E1 Ortho- Intro
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
What is the job of a tendon?
connects muscle to bone
What is the job of a ligament?
connects bone to bone
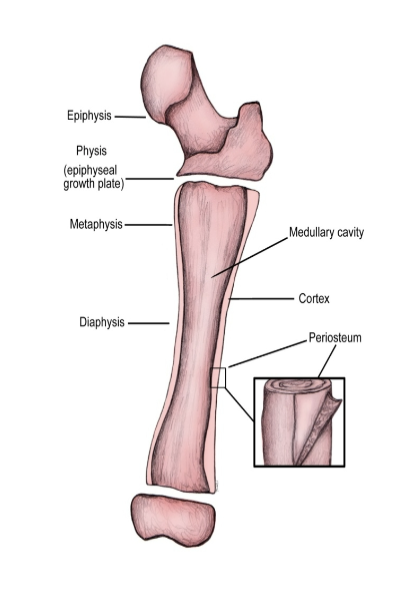
Review your bone anatomy
🙂
What type of synovial joint permits movement in 1 axis?
hinge joint
What type of synovial joint are: elbows, knees, ankles, IP joints?
hinge joint
What type of synovial joint allows for 2 axes of movement?
condyloid joint
What type of synovial joint is found between radius and carpal bones of wrist?
condyloid joint
What type of synovial joint is found as the articulation between 2 bones that are saddle shaped?
saddle joint
What type of synovial joint is found between the trapezium and 1st MCP of thumb?
saddle joint
What type of synovial joint allows for a gliding joint movement between bones that are flat and similar size?
planar joint
What type of synovial joint is found at intercarpal/intertarsal joints and AC joint?
planar joint
What type of synovial joint allows for articulation within a ligamentous ring between the round end of 1 bone and another bone?
pivot joint
What type of synovial joint is the atlantoaxial joint between C1 and C2 which allows for side to side head motion and the proximal radioulnar joint which allows for pronation and supination?
pivot joint
What type of synovial joint allows for movement of flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, and rotation?
ball and socket joint
What type of synovial joint are the shoulders and hip joints?
ball and socket joint
What synovial fluid analysis would you make based on the following:
Clear to pale yellow, transparent
WBC < 200
Normal
What synovial fluid analysis would you make based on the following:
Slightly deeper yellow, transparent
WBC < 2000
Osteoarthritis
What synovial fluid analysis would you make based on the following:
Darker yellow, cloudy, translucent, blurred
WBC < 80,000
Inflammatory
What synovial fluid analysis would you make based on the following:
Purulent, dense, opaque
WBC > 50,000
Septic
What synovial fluid analysis would you make based on the following:
Red, opaque
Hemarthrosis
Why synovial fluid analysis are seen in children?
normal, inflammatory, septic
What is the normal knee ROM?
0-130 degrees
If a joint is in hyperextension, what precedes the degree?
negative sign
What grade of muscular response is the following:
No contraction detected
0
What grade of muscular response is the following:
Barely detectable flicker or trace of contraction
1
What grade of muscular response is the following:
Active movement with gravity eliminated
2
What grade of muscular response is the following:
Active movement against gravity
3
What grade of muscular response is the following:
Active movement against gravity and some resistance
4
What grade of muscular response is the following:
Active movement against resistance without evident fatigue, "normal"
5
What is Scintigraphy?
bone scan
Which form of imaging provides the most detail for evaluating soft tissue?
MRI
When should an MRI not be ordered?
in the presence of metal (pacemaker, aneurysm clips)
Which form of imaging offers 3D models giving a more detailed exam of bones and structures?
CT scan
Which form of imaging gets images of a joint using a contrast medium?
Arthrography
Why should you be careful when ordering an arthrogram?
invasive and increases risk of join infxn
Which form of imaging uses a radioactive agent and gamma rays?
Scintigraphy
Which form of imaging is highly utilized in the US due to its low cost and safety?
Ultrasonography
What are ultrasounds variable?
highly technician dependent
Which form of imaging provides real-time Xrays and used in interventional procedures?
Fluoroscopy
What are the 2 main side effects with NSAIDs?
GI ulcers/bleeds & Kidney problems
Which inhibitors (COX-1/COX-2) is better for the GI system? (less likely to cause ulcers and bleeding)
COX-2 inhibitors
What are adverse effects to watch for with COX-2 inhibitors?
inc risk of stroke and MI (USE CAUTION), renal and hepatic complications, more expensive
What are corticosteroid injections used for?
decrease pain and inflammation (typically in arthritis pts)
Do corticosteroids work provide longer pain relief for pts with RA or OA?
RA
What pre op antibiotic is the drug of choice for ortho procedures?
Ancef
Which ASA status classification:
normal healthy pt
P1
Which ASA pt classification:
pt with mild systemic disease
P2
Which ASA pt classification:
pt w/ severe systemic disease
P3
Which ASA pt classification:
pt w/ severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life
P4
Which ASA pt classification:
moribund pt who is not expected to survive w/o the operation
P5
Which ASA pt classification:
declared brain-dead pt whose organs are being removed for donor purposes
P6
What needs to be done prior to surgery?
signed consent form
What is arthroscopy?
a pencil-sized, flexible, fiberoptic instrument is used to make 2-3 small incisions to remove bone spurs, cysts, damaged lining, or loose fragments in the joint, clear joints
What is an Osteotomy?
when the long bones of the arm or leg are realigned to take pressure off of the joint
What is Joint fusion?
surgeon eliminates the join by fastening together the ends of bone using pins, plates, rods, etc. -eliminates joint’s flexibility
What is Joint replacement (Arthroplasty)?
surgeon removes parts of the bones and creates an artificial joint w/ metal or plastic
What is an Open reduction internal fixation (ORIF)?
surgeon reduces the fracture and reinforces it with instrumentation inside the patient. Plates and screws or an intramedullary rods are used
What is an Open reduction external fixation?
surgeon reduces the fracture and applies instrumentation through the skin and reinforced with a metal frame. Utilized when a cast does not allow for proper alignment of a fracture
What is Manipulation under anesthesis (MUA)?
surgeon manipulates a pt’s joint under anesthesia
What is Manipulation under anesthesia (MUA) typically used for?
"frozen shoulders", total knee arthroplasty (TKA), and total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA)
5 Ps associated with compartment syndrome:
Pallor, Pulselessness, Poikilothermia, Pain, Paresthesias, Paralysis
What is the best tx for DVT?
prevention is key
What is Virchow’s triad?
stasis, hypercoaguability, endothelial injury
What can you use to evaluate if a pt has a DVT?
Wells criteria
How does a DVT present?
unilateral leg swelling, leg pain/calf tenderness, low-grade fever
What testing is done for DVT?
duplex U/S
What is the tx for a DVT?
LMWH (lovenox), vascular consult
What does the Axillary nerve control?
Lateral arm: deltoid (should abduction)
What does the Musculocutaneous nerve control?
Lat. prox forearm: biceps (elbow flex)
What does the Median nerve control?
Tip of thumb, volar aspect: FPL (thumb flex)
What does the Ulnar nerve control?
Tip of pinky, volar aspect: 1st dorsal (abd fingers)
What does the Radial nerve control?
dorsum thumb/web: EPL (thumb extension)
What does the Obturator nerve control?
medial thigh: adductor hip muscles (adduction)
What does the Femoral nerve control?
prox. -medial malleolus: quads (knee extension)
What does the Peroneal-deep branch nerve supply?
dorsum 1st web: EHL (great toe extension)
What does the Peroneal-superficial branch control?
dorsum lat. foot: Peroneus brevis (foot eversion)
What does the tibial nerve control?
plantar aspect of foot: FHL (great toe flex)
What is the purpose of Rehab?
return the pt to optimal function as quickly and safely as possible
What is an isometric contraction?
produces muscle contraction w/o moving the joint angle; length of muscle does NOT change
What is an isotonic contraction?
manual/mechanical resistance applied as muscle moves through the ROM; length of muscle changes
What is concentric movement?
muscles shortens
What is eccentric movement?
muscle lengthens
What is an isokinetic contraction?
muscle shortens and contracts, occurs at a constant rate of speed
What are absolute contraindications to exercise?
recent MI, ischemic EKG changes, unstable angina, uncontrolled arrhythmia, 3rd degree heart block, acute CHF
What is cryotherapy?
use of cold modalities for the purpose of vasoconstriction to produce a decrease in inflammation, pain, muscle spasm
What is Electrical modalities of rehab?
use of electrical current for contraction of muscle, reduction of pain, dx purposes, wound healing, dec spasticity
Which form of electrical modality:
stimulates muscles for strength/rehab
electrical stimulation
Which form of electrical modality:
drug (DEXA) delivered through ultrasound
iontophoresis
Which form of electrical modality:
stimulates nerves to relieve pain
TENS unit
What is Continuous Passive Motions (CPM)?
machines utilized immediately after surgery to maintain and improve mobility of joints (usually ones not used)
Which DME is usually given first?
walker (more stable)
Which walker type is best for pts w/ UE fxs?
walker w/ platform attachments
Which walker is best for stroke pts?
hemiwalker
Which walker is best for pts w/ Parkinson’s?
rolling walker
Which offers more support crutch or cane
crutches
Which crutches are best for pts w/ fxs?
platform crutches
Which type of crutches are best for pts w/ long-term disabilities?
lofstrand (forearm) crutches
What type of crutches are best for pts w/ temporary disabilities?
axillary crutches
Which type of cane offers more support (quad vs single)?
Quad cane