Humoral immunity and antibodies
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
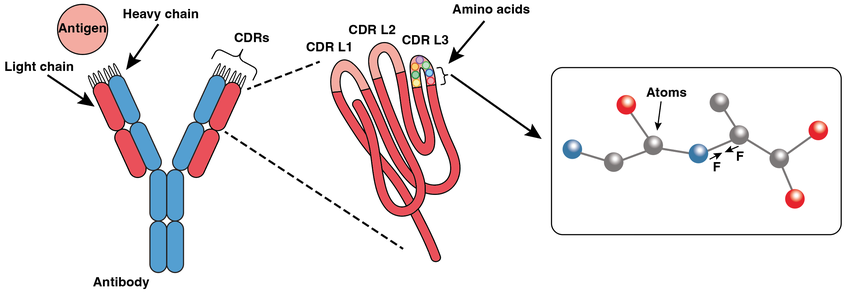
Complementarity determining region (CDR)
The part of the antibody molecule providing the complementary mirror image to an epitope. Formed from the 6 hypervariable regions in VhVL
Hapten
Small organic molecules which is not immunogenic but contribute to binding. Immunisation with hapten + carrier creates new epitopes that stimulates hapten specific Ab
examples
nickel, penicillin, dinitrophenol
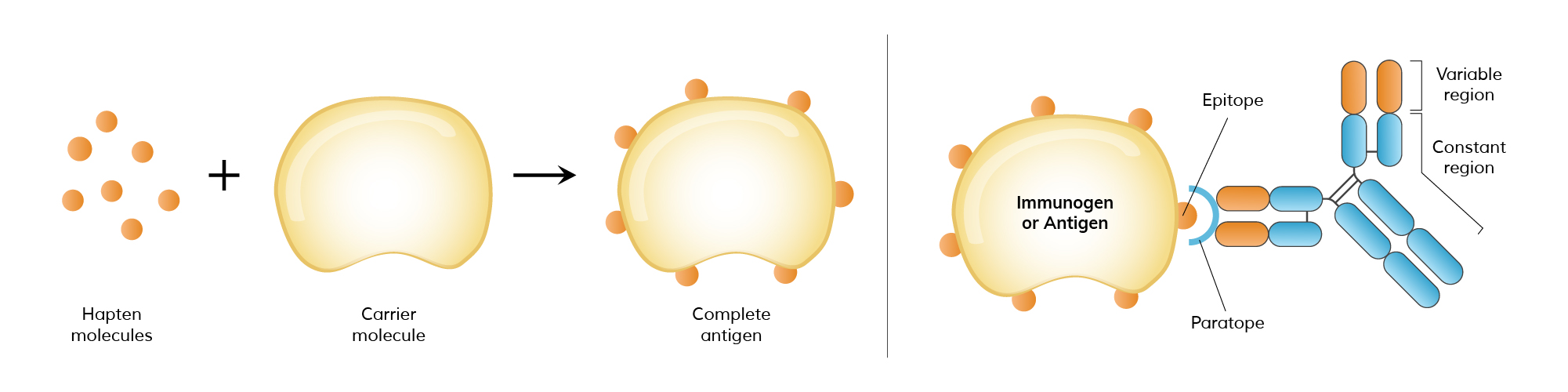
Epitope
are defined by antibody, there is no epitope with without antibody
The complete region on an antigen encompassed by the Ab binding site
Antigens can have multiple epitopes, the more complex the antigen, the more epitopes it have and the more immunogenic it is. Size does matter.
Ig amino acid sequences have conserved and …
Where are the conserved cysteine residue on the framework regions?
highly variable regions: encoded by the V(D)J gene segments in the heavy chain and VJ segment
always cysteine at 24 and 89 position
25 kDa immunoglobulin light chain
one of the two types of polypeptide chains in an antibody
Composed of one variable domain (VL) and one constant domain (CL)
The three hypervariable loops CDR are on the variable domain (VL)
The variable (V) domain is composed of 9 b-strands which provides a stable scaffold for the CDR loop
The constant (C) domain is composed of 7 b-strands , providing structural support
Pairs with a heavy chain to form one half of the antigen-binding site
What is the molecular weight of IgG?
150kDa
What are the 6 important antibody functions?
Opsonisation
Block adherence: stop bacteria/ viruses adhering to mucosal cells for entry. IgA is the best for this because it is secreted for mucosal immunity
Neutralise: direct binding to toxins to block receptor binding
Agglutination: clumping cells together as a result of multivalent antibdy
Immobilisation: eg, binding to bacterial flagellum
ADCC- antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity: antibodies binds target on cells and trggers NK clls via Fc receptor binding
IgM molecular weight and functions
900 kD
default isotypes made by all B cells
5 chains joined by J cahn
up to 10 binding sites for antigens
low affinity but very high avidity
reacts best to surfaces (ie, microbes)
powerful opsonin
fixes complement
IgG molecular weight and function
most abundant n serum
crosses placental for neonatal immunity
anti-toxin (soluble) as well as anti-bacterial (surface)
opsonises
blocks receptor binding
high affinity and high specificity
product of affinity maturation
IgA
160-300 kD
first line of defense at mucosa
blocks pathogen adhesion
secreted form linkd by J chain and secretory components (protects and transports across the epithelial barrier
IgE -200 kD
Least abundant in blood
produced by plasma B cells in mucosa (lungs, guts)
Defense against large organism (parasites) and complex antigens (eg, pollen)
Potent activator of mast clls
High affinity for FceR receptor on mast cells
Type 1 hypersensitivity
Atopic allergy
Allergy and anaphylaxis
What are the molecular forces that govern AbAg binding?
Hydrogen bonding
Electrostatic
Van der Waals
Hydrophobic
All reversible and non-covalent
First order kinetics
Affinity vs avidity
affinity: the strength of a single binding interaction between the antibody’s paratope and an antigen’s epitope
avidity: the overall binding strength of a multivalent antibody to a multivalent antigen
eg, even only with IgG, IgG bound to unfixed antibody would have an affinity, whereas binding to fixed antigen that has 2 valance would be avidity, which increase the cummulative strength