Global Systems - Unit D
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Definition of Weather
refers to SPECIFIC atmospheric conditions at a particular location at a specific instant of time.
Definition of Climate
the AVERAGE weather conditions in a REGION over a period of several years
What makes up Climate?
precipitation
temperature
What are the 3 sections of the biosphere?
Biosphere is the global sum of all ecosystems - supporting life
lithosphere (earth)
atmosphere (air)
hydrosphere (water)
What is Earth’s main energy source?
The sun
What is insolation?
the amount of the sun’s energy that is ACTUALLY received on Earth.
What is the Angle of Incidence?
the angle between the ray and a line that is drawn perpendicular to the Earth’s surface
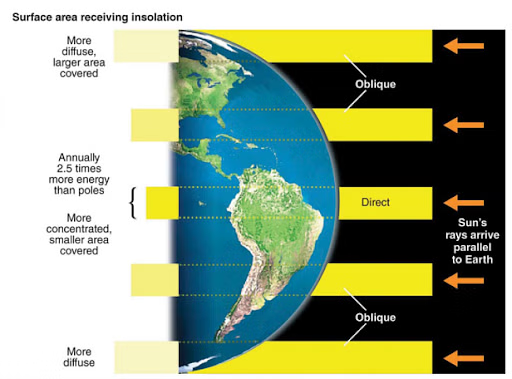
How does insolation at the equator compare to the poles?
Insolation at the equator is more direct and intense due to the sun's rays hitting at a steeper angle.
while at the poles, the rays are more oblique, resulting in less intensity and energy received.
How would this impact climate and weather in those areas?
More direct insolation at the equator leads to warmer temperatures and increased precipitation,
while oblique rays at the poles result in colder climates and less moisture.
What is the Angle of Inclination
The angle of the axis of Earth’s rotation: 23.5º from a line drawn perpendicular from its orbital plane.
It is also the reason for the seasons!
The tilt of the Earth changes the insolation at different parts of the year
What is Solstice?
one of two points in the Earth’s orbit when the poles are most tilted towards/away from the sun - resulting in the longest and shortest days of the year.
Summer solstice happens in June, while the Winter Solstice happens in December
What is Equinox?
when the # of daylight hours = # of night hours
Absorption + Reflection of Solar Radiation
Incoming energy is always 100%, but it doesn’t all reflect back.
What is Albedo
Reflectivity of a surface
Avg on Earth: 30%
percent or decimal - the rest is ABSORBED ENERGY
ex: 20% albedo = 80% absorbed energy
the lower the percent, the lower the reflectivity is
shiny, smooth, light, glossy surfaces usually have a higher albedo
Types and Amount of Radiation absorbed or reflected is affected by:
the gases in the atmosphere: different layers contain different types and amount of gas
cloud cover and atmospheric dust
What is the Natural Greenhouse Gas Effect?
when solar energy is absorbed into Earth, some of the energy is re-emitted into the atmosphere in the form of longwave radiation
Greenhouse gases, ex: carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane and water vapour prevent some of this longwave radiation from leaving atmosphere
Without the greenhouse effect, our avg. atmospheric temperature would be below 0ºC.
WE WOULD NOT BE HERE WITHOUT THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT! EARTH WOULD BE TOO COLD.
What is the Enhanced Greenhouse Effect?
human activity = build up of extra greenhouse gases = average surface temps RISING
What is Net Radiation Budget?
The rate at which energy is absorbed by Earth is approx. balanced by the rate at which it is emitted back to space keeping the Earth in equilibrium and at a stable temp
As long as the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere stay the same, and the rate of energy arriving from the sun is constant, this equilibrium is maintained.
What is Earth’s Net Radiation Budget?
Earth’s Net Radiation Budget should = 0
Incoming Radiation - Outgoing Radiation = 0
This was until the industrial revolution.
True or False: different latitudes will have different energy budgets due to different insolation
TRUE
Latitudes closer to the equator will have a higher surplus of radiation coming in compared to the poles, which have a energy deficit
What is Thermal Energy?
According to the law of thermodynamics:
Thermal energy moves from high temperature to low temperature
What is Radiation?
the emission of energy as particles/waves
when absorbed, it will increase the kinetic energy and therefore temp of the particles that make up the object
What is Conduction?
transfer of energy through direct contact between material/object (SOLIDS)
ex: butter melting on a hot pan, cooking, lightbulb filament
What is Convection?
transfer of thermal energy through the movement of particles from one location to the other
ONLY transferred through liquids and gases
ex: hot air balloon rising due to flame, swimming pools, ice melt
What is Wind?
the movement of air from areas of high pressure to low pressure
What is the Coriolis Effect?
bending of moving currents in response to
Earth’s rotation.
The Coriolis effect causes winds in the two
hemispheres to move in opposite directions.

What are Jet Streams?
a narrow, fast flowing “river” of air in the atmosphere
changes in jet streams are important in predict severe weather
