Valves and Vessels
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What keeps the AV valves from opening backwards?
Chordae tendonae between the free edges of the cusps and the papillary muscles from the walls of the ventricles
How many cusps usually attach to each papillary muscle and vice versa (by chordae tendonae)
Usually 2 cusps to each papillary muscle, 2 papillary muscles to each cusp
What is the name of the left AV valve and how many cusps does it have?
Mitral/bicuspid valve, 2 cusps
What is the name of the right AV valve and how many cusps does it have?
Tricuspid, usually 3 cusps but 2 in dogs with extra little commissural cusps at the free edges
Why don’t the semilunar valves need chordae tendonae?
Their semilunar shape and the fact they’re quite small
How many cusps do the semilunar valves have?
Both have 3
What does incompetence of a valve mean and what does this lead to?
Failure to close properly
Leads to backflow of blood (regurgitation) which can lead to congestive/backwards heart failure
What is a stenotic valve and what does this lead to?
Stenotic = narrowed
Leads to increased afterload so increased workload for the heart and increased pressure in the chambers, can cause reduced cardiac output
What distance is diffusion fast under?
<1mm
How do water soluble molecules cross into the bloodstream?
Diffusion through gap junctions in the intercellular clefts
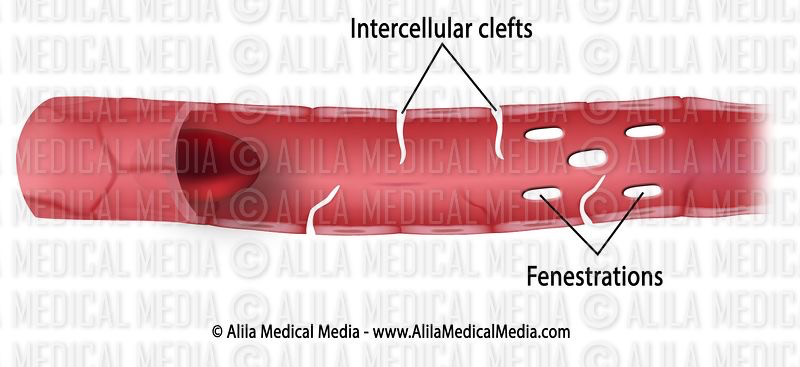
How do lipid solluble molecules cross into the bloodstream?
Can diffuse across the phospholipid bilayer
What type of junctions seal the endothelial layer in the blood-brain barrier? What type of transport is used for molecules other than sodium and water?
Tight junctions (only let water and sodium across). Facilitated diffusion is needed to transport other molecules across.
How does cross sectional area of arteries change as they branch into arterioles and then capillaries? What effect does this have in pressure and flow rate?
Cross sectional area increases, so pressure and flow rate decrease.
How is high pressure generated in arteries?
Ventricular contractions and elastic recoil of arteries.
How does the composition of arteries change as they branch (4 types)
Elastic arteries (e.g. aorta) - high proportion of elastic tissue
Muscular arteries - some elastic tissue, a lot of smooth muscle
Arterioles - some elastic tissue, thinner layer of smooth muscle
Precapillary/terminal arterioles, no elastic layer, intermittent smooth muscle (acts as precapillary sphincter zone)
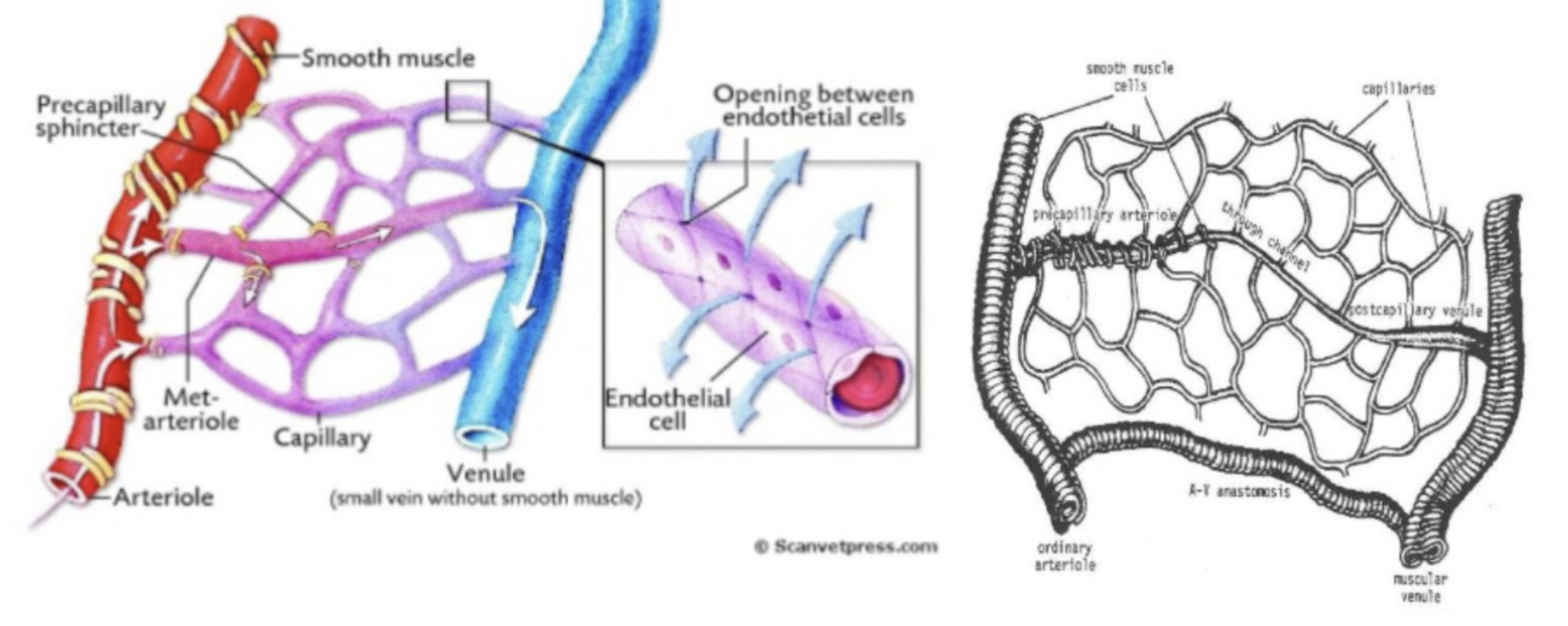
What is the purpose of the precapillary sphincter zone in precapillary/terminal arteries?
Regulates flow to capillary beds
What is collateral circulation?
When arteries give off side branches as a safety net in case of blockage
Define retia
Networks of inter-arterial anastomoses (joinings)
Define end arteries
Arteries without collateral circulation so if they are blocked there is no alternative route for blood to take, blood supply to target area is cut off (ischaemia), leading to infarction (damage) and necrosis (death) of the tissue
Describe the composition of capillary walls
Once cell thick, no smooth muscle or elastic layer
What is an arteriovenous anastomosis? How is blood flow through them controlled?
Blood vessel directly joining an artery to a vein, bypassing the capillary bed altogether.
Muscular wall acts as a sphincter.
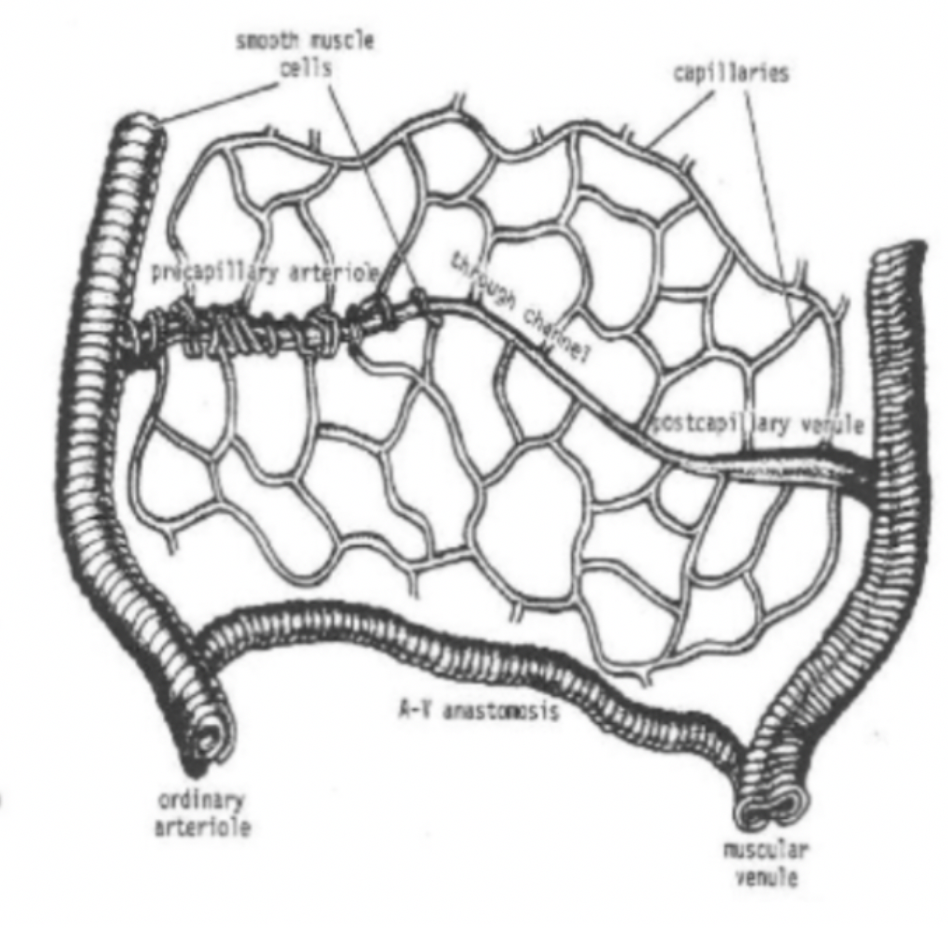
What is the name of the largest direct capillary between an arteriole and venule in a capillary bed? How is blood directed through it?
Thoroughfare channel, metarteriole or arteriovenous capillary
Precapillary sphincter zone can direct blood through them
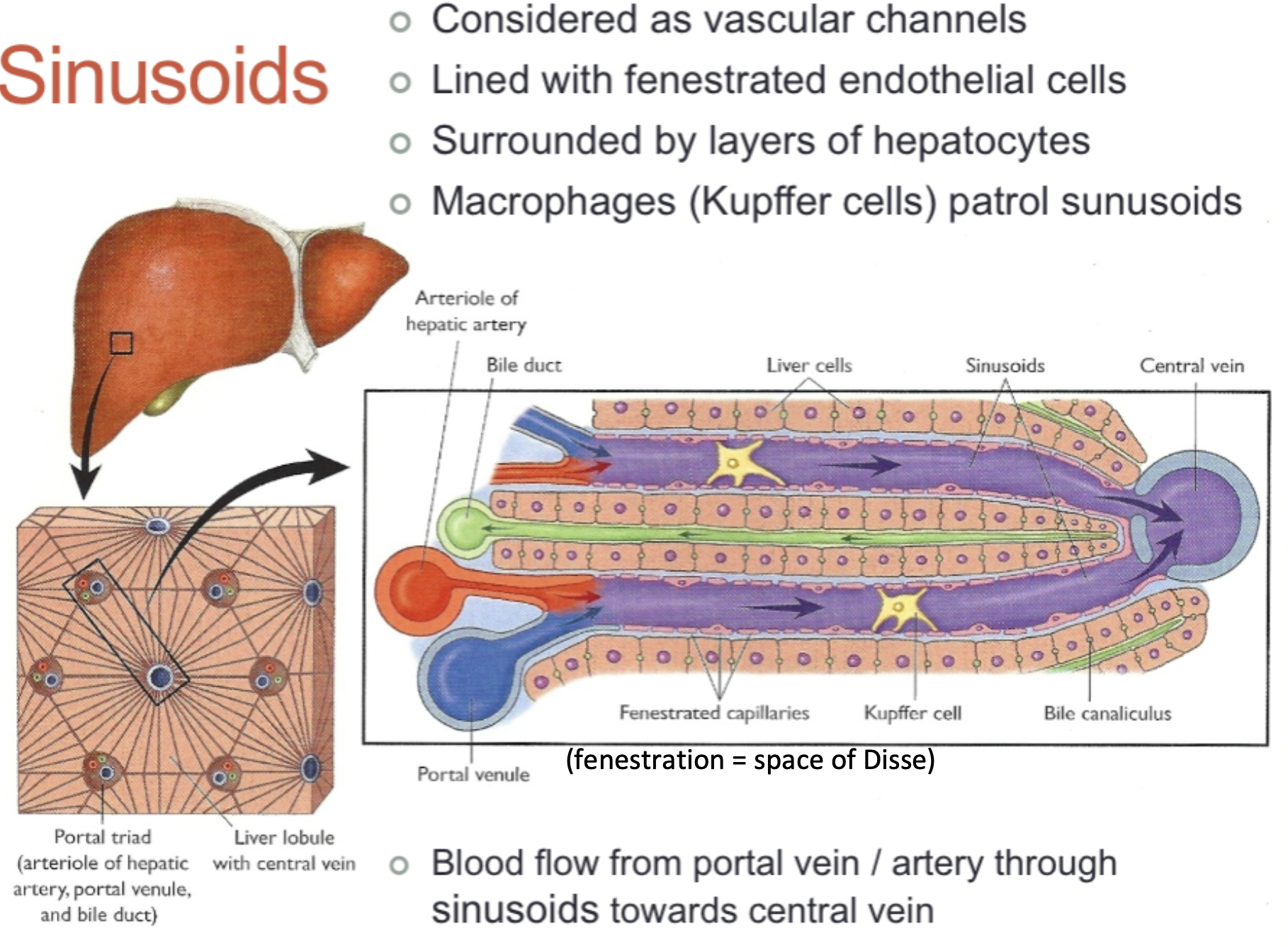
Sinusoids are modifications of capillaries (join arterial and venous circulation). Describe their structure.
Very thin walled with a relatively large diameter
Present in bone marrow and liver
Gaps between lining cells allow free communications between blood plasma and surrounding tissues
Do veins contract?
No - blood is returned passively utilising pressure from within and without the vessel
How do veins prevent backflow of blood?
Valves under gravitational pressure
Describe the composition of venules and veins
Venules - some smooth muscle
Veins - smooth muscle and some elastic fibres (thinner walled than arteries)
How do arteries act as the pressure reservoir of the circulation?
They can accommodate and store pressure generated by ventricular systole and use it to provide a continuous flow of blood throughout the cardiac cycle
How do veins act as the volume reservoir of the circulation?
They can expand and relax to deal with changes in blood volume
What are the three basic layers of blood vessels (arteries and veins)?
Tunica intima (inside) - endothelial lining
Tunica media (middle) - contains varying amounts of smooth muscle and elastic tissue
Tunica adventitia (outside) - layer of connective tissue, sometimes contains vasa vasorum
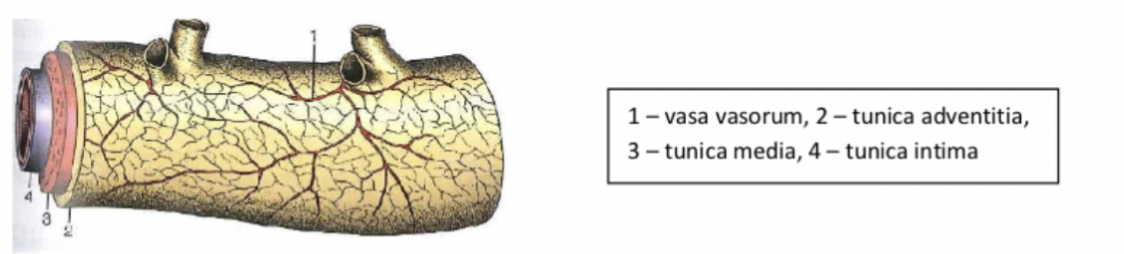
What is the vasa vasorum and which vessels does it appear in?
The blood supply of some larger arteries (because they have such thick walls) - small vessels which run in the tunica adventitia (outer connective tissue layer.
Which layers of blood vessels (tunica intima, tunica media and tunica adventitia) do capillaries have?
Just tunica intima - single endothelial cell layer which may or may not rest on a basal lamina
What is fenestration of capillaries?
Pores in the endothelial cell lining so that blood and ISF is only separated by a basal lamina (which is thicker than usual to prevent protein loss)
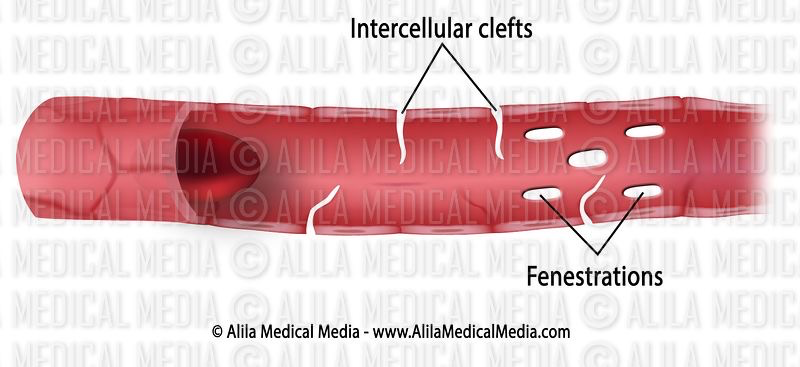
What is the purpose of fenestrated capillaries?
Allows increased transport of water soluble molecules, proteins (from liver) and new blood cells (from bone marrow)
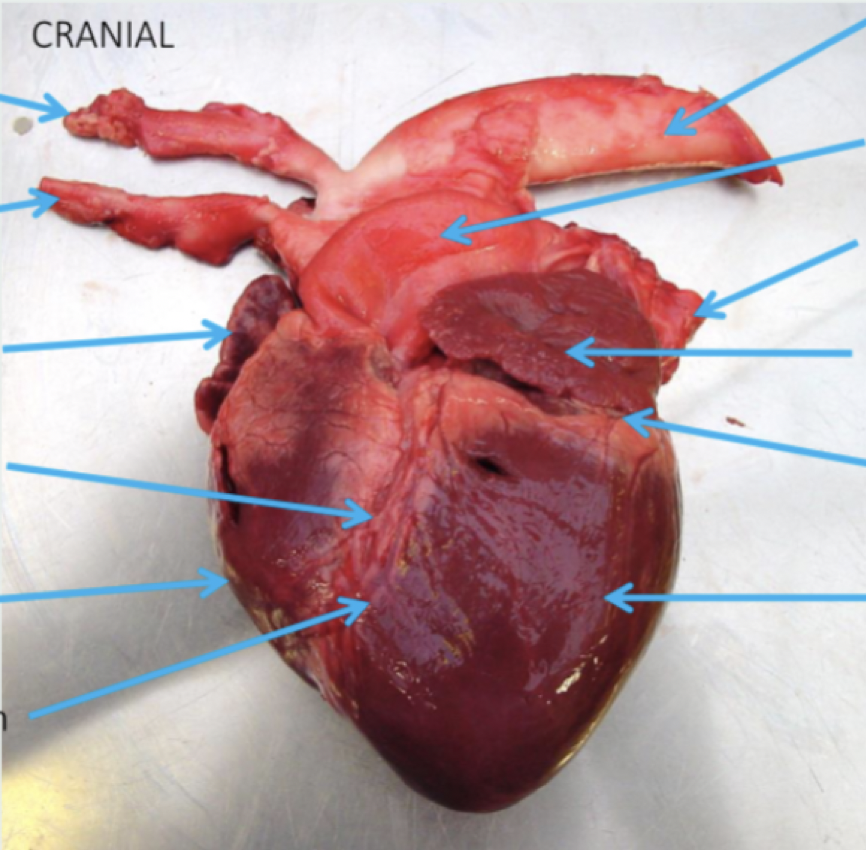
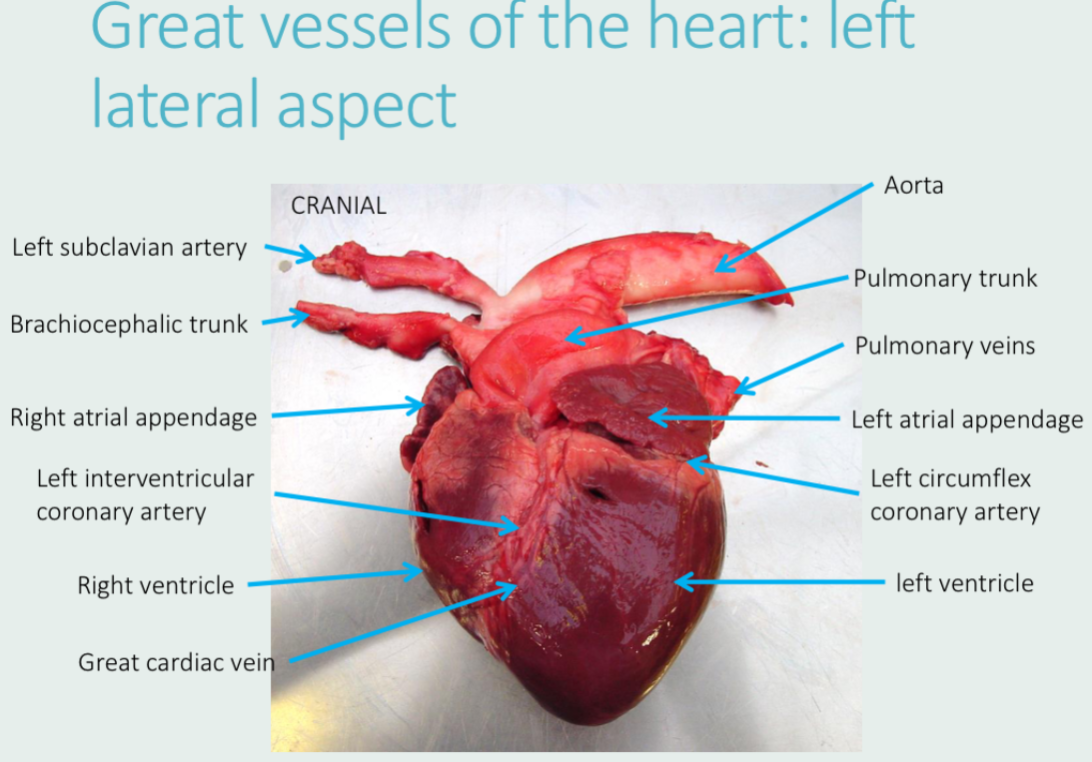
Label this with:
Left and right atrial appendages
Left and right ventricles
Aorta
Pulmonary veins
Left circumflex coronary artery
Left subclavian artery
Pulmonary trunk
Brachiocephalic trunk
Left interventricular coronary artery
Great cardiac vein
What is the name of this view?
Auricular view (from left)
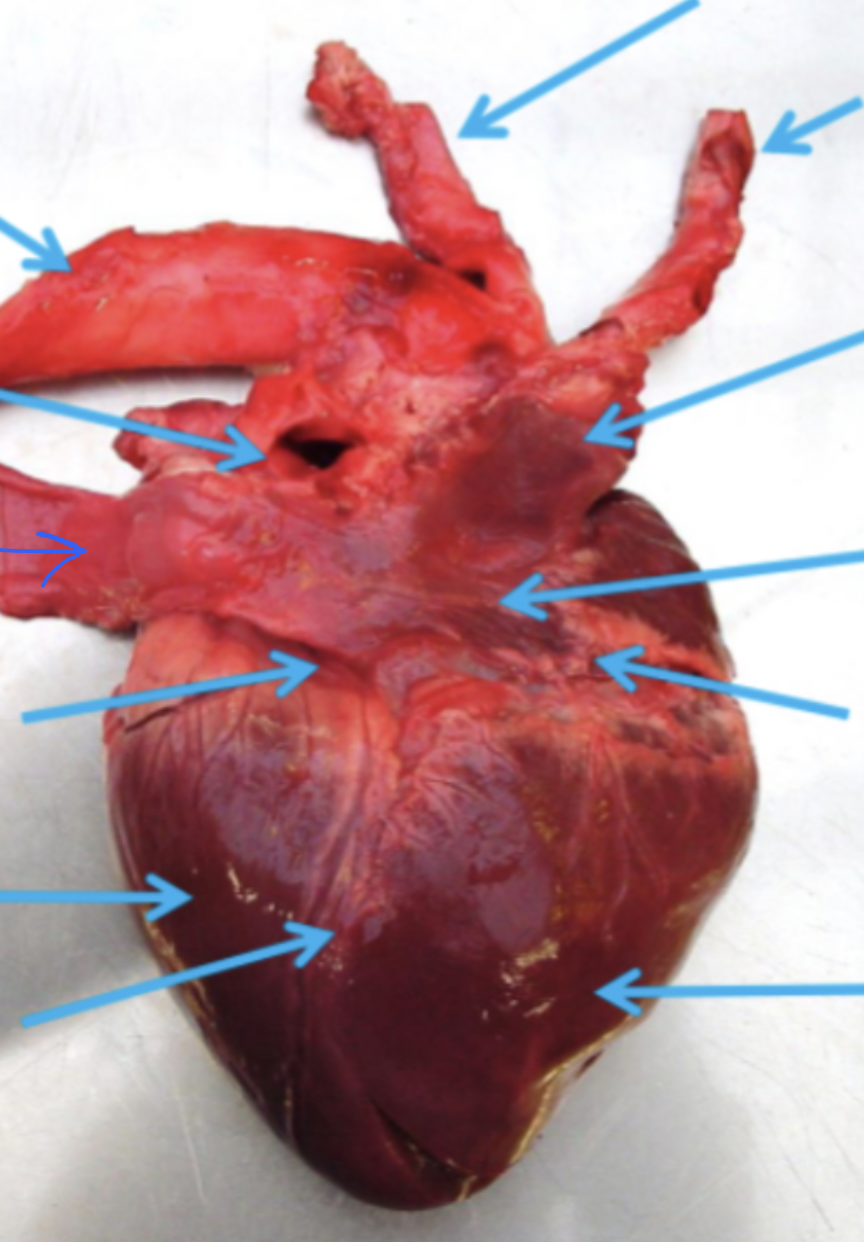
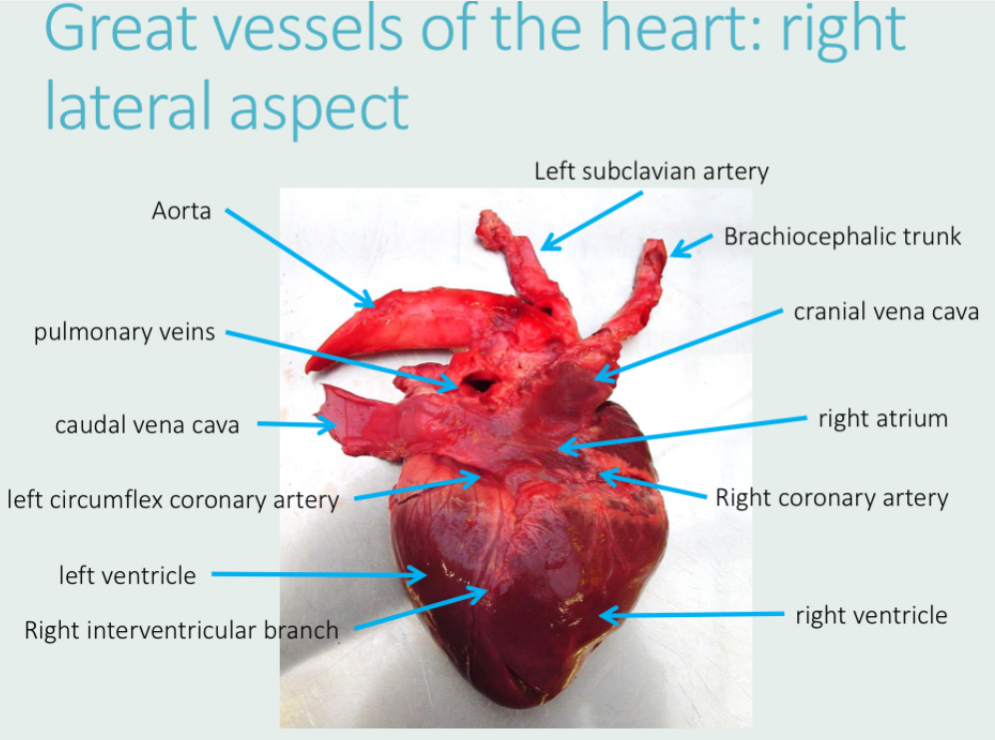
Label this with:
Right atrium
Left and right ventricles
Aorta
Pulmonary veins
Caudal and cranial venae cavae
Left circumflex coronary artery
Right coronary artery
Left subclavian artery
Brachiocephalic trunk
Right interventricular branch
What is the name of this view?
Atrial view (from right)
Whereabouts at the base of the heart does the aorta emerge?
Medially (in the middle)
When in the cardiac cycle is coronary bloodflow the highest?
During diastole as systole compresses coronary vessels and constricts blood flow
Where does the left coronary artery arise from?
Arises from the caudosinistral sinus in the aortic bulb.
Where does the right coronary artery arise from?
Arises from the cranial sinus in the aortic bulb.
Which of the left coronary artery and the right coronary artery are caudal and cranial?
Left coronary artery is on the caudal side of the heart
Right coronary artery is on the cranial side of the heart
Remember - same as ventricles
List the major. branchings of the aorta (in major domestic mammalian species)
Runs caudally from the left ventricle and immediately forms the aortic bulb after the atrial valve. The left coronary artery arises from the caudosinistral sinus and the right coronary artery arises from the cranial sinus.
More caudally, the brachiocephalic trunk branches off it. The right subclavian artery then branches off this (and sometimes the left), and then it splits in to the left and right common carotid arteries.
In the dog and the pig, the left subclavian artery branches off the aorta more caudally than the brachiocephalic trunk
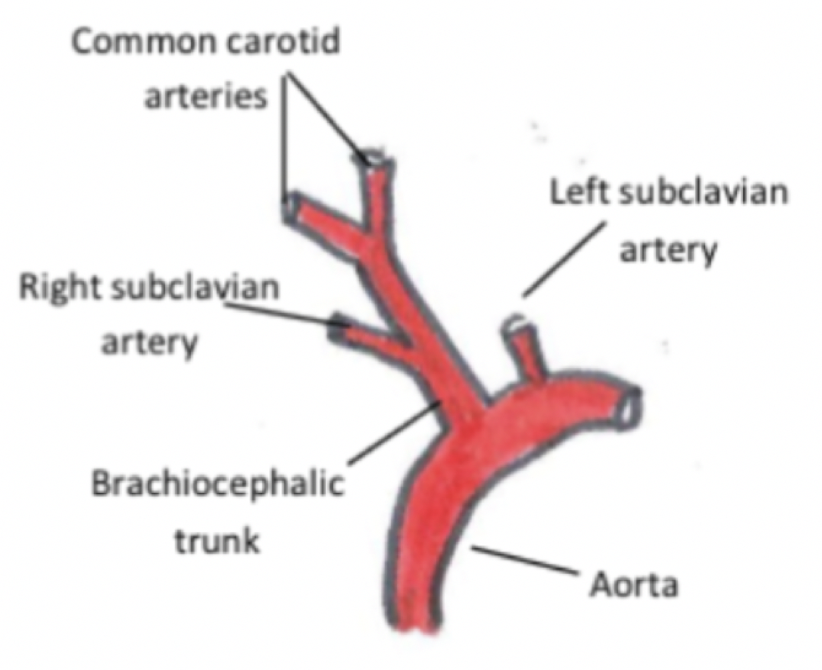
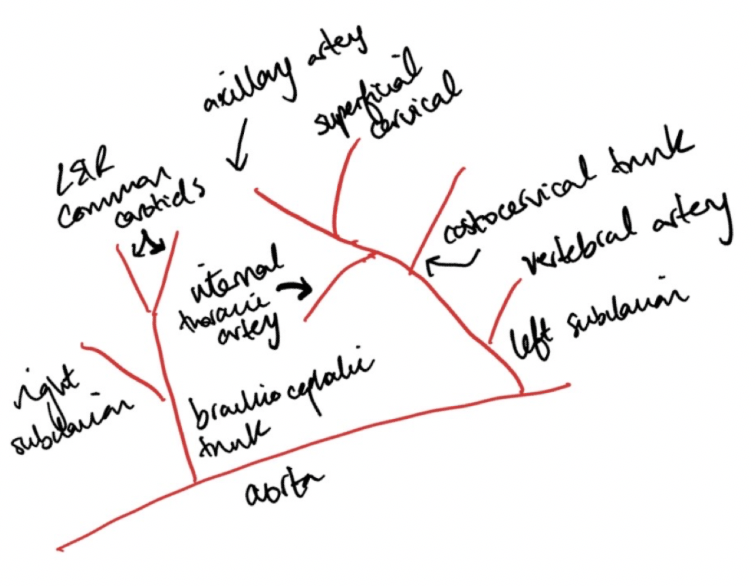
Which blood vessels branch off the left subclavian artery?
(hint: should name 5 vessels)
First is the vertebral artery (up neck to supply part of the brain)
Then the costocervical trunk (some of the neck and ribs)
Then the internal thoracic artery (ventral thorax and then through diaphragm to the abdomen)
Then the superficial cranial artery (neck)
What’s left is the axillary artery (forelimb and chest wall)
Where is the coronary sinus? Where does it receive deoxygenated blood from?
Between the left atrium and the left ventricle - not externally visible.
Receives blood from the great cardiac vein (from coronary circulation).
Also receives deoxygenated blood from the left azygous vein in ruminants and pigs (from lumbar and intercostal segments)
Where does the pulmonary vein drain into?
The left atrium
Where does the azygous vein drain blood from and which vessel does it drain into?
How is this different in pigs and ruminants?
Most species just have one azygous vein on the right hand side, which drains the lumbar and intercostal segments and drains into the cranial vena cava.
Ruminants and pigs have an additional left azygous vein which drains into the coronary sinus.