Medicine (Erin)
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Hippocrates
Galen developed idea of
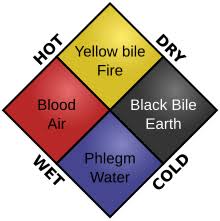
Theory of Opposites
Reasons for little progress in medieval times
Nature of work (90% of people worked on farms, children expected to help out from early age), Church controlled education, people told not to challenge old ideas
Where did Hip and Galen think miasma came from? And how to prevent?
swamps, corpses, rotting matter.
Sweet smelling herbs/flowers, lighting fires, ringing bells,
Medieval methods of purifying air (m)
sweet-smelling herbs and flowers, lighting fires, ringing bells, allowing birds to fly through house
Religious actions to protect self from illness (m)
pilgrimage, attending Church, living life free from sin, self-flagellation
Treatment methods in medieval time (give specific facts about each one)
praying for forgiveness (especially in hospitals), bloodletting and purging (cupping, leeches, laxatives), herbal remedies (50% worked, theriaca - contained up to 70+ herbs and was used as poison antidote)
Physicians training period (m)
7-10 years
Doctor’s diagnosis techniques (m)
looking at urine samples, symptoms, faeces
How many hospitals were there in the country by 1500?
1100
How many hospitals were in monasteries? (m)
30%
How many hospitals actually treated the sick? (m)
10%
Public health solutions middle ages
Exeter brought in aquaducts to improve cleanliness of water, regulations were introduced for cesspits to maintain standards, public latrines were built in Norwich
Black Death years
1348-49
Believed causes of the Black Death
Punishment from God (most prominent), astrology (in 1345 there had been an unusual alignment of Saturn, Jupiter and Mars), miasma from earthquakes and volcanoes
Religious attempts at prevention for Black Death
self-flagellation, praying for help, activities that might anger God were banned (e.g., in Suffolk, wrestling matches in church courtyards were stopped)
Herbal remedies for Black Death
theriaca was prescribed, strong herbs like myrrh were used as they were believed to have cleansing properties, apothecaries starting selling Black Death treatments
Treatment of buboes during Black Death
They were burst and/or had shaved chicken bottoms applied
Continuity in causes in Renaissance
Four Humours still used by physicians, miasma (cemented by Fracastoro’s “seeds”)
How did Thomas Sydenham group illness?
Grouped illnesses based on symptoms, observations and progression of illness
Thomas Sydenham’s new ideas
Was Humanist, relied on his own observations as opposed to textbooks, believed different diseases should be treated in different ways (e.g. iron to treat anemia)
Sydenham’s book
“Observations Medicae”, 1676
When did the printing press come to England?
1476
When was the Royal Society founded?
1660
What language did the Royal Society encourage their scientists to write in and what else did they fund?
English, not Latin - plus they funded the translation of texts
How were hospitals in Renaissance times different to the Middle Ages?
Were now secular, focused more on treating the sick, were secular due to dissolution of the monasteries, centered around care by physicians
Changes in prevention and treatment in Renaissance
More of a focus on cleaning streets to get rid of miasma, new herbal remedies (e.g. tobacco), transference, alchemy
Vesalius’ new ideas about dissection
Carried out lots of human dissections to learn, believed dissections should be performed in public and done by lecturers and doctors, wanted students to see dissections close up
Vesalius’ book and details about it
Fabric of the Human Body, 1543, dedicated to Charles V, illustrations down by renowned artist Titan, published after extensive dissection
Discoveries that Vesalius made to disprove Galen
the lower jaw is one bone not two, the heart has no holes in its septum
How did Harvey discover the system of blood circulation?
Researched Galen’s idea that blood flowed towards the heart , proved blood couldn’t be produced by the liver (disproving Galen), believed that the heart behaved like the new mechanical water pumps, discovered the arteries and veins were part of one big system
Harvey’s books + when
“An Anatomical Study of the Motion of the Heart and of the Blood in Animals”, 1628. Included detailed diagrams.
Year of the Great Plague
1665
What % of London’s population was killed by the Great Plague?
15%
What % of England was killed by the Black Death?
40%
Government action to prevent spread of GP
They created mandatory “plague orders” - theatres were closed, large gatherings were banned, barrels of tar were burnt, days of fasting and public prayer were ordered, dogs and cats were killed
Methods of warding off miasma in Great Plague
posies, strong-smelling herbs over doorways
Change in causes of illness in Industrial period
Spontaneous generation (animacules/seeds in the air were produced when something decayed, which created miasma), germ theory
Reasons for new ideas on causes of illness in Industrial period
Improved microscopes, changing attitudes
When did Louis Pasteur publish “Germ Theory”?
1861
Which diseases did Pasteur develop vaccines for?
Chicken cholera and rabies
What was the first disease that Koch identified the bacteria for?
Anthrax
What dye did Koch develop and what was it used for?
Methyl violet dye, used to identify smaller pathogens
How many different bacteria had been identified using Koch’s techniques by 1900?
21
By what proportion was Nightingale able to reduce death rates at Constantinople?
2/3
What changes did Nightingale make to Constantinople?
Emphasised hygiene and fresh air, set up a laundry service and a library, made sure nurses had good training and supplies
What substances were used as anaesthetics before 1800?
Alcohol and opium
When was chloroform first used and who by?
1847 by James Simpson
What were the pros (2) and cons (1) of chloroform?
Was highly successful with little side effects, given to Queen Victoria during childbirth, was tricky to get the right dosage so many patients were killed (e.g. one girl died due to too much chloroform during an operation on an ingrown toenail)
When did Lister first use carbolic acid and what did he do with it?
1865, soaked bandages with it to prevent post-op infection
What did Lister do with carbolic acid after his initial success? (2)
used it to sterlise equipment and wounds, created a spray to kill germs
Support for anaesthetics in Industrial (3)
allowed pain-free procedures, allowed surgeons to attempt more complex surgeries, increased success rate
When was the first public health act passed?
1848
When was the second public health act passed?
1875
What were 2 things set out in the 1848 Public Health Act?
A National Board of Health was set up, councils were encouraged to provide sewers and clean water
What were 3 things set out in the 1875 Public Health Act?
Councils were required to improve sewers and waste disposal, provide clean water for their area and appoint their own medical officer who would inspect public health facilities
Who brought inoculation to England and where from?
Lady Wortley Montague, brought it from Turkey
When were vaccinations made free for the poor? (I)
1840
When were vaccines made compulsory? (I)
1853
Why was their opposition to Jenner’s work? (3)
He couldn’t prove why it worked, people believed it went against God’s will, it would put inoculators out of business
When did Snow publish his ideas?
1855
Which was the pump that Snow focussed his work around?
Broad Street pump
When were electron microscopes created?
1931
When was the human genome project launched?
1990
Who created the first magic bullet and when?
Paul Ehrlich in 1909
Who created the second magic bullet and when?
Domagk in 1932
When was the NHS founded?
1948
What report prompted the founding of the NHS
Beveridge Report
When the NHS was established, how much did life expectancy increase by?
15 years
When was the National Insurance Act implemented and what did it involve?
1911, employers, the government and workers would pay into it and that would cover medical costs for workers but not their families
When was the Ministry of Health set up and what did it do?
1919, oversaw treatment in the country but didn’t lower costs
When did Fleming first discover the powers of penicillium mould?
1928
What animal did Florey and Chain first test penicillin on?
Mice
In what year did small-scale production of penicillin start in the USA? (Hint: during WWII)
1941
What event provoked the mass production of penicillin in the USA?
Their entry into the war in December ‘41
How many companies were given funding to mass-produce penicillin?
21
What kind of scan are potential lung cancer sufferers first offered?
CT scan
What were the symptoms of trench fever?
Persistent episodes of flu-like symptoms for months
What caused trench fever and how did they overcome this?
Lice, in 1918 troops were deloused
Describe the development of trench foot
Soldiers’ feet would become numb and swollen from standing in the waterlogged trenches, gangrene may develop, treated with amputation
Name 2 trench improvements to reduce trench foot
Pumps were used to drain the trenches, duckboards were added to keep soldiers’ feet above the water
What were the 4 main issues with bullet and shrapnel injuries?
They could penetrate organs, they could lodge themselves in bones, they could cause large amounts of blood loss, it was tricky to safely remove lodged bullets or shrapnel
Name 2 symptoms of gangrene
Flesh dies due to lack of blood circulation, flesh turns black
Name 3 symptoms of gas gangrene
Flesh would make hissing noise, gas produced in wounds, wound would turn white to green
Name 3 features of the Arras hospital
It had 700 beds, it had an operating theatre, it had running water and electricity
Name an ambulance convoy FANY drove and how many vehicles there were
Calais ambulance convoy, 22 vehicles
When did the first FANYs arrive in France? (month + year)
October 1914
How far away were the Regimental Aid Posts from the front line?
200m
How far back were the Field Ambulances from the front line?
600m or more
Who were stationed at Field Ambulances?
Stretcher-bearers, medical officers, orderlies and (from 1915) nurses
What wounds were prioritised in terms of treatment at CCS?
Life-threatening ones for those with a chance of survival
What did CCS tend to be close to? (think transport)
Canals, roads, railway lines
What kind of features did base hospitals have? (think treatment)
Operating theatres, X-ray departments
Who discovered the power of X-rays and when?
Roentgen, 1895
What did the Carrel-Dakin method involve?
Passing sterilised salt solution through a wound using tubing
What was the death rate from broken leg/limbs before and after the Thomas Splint’s invention in 1915?
80% to 20%H
How did the Thomas Splint work?
It kept the leg rigid, reducing blood loss
Who headed plastic surgery developments during WWI and where was he based?
Harold Gillies in Queen’s Hospital