Rh Blood Group System
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What are the 2 linked genes that control Rh antigens?
Fischer Race
Weiner
Fischer-Race vs Weiner Genetic Theories
Fisher-Race: 3 linked loci (D/d, C/c, E/e) control Rh antigens.
Wiener: Rh antigens controlled by alleles at one gene locus.
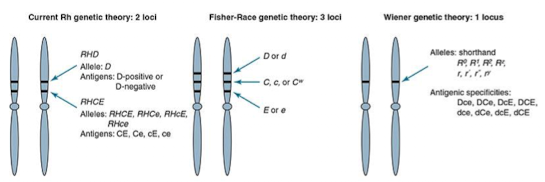
Fischer Race
Each gene expresses an antigen with the same letter
C gene → C antigen
Absence of D antigen: “d”.
Gene order: usually DCE, sometimes CDE.
Wiener
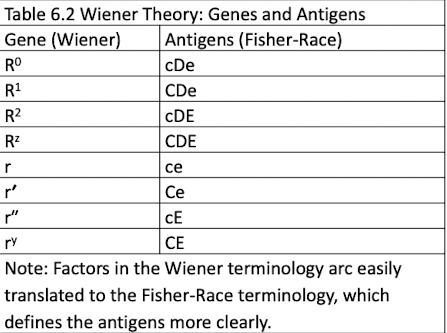
8 alleles at one Rh gene locus: R0, R1, R2 , Rz, r, r′, r″, ry
Each gene encodes an agglutinogen (factors) correlating with Rh antigens. Example 1: R1 → Rh1(Rh0, rh′ , hr″) → D, C, e
Wiener to Fisher-Race:
R = D
r = no D
1 and ′ = C
2 and ″ = E
0 = ce
Z or y = CE
Example: R2 → DcE
Significance of Rosenfield in phenotypes
Antigens designated by number:
Rh1:D
Rh2:C
Rh3:E
Rh4:c
Rh5:e
Example: D+, C+, E–, c+, e+ = Rh:1,2,–3,4,5
How does the ISBT standardize blood group nomenclature?
Six-digit numbers for each blood group specificity.
004 = Rh system.
The other numbers refer to the Rosenfield system
C antigen is RH2).
Ex: C antigen ISBT number = 004002.
Genotype vs Phenotype
Phenotype: result of RBCs reacting with antisera.
Genotype: genetic makeup, predicted by phenotype and race.
Genotype
True genotype: family studies or molecular testing.
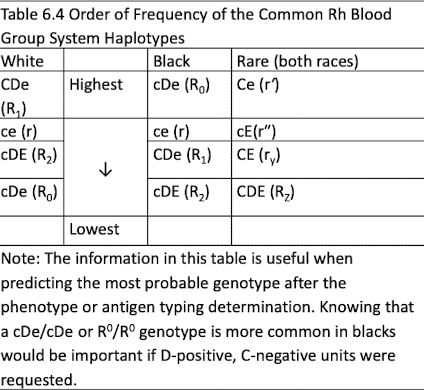
Common genotypes:
Caucasians: R1, r, R2, R0
Blacks: R0, r, R1, R2
r′, r″ , Rz , and ry are rare
Rh Genotypes and Phenotype

What are D antigens and their significance?
Most immunogenic in Rh system.
D-neg individuals get D-neg blood.
D-neg individuals may produce anti-D if given D-pos blood.
undesired effect → hemolytic reactions
Genetics of Weak D Antigens
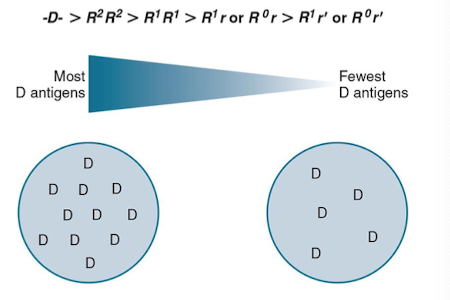
More common in black population.
Weaker form of D, often cDe haplotype.
IAT usually needed.
Patients are weak D pos, can receive D-pos blood.
IAT
used to detect antibodies in SERUM
Haplotype
A genetic combination of alleles at adjacent locations on a chromosome, often inherited together.
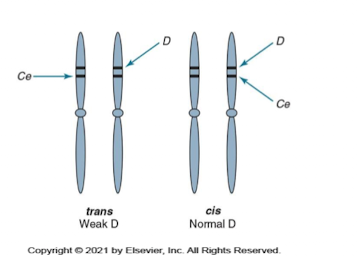
Position Effect of Weak D Antigens
D antigen appears weak when C antigen is trans to D.
Ce (r′) gene paired with Cde (R1) or cDe (R0).
Patients are weak D pos, can receive D-pos blood.
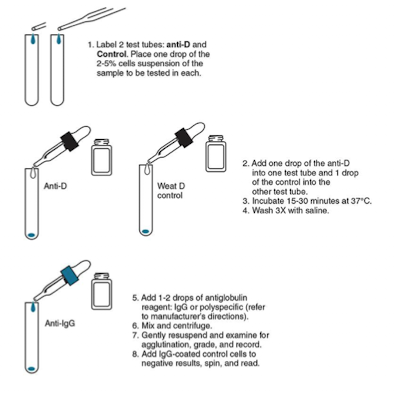
Weak D: Partial D Antigens
Individuals D pos. but missing parts of D antigen.
Exposed to “whole D antigen,” may produce anti-D to missing part.
Partial D antigen reacts strongly with monoclonal reagents.
Suspect partial D when D-positive makes anti-D not reactive with own RBCs.
Weak D Significance
AABB requires donor cells be tested for weak D if initially nonreactive.
Recipient samples don't need weak D testing
classified as D-negative, transfused with D-negative blood.
Compound Antigens
AKA cis-product antigens.
Two genes on same chromosome may form additional antigen products.
Ex: c and e antigens cause “f” to be inherited.
G Antigens
Almost all genes coding for C or D code for G antigen.
Anti-G antibody mimics anti-D and anti-C antibodies.
If neg for D/C and receive D-pos/C-pos blood, may produce anti-G (appears as anti-D or anti-C).
If anti-G present, give D-neg and C-neg blood.
Unusual Phenotypes
D-deletion
Rh-null
Rh-mod

Rh-Ab significance
Usually RBC stimulated
Most are IgG1
Agglutination best observed by IAT
Potentiators useful for identification
Antibodies to C, c, E, e react stronger to homozygous antigens (dosage)
Do not activate complement
E-neg and c-neg blood sometimes given when anti-E is identified (weak anti-c often seen with anti-E).
Clinical Considerations: Transfusion Rxns
Rh antibody levels may be undetectable for years but produce a rapid response upon exposure to the antigen
Ag-neg RBCs should be transfused if Rh antibodies are identified
Clinical Considerations: Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN)
HDFN may occur when a woman is Rh neg and the fetus/infant is Rh pos
Ab may form during the 1st pregnancy
Maternal antibody may destroy fetal RBCs in subsequent pregnancies
Rh immune globulin will protect the mother from forming anti-D antibody
LW Blood Group System
LW antigens/antibodies similar to Rh but not genetically related.
Anti-LW antibody reacts with D-positive (strong) and D-negative (weak) cells.
Alleles: Lwa , LWb , and LW
Most common phenotype: LW