Chemistry 1.4 The Ever-Changing Earth
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are the four main layers of the Earth?
Solid iron inner core
Molten iron outer core
Mantle
Crust
What is the theory of plate tectonics?
The idea that the Earth’s lithosphere is divided into separate parts known as tectonic plates
These plates move over the mantle at a rate of a couple of cm/year, and the process is called continental drift
What was Alfred Wegener’s early theory of continental drift?
The continents all used to be joined together in a supercontinent called Pangea. The Earth’s crust and upper mantle are made up of sections which drifted apart over millions of years.
What occurs at a conservative plate boundary?
Two plates slide past each other
If the movement is sudden and large enough, then there is an earthquake
No volcanoes are found at these boundaries
What occurs at a destructive plate boundary?
Two plates move towards each other
The denser plate is pushed beneath the other and melted
This forms magma, which rises up and leads to the formation of a volcano or an earthquake
The magma then cools, forming igneous rock
What occurs at a constructive plate boundary?
Two plates move away from each other
Magma from the mantle rises up and forms new rock to fill the gap created
If the pressure is high enough, a volcanic eruption may occur
How was the early atmosphere formed?
The intense volcanic activity released gases such as CO2 and water vapour.
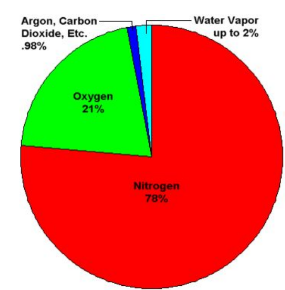
What is the present composition of the atmosphere?
78% Nitrogen
21% Oxygen
~0.9% Argon
~0.04% Carbon dioxide
~0.04% Water vapour
What are the causes which lead to the increase of atmospheric concentration of oxygen?
Algae and plants release O2 into the atmosphere during photosynthesis
As plants evolve, the concentration of oxygen gradually increases, enabling animals to evolve and exist
How has carbon dioxide concentration changed in the atmosphere?
Algae and plants decrease the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere by using CO2 for photosynthesis
Formation of sedimentary rocks and fossil fuels which contain carbon decreases atmospheric CO2
Atmospheric CO2 decreases when it dissolves in the ocean
How has the concentration of ammonia and methane in the atmosphere changed?
As oxygen levels increase:
Ammonia reacts with oxygen to form nitrogen and water
Methane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water
Which three processes maintain oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere?
Respiration
Combustion
Photosynthesis
Why has the concentration of CO2 increased considerably in the last 100 years?
Deforestation
Increased burning of fossil fuels
Population growth
What is the major cause of climate change?
Global warming that results from the increase in carbon dioxide and greenhouse gas levels.
What are the potential effects of global climate change?
Destruction of animal habitats that may cause extinction of species
Rising sea level due to the melting of polar ice caps
Increased risk of skin cancer due to more exposure to UV rays
More extreme weather conditions (such as droughts)
What is another byproduct of burning fuels other than CO2?
Sulfur dioxide.
How is acid rain formed?
Sulfur dioxide, released from the burning of fuels, dissolves in rainwater, forming sulfuric acid (also known as acid rain).
What are the effects of acid rain?
Damages buildings and statues made of limestone
Causes corrosion of metal
Reduces the growth of or kills trees and crops
Lowers pH of water in lakes, killing aquatic organisms
What measures are used to address the problems of global warming?
Reduce fossil fuel usage and use renewable sources instead
Encourage eco-friendly travel, recycling, and reusing
Reforestation and creation of more green areas
International deals and targets for emissions between countries
What measure is used to address acid rain?
Sulfur scrubbing - this technique removes 95% of sulfur dioxide from gases released by burning fuels.
Which elements can be found in air?
Nitrogen
Oxygen
Argon
Neon
What is the chemical test to identify oxygen gas?
A glowing splint will relight if placed into a test tube containing oxygen gas.
What is the chemical test to identify carbon dioxide?
When bubbled through limewater, carbon dioxide turns limewater cloudy due to the formation of calcium carbonate precipitate.