Theme 2
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Peer-to-peer funding
Funding from an individual that the business has no relationship with through a lending marketplace.
Business angels
Wealthy individuals that lend their disposable finance in return for shares. Small loans, but cangive knowledge and advice.
Venture capital
An established business give large sums of money in return for shares.
Business plan
A document that describeshow they propose to set up the buisness, the nature of the product/service, objectives etc.
Cash-flow forecasts
Predicts all likely inflows and outflows of a business month by month.
Sales forecast
Estimates the volume or value of future sales using market research.
Sales revenue (turnover)
Sales revenue
Sales volume x selling price
Total variable costs
Average variable cost x quantity
Calculate changes
(Difference/original) x 100
Break-even
The point at which revenue equals cost.
Contribution
The amount that each unit produced ‘contributes’ to fixed costs.
Contribution
Selling price - variable cost per item
Break-even
Fixed costs/contribution per unit
Margin of safety
Difference between break-even level of sales and actual level of sales.
Margin of safety
Actual sales - break even sales
Budget
An estimate of income or expenditure over a set period of time.
Variance
Difference between actual and budgeted income and expenditure. Favourable = underspent. Adverse = overspent.
Historical budget
Set based off data of previous performance of the business.
Zero-based budget
Set using figures based off potential performance (e.g. number of probable customers).
Statement of comprehensive income (SOCI)
Accounts UK businesses have to publish showing their profit and loss.
Gross profit
Total revenue - total variable costs (cost of sales)
Operating profit
Total revenue - total costs
Net profit
Total revenue - total costs - tax and interest
Cash and profit
Cash is the amount of money a business has currently or soon. Profit is the money left over when all expenses are paid.
Liquidity
The ability of a business to turn its assets into cash to pay off current liabilities.
Statement of financial position (SOFP)
A balance sheet which is a summary of financial balances.
Current ratio
Current assets/current liabilites
Acid test
(Current assets - inventory) / current liabilities
Business failure
When a business ceases to trade or doesn’t trade in a profitable way or makes a terrible decision.
Liquidation
The process of closing a PLC or LTD.
Offshoring
A business moves overseas.
Productivity
The output per input (person or machine) per hour.
Job production
Unique products made by skilled craftspeople.
Batch production
Goods made in batches and can be switched over to make something different on the same production line.
Flow production
Standardised goods made on production line swith continuous movement of items (capital intensive).
Cell production
Dividing a production line into separate areas responsible for different sections of work.
Capacity utilisation
(Actual level of output/maximum possible output) x 100
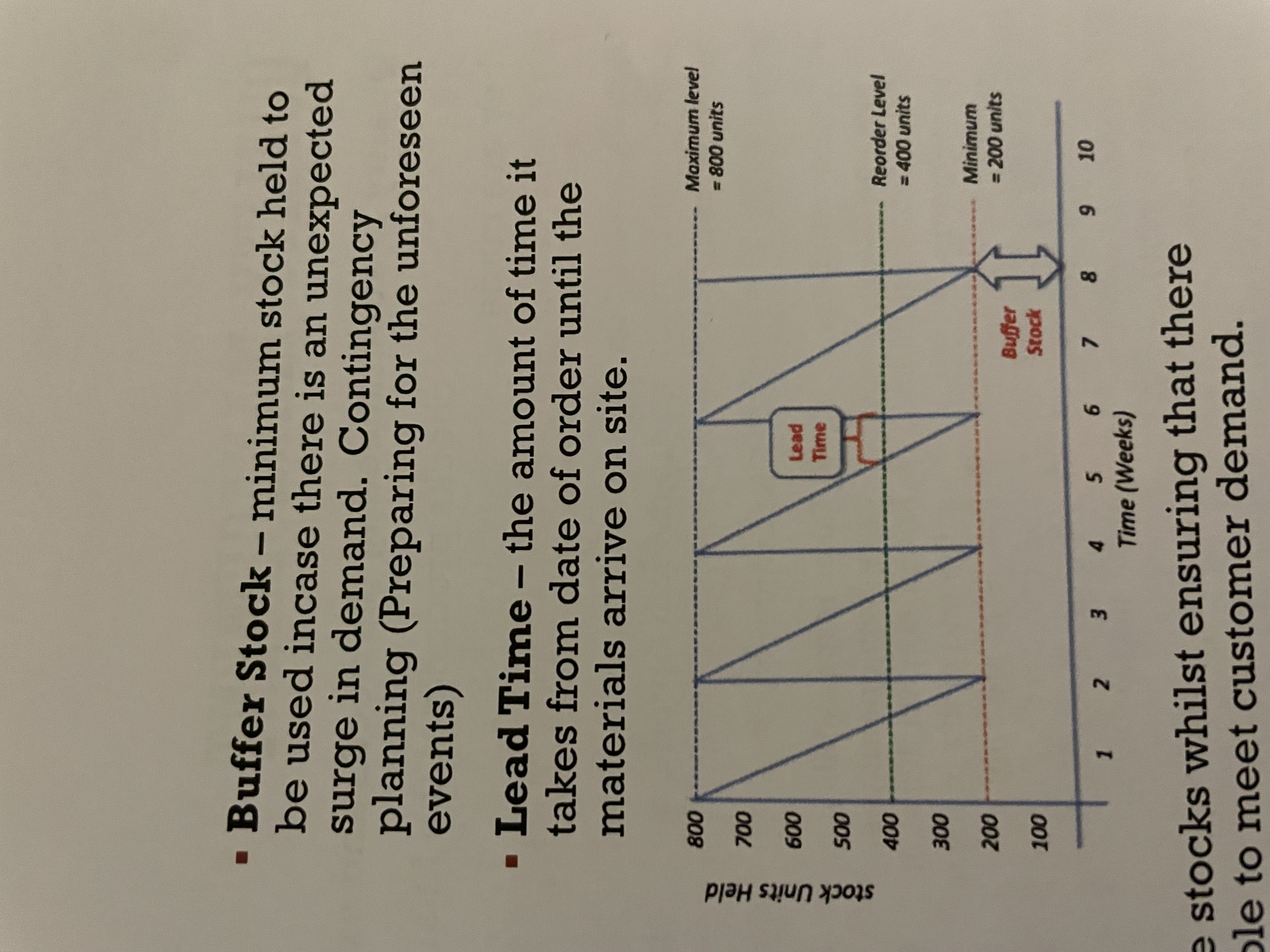
Stock control
Quality control verses quality assurance
Quality control checks products at the final stage while quality assurance ensures quality is built in at every stage.
Total quality management
Every stage of the production process is investigated to take into account quality at all times.
Benchmarking
Assessing competitors and then comparing performance standards.
Quality circles
Small groups opf workers in the same area of production meet to solve production problems.
Kaizen
‘Continuous improvement’ constantly introducing small incremental changes in a business to improve quality.
Inflation
The increas in the average price level of goods and services.
Exchange rates
The price of one currency in terms of another. SPICED.
Interest rates
Cost of borrowing and reward for saving.
Direct and indirect taxes
Direct are taxes on income e.g. income tax. Indirect are taxes on spending e.g. VAT.
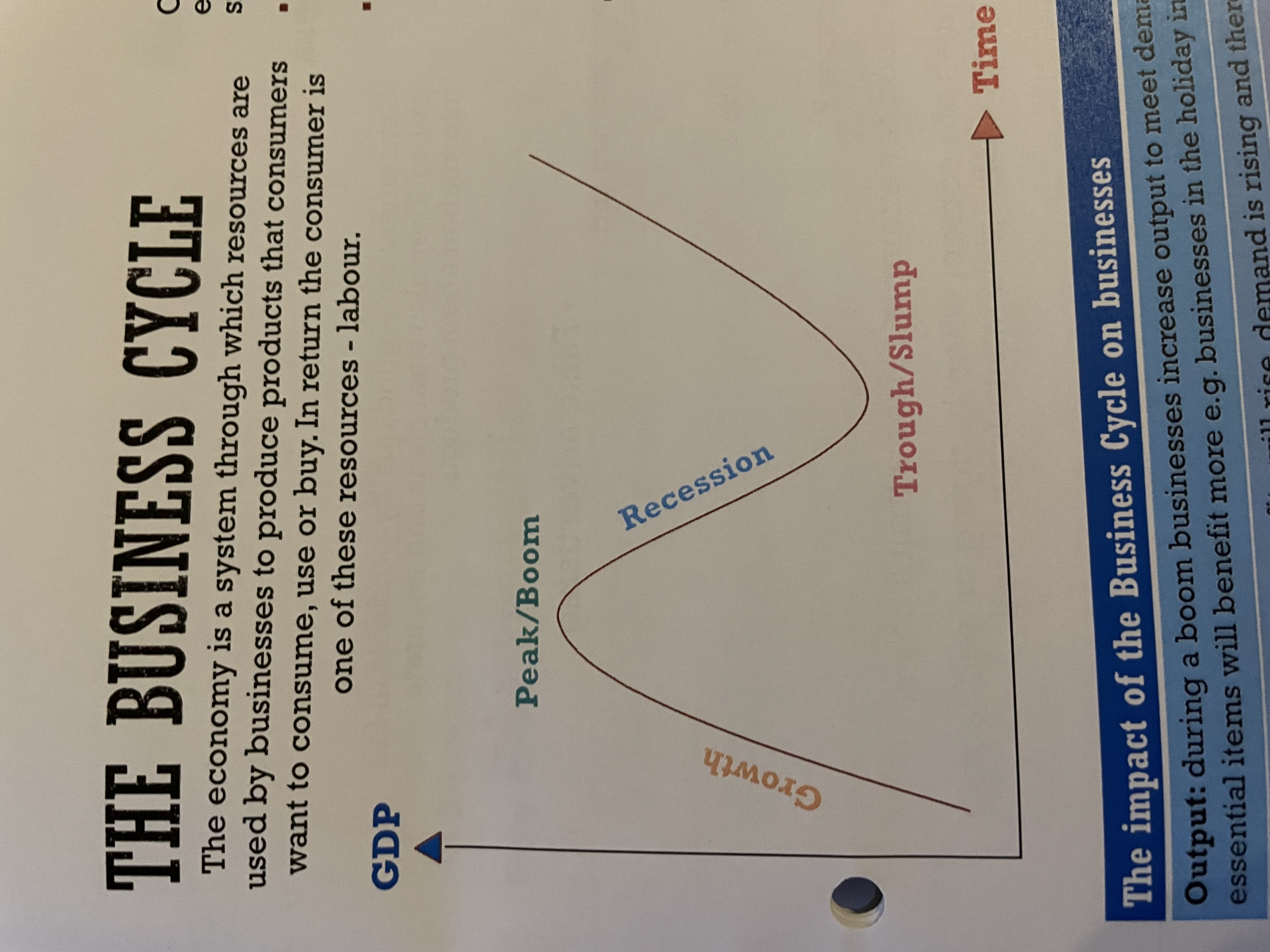
The business cycle