A&P Chapter 4 - TISSUES
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Histology Tissues
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Simple Squamous Epithelium
structure: single layer of flat cells (fried eggs)
function: protection against friction, diffusion, and filtration
location: lining serous membranes in body cavities, lining blood vessels and heart
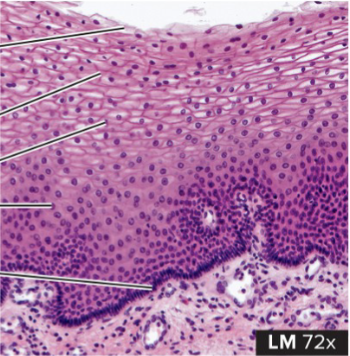
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
structure: several layers of cells that are progressively flat (lots of fried eggs)
function: barrier against infection, reduces water loss from the body
location: outer layer of skin, mouth down through to the esophagus
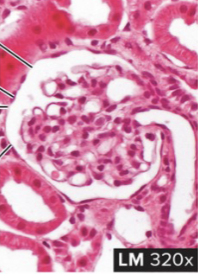
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
structure: single layer of rounded cube-shaped cells (like tadpole eggs)
function: secretion by the glands and kidney tubules, movement of particles out of the lungs
location: kidney tubules, glands/ducts, lining of lung bronchioles
Transitional Epithelium
structure: several layers of stratified that appear mostly cuboidal (like polka dots)
function: accommodates fluctuations of fluid volume in an organ or tube
location: lining of bladder, urethra/ureters
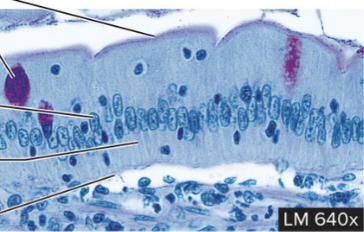
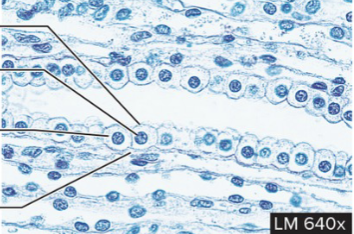
Simple Columnar Epithelium
structure: single layer of tall and narrow cells, contain microvilli (like river)
function: secretion by stomach and absorption by intestines
location: stomach, intestines, gallbladder
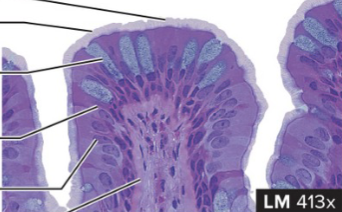
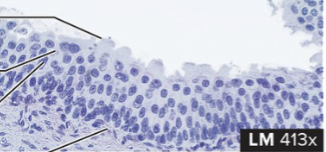
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
structure: single layer of tall and thin cells that can reach the free surface. nuclei of these cells appear at different levels and stratified (like coral reefs)
function: create and secrete mucus onto free surface and remove foreign particles from respiratory passages
location: lining of nasal sinuses, trachea, and bronchioles of lungs
functions of epithelial tissues?
act as a barrier and protect underlying tissues
secrete and absorb substances
permit passage of substances
functions of connective tissues?
support and movement
connect tissues to one another (tendons and ligaments)
enclose organs and separate layers
three types of cells in connective tissues and their function
blasts: build the matrix
cytes: maintain the matrix
clasts: breakdown matrix for remodeling
components of extracellular matrix
ground substance
protein fibers
fluid
protein fibers of the extracellular matrix
collagen
like a rope
strong and inelastic
reticular
fill spaces between tissues and organs
form branching networks
elastic
returns to original shape after stretching and decompression
resemble coiled springs
components of ground substance of extracellular matrix?
hyaluronic acid
proteoglycans
adhesive molecules
what are the connective tissue propers?
loose: fewer fibers, more ground substance
areolar, adipose, reticular
dense: more fibers, less ground substance
dense regular and irregular
what are the supporting tissues?
cartilage: semisolid
hyaline, fibrocartilage, elastic
bone: solid, spongy and compact
what are the two fluid tissues?
blood
hematopoietic (red and yellow bone marrow)
functions of connective tissue proper
packing material of the body
cushions cells
stabilizes organs
support epithelium
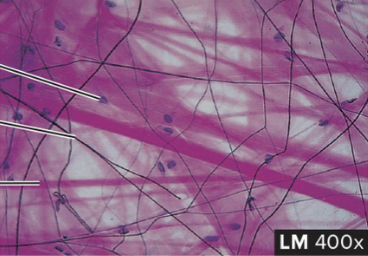
Areolar Connective Tissue
structure: fine network of fibers (collagen) with spaces in between (like threads of yarn or string)
function: loose packing and support
location: packing between glands, muscles, and nerves. attaches skin to underlying tissues
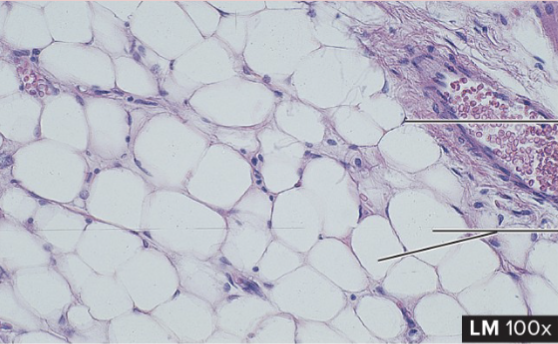
Adipose Connective Tissue
structure: little extracellular matrix surrounding cells, large size (like rocks/pebbles)
function: energy storage, insulation, packing material
location: subcutaneous (skin) areas, mammary glands
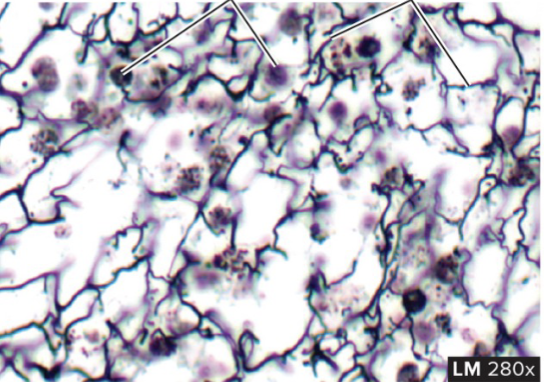
Reticular Connective Tissue
structure: fine network of irregular arrangement of fibers (like veins in the eyes)
function: provides structure for lymph nodes and hematopoietic bone marrow
location: lymph nodes, bone marrow, spleen
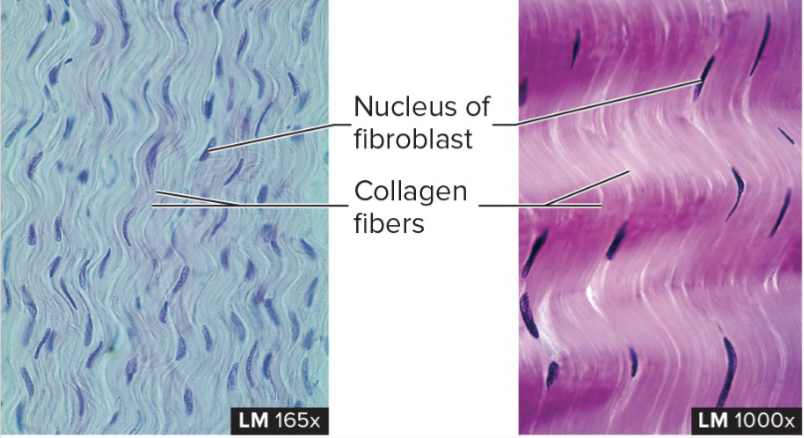
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
structure: composed of collagen fibers running in almost same directions (like waves)
function: withstanding pulling forces and stretch resistance
location: tendons (attached to bone) and ligaments (attach bones to each other)
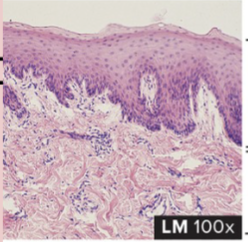
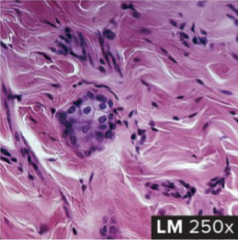
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
structure: composed of collagen fibers running in different directions (like storm eye of Jupiter)
function: strength capable of withstanding stretching in all directions
location: dermis of the skin, outer covering of body tubes, sheaths
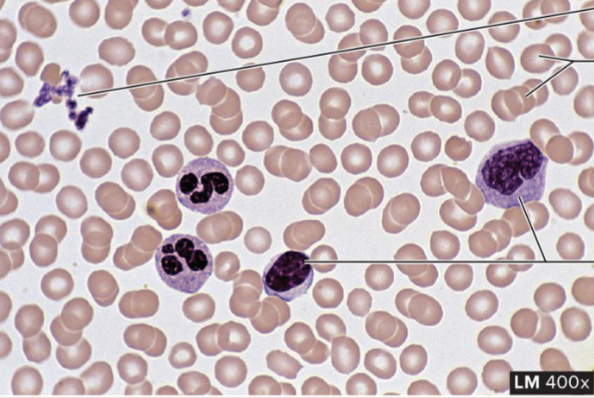
Blood Fluid Connective Tissue
structure: formed red/white cells and platelets/clotting (like frisbee discs)
function: transport O2 and CO2, protect the body against infections
location: within blood vessels
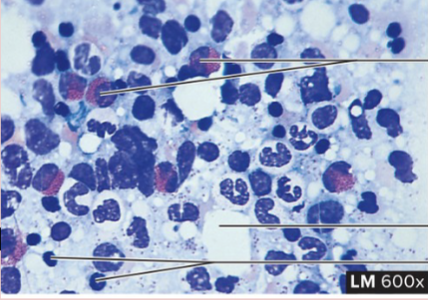
Hematopoietic Fluid Connective Tissue
structure: numerous blood-forming cells, red marrow
function: produces new blood cells, red marrow. stores lipids, yellow marrow
location: within marrow cavities of mostly long bones
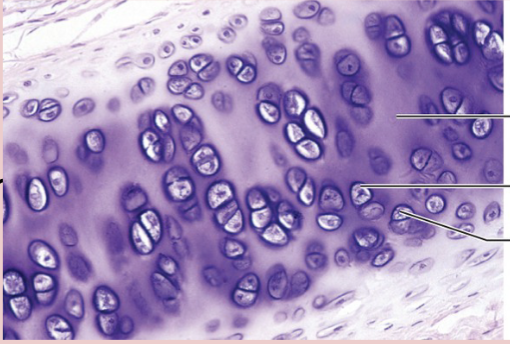
Hyaline Cartilage Supportive Tissue
structure: matrix appears transparent, chondrocytes are found throughout (like swiss cheese)
function: forms smoother cushion surfaces between joints, growth of long bones
location: surface of bones, rings of respiratory system, long bones
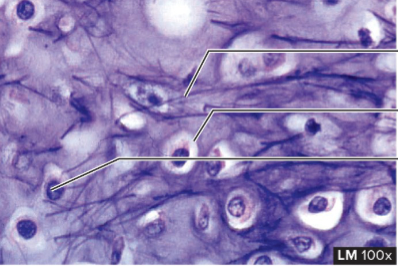
Elastic Cartilage Supporting Tissue
structure: matrix contains elastic fibers, also somewhat transparent (like eyeballs)
function: provides rigidity with flexibility because elastic fibers can return to their original shape after stretching
location: external ears, auditory tubes, epiglottis
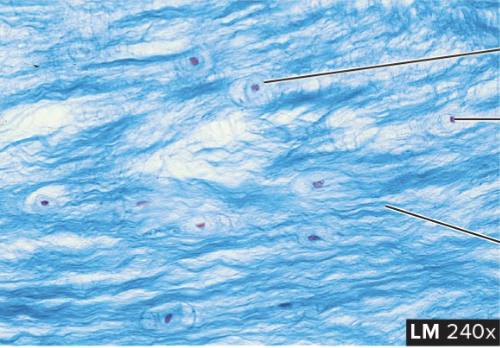
Fibrocartilage Supportive Tissue
structure: higher numbers of fibers and are arranged in thicker bundles (like hairs on a head)
function: capable of withstanding pressure, connects structures that can withhold pressure (spine)
location: intervertebral discs, knee and jaw joints
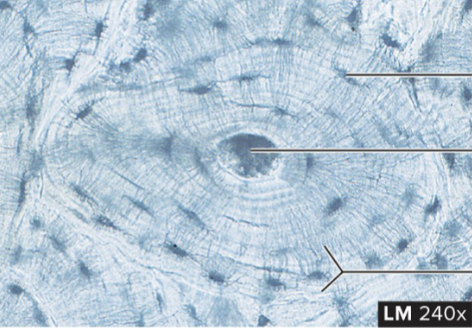
Compact Bone Supportive Tissue
structure: hard matrix, lacunae distributed in a circular fashion around a central point (like tree stump)
function: provide strength and support, forms solid shell that keeps bones from easily breaking or puncturing
location: outer portions of bones, shafts of long bones
functions of muscle tissue
contracts and shortens with force
moves the body and helps to pump blood
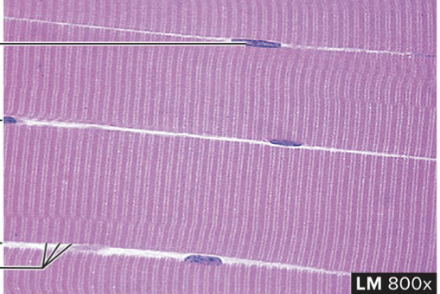
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
structure: fibers that appear striated and banded, cells are large/long and cylindrical, multiple nucleus’
function: movement of the body under voluntary control
location: attached to bone or other connective tissue
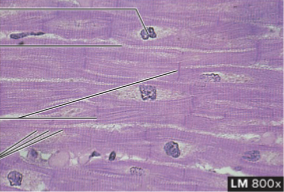
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
structure: cylindrical and striation with only single nucleus, branched and connected to each other by intercalated disks with gap junctions
function: pumps blood for the body and under involuntary control
location: in the heart
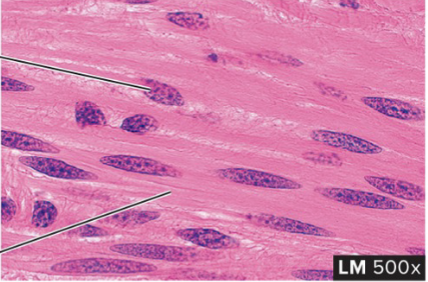
Smooth Muscle Tissue
structure: not striated, single nucleus, and tapered/cut off at each end
function: regulates size of organs and allows for flowing of substances/fluid through tubes and organs (digestive tract). under involuntary control
location: hollow organs such as stomach and intestines, skin and eyes
components of nervous tissue
neurons and tissue have the ability to produce electrical signals called action potentials
cell body: contains nucleus
axon: conducts impulses away from the cell body. only one per neuron
dendrites: receive impulses from other neurons. can be many per neuron
glia: supporting cells of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
nourish, protect, and insulate neurons
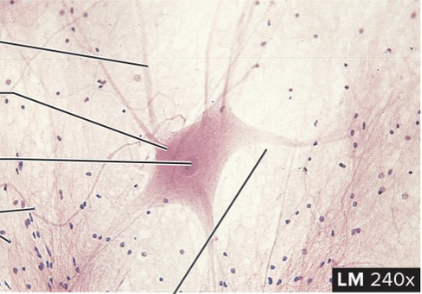
Nervous Tissue (Neuron)
structure: consists of dendrites, cell body, and long axon. glial cells surround the neurons
function: transmit information in the form of action potentials, store information, and evaluate data
location: brain, spinal cord, ganglia