Chap 2 - Data transmission
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Data packet structure
Packet header, payload, trailer
Inside the packet header
-Ip address of receiver and sender
-sequence of the packet
-packet size
Inside the payload
the actual data in the packet
Inside the trailer
-identification method
-error checking method
Cycle Redundancy Check (CRC)
the sending computer will add up all the 1-bits and stores it into the trailer, the receiver adds them to see if it's the same
Packet switching
A method of transmission when a message is broken up into a number of packets and sent through many routers
Pros of packet switching
relatively easy to expand package usage
Cons of packet switching
packets can be lost and need to be re sent
data may be skewed (when received)
Simplex transmission
one-way transmission
Half-duplex transmission
both directions but not at the same time
Full Duplex
Both directions at the same time
Serial data transmission
one bit at a time over a single wire
- longer distance
-slower

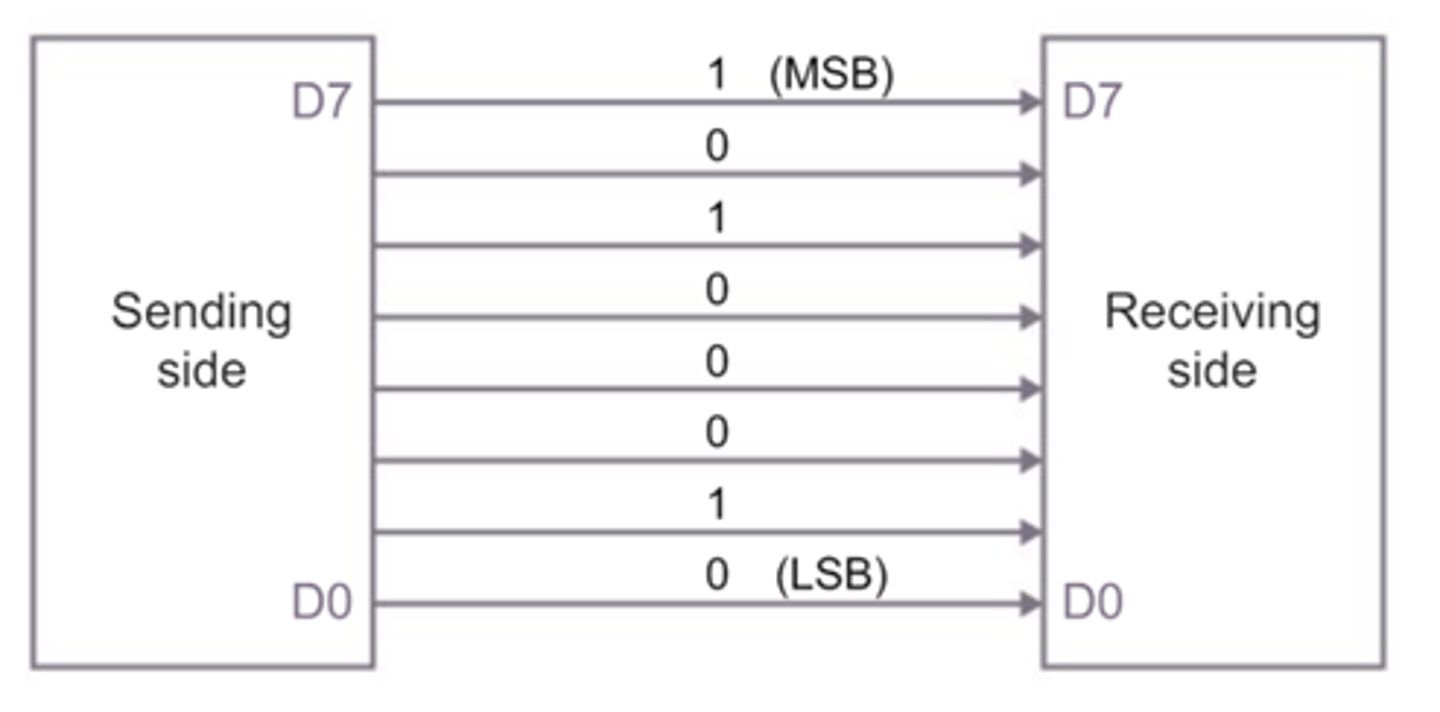
Parallel data transmission
Several bits of data over several wires/channels
USB general facts
Universal Serial Bus
-serial data transmission
-allows half and full duplex
Red and black wires in a usb
Used for power
Parity checks
Counting up the 1's for an even or odd parity
Check sum
when dats is sent, an additional value is sent as the checksum
Echo check
Data is sent and then sent back for the original sender to check, if it's correct it will be sent back
Check digit
A final digit included in a code that is calculated from the other digits in the code

ISBN 13
add even and odd, times odd by 3, add both together divide by 10 then 10- remainder is your check digit
Modulo-11
Multiply the number with the weighted number and add them all up, divide total by 11 and do 11-remainder
Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ)
Uses positive and negative acknowledgements and timeouts for error checking
Plaintext
data before encryption
Cipher text
Data that has been encrypted.
Symmetric encryption
uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt data
Asymmetric encryption
uses public and private keys to encrypt and decrypt data.
White and green wires in a usb
For data transmission