module 25 - monetary policy
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
wealth effect
when the price levels falls, consumers feel wealthier, which stimulates consumer spending and increases the quantity of goods and services demanded
interest rate effect
when the price level falls, people need to hold less money, which can be loaned out, lowering interest rates and stimulating investment spending
increasing quantity of goods and services demanded
one of the most important effects!
exchange rate effect
when price level falls, domestic interest rates fall, leading to a depreciation of the domestic currency
stimulates net exports and increases quantity of goods and services demanded
theory of liquidity preference
keynes’ theory that interest rate adjusts to bring supply and money demand into balance
assumes the expected rate of inflation is constant
money supply
the quantity of money available in the economy, controlled by the federal reserve (fed)
fixed by the fed policy and does not vary with interest rate
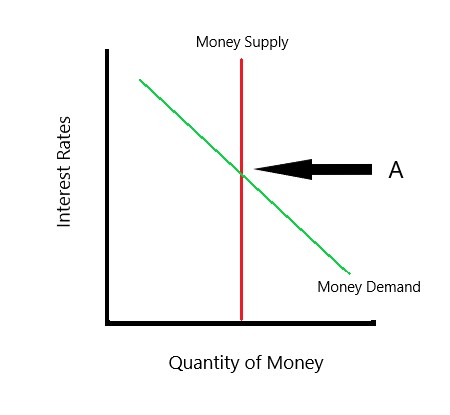
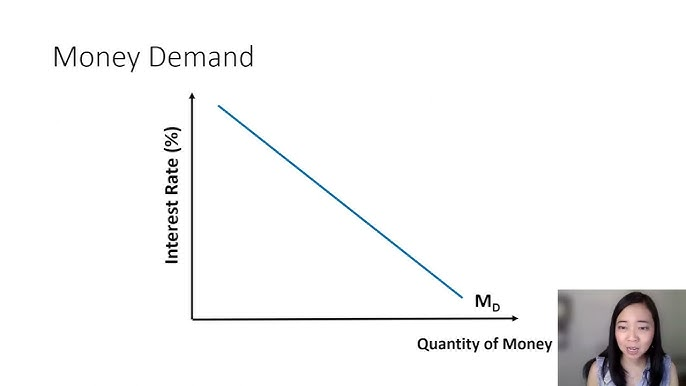
money demanded
quantity of money people want to hold
interest rate is opportunity cost of holding money, so money demand curve slopes downward
increase in interest rates raise the costs of holding money and reduces the quantity of money demanded
equilibrium interest rate
interest rate at which quantity of money demanded exactly balances the quantity of money supplied
monetary policy
setting of the money supply by the fed
influences ad and as
federal funds rate
interest rate that banks charge one another for short term loans
fed targets this rate through open market operations to adjust the money supply
fiscal policy
the government’s decisions regarding the level of government spending and taxation
it can shift ad through multiplier effect and crowding out effect
multiplier effect
additional shifts in ad that result when expansionary fiscal policy increases income and thereby increases consumer spending
investment accelerator
a positive feedback from demand to investment, where higher government demand leaders to higher demand for investment goods
marginal propensity to consume (mpc)
fraction of extra income that consumers spend
size of spending multiplier depends on mpc
large mpc leads to large multiplier
spending multiplier
calculated as 1/(1/ - mpc)
indicates that 1 dollar of government purchases (or consumption, investment, exports) can generate more than 1 dollar of ad
crowding out effect
offset in ad that results when expansionary fiscal policy raises interest rate, thereby reducing investment spending
increase in gov spending increases income, which increases money demand and raises interest rate, partially offsetting the initial increase in ad
automatic stabilizers
changes in fiscal policy that stimulate ad when the economy goes into recession, without policymakers having to take any deliberate action (like tax system or gov spending)