Ch 17 Viewing the Medical Images & Ch 18 Picture Archiving and Communication System
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Human Eyes can see…?
bright light easier than dim light
Eye Cones see
bright light
Eye Rods see
dim light
Lumen
basic unit of Photometry
Luminous Flux
the total intensity of light from a source
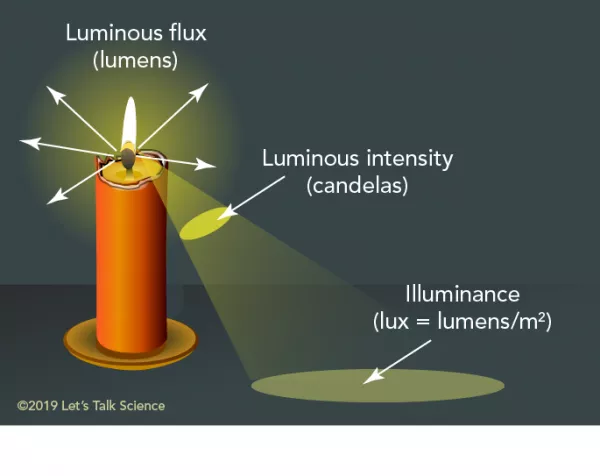
Illuminance
The intensity of light incident on a surface
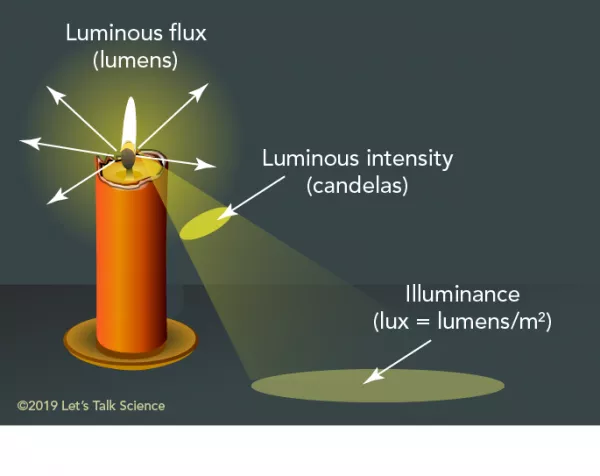
Luminance Intensity
Luminous flux emitted into the entire viewing area
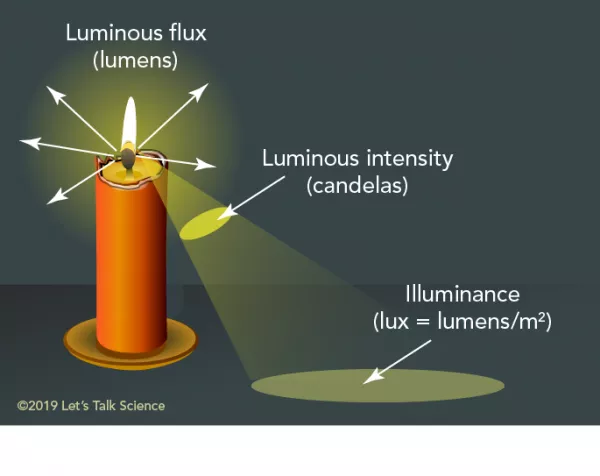
Luminance
Similar to luminance intensity
Cosine law and Luminous Intensity
decrease in proportion to the inverse square law
(the same amount of light photons but spread out, they lose intensity when viewing the monitor)
Cosine Law: when monitor is viewed straight
the luminous intensity is greatest
Cosine Law: when viewed from an angle
Contrast and luminous intensity are reduced
Hard Copy
film on a view box
Soft Copy
digital images read from a monitor; LCD or LED. No longer CRT
LCD stands for
Liquid Crystal Display
LCD has
properties of a solid (crystal) and a fluid
LCD are
electrically charged forming a natural molecular dipole ( + & - )
LCD Crystals can be
aligned by an electrical field
Display Characteristic color LCD have
Red, Blue, Green filters built into each pixel
Medical LCDs are
MONOCHROME devices
how is the backlight of the LCD display?
(fluorescent or LED) illuminates all pixel and is blocked or transmitted by the orientation of the liquid crystals
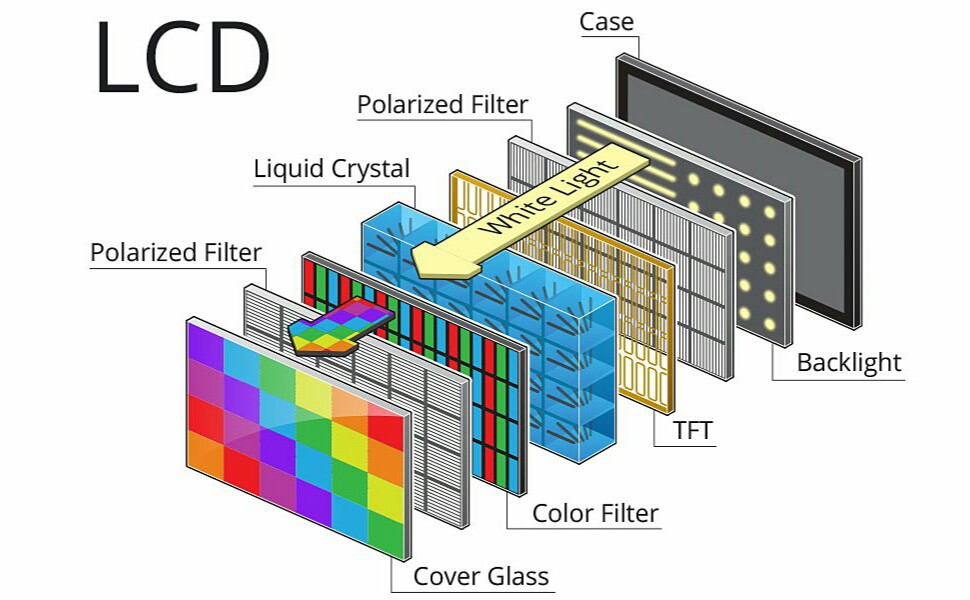
How much backlight is transmitted through monochrome monitor?
10%
What happens to some light?
absorbed in filters and polarizers; blocked by the TFT and bus lines
LCD have what ability?
to control each pixel individuality
LCDs have better
gray-scale definition and better contrast resolution than CRTs
LCDs do not have
glare or reflection; have less noise
how does Crosstalk occur?
when photons falling on one pixel are “falsely” sensed by other pixels around it.
(Crosstalk in the context of LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) monitors used in radiology refers to a visual defect where the luminance (brightness) of a pixel can be affected by the luminance of neighboring or surrounding pixels)
(the phenomenon where light or signals intended for one pixel on an image sensor are unintentionally detected by neighboring pixels)
LED stands for?
Light Emitting Diode
LED diode allows electrical current to flow…
in one direction
LED light is
the backlight for LCD display
LED displays are thicker or thinner?
thinner
LEDs have __________________ for the visual screen?
large active area
LED displays have _____________ than fluorescent lights
longer life
What is Ambient Light?
the light around us
AMLCD’s (Active Martrix Liquid Crystal Display) reduce
the effect of ambient light on image contrast
Ambient light level should be
near darkness
What is the ergonomic design of reading workstation?
Perpendicular Viewing
With Preprocessing the Digital image, it automatically manipulates
the image before display
Preprocessing is designed to produce?
artifact-free images
Flatfielding
helps to correct the heel effect, given a more even image
Flatfielding makes the
response of the image receptor uniform
Signal Interpolation
a dead or defective pixels value is averaged from surrounding
(when a pixel is bad, the pixels around can carry the load and still provide an image)
Postprocessing is
anything done to a digital image after it is acquired
Why is POSTprocessing done?
to optimize appearance of image to better detect pathology
Annotation
adding text
window and level
contrast and brightness
image inversion
black to white, white to black
DSA
Digital Subtraction Angiography (ex: remove bone to see blood vessels)
Pixel Shift
corrects misregistration
ROI
quantitive radiology - measured density of pathology
Edge Enhancement is for
small fractured and small, high contrast tissues
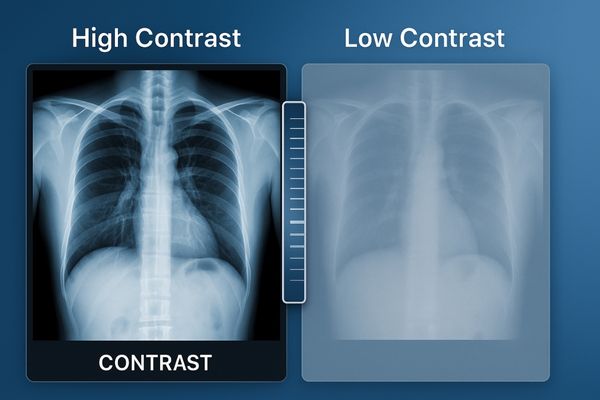
highlighting is for
diffuse, non-focal disease
(DIFUSSE - SPREAD OVER AN AREA; NON-FOCAL NOT SPECIFIC TO)
pan, scroll, zoom
to see precise regions of an image
Chapter 18
Name Four Principles for PACS *
IDSN;
Image acquisition System - WHERE xrays are taken (portable, rad room)
Display System - where image is viewed
Network - connects everything together between computers
Storage - archiving part of PACS
aka I Do Need Sushi
What does the Network do?
Connects each client (image system and workstation) to Central Computer
Teleradiology is?
remote transmission and viewing of images
*TELE because they used to use telephone lines
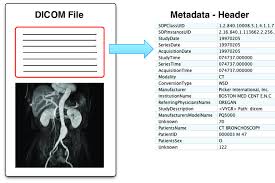
DICOM
Digital Image and COmunnication in Medicine
What does DICOM ensure?
adaptability between different imaging systems - national standard for image transmission in teleradiology
Network begins with imaging system -
acquired and processes images, transmits to PACS
What does DICOM contain?
contains metadata that provide information about the image data
What is involved in Metadata?*
size,
dimension's,
bit depth,
modality used to create the data
equipment settings used to capture the image
Where can images be transferred?
images can be transferred to other clients within or outside the hospital
What is necessary to have regarding Network?
fast computers and high-band with networks necessary
RIS stands for?
Radiology Information System
What is subcategory to RIS
PACS
MIMPS
What is RIS?
information management and database system for radiology department - stores imaging patient info, reports, accounting..
What can secretarial workstations do?
generate reports, schedule pt, copy images
List the devices/clients that are interconnected in a radiology network *
imaging system,
hospital mainframe,
workstations,
radiologist computer,
web server,
archive server,
web clients
What does PACS prevent?
prevents lost images
What was film and file room replaced by
a magnetic or optical memory device

EMR stands for?
Electronic Medical Record
HIS stands for
Hospital Information System