ROMAN ARCHITECTURE
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
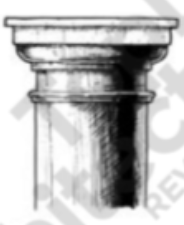
Tuscan
The Etruscans’ simplified version of the Doric Order.

Composite
A classical Roman order, a hybrid of Ionian and Corinthian.
Limestone, Concrete and Mortar
Materials used by Romans.
Concrete
Combined volcanic ash - called pozzolana - and lime with sand, water, and gravel.
Opus
An artistic composition or pattern, especially as used in relation to Roman stonework and walling construction.

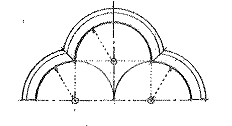
Arch
Curved structure for spanning an opening, designed to support a vertical load primarily by axial compression.
Keystone
The wedge-shaped, often embellished voussoir at the crown of an arch, serving to lock the voussoirs in place.
Masonry Arch
An arch constructed of individual stone or bricks voussoirs.
Voussoir
Any of the wedge-shaped units in a masonry arch or vault, having side cuts converging at one of the arch centers.
Springer
The first voussoir resting on the impost of an arch.
Extrados
The exterior curve, surface, or boundary of the visible face of an arch. Also called back.
Archivolt
A decorative molding or band on the face of an arch following the curve of the intrados.
Intrados
The inner curve or surface of an arch forming the concave underside.
Spring
The point at which an arch, vault, or dome rises from its support.
Rise
The height of an arch from the spring line to the highest point of the intrados.
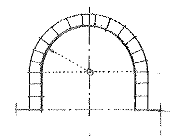
Roman Arch
An arch having a semicircular intrados.
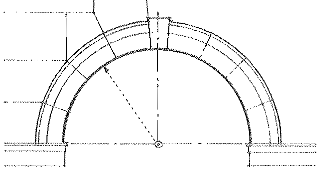
Stilted Arch
An arch resting on imposts treated as downward continuations of the archivolt.
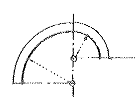
Rampant Arch
An arch having one impost higher than the other.
Bell Arch
A round arch resting on two large corbels with curved faces.
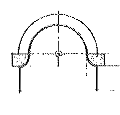
Horseshoe Arch
Also called Moorish Arch an arch having an intrados that widens above the springing before narrowing to a rounded crown.
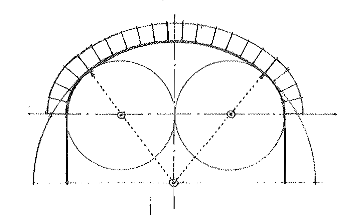
Basket-Handle Arch
A three-centered arch having a crown with a radius much greater than that of the outer pair of curves.
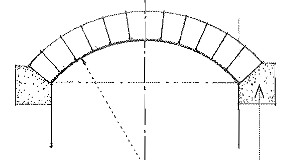
Segment Arch
An arch struck from one or more centers below the springing line.
Trefoil Arch
An arch having a cusped intrados with three round or pointed foils.
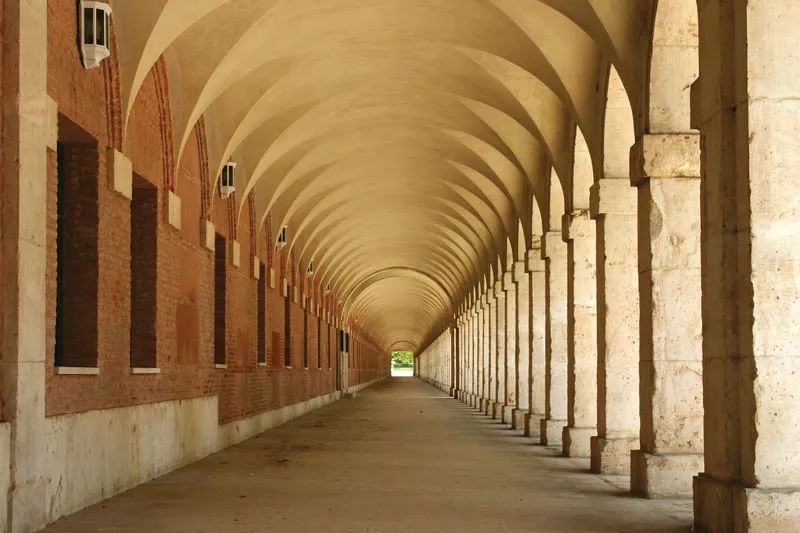

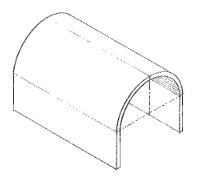
Vault
An arched structure of stone, brick, or reinforced concrete, forming a ceiling or roof over a hall room, or other wholly or partially enclosed space.
Barrel Vault
A vault having a semicircular cross section. Also called cradle vault, tunnel vault, wagon vault.
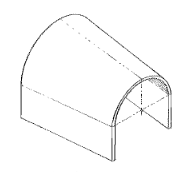
Conical Vault
A vault having a circular cross section that is larger at one end than the other.
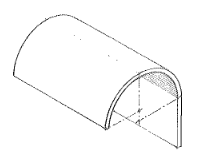
Rampant Vault
A vault springing from an abutment higher at one side than at the other.
Annular Vault
A barrel vault having a circular plan in the shape of a ring.
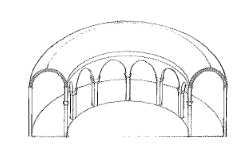
Groin Vault
A vault having a groin with one of the curved lines or edges along which two intersecting vaults meet.
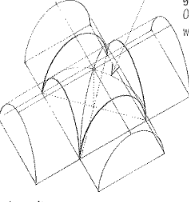
Tripartive Vault
A compound vault for covering a triangular space, formed by the intersection of three-barrel vaults.
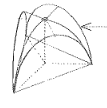
Cloister Vault
A compound vault formed by four coves meeting along diagonal vertical planes.
Basilica
It is a Roman building-type, used as a meeting place, courthouse, marketplace, and lecture hall. Rectangular in shape with an apse at either end.
Forum
It is a place of assembly for the people, public square or marketplace of an ancient Roman city, the center of judicial and business affairs, usually including a basilica and a temple.

Imperial Fora
It is a series of monumental for a constructed in Rome between 46 BC and 113 AD. It is not part of the Roman Forum but is located relatively close to each other.
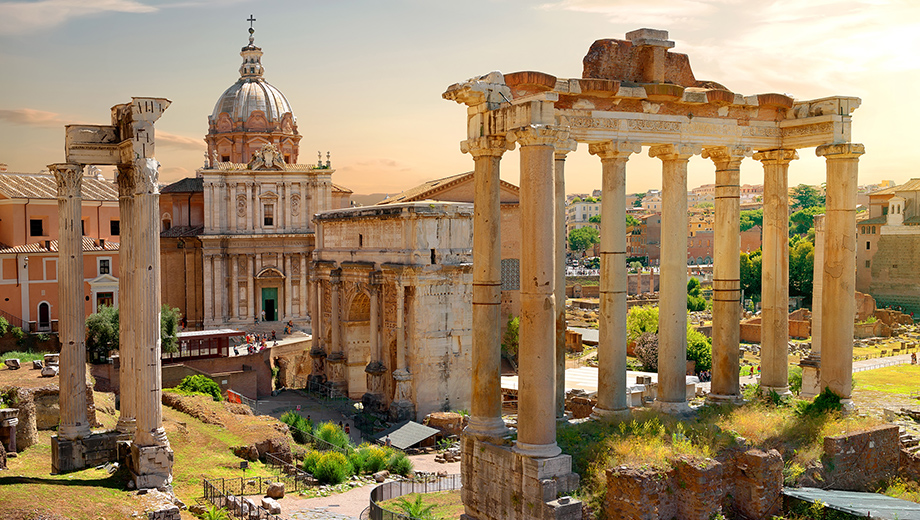

Forum Romanum
Oldest forum in Rome; Republican Forum; Open space, rectangular in shape, enclosed by different institutional and public buildings, serving as the city's marketplace and; center of public business.

Thermae
Establishments that were built for bathing, washing, as well as exercising, entertaining, and conducting business.
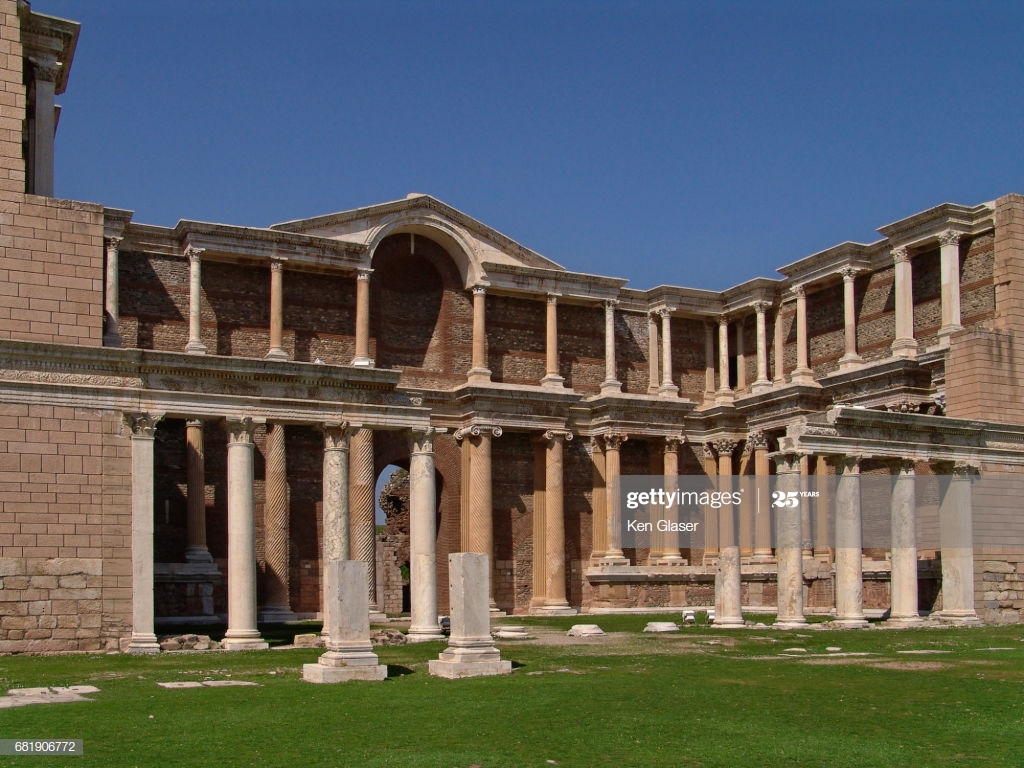

Gymnasium
A Centre used for athletic activities- sports, playing areas and baths. All exercise were done by male members could train and improve their fitness to make them ready for warfare. Wrestling boxing and running were the typical activities.
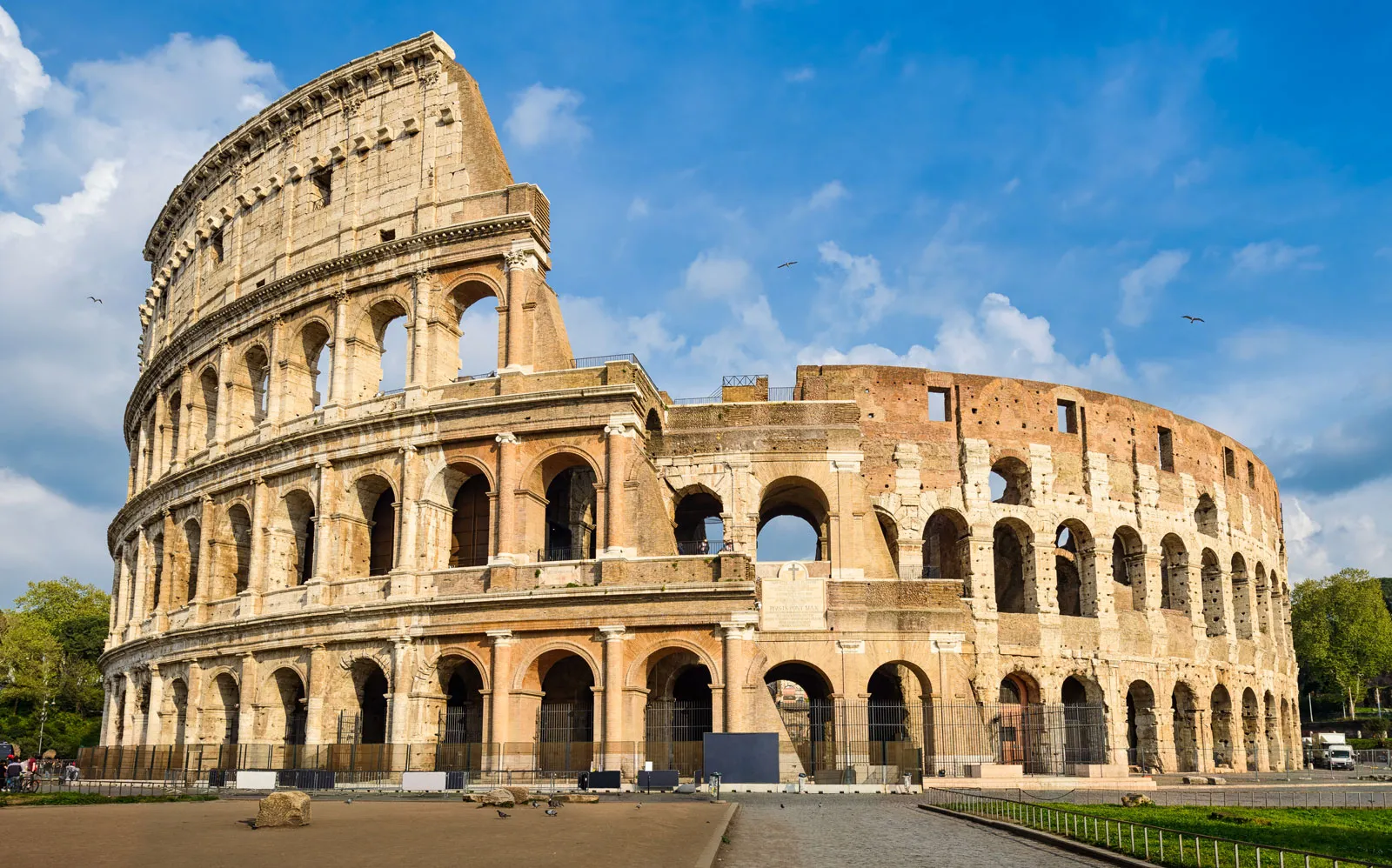

Amphitheater
A classical arena for gladiatorial contests and spectacles consisting tiered seating for spectators around an oval or round space.
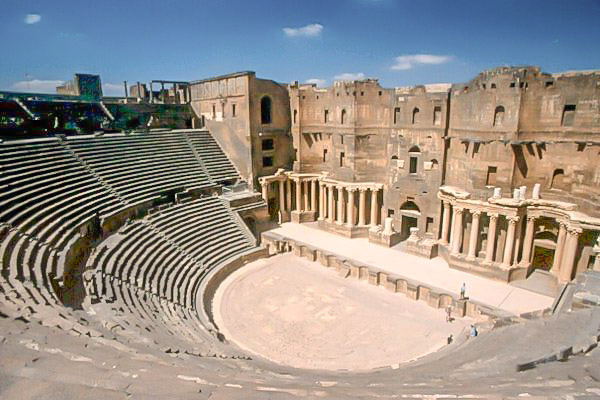

Theatrum
A Roman theatre building or structure for the production and performance of theatrical works. An arena with a stage and an auditorium.
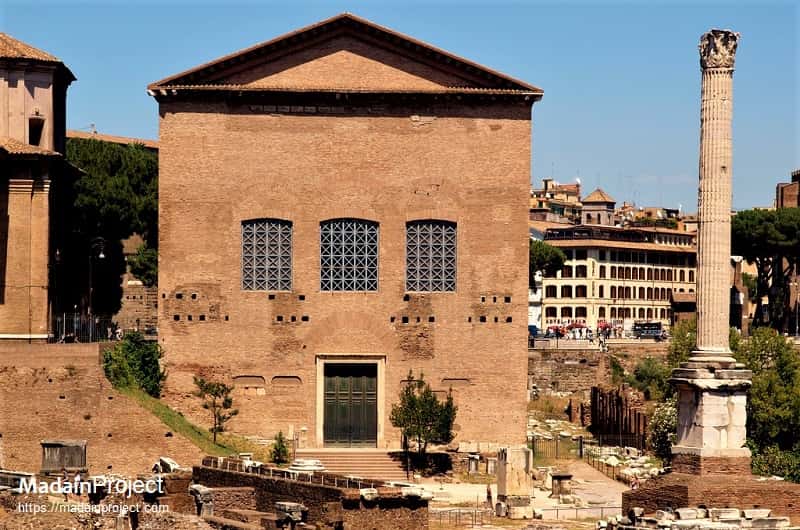

Curia
Given to the administrative offices of the pope of the Catholic Church This government-like structure.
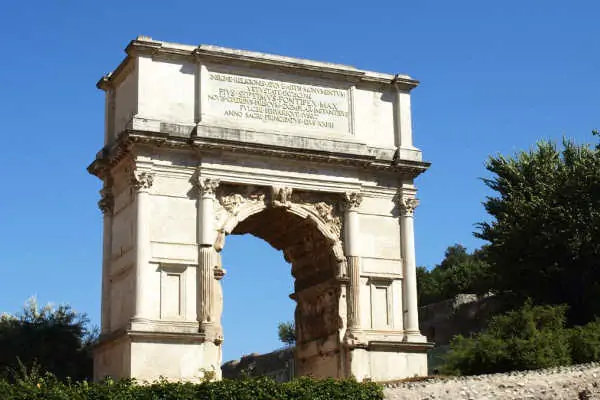
Triumphal Arch
A large arched monument to commemorate a great event usually a victory in war. Constructed in a public urban place
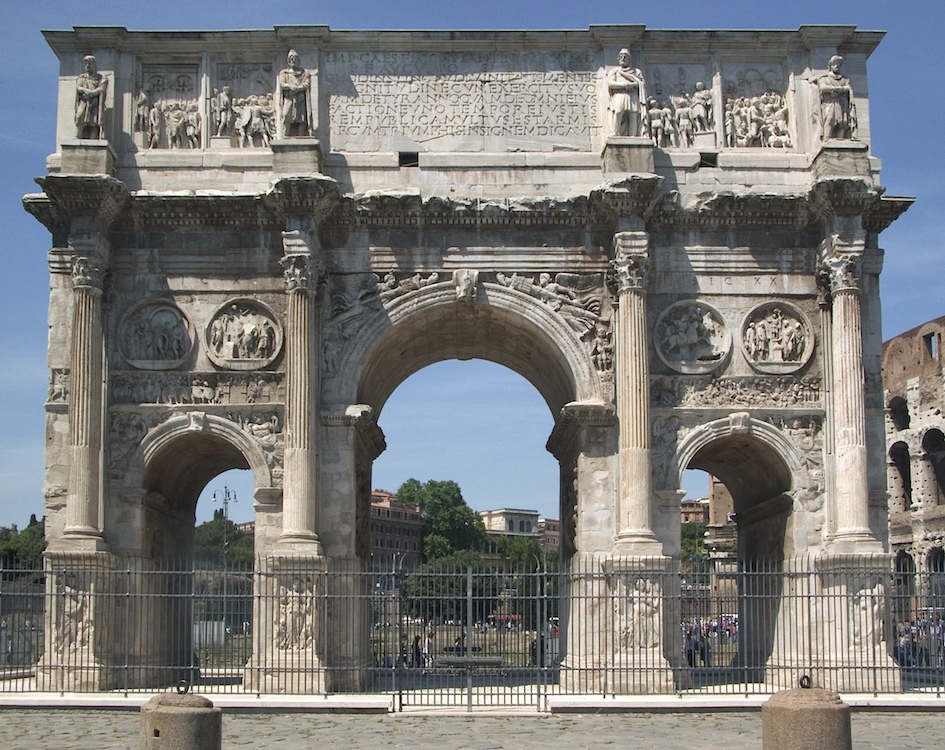

Arch of Constantine
The largest surviving Roman Triumphal Arch. It is situated between Colosseum and Palatine Hill to commemorate Constantine's victory over Maxentius at the Battle of Mivian Bridge.
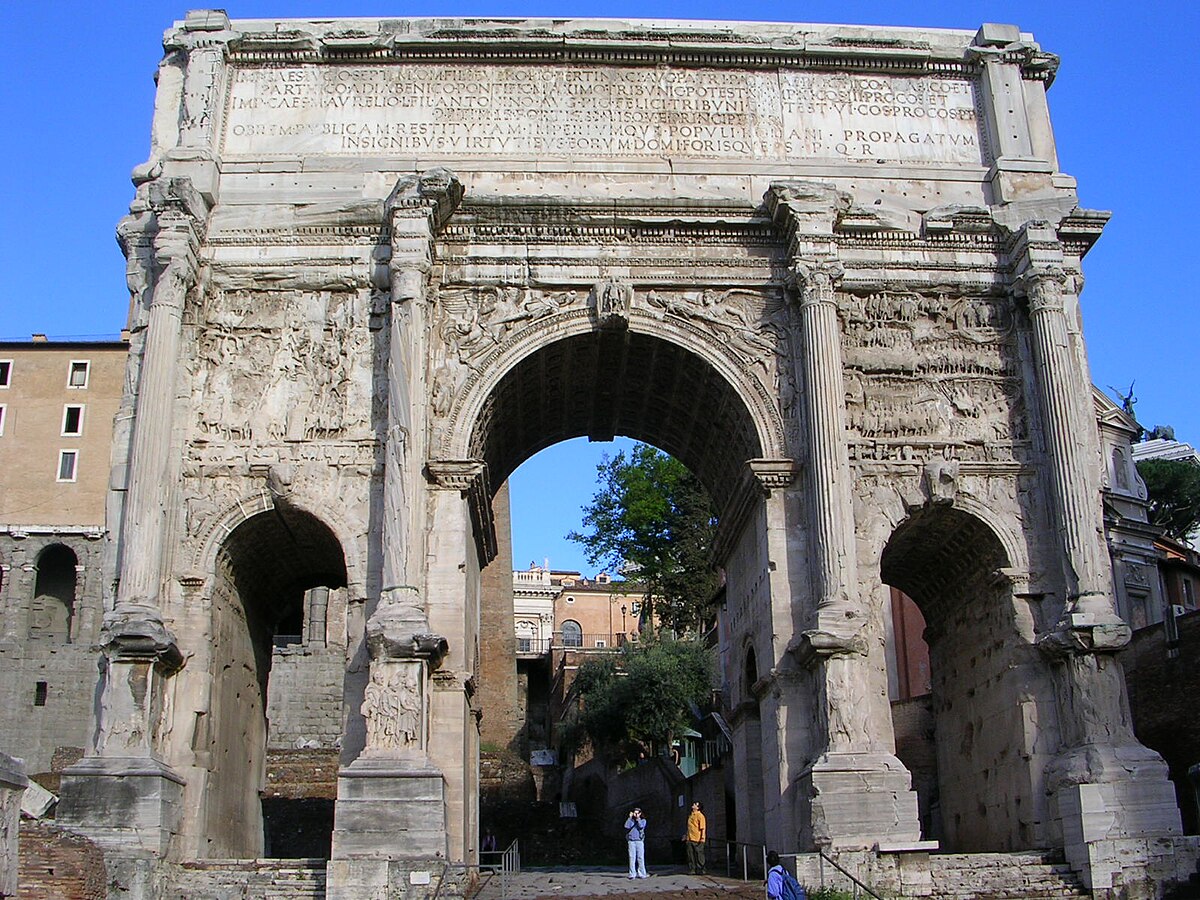

Arch of Septimius Severus
It is a white marble triumphal arch dedicated in 203 ADS to commemorate the Parthian victories of Emperor Septimius Severus and his two sons, Caracalla and Geta, in the two campaigns against the Parthians.
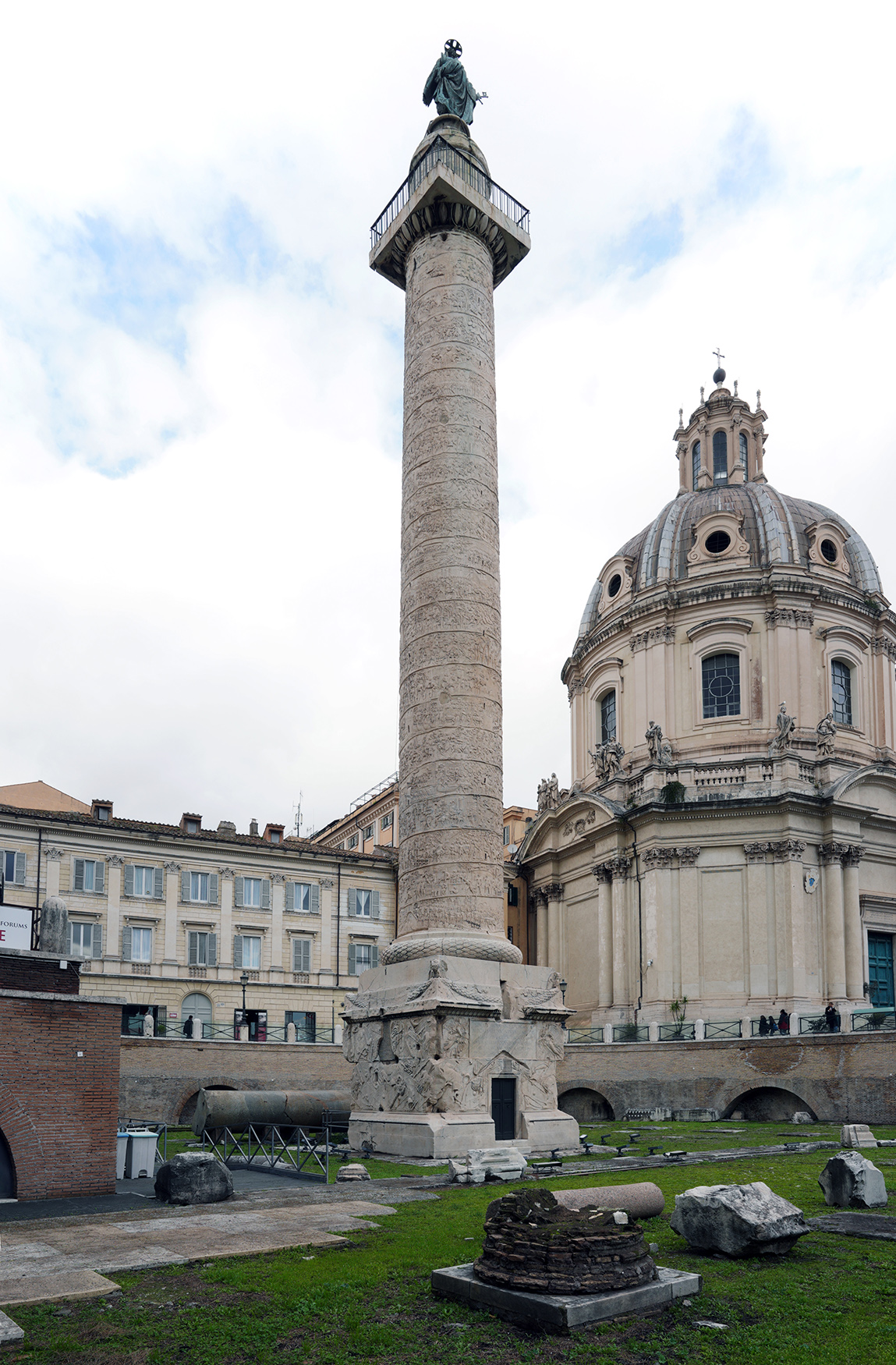

Trajan’s Column
Is a Roman triumphal column in Rome, Italy, that commemorates Roman emperor Trajan's victory in the Dacian Wars.

Pompey’s Column
is a Roman triumphal column in the city of Alexandria, Egypt. It commemorates the victory of Roman emperor Diocletian over an Alexandrian revolt. It is the only ancient monument still standing in Alexandria in its original location today.
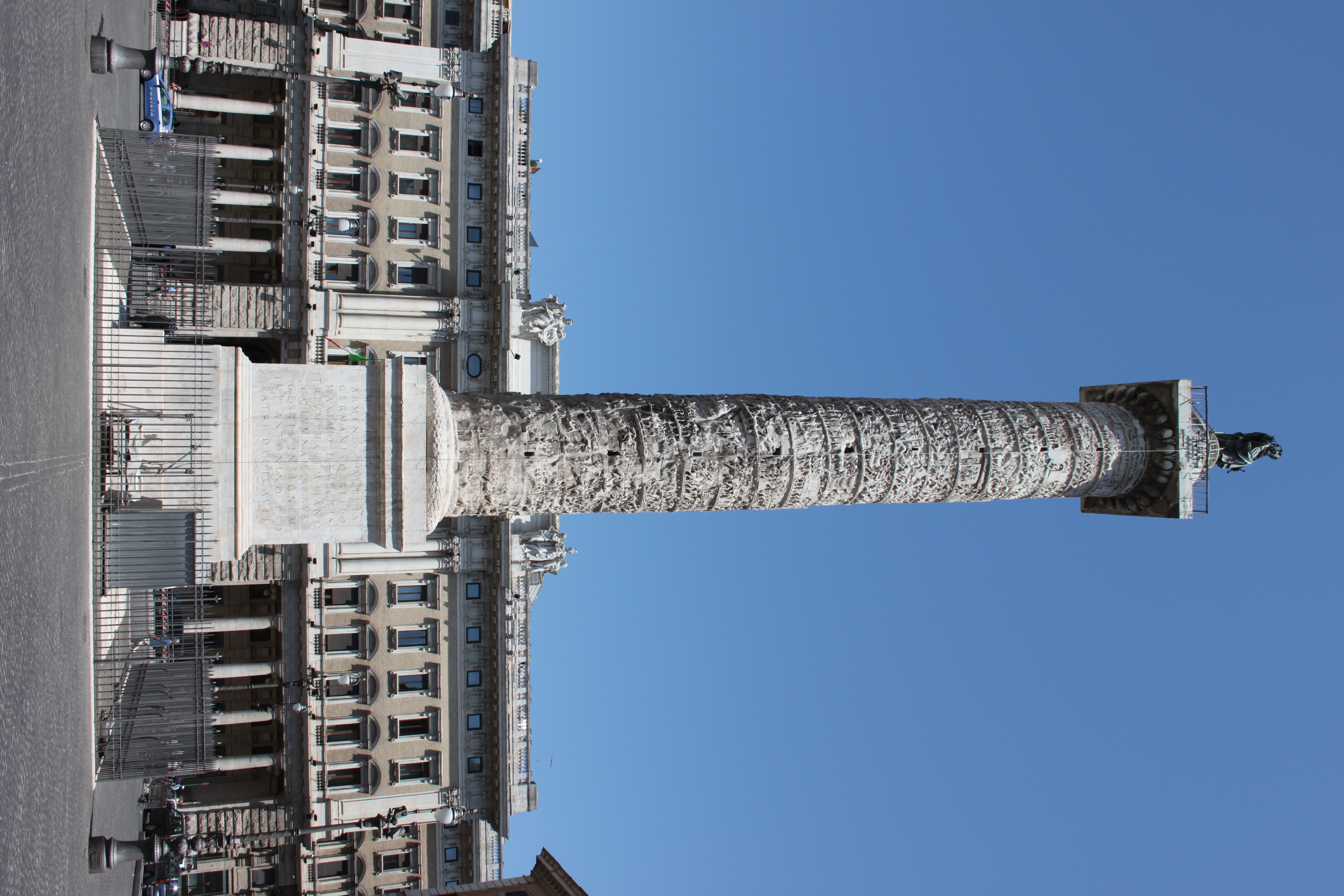

Column of Marcus Aurelius
Inspired by the Trajan's Column and has the honorary inscription. The base was decorated with reliefs. The column is of Doric order and made up of 28 cylindrical stone blocks of "Lunense” marble, white Carrara marble, sculpted with relief friezes. It depicts the military campaigns of Marcus Aurelius against the Germans and the Sarmatians.

Column of Antoninus Pius
It was erected in Rome to commemorate Antoninus and his wife Faustina by his adoptive sons and heirs, Marcus Aurelius and Lucius Verus after the emperor's death in 161.

Circus
A U-shaped or enclosed arena for chariot and horse racing.

Drainage
Cloaca Maxima is one of the world's earliest sewage systems and the main sewage system.
Adequate
A structure or a bridge designed to convey fresh water, usually 3 canal or river supported by piers and arches, or a tunnel. Latin, aquaeductus. - ‘conveyance of water.
Pons
Latin word for bridges, employing the use of arches built from stone.
Palaces
A royal residence, sometimes a seat of government or religious centre.

Pantheon
Served as a temple tomb and church. It is the world's largest unreinforced concrete dome.
Domus
The patrician townhouse: Has party walls on its flanks and an enclosed back area, its principal opening to the exterior is located on the street front.
Inusla
A structure or a multi-storey structure with commercial premises and workshops (tabernae) at street level.
Villa
A large classical Roman country house with an estate.
Atrium House
A Roman dwelling type in which the building surrounds a main central space, the atrium, open to the sky.
Pars urbana
Living area
Pars Rustica
Working Area
Odeon
Large Theatre