Introduction to Critical Infrastructure Security
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
What does TCSEC stand for?
Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria. a set of standards for evaluating the security capabilities of computer systems, commonly known as the "Orange Book."
What does the term 'Trusted Code Base' refer to?
The environment that conforms to the evaluated design as per TCSEC.
What were the explicit requirements of the U.S. DoD TCSEC regarding software?
Configuration management and trusted distribution to ensure a trustworthy environment.
How were software updates typically shipped in the 1970s?
On magnetic tapes secured with tamper-evident labels.
they were supposed to be qualified before installation in production environments

how did attackers infiltrate code?
by mimicking legitimate update tapes
What is the purpose of digital signatures in software updates?
To validate the integrity and authenticity of the updates.
What assumption is made when using digital signatures for software updates?
That the code being signed is trustworthy and that the signing keys and certificate are secure. This is part of the configuration management and distribution system
What is a significant limitation of the software supply chain ?
The visibility of the software supply chain is limited and fast-moving, increasing the risk of vulnerabilities and attacks on software updates.
What does PCI-DSS require regarding critical patches?
Critical patches must be installed within 30 days.
What is the significance of trust relationships in software development?
Trust relationships are transitive for components used in development and distribution. Trust relationships extend to components that depend on other trusted components.
What is the main challenge with the current cycle of software updates?
They are released on a much faster cycle and frequently installed automatically.
What historical software systems are mentioned in relation to software updates?
DEC's VMS and IBM MVS operating systems.
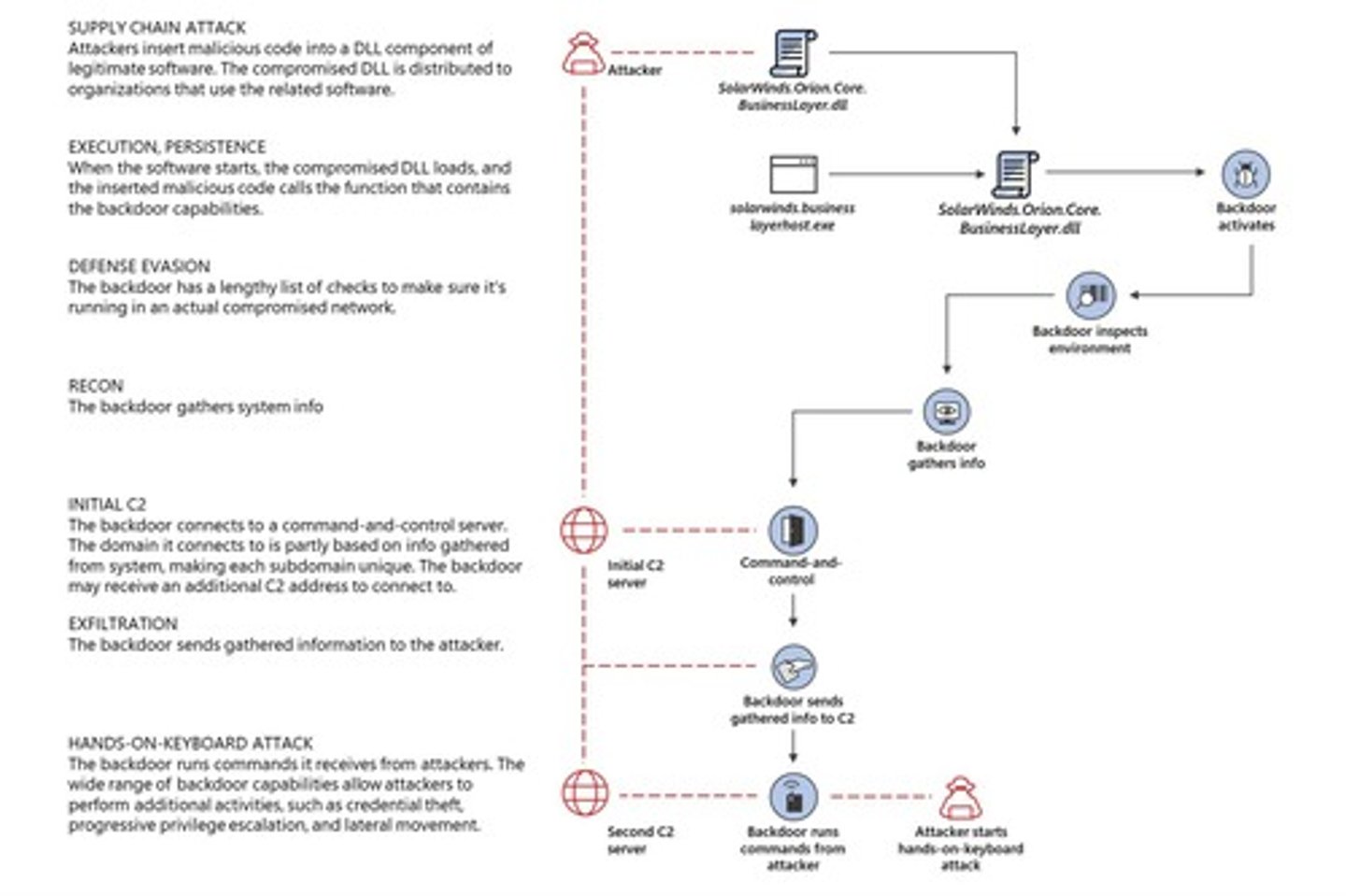
What is the Orion platform by SolarWinds used for?
It is a network monitoring platform used by industry and government to monitor operational and performance aspects of networks.
What significant security incident is associated with the Orion platform?
The Sunburst Attack, where an adversary penetrated the build system for Orion and installed a backdoor.
How did the adversary gain access to the Orion build system?
By finding credentials ('SolarWinds123!') on a repository for the build system.
How many sites were affected by the installation of the backdoored component?
Over 18,000 sites.
What was the purpose of the compromised component in the Sunburst Attack?
It was part of a legitimate hotfix bundle that loaded the backdoored module.
What checks did the backdoor perform to avoid detection?
It included a two-week dormant period to avoid sandboxes and carried an anti-forensics blacklist.
How did the backdoor communicate with the command and control (C2) system?
Through encoded DNS queries and steganographically hiding exfiltrated data in .NET XML assemblies.
What was the main task of the Sunburst component?
To identify and select secondary targets for memory-only droppers.
Why were users of Orion particularly vulnerable during the Sunburst Attack?
They typically had full visibility of victim networks and often relied on privileged accounts to access the software.
What did SolarWinds advise clients regarding antivirus software before the incident?
Clients were advised to include their software in any antivirus' whitelist of benign code.
How long did the intelligence operation remain unnoticed during the Sunburst Attack?
From March to December 2020.
What was a key factor in the attackers' ability to remain undetected?
Well-designed steganographic communication that evaded detection by threat intelligence and traffic monitoring systems.
What incident led to the discovery of the Sunburst Attack?
An earlier breach of the security company FireEye in December 2020.
What information was obtained by the attackers during the FireEye breach?
Information on clients of FireEye and a tool database used for red-teaming.
What was discovered while investigating the SolarWinds Orion code?
A second implant named 'Supernova,' indicating the presence of another threat actor.
What questions arise after incidents like the Sunburst Attack?
Questions include how long adversaries were inside the systems, which accounts and data were compromised, and whether systems can be recovered.
What type of communication did the backdoor utilize to disguise its activity?
Encoded DNS queries.
What was the appearance of the code inserted by the adversaries?
It had similar appearance and coding conventions to the original code base.
What was the significance of the Sunburst Attack in terms of cybersecurity?
It highlighted vulnerabilities in widely-used software and the potential for significant breaches in critical infrastructure.
What did the compromised component communicate with?
Third-party systems, which helped obfuscate extraneous traffic.
What is the implication of having privileged monitoring services like Orion in terms of security?
They can provide full visibility of networks, making them attractive targets for adversaries.
What is the role of steganography in the Sunburst Attack?
It was used to hide exfiltrated data within legitimate communication channels.
What was the nature of the operation related to the xz utilities back door?
It was a straightforward intelligence operation rather than an outright attack.
What is the xz compression library known for?
It is an open-source library widely used in many packages, including most Linux distributions, often with admin privileges.
What was the main goal of the Sunburst Attack?
To gain a position of trust with the head maintainer of a project and pressure them to hand over work to an attacker's account.
How was the backdoor in the OpenSSH sshd server hidden?
It was carefully hidden so that it would not appear in the Git repository as code but was patched in from test files during the build process.
When was the backdoor actually constructed in the Sunburst Attack?
During the build stage for a release build.
What did the backdoor in the Sunburst Attack scan for?
It scanned for a steganographic code embedded in a key sent during RSA authentication.
How was the steganographic key generated in the Sunburst Attack?
It was generated on the fly using odd features of the x86 instruction set to avoid detection during memory analysis.
What was the consequence of the xz utilities back door?
It enabled random root access to all systems with a contaminated version of the xz utilities, with logins hidden from regular logs.
What unusual behavior led an admin to investigate the xz utilities back door?
The admin spotted unusual timing of SSH connections.
What significant event occurred on May 7, 2021, involving Colonial Pipeline?
Colonial Pipeline became the victim of a ransomware attack.
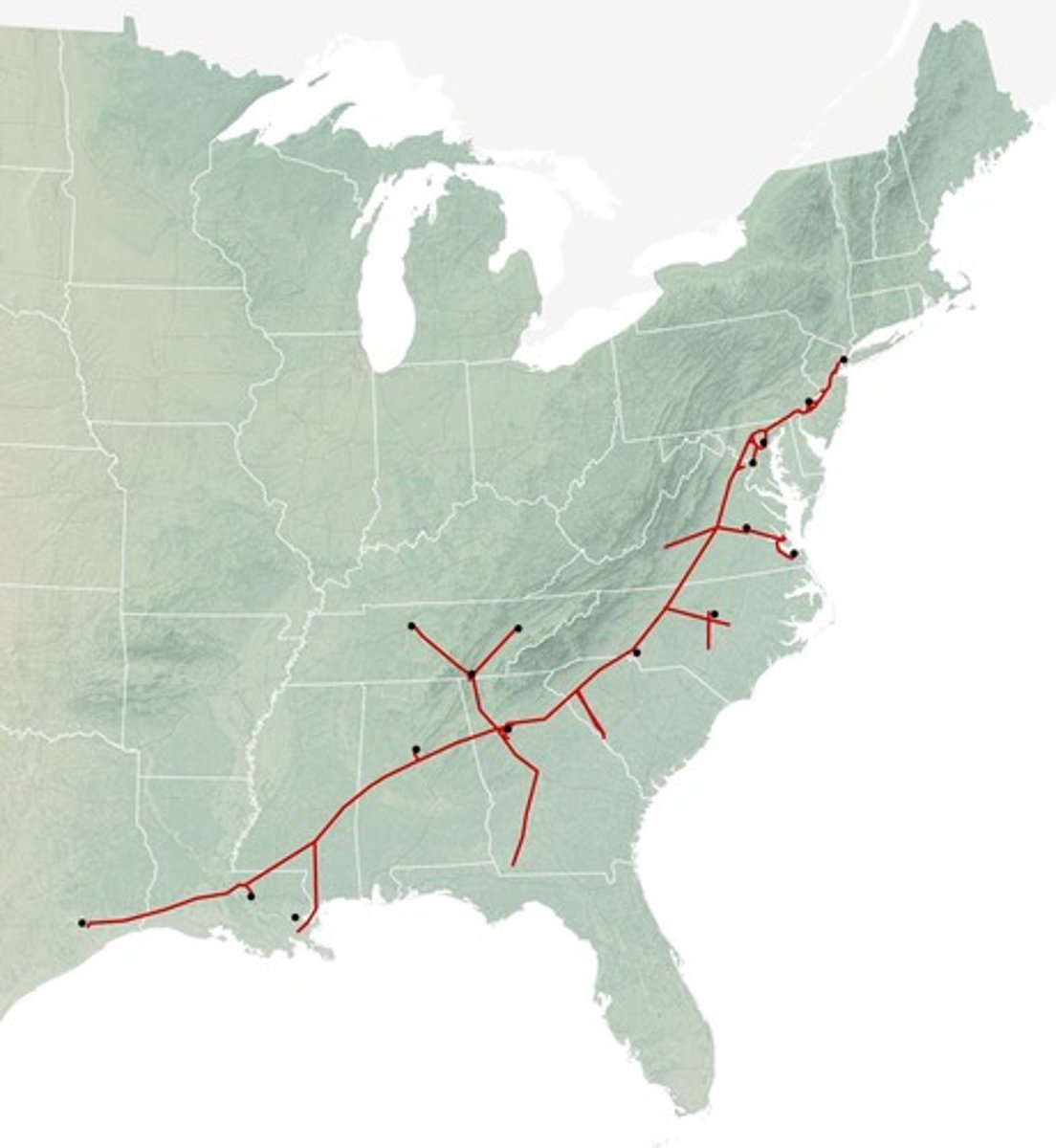
What area does Colonial Pipeline serve?
Much of the U.S. Eastern Seaboard.
What systems were affected by the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack?
Only IT systems were affected, but all of Colonial's accounting was non-functional.
What uncertainty did Colonial Pipeline face after the ransomware attack?
They were unsure if operational technology (OT) networks were breached.
How long did it take for Colonial Pipeline to restart after the attack?
The restart took until May 12, resulting in fuel outages and panic buying.
What lesson is emphasized regarding ordinary criminals in the context of cybersecurity?
Do not underestimate ordinary criminals.
What was the name of the group responsible for the attack on Colonial Pipeline?
DarkSide, based out of the Russian Federation.
What tactic did DarkSide employ in their attack?
They used a 'Big Game Hunting' tactic.
What significant action did the U.S. Federal Government take in response to the SolarWinds and Colonial Pipeline attacks?
They issued Executive Order 14028, 'Improving the Nation's Cybersecurity', focusing on software and supply chain security.
What is the primary difference between intelligence-gathering and destructive attacks according to the notes?
The difference is largely based on intent, as the tool-chain is largely equivalent.
What type of attacks did Russian Federation actors switch to after the invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022?
They switched from ransomware to almost exclusive use of wiper payloads.
What has been a trend in supply chain attacks in 2023 and 2024?
There has been a good share of supply chain attacks, including those against MOVEit managed file transfer software.
What ransomware was associated with the MOVEit attacks?
Cl0p ransomware.
What issue persists with open source packages according to the notes?
Users remain sloppy with log4j downloads of vulnerable versions, continuing from archives over two years after a critical vulnerability was discovered.
Which major software company was mentioned as a victim of a supply chain vulnerability?
Microsoft.
What was the irony mentioned regarding the JFrog Artifactory toolkit?
It is a tool for securing software supply chains but was itself a victim of a supply chain vulnerability.
What are some characteristics of the efforts originating from state actors in cyber attacks?
They bring not just competence but also patience.
What is the format in which the course material is presented?
The material is presented in units that do not biject onto term weeks exactly.
What is the focus of Unit 1 in the course overview?
Introduction to Administrative Matters and Module Overview, Critical Infrastructures and Advanced Threat Agents, and National Cyber Security Strategies.
What topics are covered in Unit 2 of the course?
Complex Attacks, Cyber Kill Chain, MITRE ATT&CK Framework, and Defences, along with Selected Campaigns.
What does Unit 3 of the course focus on?
Models of Large-Scale Networks: From Random to Scale-Free Graphs and Robustness of Networks and Cascading Failures.
What is the focus of Unit 4 in the course?
Network and Internet Robustness.
Who is the instructor for the course?
Stephen D. Wolthusen.
What are the office hours for the instructor?
Monday 1300-1400 and Wednesday 1300-1400, with appointments required.
What is the significance of the attacks on SolarWinds and Colonial Pipeline?
They motivated the U.S. Federal Government to enhance cybersecurity measures.
What does the term 'adversarial intent' refer to in the context of cybersecurity?
It refers to the motivations behind attacks, distinguishing between intelligence-gathering and destructive actions.
What was the impact of the attacks on critical infrastructure?
They highlighted vulnerabilities and prompted regulatory responses to improve cybersecurity.
What is the importance of software and supply chain security in cybersecurity?
It is crucial for protecting against vulnerabilities that can be exploited in attacks.