Size Exclusion Chromatography
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is the primary purpose of protein purification?
To conduct detailed studies on function, determine structure, and for industrial/pharmaceutical applications.
What are the key factors to consider in protein purification?
Amount and purity of protein, application, source, feasibility, native configuration, and detection methods.
What are the common methods for protein purification based on properties?
Methods include solubility (ammonium sulfate), size/shape (size-exclusion chromatography), and charge (ion-exchange chromatography).
What is affinity chromatography used for in protein purification?
It is used for binding proteins to small molecules to separate them based on specific interactions.
What is the first step in the protein purification strategy?
Select a source that is cheap and readily available, such as tissues rich in specific proteins.
What is the importance of maintaining the protein in its native form during purification?
Most proteins cannot be re-natured, so maintaining their native form is crucial for functionality.
What are some analytical assays used to determine protein concentration?
UV/Vis, BCA, Bradford, Lowry, and ELISA.
What techniques are used to assess protein purity and structure?
SDS PAGE, HPLC, IEF, and Western blot.
What are some common impurities that need to be monitored in protein purification?
Allergens, immunogenic proteins, endotoxins, viruses, and bacteria.
What is the elution profile in protein purification?
It is a graph that plots protein concentration against fraction number, indicating where proteins are present.
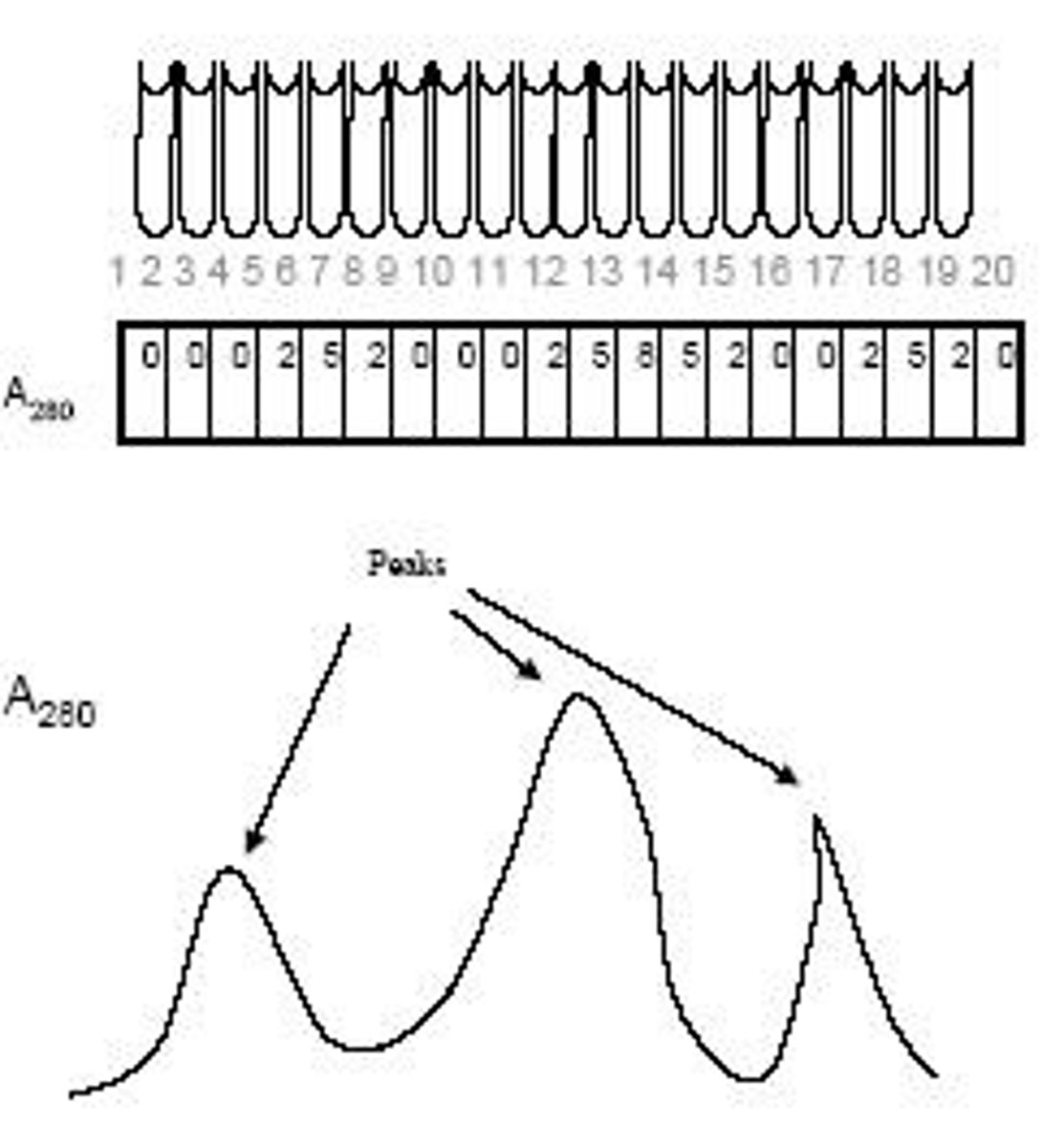
What is the role of size exclusion chromatography in protein purification?
It separates proteins from small molecules based on size as they pass through a column.
What is the exclusion limit in size exclusion chromatography?
It is the maximum size of molecules that can enter the pores of the stationary phase.
What happens to larger molecules in size exclusion chromatography?
Larger molecules are excluded from the pores and elute first from the column.
What is the significance of the stationary phase material in size exclusion chromatography?
Materials like agarose, dextran, and cross-linked acrylamides determine the separation range and efficiency.
What is the typical separation range for size exclusion chromatography?
About 10^2 to 10^6 Da.
What is the procedure for equilibrating a size exclusion chromatography column?
Apply Gel Filtration Buffer to the column, allowing it to drain completely while ensuring the resin does not dry.
How should samples be loaded into the size exclusion chromatography column?
Carefully load the sample without disturbing the resin, then allow it to flow into the column.
What is the procedure for eluting samples from the size exclusion chromatography column?
Apply Gel Filtration Buffer to the column and collect fractions as they elute.
What is the importance of monitoring the elution of fractions?
To determine which fractions contain the desired protein and assess their purity.
How can enzyme activity assays be used in protein purification?
They can be performed on fractions to determine if they contain active enzymes.
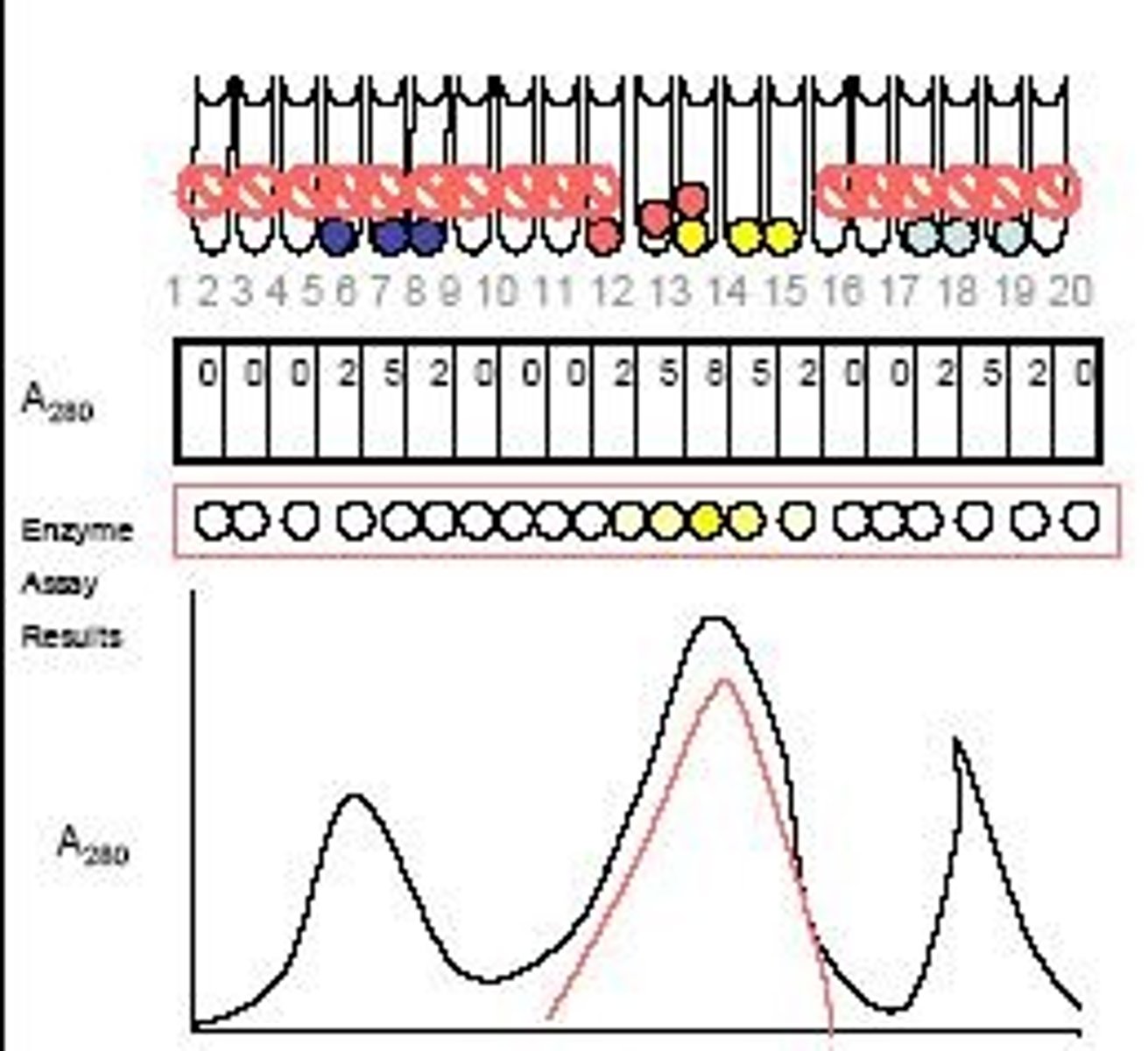
What is the significance of using a spectrophotometer in protein assays?
It allows for monitoring protein content as a change in absorbance.
What should be avoided during the operation of a size exclusion chromatography column?
Allowing the resin to dry, creating air bubbles, and thermal gradients.
What is the purpose of using a 96-well plate in the protein assay?
To measure the absorbance of hemoglobin and Vitamin B fractions at specific wavelengths.
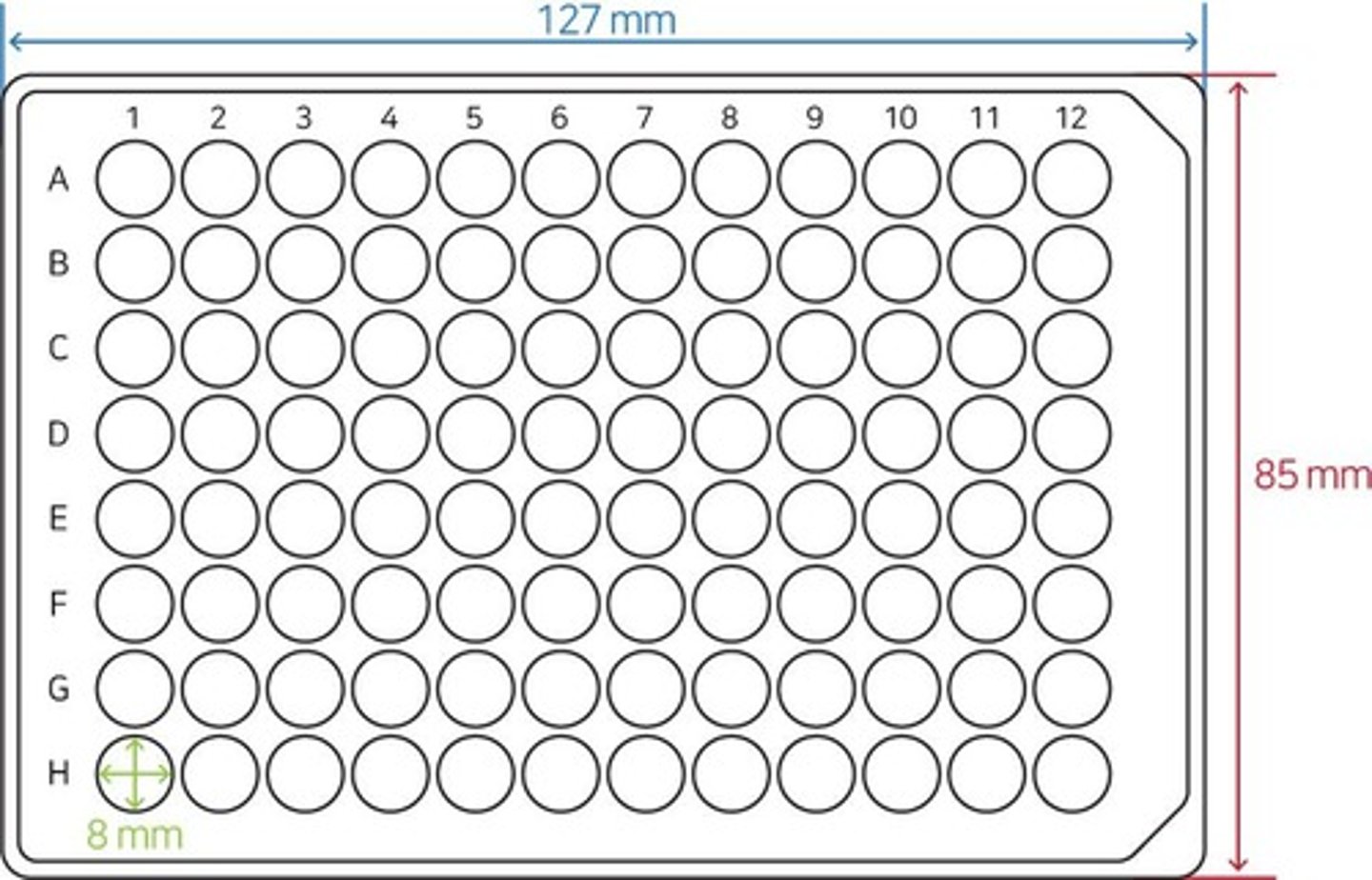
What is the typical absorbance wavelength for hemoglobin in assays?
630 nm.
What is the typical absorbance wavelength for Vitamin B in assays?
420 nm.
What are the final steps after completing the protein assay?
Dispose of waste properly, clean the plate, and rinse it with deionized water.
What is the significance of collecting multiple fractions during elution?
To ensure that all desired proteins are captured and to assess their purity.