pre-ib grade 9 science exam revision
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
this is practice especially for topics that i forgot or are complex regarding the subjects physics, space, biology and chemistry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
triboelectric series
since different materials hold onto their electrons with different strengths, the triboelectric series helps us to understand which materials would gain or lose electrons when rubbed together!

grounding
we assume that all excess electrons move from a smaller conductor to a larger conductor. electrons will move from the smaller to the larger (ground) until all excess electrons move, making it neutral
charging by induction
a charged object is brought near a neutral object; polarizing it
another larger conducting object touches the neutral object allowing the flor of electrons to a ground
after the conductor is removed, this results in a permanent change left upon the subject
conductor
materials that allow electrons to move easily
the solid matter assumption
small negatively charged particles have the ability to move. protons do not move
power formula
P = I ΔV
P = Power (W)
I = Current (A)
ΔV = Potential Difference (V)
Ohm’s Law (definition and formula)
Ohm’s law states that the potential difference of a circuit is proportional to the current running through it provided that the physical properties of the conductor stay constant
V = IR
V = Potential Difference (V)
I = Current (A)
Resistance = Resistance (Ω)
potential difference (definition)
related to the amount of energy per charge required to move a positive test charge between two points
change in electric energy (formula)
Δe = qΔv
Δe = change in electric energy (J)
q = charge (C)
Δv = potential difference (V)
equivalent resistance (definition and formulas)
the measure of how much resistance is provided by all the resistors calculated by taking the voltage across the battery and dividing it by the current that goes through the battery
resistance = V/I
in a series connection: R[total] = R1 + R2 + R3…
in a parallel connection: R[total] = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3…
energuide and energy star
energuide is a label found on househould appliance in markham stating the amount of energy the product uses in one year of normal use
energy stars are given to any household appliance that uses 10-50% less energy compared to the standard product
power (definition and formula)
how much energy is provided or released by a component in a circuit
P = IΔV
P = power (W)
I = current (A)
V = potential difference (V)
to turn into kW /100
absorption spectrum
when light is shined on atoms, specific colours of light will excite the atoms and become absorbed. these colours disappear from the full spectrum and appear as black lines. atoms absorb and emit the same colours of light
stellar composition
the main elements in most stars are hydrogen and a bit of helium since their particle collisions are so strong that they bump right off the nuclei
stellar equilibrium
in order for a star to maintain stellar equilibrium, it must have a balance of the inward pull of gravity and outwards pressure caused by particle collision. for this to happen, stars must have a steady supply of thermal energy to replace the energy it loses from space
nuclear fusion
in the core of the star, very great pressure occurs. the nuclei of atoms are pushed so close to one another that they forge one large nucleus which produces a tremendous amount of energy
photons/electron shift
when an electron moves from a higher energy level to a lower energy level, it releases energy in the form of a photon. the energy of a photon is equal to the difference of energy between the two levels
ionization
the process by which electrically neutral atoms/molecules are converted to electrically charged atoms/molecules through gaining or losing electrons
the harvard classification scheme
the colour of stars determines its temperature range. scientists use a spectrogram to analyze the spectrum of a star using the harvard classification scheme. this categorizes stars by letter depending on their colour.
O : blue - > 25 000ºK
B: blue/white — 11 000-25 000ºK
A: white — 7500-11 000ºK
F: white — 6000-7500ºK
G: yellow — 5000-6000ºK
K: orange — 3500-5000ºK
M: red — <3500ºK
the expansion of the universe
space itself is stretching outwards, carrying distant galaxies apart from one another. therefore, the universe is always expanding in size and galaxies are becoming further apart
the big bang theory
the big bang theory hypothesizes that the universe started at a tiny point and then expanded rapidly in a massive explosion approximately 14 billion years ago
unusual characteristics of stars and what they indicate
lines narrower - giant stars
lines shifted - red (or blue) shift
inverted colours - nebula (emission spectrum)
colours brighten/dim - star is expanding and contracting
lines move randomly - star is in orbit of another star
lines move similarly - star is orbiting a large planet
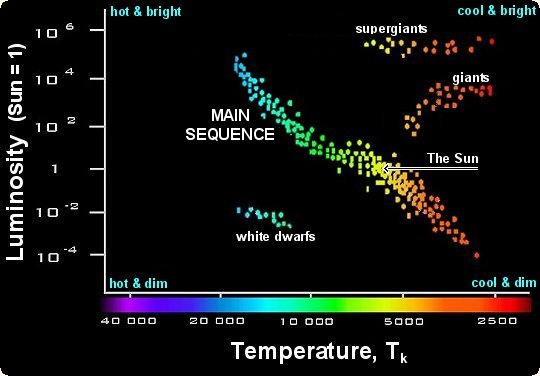
HR diagram (hertz-russel diagrams)
uses star characteristics such as mass, colour, temperature, and luminosity and sees relationships between the differences
main sequence stars: range in temperature/luminosity/size; stretch diagonally across an HR diagram
red supergiants: have low temp, but high luminosity; located top right corner of diagram
red giants: located upper right: smaller mass, low lumonisty
white dwarfs: hot, dense, small, faint; lower left corner
bohr-rutherford’s gold foil experiment
ernest rutherford conducted the gold foil experiment where he shot positvely charged aplpha particles through a thin piece of foil. most particles passed straigth through while others went in different directions. this proved that:
atoms contain a small positvely charged nucleus; which repels positve charges
particles are mostly empty space
isotopes
isotopes are elements with the same number of protons/electrons but different number of neutrons. two ways of identifying an isotope is through
their mass number
their atomic notation
characteristics of transition metals
hard, strong, and lustrous with high melting and boiling points. transition metals make good conductors
electric shielding
when inner electrons of an atom reduce attraction between nucleus and other electrons
the more inner electrons an atom has, the larger its size, the more electron shielding
since there is less shielding, atoms with less shells will be more reactive since they have more attractive energy from the nucleus
molecule
two or more atoms connected by chemical bonds that are the same or different
particle
a small object that can have different properties (e.g. mass, volume, density)
evidence of a chemical change
COBLSS
change of colour
a change of odour
bubbles are seen (without heating)
a change of light, temperature or sound
a solid is seen
properties of ionic compounds
crystals
high melting/boiling points
solid/hard
brittle
usually soluble
electrolyte/conductive
properties of covalent compounds
solid/liquid/gas
lower melting/boiling points
non-electrolyte — not conductive
non-soluble
flammable
algae growth throughout the year
photosynthesis - algae uses this process to convert CO2. this allows algae to produce their own food. generally, photosynthesis is higher in the spring/summer
cellular respiration - allows algae to use the energy it stored. generally occurs more during the winter where oxygen is more available
decomp - decomposers like fungi and bacteria is most common in autumn with right temperature, moisture and availability to oxygen