fish reproduction
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
fish life cycle
oceanic phase
larval 36-47 days
metamorphosis
settlement
reef phase
recruitment
embryonic phase 4-5days
pelagic and demersal
2 types of eggs
CR fishes lay eggs
fertilisation happens in water
demersal spawning
glue their eggs onto some substrate, corals/rocks, eggs stick there and guarded by parents
pelagic spawning
fertilised eggs float away, no parental care
pair formation
common in some fam-especially demersal eggs, rare in others
Blueheaded wrasse
sexual dimorphism
male comp→winner takes polygyny→mating→sequential hermaphrodites→ protogynous sex change→ sneakers
Pajama cardinalfish
high paternal investment → mouthbrooding
mouthbrooding
a reproductive strategy where animals carry and incubate their fertilized eggs or young in their mouths
polygyny
multiple matings by males
polyandry
multiple matings by females
spermatophore
a capsule, packet, or mass enclosing spermatozoa that is extruded by the male of various lower animals and is transferred to the reproductive tract of the female.
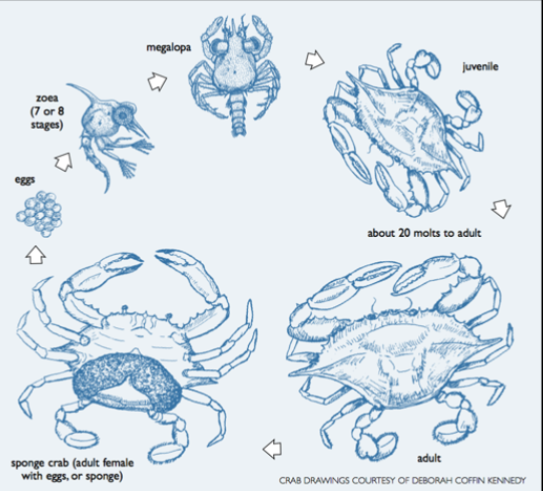
crab life cycle
eggs → zoea (7/8 stages) → megalopa → juvenille → 20 molts to adult → adult
crabs maternal care
mother clear leaf litter → enhance dissolved O2 in axil water
add empty snail shells →increase pH and Ca2+ in water
feed young with prey caught on bromeliad
defend nursery axil by removing predators → damselfy, nymphs, spiders
size heirachy
male→female→subordinates
protogynous sex change
subordinates→ male → fem
planktotrophic larvae
bipartite life cycle
dispersive larval phase
deplete yolk sac quickly (hrs-days)
actively feed on planktonic organisms
most marine fishes
larval dispersal phase
primary agents of dispersal - connect pops, supply recruits, colonise new habitats
→ cause low genetic substrcuture in pops
aplanktonic larvae
not rly larvae
hatch fully developed from egg capsule/parent
viviparous, ovoviviparous, oviparous
less opportunity to disperse
genetic parentage methods
catch fish
take tissue sample
take sample from eggs/juveniles
create genetic markers (mircosatellites/SNPs)
compare sequences of parents to juveniles
vivipary
Seeds of some species, such as mangroves, germinate while
they are still on the maternal plants, which are called 'vivipary.
' In viviparous plants, germinated seedlings are dropped to the
soil and continue to grow. In nonviviparous species, seed
dormancy plays an important role in preventing precocious
germination.