Cell Bio Final Exam
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
- Prokaryotes have no nucleus or membrane bound organelles
- Eukaryotes have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
- Both can reproduce and have ribosomes
-prokaryotes are more diverse: archaea and bacteria
Aerobic vs anaerobic cells
aerobic uses oxygen, anaerobic does not require oxygen
Golgi apparatus
stacks of membranes called cisternae
things are shipped here and packaged and shipped to parts of cell or outside cell; cis faces nucleus trans faces cell membrane
peroxisomes
break down toxic metabolities and fatty acids, producing h2o2
nucleus
covered by nuclear enevelope and has nuclear pores; stores dna in chromosomes
mitochondria
generates usable energy from food (ATP)
rough er
contains 3 types of rna: rRNA tRNA mRNA
structure of flagella and cilia
9 (outer doublet microtubules) + 2 (central singlet microtubules). dynein helps cilia and flagella move
different types of intermediate filaments
3 cytosolic: keratin (epithelial: hair,nails, most diverse), vimentin (connective tissue, muscle, glial), neurofilaments (axons of nerve cells)
1 nuclear: nuclear lamins: supports nuclear envelope of all animal cells
dynamic instability
Rapid growth and shrinkage of microtubules.
when beta (pos) subunit has GTP it has affinity for more subunits, so it grows. when gdp bound, shrinks
Kinesins vs. Dyneins
Both are MOTOR PROTEINS with 2 globular heads (ATPase) and 1 tail
KINESINS: moves thing from (-) to (+)
DYNEINS:
moves thing from (+) to (-)
Muscle contraction
Myosin moves on actin which pulls actin filaments closer. No change in length of myosin or actin BUT sarcomeres length decreases
Cohesins vs condensins
Cohesins - link sister chromatids
Condensins - help condense chromosomes in prophase
Relationship between cdks and cyclin
cyclin is required for cdk-cyclin complex to be active/functional
allow cells to progress through cell cycle
ex. phosphorylated cdc25 phosphatase dephosphorylates/activates m-cdk/cyclin complex driving entry into mitosis
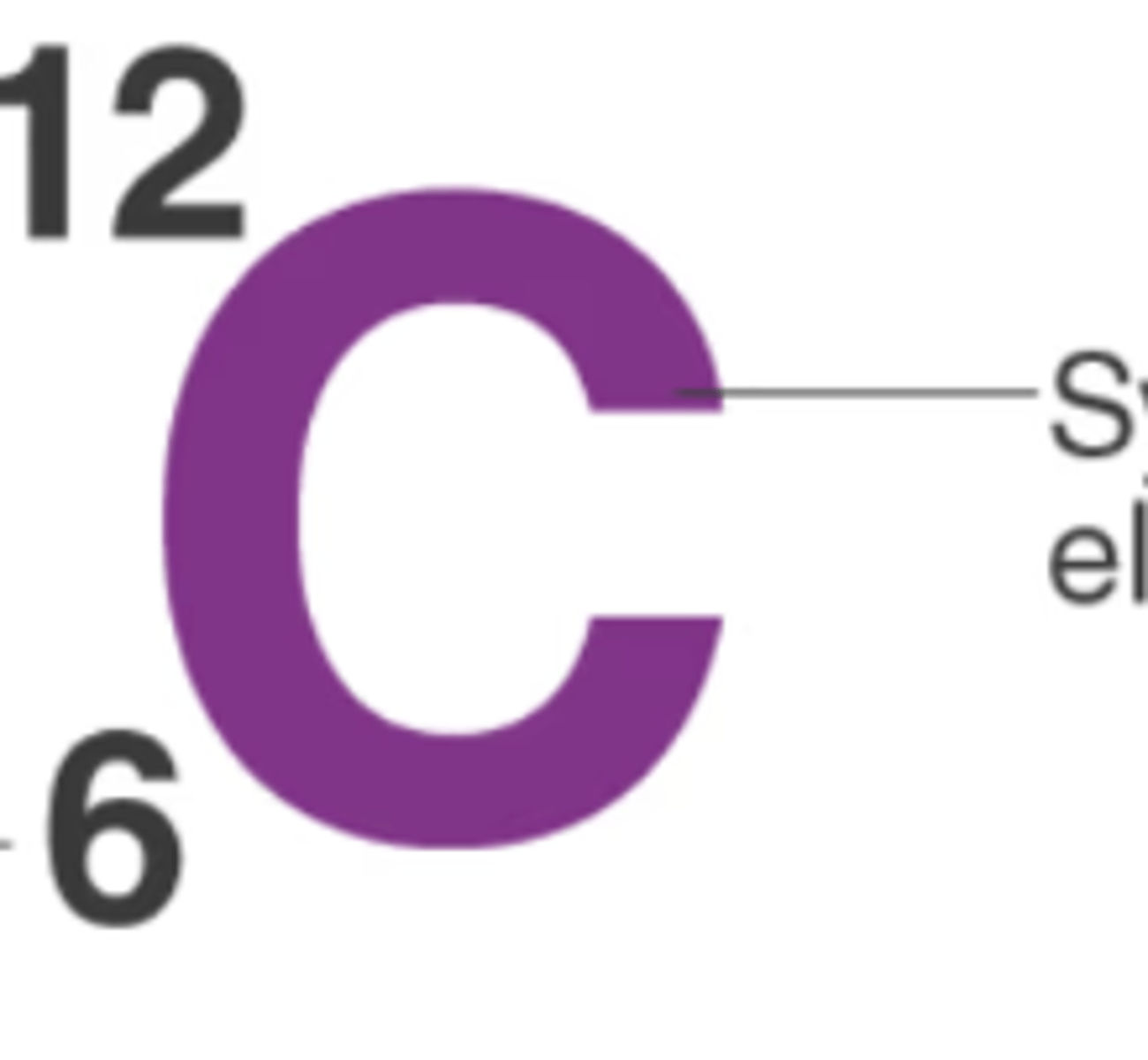
Atomic Mass vs Atomic Number
12=atomic mass (protons+neutrons); 6=atomic number (protons)
Acidic Amino Acids
aspartic acid, glutamic acid
Asp, Glu
D, E
Basic Amino acids
histidine, arginine, lysine
His, Arg, Lys
H, R, K
Noncovalent Interactions
hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces, ionic interactions, electrostatic, dipole-dipole and hydrophobic interactions
Cell respiration equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 >>>> 6H20 + 6CO2 +ATP (30)
Energetically favorable reactions
have a negative delta G; make more disorder; dissipate heat; only compare at STP
Catalysts/enzymes
speed up reactions by lowering activation energy; not consumed in reaction
myosin
with actin, helps with contraction
makes up contractile rings (with actin) for cytokinesis
attaches atp which detaches from actin. when adp and pi have been released back to normal conformation
condensation reaction
A reaction in which two molecules become covalently bonded to each other through the loss of water; also called dehydration reaction.
ex. synthesis of peptides, polysaccharides
molecular chaperones are
proteins that help other proteins fold
proteins with fibrous structure
collagen, elastin, keratin
actin, tubulin (microtubules)
Hydrolase
hydrolysis (addition of water)
Nuclease
break down nucleic acids by hydrolyzing bonds between nucleotides
Protease
enzyme that digests protein
Ligase
joining of molecules
Isomerase
catalyzes the rearrangement of bonds within a single molecule
Polymerase
catalyzes polymerization such as DNA or RNA synthesis
Kinase
adds phosphate
Phosphatase
removes phosphate
Oxidoreductase
catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions (trasnfer of e- or h+)
ATPase
hydrolyzes ATP to adp
Allosteric Binding/Inhibition
Molecule binds somewhere other than active site which changes its structure/function
Structure of Cell Membrane
Phospholipid bilayer; hydrophilic head, hydrophobic fatty acid tails.
Cholesterol decreases fluidity in membrane
Membrane proteins- transporters, ion channels, anchors, receptors, enzymes
Flippases
In Golgi membrane, cause some to go from lumen to cytosolic side. More specific (only for glycolipids, glycoproteins)
Scramblases
In ER membrane, randomly throws fatty acids from cytosolic to lumen side which allows for flip flop and makes a symmetrical bilayer
BRCA gene
Mutation in this gene increases the risk of ovarian and breast cancer
Spectrin
Cortex/fibrous protein that gives shape to an RBC plasma membrane
Transporters
require energy, such as Na+ Pump
Channels
allow ions and water to cross membrane
Pores
Porins (mitochondria and bacteria) allow small solutes in
Aquapores- allow water in
Valium
Binds GABA gated Cl- channels facilitating their opening. Inhibitory; tranquilizer
Action Potential
Starts when enough ligand gated Na+ channels. At threshold potential, Na+ voltage gated channels open (depolarization). Then Na+ VG channels close and K+ VG channels open (repolarization). Hyperpolarization if below the threshold potential
Ion gated channels
Allow ions to come in when certain neurotransmitters are bound
Inhibitory neurotransmitters
GABA and glycine (gated Cl- channels)
Excitatory neurotransmitters
acetylcholine and glutamate
Step 1 glycolysis: Glucose to
Glucose 6 phosphate; Enzyme: Hexokinase
Glucose 6 phosphate to
fructose-6-phosphate
phosphoglucose isomerase
fructose 6 phosphate to
fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
phosphofructokinase
fructose 1,6 bisphosphate to
dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
Aldose
G3P to DHAP
triose phosphate isomerase
G3P to
1, 3 bisphosphoglycerate
G3P Dehydrogenase
NAD+ to NADH
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to
3-phosphoglycerate
Phosphoglycerate Kinase
ADP to ATP
3 Phosphoglycerate to
2-phosphoglycerate
phosphoglycerate mutase
2-phosphoglcyerate to
phosphoenol pyruvate
enolase
phosphoenol pyruvate to
pyruvate
pyruvate kinase
ADP to ATP
Pyruvate to Acetyl CoA
pyruvate dehydrogenase
NAD+ to NADH
Acetyl CoA + Oxaloacetate
citrate
citrate synthase
citrate to
isocitrate
acontitase
isocitrate to
alpha-ketoglutarate
isocitrate dehydrogenase
NAD+ to NADH
alpha-ketoglutarate to
succinyl coa
a-keto dehydrogenase complex
NAD+ to NADH
succinyl coa to
succinate
succinyl coa synthetase
GDP to GTP
succinate to
fumarate
succinate dehydrogenase
FAD to FADH2
fumarate to
malate
fumerase
malate to
oxaloacetate
malate dehydrogenase
NAd+ to NADH
oxidative phosphorylation
The production of ATP using energy derived from the redox reactions of an electron transport chain. ETC + Chemiosmosis
ETC pathway/complexes
NADH Dehydrogenase complex (NADH to NAD+) --> ubiquinone --> cytochrome c reductase complex --> cytochrome c --> cytochrome c oxidase complex (2 H+ + 1/2O2 to water)
Complexes pump H+ out
Nuclear localization signal
Allows proteins made in cytosol to be sent to nucleus
Binds to receptors known as nuclear import receptors which allow proteins to go through nuclear pore unchanged
Wnt signaling is related to
colorectal cancer
Trimeric subunits of G proteins
A subunit: when GDP bound inactive, when GTP bound active and disassociates
B subunit:
Cytoskeleton is made up of
Actin, microtubules, and intermediate filaments
G1 phase
growth, inactive cdks
S phase
S-CDk initiates DNA replication and prevents rereplication
Prophase
chromosomes condense and mitotic spindle forms
prometaphase
mitotic spindle breaks down
chromosomes attach to spindle microtubules via kinetochores
metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the equator of the cell
kinetochores attach to opposite poles of cell
Anaphase
sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles
kinetochore microtubules get shorter AND spindle poles move apart
Telophase
nuclear envelope reassembles around each set of chromosomes
Cytokinesis
cytosol is divided into two by contractile ring made of actin and myosin
Function of centrioles
where spindle fibers organize, found in matrix of centrosome
Protein translocators
Binds signal sequences and allows protein to be threaded into organelle