Endocrine Biomed Capstone
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What causes hyperthyroidism
overstimulation of thyroid producing excess thyroid hormones. graves disease, multi-nodular goitre, pituitary tumour, increased T3
more common than hypothyroidism
What causes hypothyroidism
chronically low plasma TH levels mostly due to primary loss of thyroid gland func
Two types of hypothyroidism
Primary (thyroid gland problem) = low T3 + T4, HIGH TSH (caused by iodine deficiency, hashimotos disease)
deficiency in thyroid gland, doesn’t recognise TSH
Secondary (anterior pituitary problem) = low T3, T4, TSH
TSH and impact on thyroid function
TSH inversely related to thyroid gland activity
If primary hypothyroidism -> Increase TSH -> Decrease T3 + T4
If hyperthyroidism -> Decrease TSH -> Increase T3 + T4
TSH impact on follicles
Increase T3 + T4 -> Decrease TRH + TSH -> follicles shut down
Decrease T3 + T4 -> TSH secretion -> follicles activated
Cushings syndrome pathology
caused by high blood cortisol, adrenal hyperplasia due to excess ACTH stimulation from anterior pituitary due to pituitary neoplasms
Cushings syndrome symptoms
Increased fat + redistribution to central areas, increased protein breakdown + gluconeogenesis, muscle wasting, hyperglycemia
Addisons vs Cushings disease
Addisons = adrenal HYPOfunction
- low cortisol, hypoglycaemia, weight loss
Cushings = adrenal HYPERfunction
- high cortisol, hyperglycaemia, weight gain
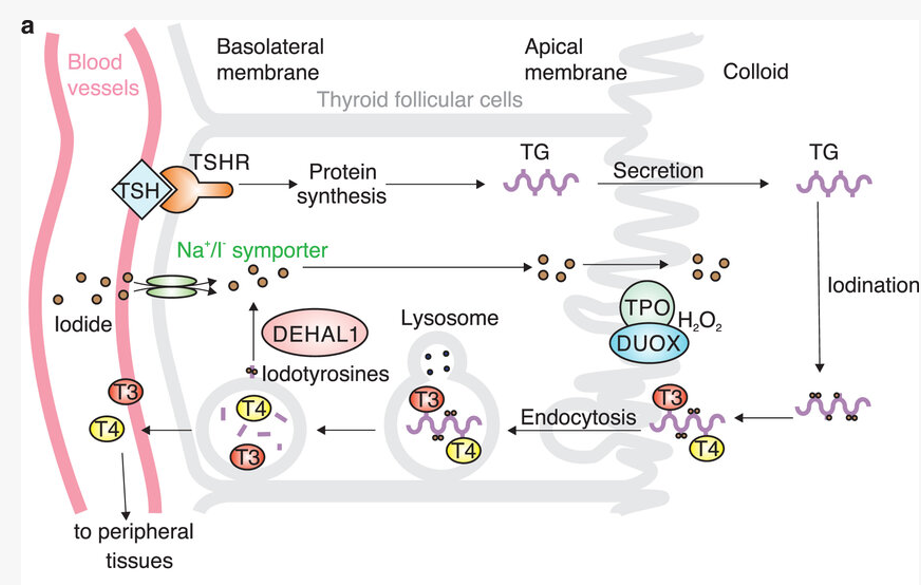
Iodine degrades TG into T3 + T4
1. TSH binds to receptor -> TG synthesised in apical membrane + secreted into colloid
2. TG is iodinised and translocates back into apical membrane
3. Endocytosis + degradation of TG into T3 + T4 occurs
4. T3 + T4 released to peripheral tissues
How does iodine deficiency cause a goiter
Without iodine degrading TG into T3 + T4, TSH overstimulation occurs to compensate for decrease in circulating T3 + T4. Causes thyroid to enlarge = goiter
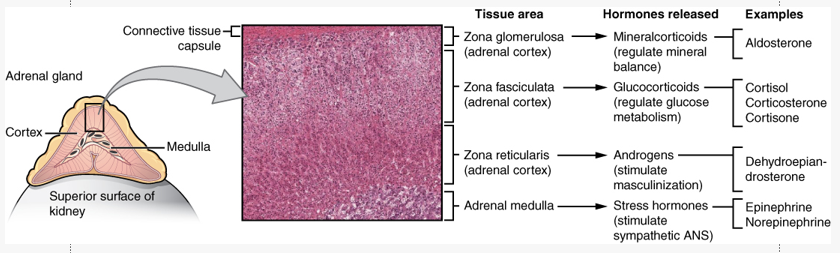
Regions of the adrenal gland
Outer cortex = produces steroid hormones (glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, gonadocorticoids)
Inner Medulla = produces catecholamines (adrenaline, noradrenaline, dopamine)
Conn's disease
primary hyperaldosteronism. affects aldosterone producing adrenal adenoma of zona glomerulosa. pathology = increased blood pressure, decreased potassium, decreased H+ (alkalosis)
Hypersecretion of growth hormone can lead to 2 disorders based on timing of hypersecretion :
If hypersecretion occurs during childhood = gigantism
If hypersecretion occurs during adulthood = acromegaly (thickening of features)
Suspect thyroid disorder
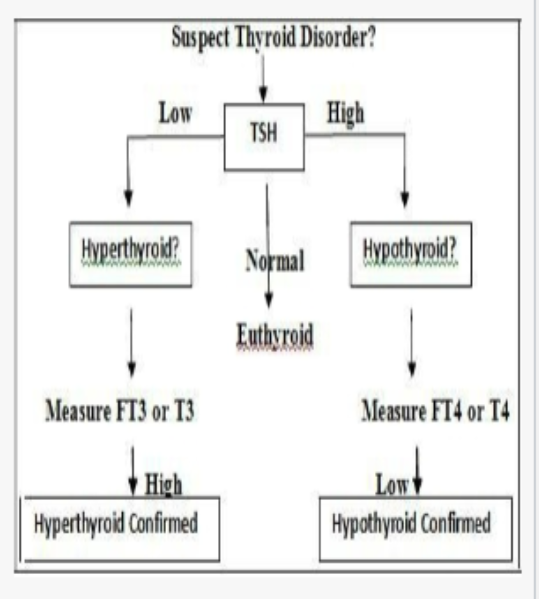
Clinical Features Hypothyroidism (low concentraiton)
enlarged thyroid (Goiter)
cold intolerance
weight gain
Clinical Features Hyperthyroidism (higher concentration)
enlarged thyroid (goiter)
heat intolerance
weight loss
Hashimoto’s Disease
autoimmune body attacks thyroid
inflamed thyroid, thyroid autoimmune disease (Cell and Ab mediated), detect anti-thyroid peroxidase
treatment = thyroid hormone replacement therapy
most common hypothyroidism in USA
Graves Disease
autoimmune disease (more prevalent in females)
Abs stimulate TSK (or thyrotrophin) receptor
increase T3 and T4 feedback onto hypothalamus / pituitary and supress TSH —> antibodies biding to TSH receptors because increase T3 and T4 message to hypothalamus to stop producing TSH
thyroid gland atrophies due to constant stimulation
Clinical signs Graves Disease
exophthalmos (bulging eyes)
goitre —> irregular growth of thyroid gland (TSH overstimulation of thyroid due to increased circulating T3 and T4
Iron deficiency and thyroid hormone *** IMPROTANT SHORT RESPONSE Q****
Thyroglobulin (TG) is precursor of T3 and T4
TSH binds to receptor leading to TG production
Iodine translocated to basolateral membrane to iodises TG which promotes endocytosis then degradation into T3 T4
process
TSH leaves blood vessels and binds to TSHR in basolateral membrane —> protein synthesis —> TG —> secretion across the apical membrane —> iodination —> internalised via endocytosis (splits into T3 and T4) —> Iodotyrosines —> DEHAL 1 —> in endosome fuse with lysosome
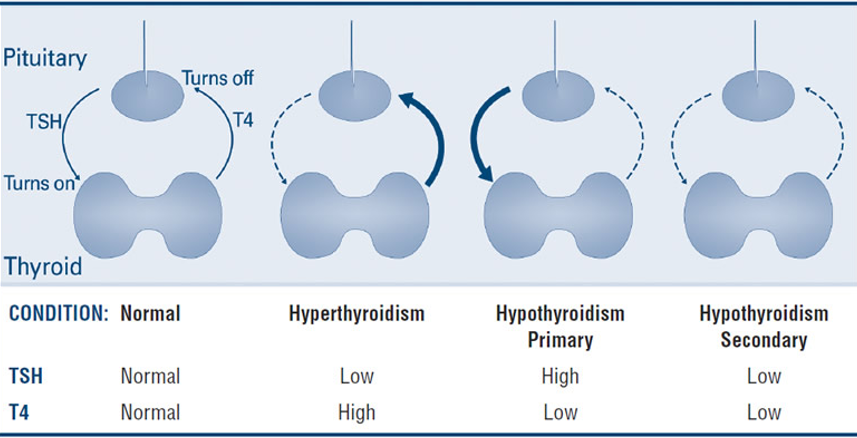
Normal, hyer, hypo primary and seocndary TSH & T4
Normal - TSH = Normal, T4 = Normal
Hyperthyroidism - TSH = Low, T4 = High
Hypothyroidism Primary - TSH = High, T4 = low
Hypothyroidism Secondary - TSH = Low, T4 = low
Pituitary Disorders - hypersecretion and hyposecretion of GH
hypersecretion
during childhood = gigantism
during adult hood = acromegaly (thickening of features)
hyposecretion
pituitary dwarfism (lower somatic growth)
Acromegaly
hypersecretion of somatotropin during childhood
over production of growth hormone throughout development
excessive amount of growth hormone in adulthood
causes = thickening of bones in hands, feet, cheeks, jaws (happens in adults)
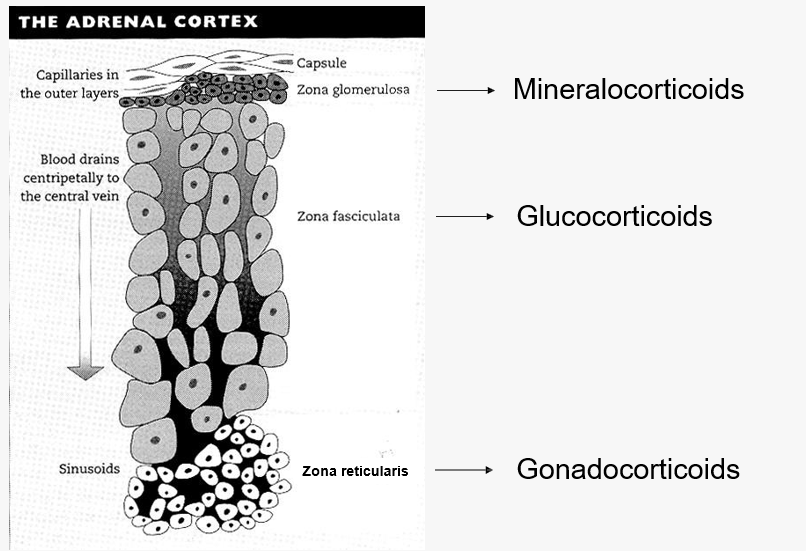
Adrenal Cortex
adrenal corticosteroid hormones
glucocorticoids (cortisol, corticosterone)
mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) (regulates renal function)
gonadocorticoids
Adrenal Medulla
Catecholamine
adrenaline (epinephrine)
noradrenaline (norepinephrine)
dopamine
Adrenal cortex compoenents
Zona glomerulosa = mineralocorticoids
zona fasciculata = glucocorticoids
zona recticulans = gonadocorticoids
Adrenal Hormones - NEED TO KNOW
Addisons Disease
Adrenal Cortex Hyposecretion
low cortisol
hypoglycemia
frail and weak (low weight)
hyperkalaemia and ST elevation
hyponatraemia and salt craving
Cushings Disease
Adrenal Cortex hypersecretion
excess cortisol
hyperglycemia
hyperatreamia
hypokalaemia
truncal obesity