hearing aids
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
how do hearing aids generally work?
amplifying sound to assist individuals with impaired hearing
what are the indications of hearing aids?
CHL and SNHL
what are the two different types of hearing aids in terms of mechanism?
analogue and digital
how do analogue hearing aids work?
convert sound waves into electrical signals, which are amplified
how do digital hearing aids work?
- convert sound waves into numerical codes before amplifying them
- code also includes info about a sound's pitch or volume, so it can be specifically programmed to amplify some frequencies more than others
what are the different types of placement of hearing aids?
- completely in the canal (CIC)
- in the canal (ITC)
- in the ear (ITE)
- behind the ear (BTE)
what does a CIC hearing aid look like?
what does an ITC hearing aid look like?
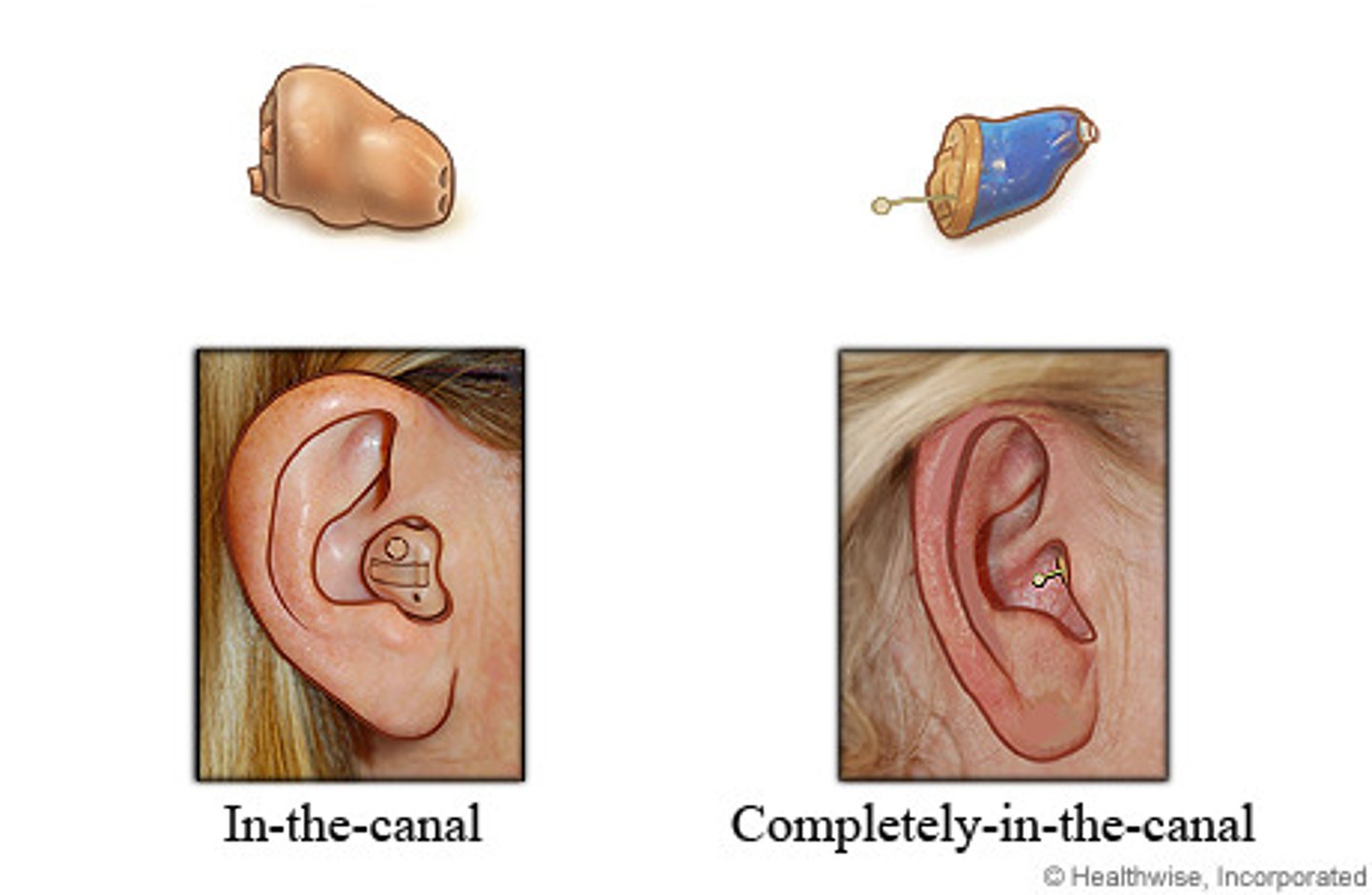
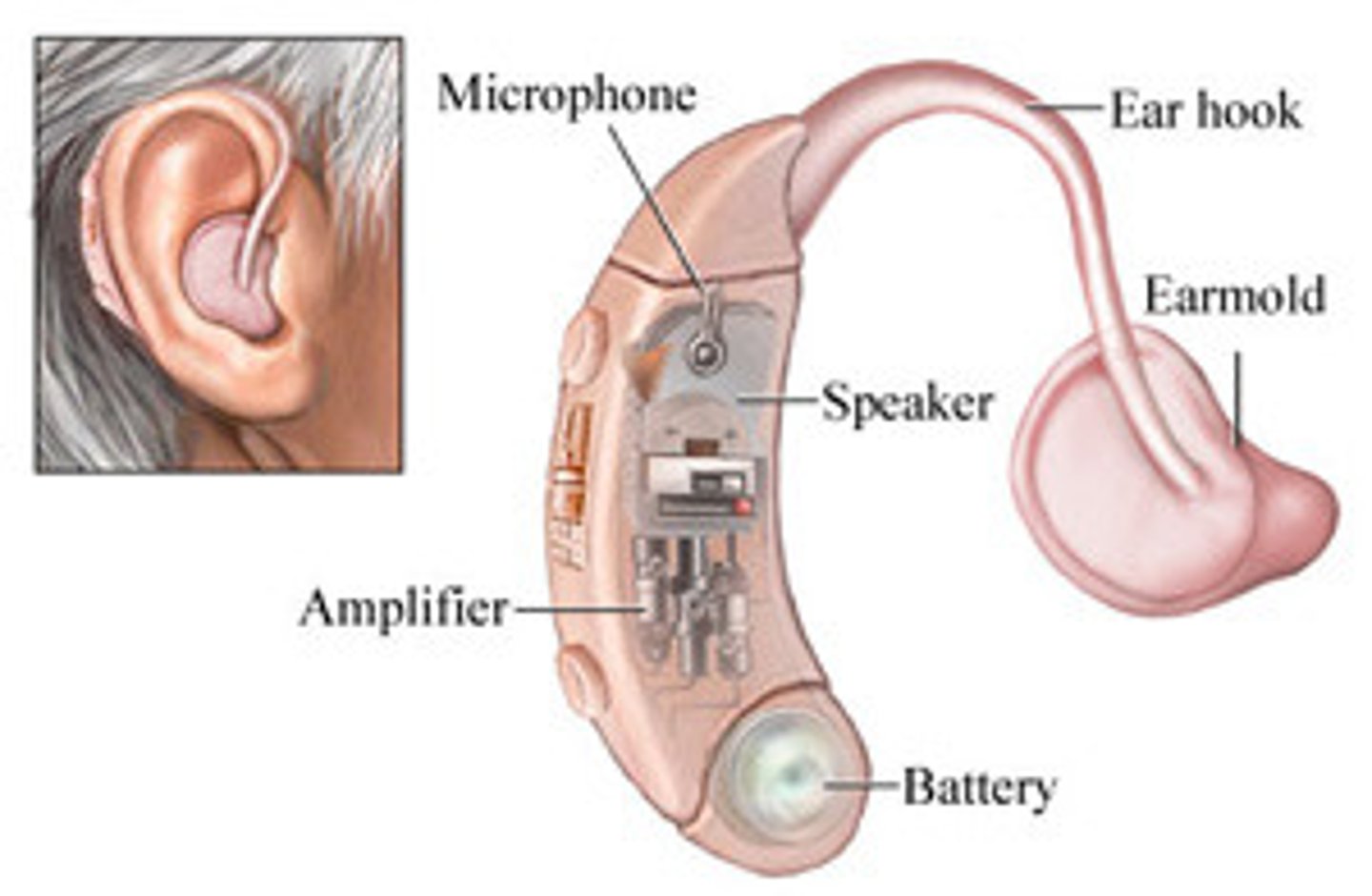
what does a behind the ear hearing aid look like?
what is a BAHA?
bone-anchored hearing aid
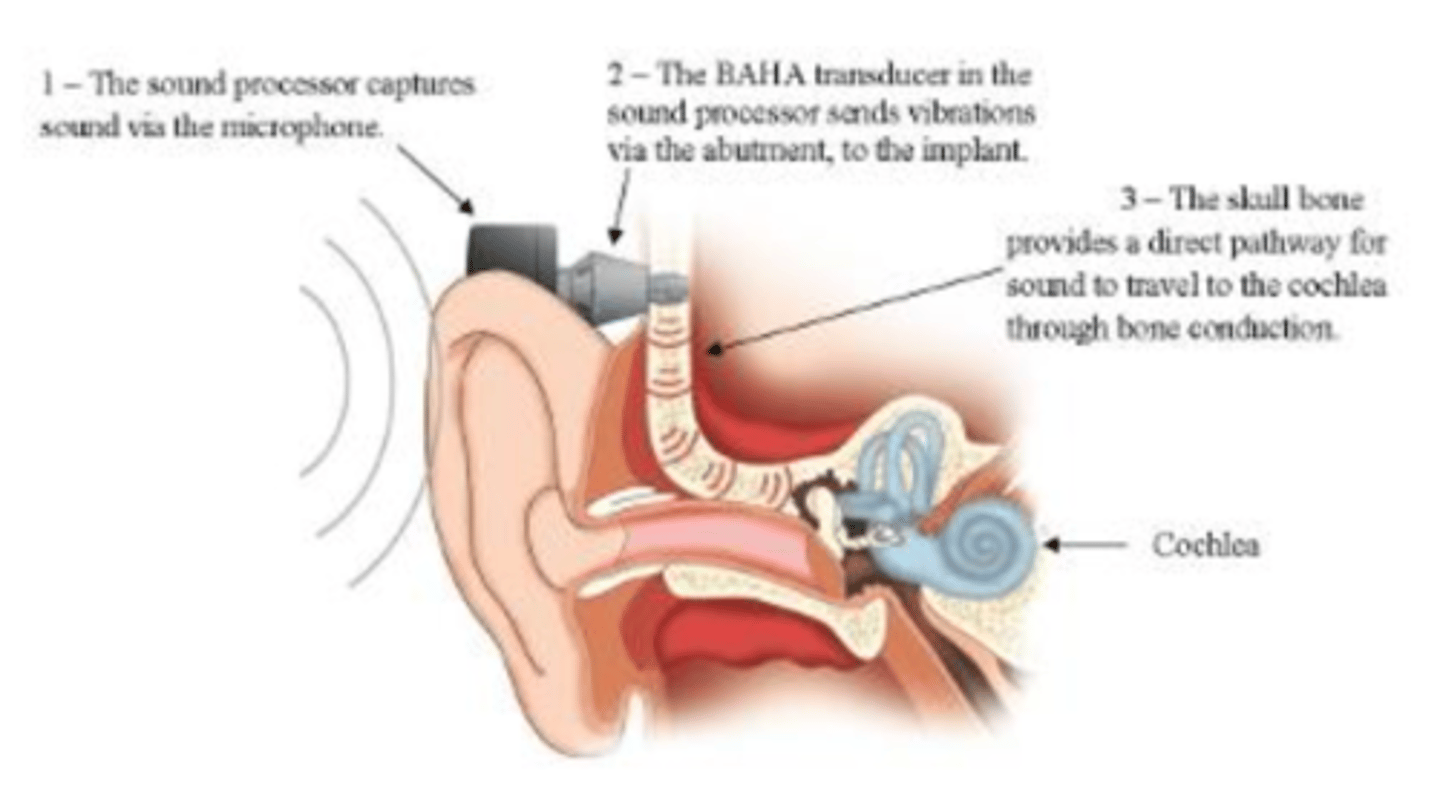
how do bone-anchored hearing aids work?
sound is transmitted to cochlea via bone conduction
what would be the indications of bone-anchored hearing aids?
intolerance of conventional hearing aids:
- persistent draining ear
- congenital malformations
- unilateral deafness
what are the complications of bone-anchored hearing aids?
skin regrowth around titanium screw and non-osseointegration
what is non-osseointegration?
when an implant becomes so fused with a bone that it is impossible to separate them without fracture
what are cochlear implants?
surgically implanted electronic devices that electrically stimulate CNVIII
what is a prerequisite for cochlear implants?
auditory nerve and system are intact
what are the indications for cochlear implants?
children - audiological assessment and/or difficulty developing basic auditory skills
adults - unsuccessful prior attempt with hearing aids for 3 months
what do cochlear implants look like?
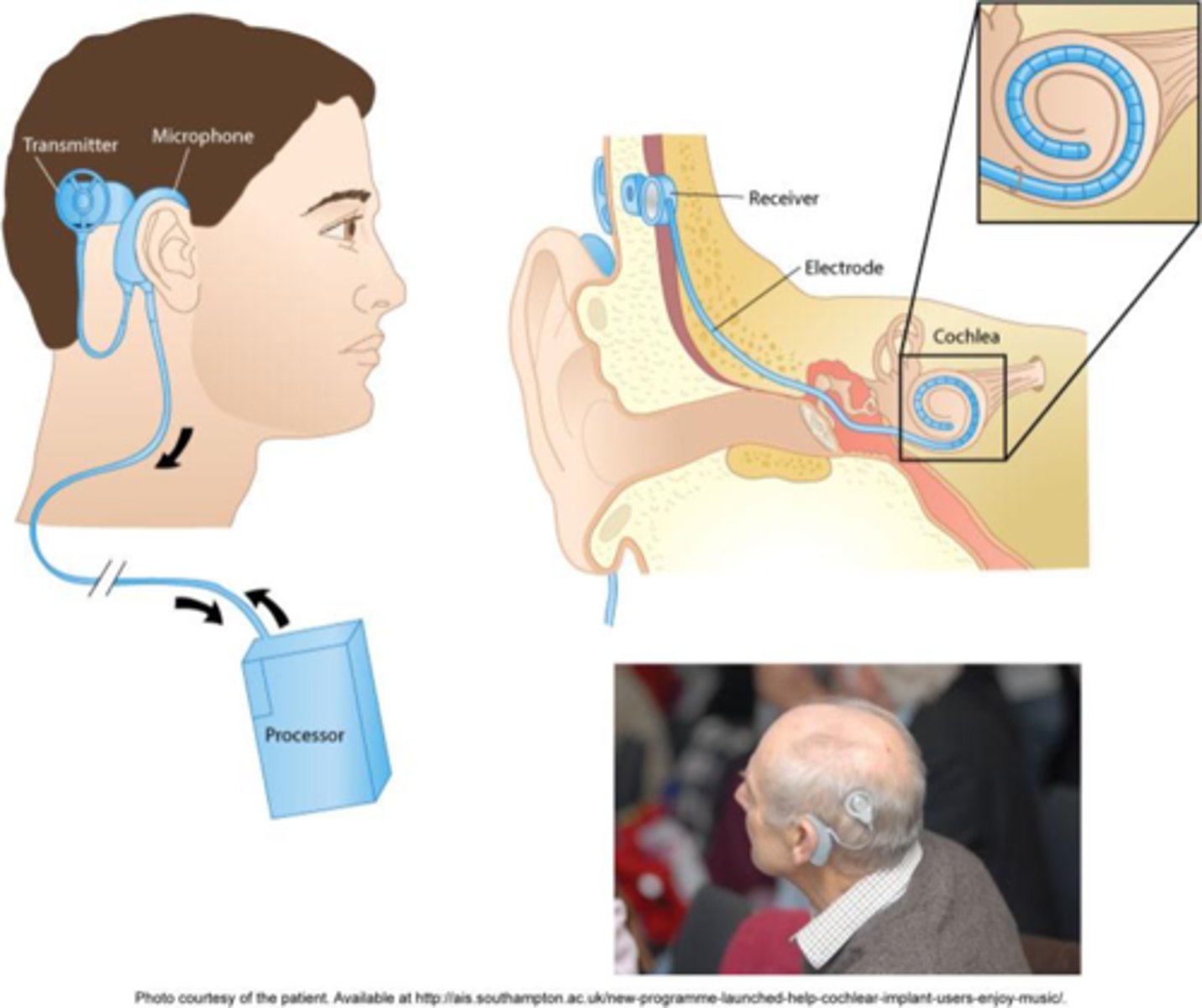
what are the contraindications to cochlear implants?
- lesions of CNVIIII or the brainstem
- chronic infective otitis media
- mastoid cavity or tympanic membrane perforation
- cochlear aplasia
what are the complications of cochlear implant surgery?
- facial nerve injury
- CSF leakage
- meningitis
what should be ensured to reduce the risk of meningitis?
up-to-date vaccinations against streptococcus and haemophilus