Lecture 3: Five factor model
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
How do we predict what other's will do?
Observations (Kelley's covariance model) - person or situation influencing them?
What is the Whorfian hypothesis?
Language develops relative to the cultural context - descriptors used describe the culture of the time.
- use language to understand and describe consistent behaviours
How does biology predict behaviour?
Observe pattern of behaviour in the real world (ecology) - behavioural reaction norms and look to distinct patterns and contextual variations
- identify associations between behaviour and biological substrates.
- examine gene expression
What is the Big 5 ? (Lewis R goldberg)
A lexical (language) approach to personality - looked at natural language used to identify personality traits based on grouped adjectives.
- based on how people use language to describe their own and others behaviour.
What is the FFM? (Costa & McCrae)
Biological and Behaviourally driven thats questionnaire based to tap into behaviours.
- developed due to a lack of sufficiently comprehensive model (McCrae & John, 1992)
How is the FFM and Big 5 similar?
They come to very similar conclusions in how to describe behaviour.
What are the 5 personality traits are used in the FFM (Questionnaire items)
Neuroticism
Extraversion
Openness
Agreeableness
Conscientiousness
What the 5 personality traits are used in the Big 5 (lexical approach)
Emotional stability
Extraversion
Intellect
Agreeableness
Conscientiousness
What is the main difference between the FFM and Big 5?
The FFM has a trait hierarchical model of traits (trait > facets > behavioural tendencies > behaviours) whereas there is no hierarchy in the Big 5 as its developed from natural language - no tendency to build behaviours from facets.
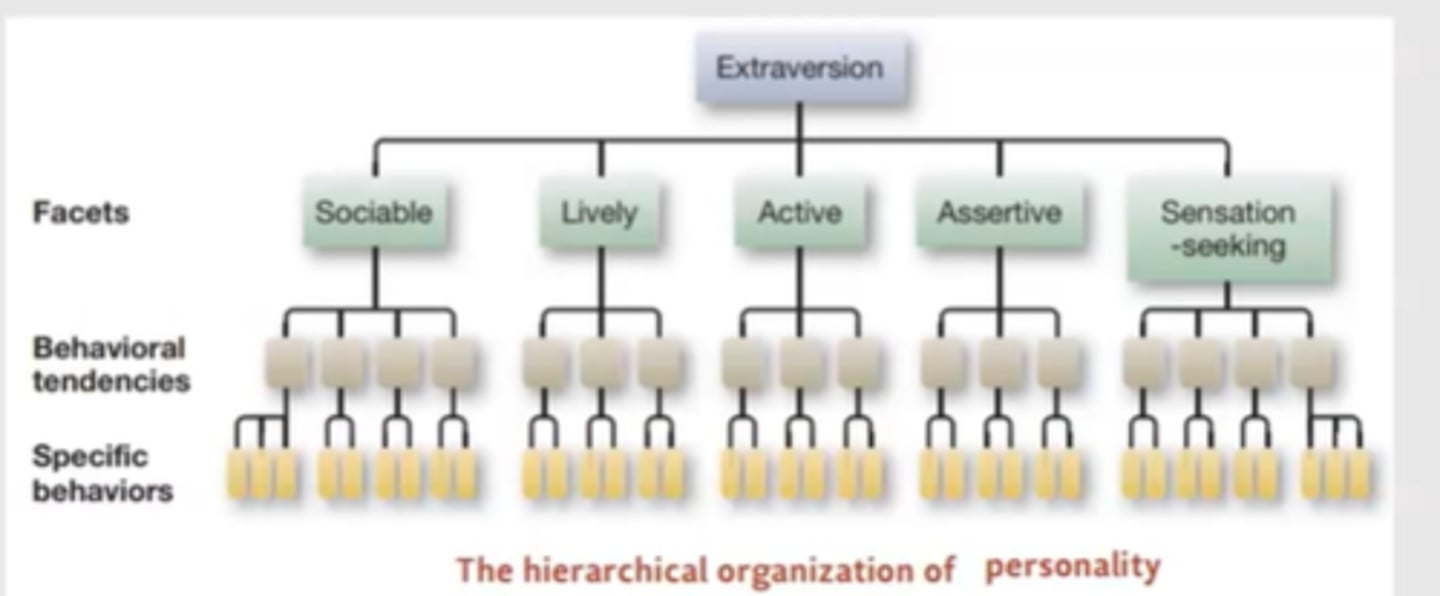
Why does the FFM have a hierarchy?
Allows you to predict somebody's behaviour by analysing each hierarchical domain
- levels of specificity in prediction models
How is the FFM measured?
Via questionnaire items that are designed to reflect the causal role in behaviour at the facet levels.
- 6 facets underlie each of the domains
- "I am easily frightened"
How is the Big 5 measured?
Via adjectives only
- "calm, agreeable"
how does the FFM describe causality?
Traits cause behaviour - have evolved traits for survival function. this has a causal role in behaviour on an everyday basis to help us function in social world
how does the Big 5 describe causality?
No formal cause statement - they just represent natural language - which may have developed to help us understand and describe people.
What is the origin of the FFM?
Biological model - makes predictions about genetic, neurology, evolution.
- traits are derived from a biological basis - stable across time and cultutr
What is the origin of the Big 5?
Natural language that has evolved - rich corpus of adjectives used to describe our own and others behaviours.
Does the FFM emerge in both adjectives and questionnaire items?
YES - consistently across studies the adjectives load onto 5 domains and the FFM facets into their target domains when measuring behavioural traits.
- similar structures across many cultures
What did Bainbridge et al (2022) find?
all different traits identified map statistically onto the FFM/Big 5 domains (5 domains all highly correlate to the other traits)
- e.g all trait models map onto the FFM/BIG 5
How does Eysenck's P-E-N model map onto the FFM? (Costa & McCrae 1995)
They suggests that 'P' in Eysenck's model is a conflation of conscientiousness and agreeableness (people who are high in P are low in these 2) low C and A predicts a high P
- P should be separated
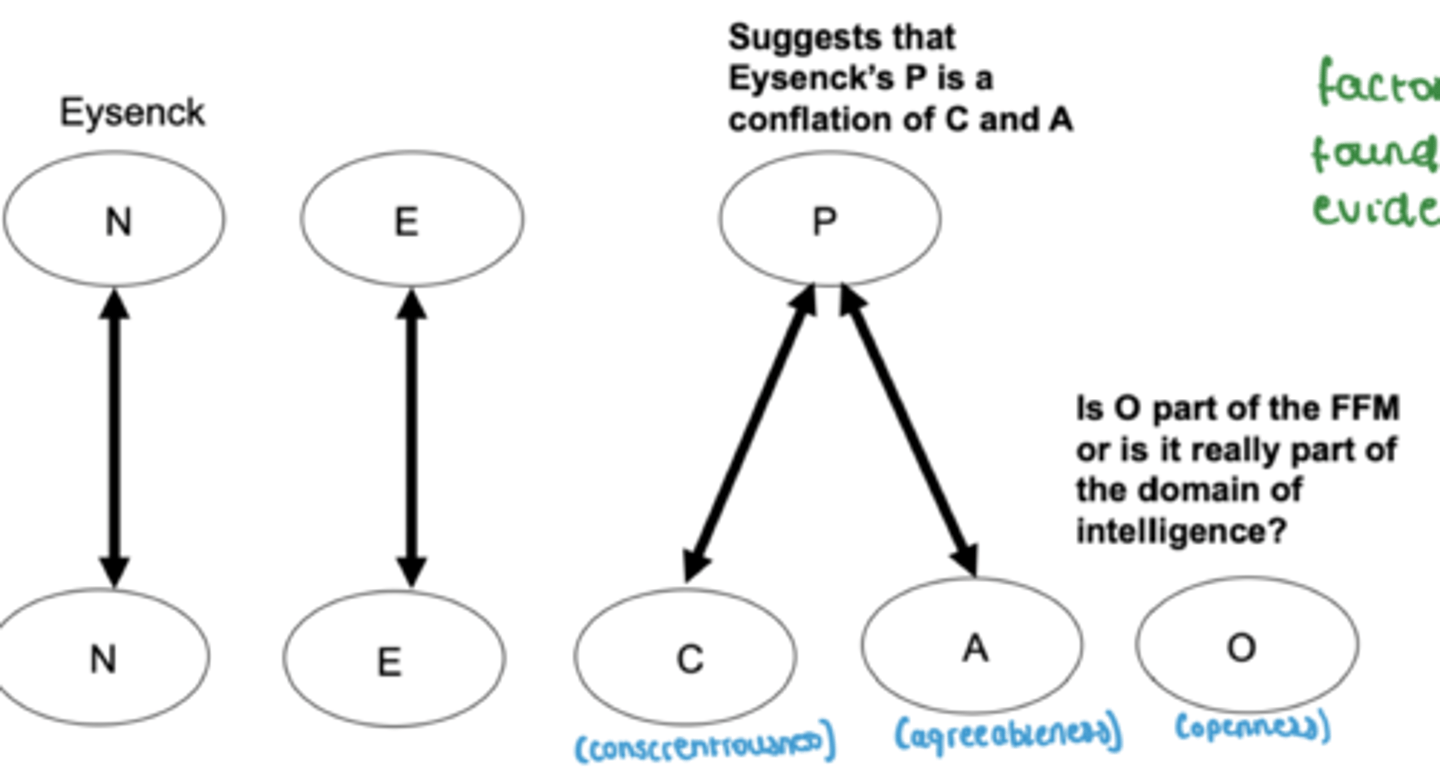
What is suggested by others about 'O' in Costa & McRae's (1995) FFM?
They argue that openness sits outside al the models - is it really a part of personality or should it be part of domain related to intelligence?
- But openness is about how you use your IQ/cog abilities to address problems and understand the world.
What does Gurven et al 2013 say about the FFM as a critique?
The WEIRD problem - many cross-cultrual studies into the FFM work on WEIRD samples.
- if FFM is universal, should see FFM in preliterate tribes etc...
What does Gurven et al (2013) examine?
examined the FFM in the Tsimane - forager-horticulturalist in lowland Bolivia
- live in extended family clusters - small villages
what did Gurven et al (2013) find?
No evidence for FFM!! no factor structure - global north findings aren't reliable measures in a non global WEIRD culture.
What did Steyn & Ndodirepi (2022) find for FFM in WEIRD and non-WEIRD communities?
when each measure of the FFM was assessed - factors nearly replicate in Germany (bar agreeableness)
- South Africa sample - no replications in this culture!!
How did Block (1995) critique the Big 5?
There is a problem with using factor analysis to determine personality. Can't just minimse to 5 adjectives from a huge corpus of adjectives to describe personality. what happens to the words that aren't used/don't fit into model?
How does Deary (1996) address the temporal stability of the Big 5?
Re-analyse data from 1915 (65 years before big 5) pre Big 5 (no selection bias)
- is the Big 5 observed before the model was ever thought of? can't then be due bias item selection.
Deary (1996) findings?
Found 5 factors and items similar to the Big 5 - agreeableness seems to split into 2:
'Not modest' 'pursuit of pleasures' and 'Being' (a desire to be liked)
- other traits were found.
How does Allen et al (2022) critique the neural basis of traits?
current Neuroimaging studies are descriptive rather than mechanistic. doesn't show causality.
- exploratory in nature - no hypothesis
- no behavioural manipulations