Psych 125 Quiz 2
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Memory as types
Explicit and Implicit
Memory as stages
Sensory, short-term, and long-term
Memory as processes
Encoding, Storage, and Retrieval
Explicit memory
Knowledge or experiences that can be consciously remembered
Types of explicit memory
Semantic and Episodic
Episodic Memory
Refers to the firsthand experiences that we have had
Semantic Memory
Refers to our knowledge of facts and concepts about the world
Types of implicit memory
Procedural Memory, Priming, Learning through classical conditioning
Recall Memory test
a test of memory of mind in which participants are presented with stimuli and then, after a delay, are asked to remember as many of the stimuli as possible.
Recognition Memory Test
Measure of explicit memory that involves determining whether information has been seen or learned before
Implicit Memory
a form of long-term memory that operates without conscious awareness and does not require intentional recollection of previous experiences.
Procedural memory
Often unexplainable knowledge of how to do things
Priming
exposure to one stimulus influences how a person responds to a subsequent, related stimulus
Sensory Memory
Brief storage of sensory information
Iconic Memory
Visual sensory memory
Echoic memory
Auditory sensory memory
Short-term Memory
A place where small amounts of information can be temporarily kept for more than a few seconds but usually for less than one minute
Working Memory
the small amount of information that can be held in mind and used in the execution of cognitive tasks,
Maintenance Rehearsal
process of repeating information mentally or out loud with the goal of keeping it in memory
Encoding
the act of getting information into our memory system through automatic or effortful processing
Elaborative Encoding
process new information in ways that make it more relevant or meaningful
Spacing Effect
the fact that learning is better when the same amount of study is spread out over periods of time than it is when it occurs closer together or at the same time.
Retrieval
the process of reactivating information that has been stored in memory.
Context-dependent Learning
the context in which information was learned enhances the recall of that information
State-dependent Learning
refers to superior retrieval of memories when the individual is in the same physiological or psychological state as during encoding
Primacy Effect
tendency to better remember stimuli that are presented early in a list
Recency Effect
the tendency to better remember stimuli that are presented later in a list.
Retroactive Interference
learning something new impairs our ability to retrieve information that was learned earlier.
Proactive Interference
earlier learning impairs our ability to encode information that we try to learn later
Prototype
member of the category that is most average or typical of the category.
Schemas
patterns of knowledge in long-term memory that help us organize information
Long-term Potentiation
the strengthening of the synaptic connections between neurons as result of frequent stimulation\
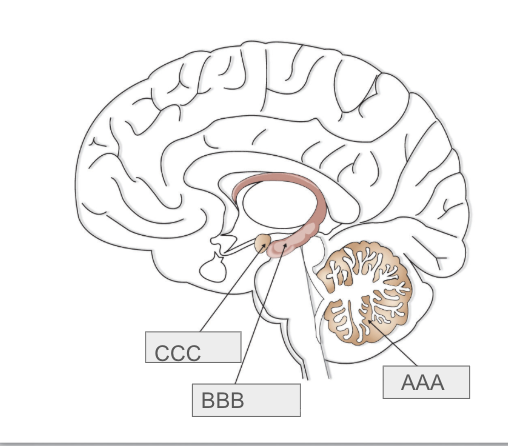
What is A
Cerebellum
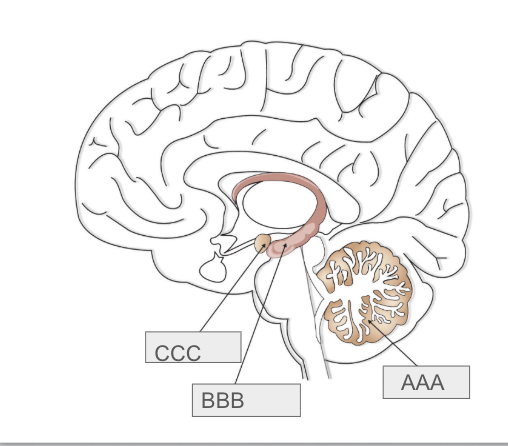
What is B
Hippocampus
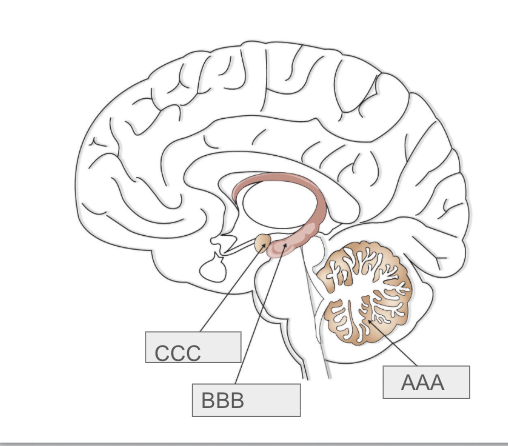
What is C
Amygdala
Amnesia
Memory Disorder that involved the inability to remember information
Retrograde Amnesiua
memory disorder that produces an inability to retrieve events that occurred before a given time.
Anterograde Amnesia
the inability to transfer information from short-term into long-term memory, making it impossible to form new memories.
Construction
Formulation of new memories
Reconstruction
Process of bringing up old memories
Misinformation Effect Paradigm
holds that after exposure to additional and possibly inaccurate information, a person may misremember the original event.
False Memory Syndrome
Recall of false autobiographical memories
Schacter’s Seven Sins of Memory
Transience
Absentmindedness
Blocking
Misattribution
Suggestibility
Bias
Persistance
Transience
memories can fade over time
absentmindedness
lapses in memory caused by breaks in attention or our focus being somewhere else
Blocking
can’t access stored information (
Misattribution
when you confuse the source of your information.
proactive interference
when old information hinders the recall of newly learned information.
Retroactive interference
happens when information learned more recently hinders the recall of older information.
Problem solving strategies
Trial and Error
Algorithm
Heuristic
Algorithm
problem-solving formula that provides you with step-by-step instructions used to achieve a desired outcome
heuristic
a general problem-solving framework- Mental shortcuts
Functional fixedness
type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for.
Hindsight bias
leads you to believe that the event you just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t.
Representative bias
describes a faulty way of thinking, in which you make a decision or judgment based on your perception of the similarity of the person or thing to your existing stereotypes and prior beliefs
availability heuristic
you make a decision based on an example, information, or recent experience that is that readily available to you, even though it may not be the best example to inform your decision
Decision Biases
Anchoring
Confirmation
Hindsight
Representative
Availability
Anchoring bias
Tendency to focus on one particular piece of information when making decisions or problem-solving
Availability Bias
Decision is based upon either an available precedent or an example that may be faulty
Classical Conditioning
a process by which we learn to associate stimuli and, consequently, to anticipate events.
unconditioned stimulus (UCS)
a stimulus that elicits a reflexive response in an organism
unconditioned response (UCR)
a natural (unlearned) reaction to a given stimulus.
neutral stimulus (NS)
a stimulus that does not naturally elicit a response.
conditioned stimulus (CS)
a stimulus that elicits a response after repeatedly being paired with an unconditioned stimulus.
conditioned response (CR)
The behavior caused by the conditioned stimulus
higher-order conditioning, or second-order conditioning
the first stimulus is classically conditioned to an unconditioned stimulus, then a second stimulus is classically conditioned to the first, thereby conditioning it back to the original unconditioned stimulus
spontaneous recovery
the return of a previously extinguished conditioned response following a rest period
stimulus discrimination
When an organism learns to respond differently to various stimuli that are similar,
stimulus generalization
when an organism demonstrates the conditioned response to stimuli that are similar to the conditioned stimulus,
Rooting Reflex
When the baby’s cheeck is stroked the baby will turn their head toward the stroking, open theur mouth and try to suck
Thus ensures the infants feeding will be a reflexive habit
Blink Reflex
A light is flashed in the baby’s eyes and the baby closes both eyes.
Protects the eyes from strong and potentially dangerous stimuli
Withdrawl Reflex
A soft pinprick is applied to the sole of the baby’s foot then the baby will flex the lef
Keeps the exploring infant away from painful stimuli
Tonic Neck Reflex
The baby is laid down on its back and the baby turns its head to one side and extends the arm on the same side
helps develop hand-eye coordination
Grasp reflex
An object is pressed into the palm of the baby- the baby grasps the object pressed and can even hold its own weight for a brief period
Helps in exploratory learning
Moro Reflex
Loud noises or a sudden drop in height while holding the baby- the baby extends arms and legs and quickly brings them in as if trying to grasp something
Protects from falling; could have assisted infants in holding onto their mothers during rough traveling
Stepping reflex
The baby is suspended with bare feet just above a surface and is moved forward-baby makes stepping motions as if trying to walk
Helps encourage motor development
Habituation
the decreased responsiveness toward a stimulus after it has been presented numerous times in succession
Habituation procedure
baby is placed in a high chair and presented with visual stimuli while a video camera records the infant’s eye and face movements
Assimilation
they use already developed schemas to understand new information
sensorimotor stage
the cognitive stage that begins at birth and lasts until around the age of 2. It is defined by the direct physical interactions that babies have with the objects around them
Object Permanence
refer to the child’s ability to know that an object exists even when the object cannot be perceived.
preoperational stage
children begin to use language and to think more abstractly about objects, but their understanding is more intuitive and without much ability to deduce or reason
Theory of mind
the ability to take another person’s viewpoint, and the ability to do so increases rapidly during the preoperational stage.C
Concrete operational stage
marked by more frequent and more accurate use of transitions, operations, and abstract concepts, including those of time, space, and numbers.
Conservation
the understanding that changes in the form of an object do not necessarily mean changes in the quantity of the object.
Formal operational Stage
marked by the ability to think in abstract terms and to use scientific and philosophical lines of thought.
Self-concept
a knowledge representation or schema that contains knowledge about us, including our beliefs about our personality traits, physical characteristics, abilities, values, goals, and roles, as well as the knowledge that we exist as individuals
longitudinal research designs
research designs in which individuals in the sample are followed and contacted over an extended period of time, often over multiple developmental stages.
cross-sectional research design
age comparisons are made between samples of different people at different ages at one time
Cohort Effects
refer to the possibility that differences in cognition or behavior at two points in time may be caused by differences that are unrelated to the changes in age.
Puberty
developmental period in which hormonal changes cause rapid physical alterations in the body, culminating in sexual maturity
primary sex characteristics
the sex organs concerned with reproduction
secondary sex characteristics
(features that distinguish the two sexes from each other but are not involved in reproduction
Menarche
the first menstrual period, typically experienced at around 12 or 13 years of age
Marcia’s stages of identity development
Identity-diffusion status
Foreclosure Status
Moratorium Status
Identity-achievement status
Identity-diffusion Status
The individual does not have firm commitments regarding the issues in question and is not making progress toward them.
Foreclosure Status
The individual has not engaged in any identity experimentation and has established an identity based on the choices or values of others.
Moratorium Status
The individual is exploring various choices but has not yet made a clear commitment to any of them.
Identity- Achievement Status
The individual has attained a coherent and committed identity based on personal decisions.
Self-reference effect
Info better learned if it is linked to thoughts about self