Laws of thermodynamics(and more)
1/19
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
1st law of thermodynamics
There is an equation of state called the internal energy(E). In an adiabatic system, the internal energy is equal to the work done in the system. In a system with thermal contact with its environment, the heat flow (or heat absorbed) called Q is given by Q=delta(E)-w
The first law does not describe the direction that a natural process takes during a reaction
The first law describes heat as a form energy
The first law is a statement on the conservation of energy(energy cannot be created or destroyed)
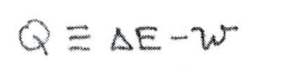
2nd law of thermodynamics
There is an equation of state called the entropy(s). In an isolated system delta(s)=integral((dQ)/T) where delta(S)>=0. If the system process is reversible, then delta(s)=0
The second law defines the direction a natural process will take during a reaction
Entropy→Measure of disorder (pessimistic view)
Entropy→Measure of the number of options(optimistic view)
S=KblnΩ-Ω=# of accessible states(options)
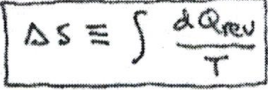
3rd law of thermodynamics
In a homogeneous system in complete internal equilibrium, the entropy approaches zero as the absolute temperature approaches zero
S→0, T→0. S=0 → 0=kblnΩ→lnΩ=0→Ω=1→T=0
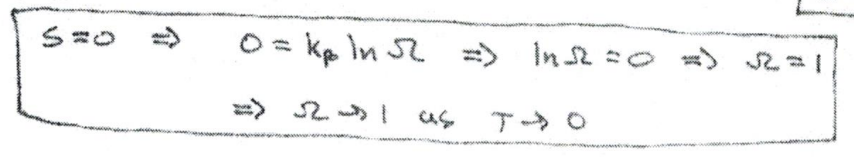
zeroth law of thermodynamics
If two bodies are in thermal equilibrium with a third body, then they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other.
1st law energy balance
((Qi+Wi+mi((vi2/2)+gz+viPi)/Ein)-((Qo+Wo+mo((vo2/2)+gzo+voPo))=delta(u)
Specific heat at volume
Cv=(delta(Q)/delta(T))
What is the energy balance expression for an unsteady process of a closed system?
(Qi-Qo)+(Wi-Wo)-delta(U)=0
What is the energy balance expression for an unsteady process of an open system?
(𝑄 ̇𝑖𝑛− 𝑄 ̇𝑜𝑢𝑡) + (𝑊 ̇ 𝑖𝑛− 𝑊 ̇ 𝑜𝑢𝑡) + (𝐸̇𝐼𝑛𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠− 𝐸̇𝑜𝑢t𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠) = 0
output gas velocity V2 in equation form
[2(ℎ1 − ℎ2 ) − ( (8𝜗𝑠1) /(𝜋𝐷1 2𝑉⃗ 1) ) 𝑄̇ 𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠 + 𝑉⃗ ^2 ]^ (1/2)
output diameter in equation from
((4vm)/(piV2))^0.5
Entropy Balance Equation
(Sum(Qi/Tb)+Sum(mi)(Si))-(Sum(Qo/To)+Sum(Mo)(So))+Sgen=Sum(delta(Sk))
Properties of an system(in the context of an entropy balance)
No work in entropy balance, must have Sgen, no summation
integral forms for entropy transfer due to heat and mass
Heat: Sheat=integral(dQ/T) Mass: Smass=integral(sdm)
What happens to entropy in an Adiabatic process with a gas?
Entropy constant if reversible, increases if irreversible.
What happens to entropy in an Isothermal process with a gas?
Entropy increases if heat is absorbed, decreases if heat is released
What happens to entropy in an Isobaric process with a gas?
Entropy changes based on heat transfer.
What happens to entropy in an Isentropic process?
Entropy remains constant
What is the rate of work input for an adiabatic compressor is running with a known second-law efficiency of 𝜂II = 0.8.
Win=m(h2-h1)+(m/2)(v²2-V²1)
What is rate of entropy generated for an adiabatic compressor is running with a known second-law efficiency of 𝜂II = 0.8.
Sgen=(0.2/To)((m(h2-h1)+(m/2)(V²2-V²1))
What is entropy generated during start-up of the compressor?
Sgen=integral(Sgen)dt→Sgen=integral((1/To)(Win(t)(1-𝜂II (t))))dt