads over large expanses of land with little concern with urban planning
What are the 10 principles of new urbanism?
walkability
Connectivity
Mixed use and diversity
Diverse housing options
Quality agriculture and urban design
Traditional neighborhood structures
Increased density
Smart transportation
Sustainability
Quality of life
What is the definition of greenbelts?
A zone of grassy, forested or agricultural land separating urban areas
What are the benefits of greenbelts?
Connects urban dwellers to nature and promotes ecological health
What is the definition of smart growth polices?
Large scale governmental polices that combat regional sprawl by addressing issues of population density and transportation
What are examples of smart growth polices?
mixed land use-different types of developments in a walkable area like businesses, residential and entertainment
Compact design
Infill development-building on unused or underused land with existing settlements
Walkability
Variation of transportation
Randle of housing opportunities
What is the definition of quantitative data?
Information that can be counted and presented in number form
What are some examples of quantitative data?
Percentages, average income of a population
What is the definition of qualitative data?
Information that is opinion based and that could be argued appon; subjective
What are some examples of qualitative data?
Thoughts, presidential approval ratings(all though it is a percentage is based on opinions)
How do governments use qualitative and quantitative data?
They use data to make informed decisions about what policies to in-act;by gettin data on things like traffic accidents and where they occur they can build stop lights to keep the public safe
What is the definition of shanty towns?
They are neighborhoods or communities where people live and build their own homes with out legal permit on or any claim to the land. They are over crowded and have poor living conditions die to the lack of infrastructure
What are shanty towns also referred to as?
Squatter settlements or informal settlements
Why do shanty towns form?
When pressure is put on the CBD of LDC’s because of strain of housing which causes housing costs to rise
What is the definition of urban heat islands?
A mass of warm air in cities, generated by urban building and human activity’s, that sits over a large urban area
What is the definition of brownfields?
A property that is potentially contaminated by dangerous substances, pollution or contaminants
How do brownfields form?
By abandoned or underused industrial or commercial facility often first created as a result of urban sprawl
What is the definition of urban sustainability?
The ability of a city or urban area to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of the future generations to meet their own needs
how does limited resources affect urban city’s when it related to urbanism and urban sprawl?
Urban areas can place significant demand on natural resources such as water, energy, and land which leads to limited supplies
how does pollution and environmental degeneration affect urban city’s when it related to urbanism and urban sprawl?
urbanization and urban sprawl causes problems like air and water pollution and the loss of green spaces and natural habitats
how does traffic and transportation strain affect urban city’s when it related to urbanism and urban sprawl?
Urbanization can lead to increased traffic congestion and reliance on private vehicles which contributes to pollution
how does poverty and inequality affect urban city’s when it related to urbanism and urban sprawl?
Urbanization can also lead to the consecration of poverty in certain areas or neighborhoods which can have negative effects on the health and well-being of these residents and create social and economic disparities
how does climate change affect urban city’s when it related to urbanism and urban sprawl?
Extreme weather events(hot+cold) can cause blackouts and energy shortages which leave people with out heating or cooling
how does sewage and sanitation issues affect urban city’s when it related to urbanism and urban sprawl?
When urban sprawl occurs at a fast rate it puts strain on sewage and sanitation systems, even failure. This can lead to health concerns like disease outbreaks
What acronym do geographers use to understand weather a map is good or not?
TODALS
What does TODALS stand for?
T-title
O-orientation
D-date
A-author
L-legend
S-scale
What is the definition of thematic maps?
Maps that are specifically designed to show a particular theme rated to a geographic area
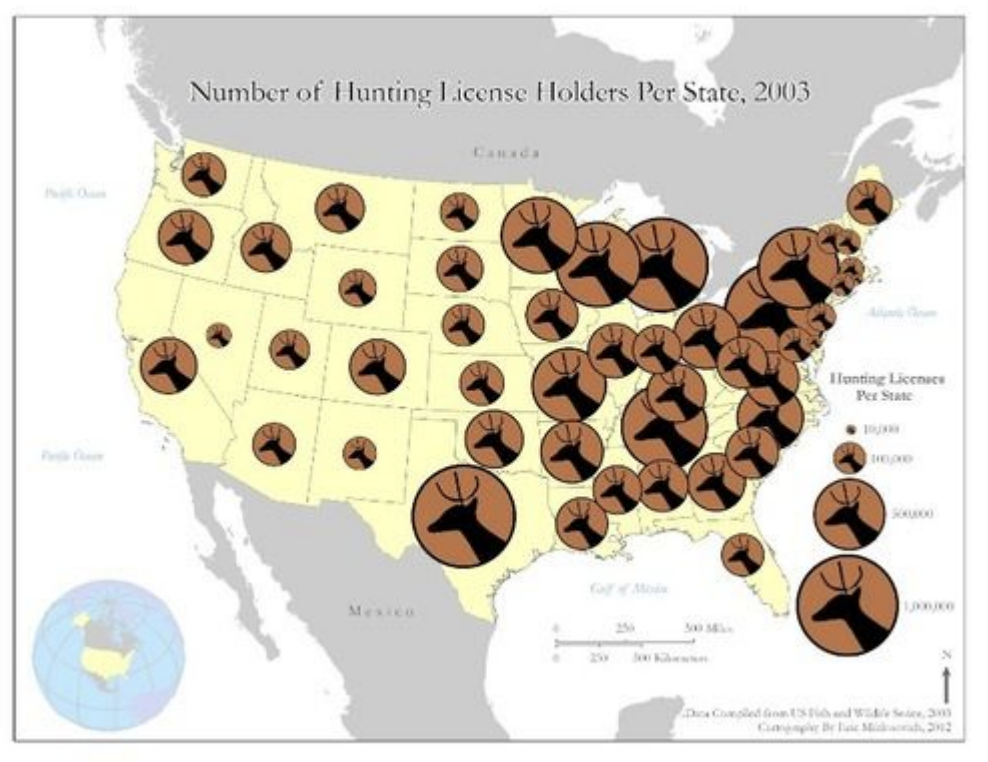
What is the definition of a graduate or proportional symbol map?
A thematic map in which the size of the symbol varies in proportion to the frequency or intensity of the mapped variables
What does a graduated or proportional symbol map look like?
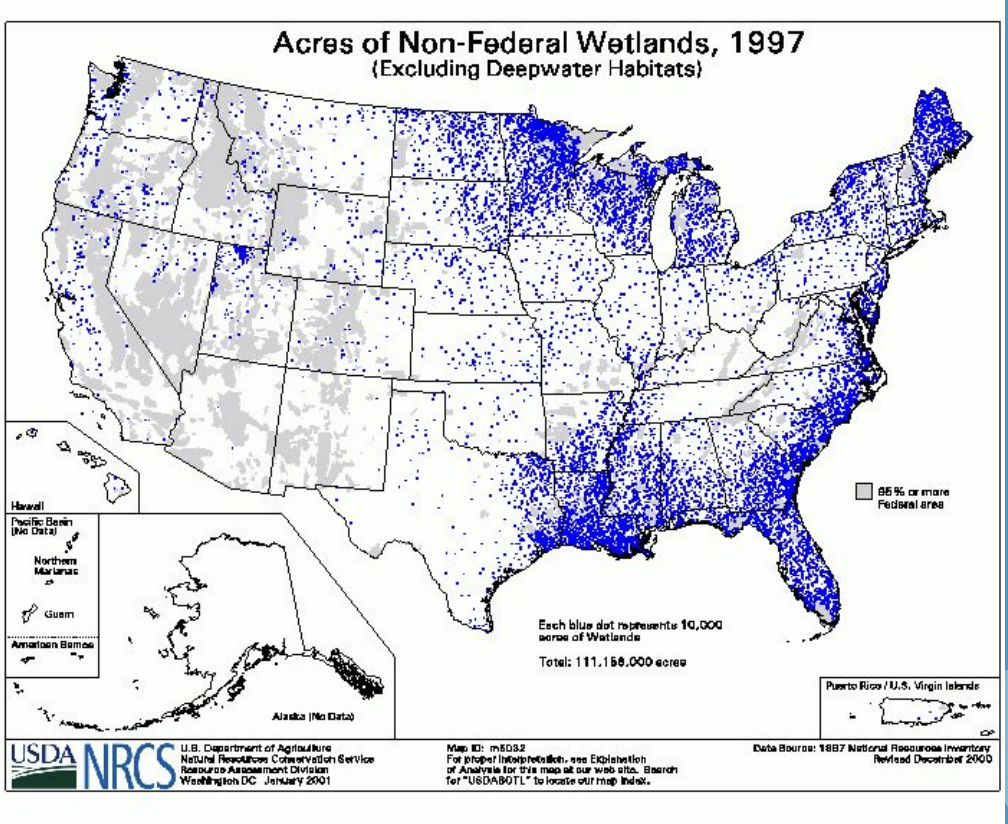
What is the definition of a dot distribution map?
A thematic map in which a dot is used to represent some frequency of the mapped variable
What does a dot distribution map look like?
What is the definition of a choropleth map?
A thematic map in which areas are shaded or patterned in proportion to the measurement of the statically variable being displayed on the map, such as population density or per capita income
What is a example of a cholorpleth map?
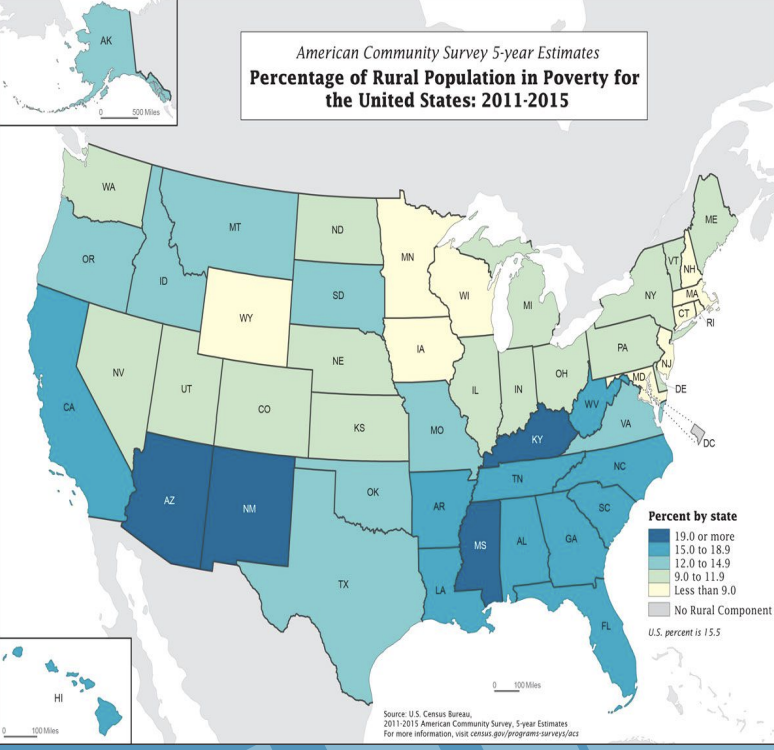
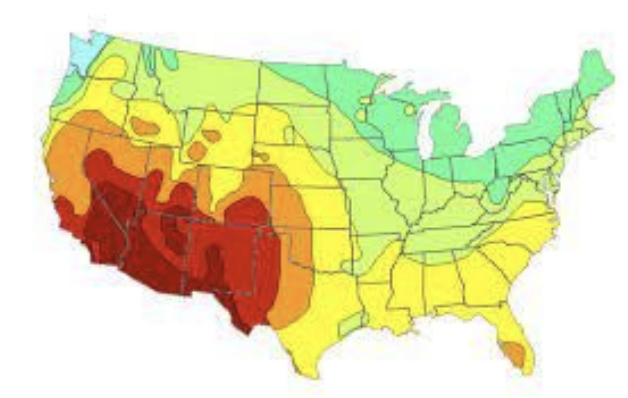
What is the definition of a isoline map?
A thematic map with lines that connect points of equal value (elevation and temperature)
What is a example of a isoline map?
What is the definition of a cartogram maps(bouncy map)?
A thematic map in which some thematic mapping variable is substituted for land area meaning the geometry or space of the map is distorted sometimes extremely, in order to convey the information of the alternative variable
What is an example of cartogram map?
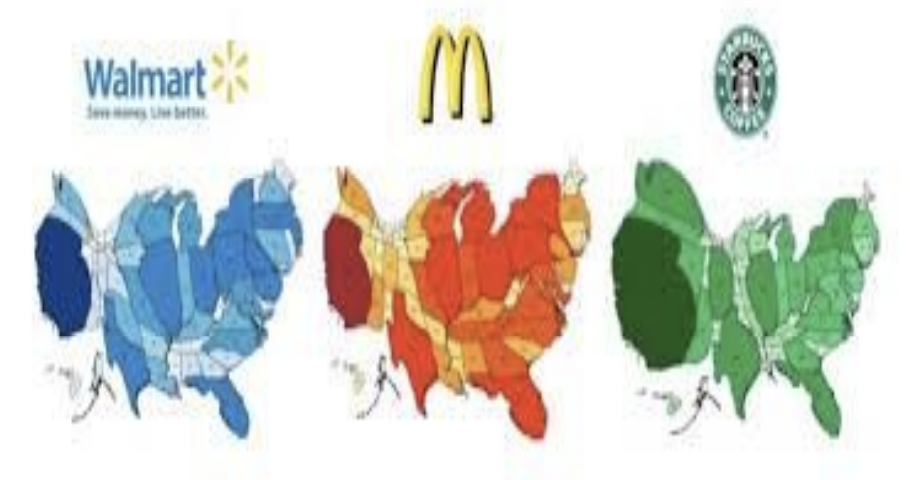
What are the examples of geospatial technology?
GPS(geographic positioning system), GIS(geographic information system), and remote sensing