Developmental Defects
1/181
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
182 Terms
in a clinical description, you should describe what 5 things
color
consistency
location
shape and base
architexture
color definition
predominant impression
consistency definition
how the area feels
location definition
anatomic site
shape and base definition
general outline
architecture definition
surface appearance
how do you describe a flat shape/base
sessile
how do you describe a stalk-like shape/base
pedunculated
how do you describe a shape/base of a lesion that is in between pedunculated and sessile
polypoid
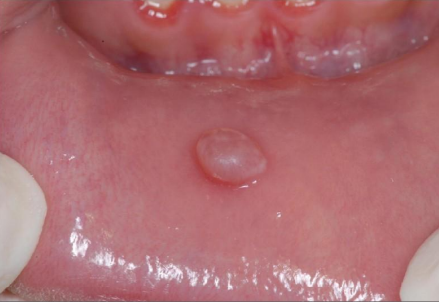
what is the shape/base description
sessile
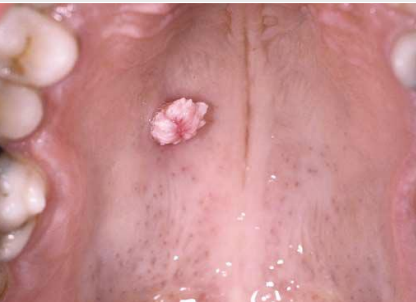
what is the shape/base description
polypoid
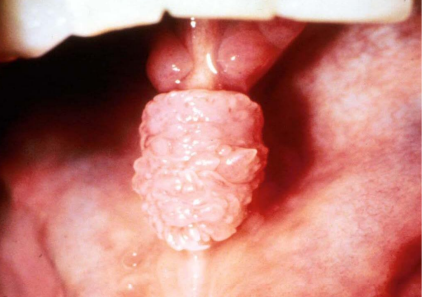
what is the shape/base description
pedunculated
what are the four descriptions you can use to describe architecture
corrugated
fissure
papillary
folded
describe corrugated
wrinkled
describe fissure
a cleft/deep groove showing predominant depth
describe papillary
small projections or elevations found in clusters
when the descriptor words are “folded, smooth, rough, or ulcer”, what is this describing
the surface appearance (architexture) of a lesion
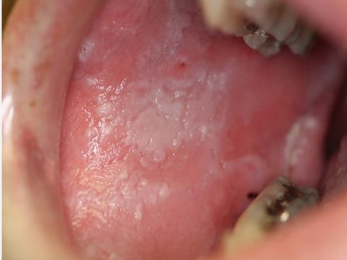
describe the architecture
corrugated
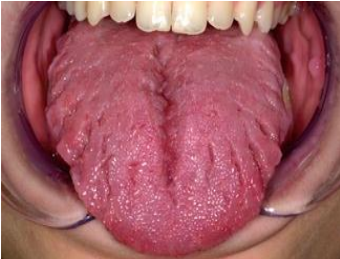
describe the architecture
fissure
describe the architecture
papillary
describe the architecture
folded
describe a macule
distinguished by its different color from its surroundings, is flat (freckle)
describe a papule
small and elevated lesion (<1 cm)
describe a nodule
palpable, solid, small lesion- can be above, level w/, or beneath skin surface
describe a lobule
segment or lobe that is part of a whole lesion → appears fused together
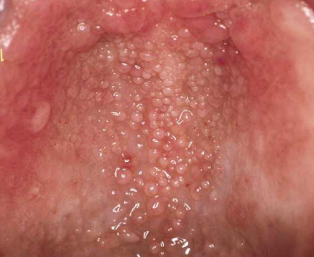
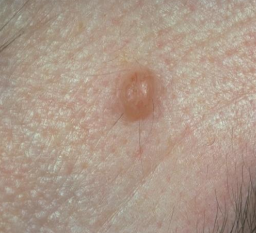
is this a macule, papule, nodule, or lobule
macule
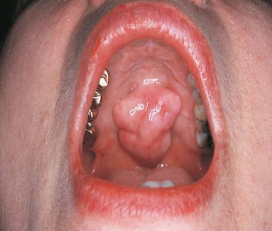
is this a macule, papule, nodule, or lobule
papule
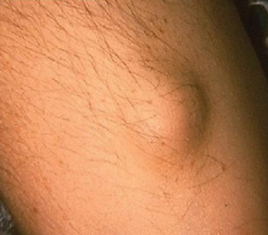
is this a macule, papule, nodule, or lobule
lobule
s this a macule, papule, nodule, or lobule
nodule
describe a vesicle
small, elevated lesion that contains serous fluid
describe a pustule
variously sized, circumscribed lesion that contains pus
describe bulla
circumscribed, elevated, large (>5 mm) lesion that contains serous fluid
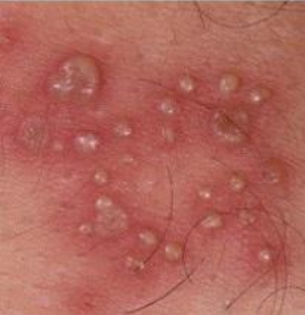
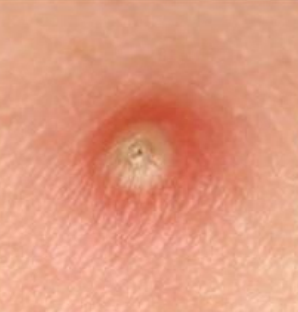
vesicle, pustule, or bulla
vesicle
vesicle, pustule, or bulla
pustule
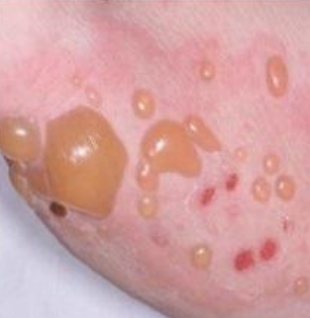
vesicle, pustule, or bulla
bulla
what descriptions do you wanna include when describing a radiograph
density
border
shape
adjacent structures
what are the three descriptions you can use to describe density
radiolucent
radiopaque
mixed
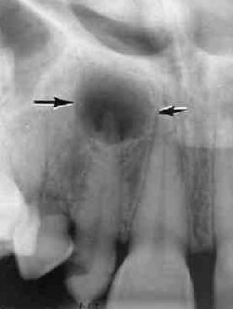
describe the density of lesion at the apex of #7
radiolucent
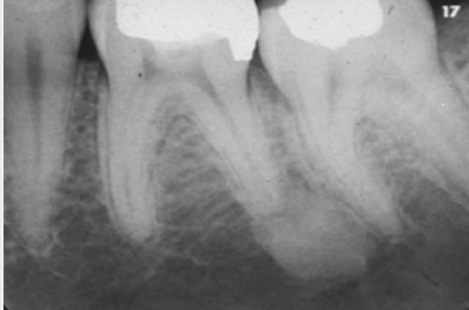
describe the density at the apex of the D root of #19
radiopaque
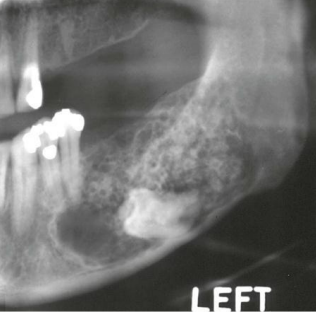
describe the density of the lesion adjacent to the molar
radiolucent and radiopaque
what can cause a radiolucent and radiopaque lesion
mix of different densities of tissue
what are the two descriptors you can use to describe a border of a lesion
ill-defined
well-circumscribed
describe an ill-defined border
cannot detect the exact parameters of the lesion bc borders are not defined
describe a well-circumscribed border
borders are defined well enough to see the exact margins
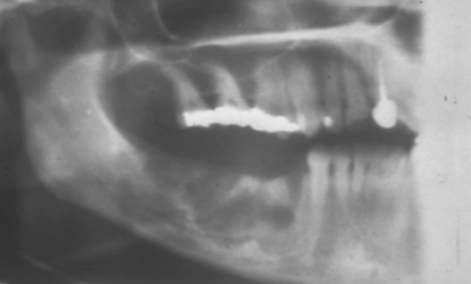
well circumscribed or ill defined
ill defined
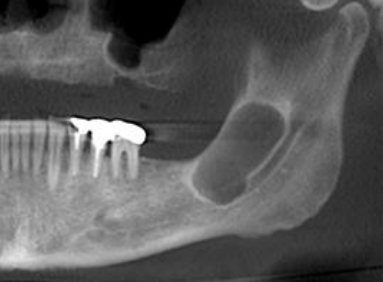
well circumscribed or ill defined
well circumscribed
what are the four descriptor names you can use to describe shape in a radiograph
uniocular
multilocular
round
oval
describe a uniocular shape
a single, well-defined unit
describe a multiocular shape
multiple uniocular lesions somewhat fused together (soap bubbles)
what are the three descriptors that can be used to describe adjacent structures in radiograph
resorption
fracture
divergence
resorptions usually starts…
at the apex of a root
describe what resorption looks like
apex of the tooth appears shortened, blunted, irregular
describe scalloping
radiolucent lesion that extends between roots and teeth
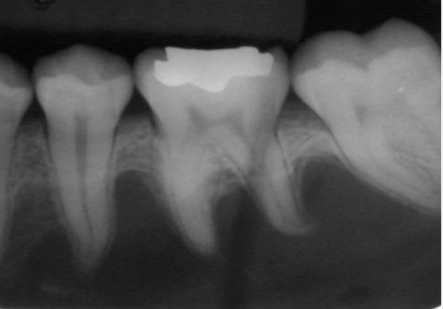
describe the radiolucency is relation to the adjacent structures
scalloping
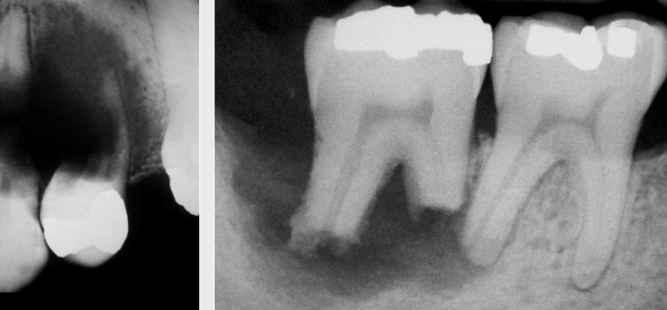
describe the radiolucency is relation to the adjacent structures
resorption (usually wouldn’t see the L image, not v common to start outside of the apex)
origin of Fordyce Granules
clusters of ectopic sebaceous glands- common in adults and during puberty
clinical appearance of Fordyce Granules
yellow/yellow-white papular lesions
location for Fordyce Granules
buccal mucosa, lateral portion of vermillion upper lip
tx for Fordyce Granules
none
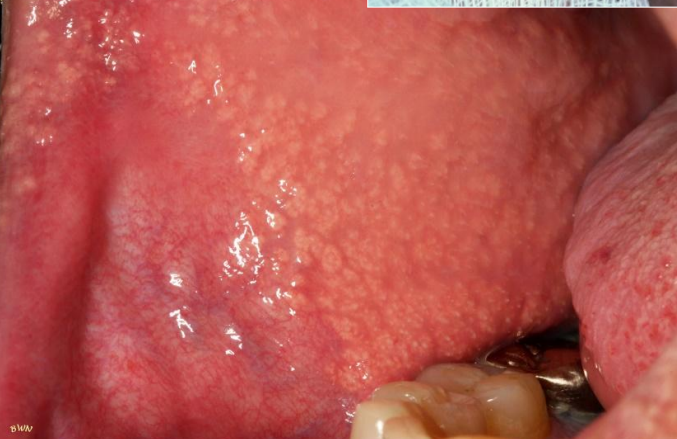
dx
Fordyce Granules
origin for Leukoedema
90% of African American adults (50% in children)
clinical appearance for Leukoedema
diffuse, gray-white, milky, opalescent lesion
location for leukoedema
bilaterally on B mucosa → localized, NOT generalized
tx for leukoedema
none
how to confirm leukoedema dx
when stretched, the white appearance will disappear
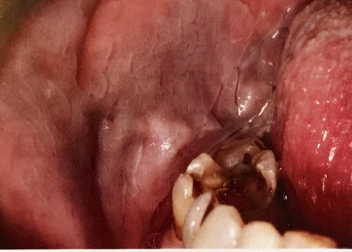
dx
leukoedema
origin of linea alba
prominent in clenching or bruxing
clinical appearance of linea alba
white line
location of linea alba
extends A-P on B mucosa along occlusal plane
tx for linea alba
none- in parafunx habit is severe, consider NG
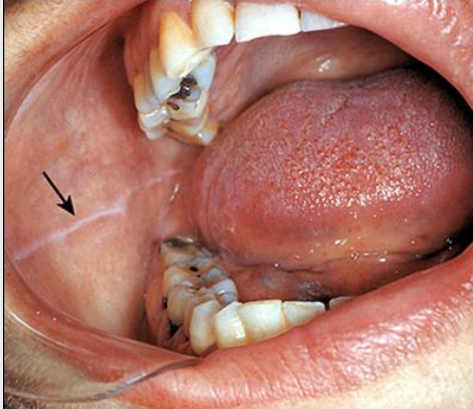
dx
linea alba
origin of physiological pigmentation
most common is dark-skinned people
clinical appearance of physiological pigmentation
melanin pigmentation of oral mucosa
location of physiological pigmentation
generalized along gingival margin
tx for physiological pigmentation
none
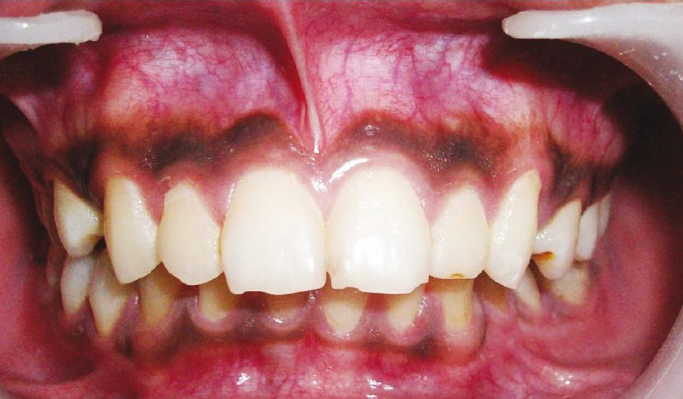
dx
physiological pigmentation
origin of lingual varicosities
most common in people >60 yrs, NOT associated w systemics
clinical appearance of lingual varicosities
ventral/lateral surface of the tongue
tx for lingual varicosities
none- DO NOT BIOPSY
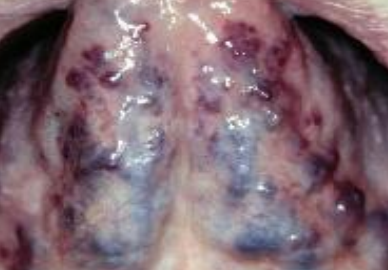
dx
lingual varicosities
clinical appearance of retrocuspid papilla
sessile nodule
location of retrocuspid papilla
gingival margin on the lingual of mandibular canines/cuspids
tx for retrocuspid papilla
none
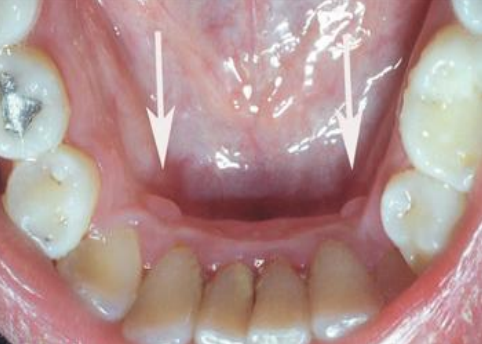
dx
retrocuspid papilla
what is a diascopy
use a clear slide and put pressure on the lesion → will blanch if vascularized → if doesn’t blanch, is a concern
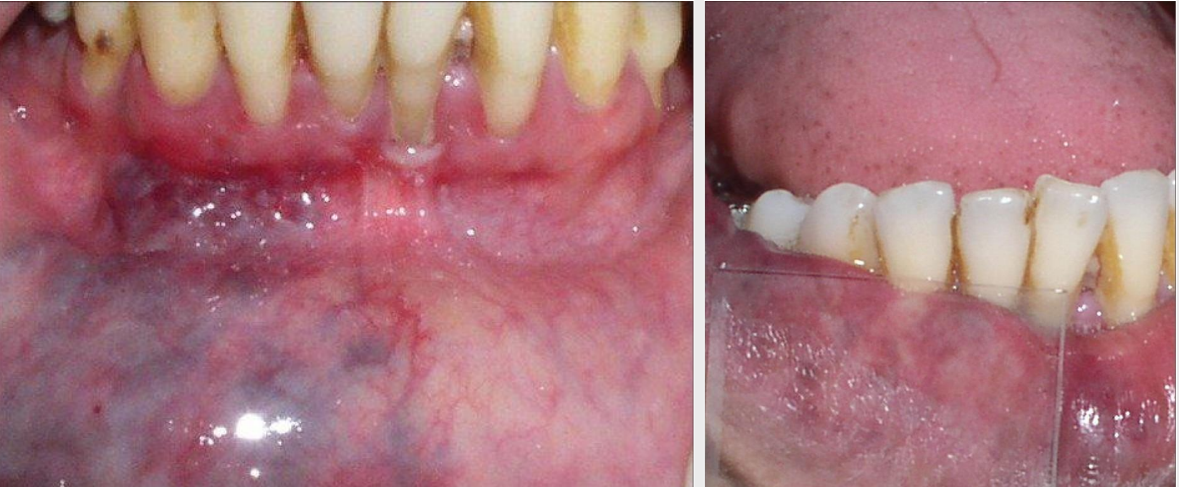
origin of torus palatinus
exophytic growth of normal compact bone
location of torus palatinus
hard palate
tx for torus palatinus
none unless affecting pts QOL
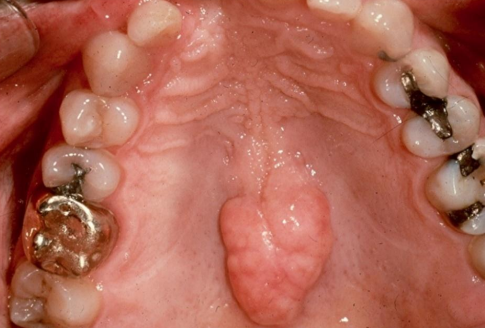
dx
torus palatinus
origin of mandibular tori
outgrowths of normal dense bone
location of mandibular tori
lingual aspect of mandibular premolars
tx for mandibular tori
none unless affecting pts QOL
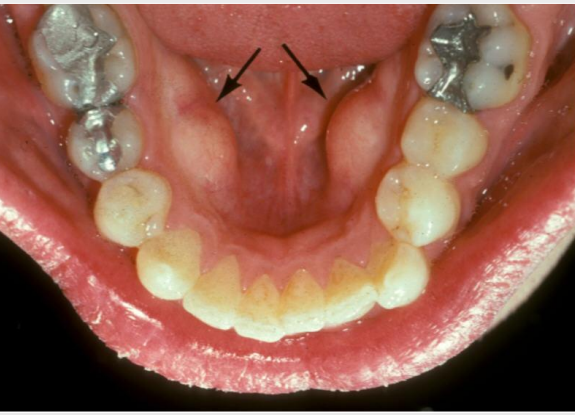
dx
mandibular tori
origin of lingual thyroid
thyroid doesn’t end up descending in the 7th week of fetal development, F>M, 90% of ectopic thyroids are in this position
clinical appearance of lingual thyroid
normal thyroid
location of lingual thyroid
posterior midline dorsum of the tongue, posterior to circumvallate papillae- in area of foramen cecum
tx for lingual thyroid
to dx- use radioactive iodine
DO NOT BIOPSY
no tx unless problems → otherwise surgery
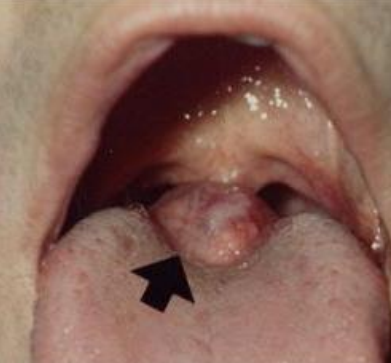
dx
lingual thyroid
origin of geographic tongue
etiology unknown, F have 2:1, 10% of psoriasis pts have
clinical appearance of geographic tongue
erythematous patches surrounds by white/yellow serpentine borders, can be multiples or single