2.2 and 2.3- Spinal Cord and Somatic Nervous System and Intro to the visceral nervous system
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
brain and spinal cord
Anatomical division of the CNS
nerves that emanate from the CNS
Anatomical division of the PNS
12
How many pairs of cranial nerves are there?
Foramina of the skull
What do the cranial nerves pass through?
Spinal nerves
carry impulses to and from the spinal cord, # can change species to species
Intervertebral foramina
openings providing for exit of spinal nerves
Sensory and motor pathways
Two MAIN divisions of the PNS
somatic and autonomic
two divisons of the PNS motor pathways
sympathetic and parasympathetic
two divisions of the autonomic nervous system
afferent
Is sensory information afferent or efferent
efferent
Is motor information afferent of efferent
SAME
pneumonic to remember direction of sensory vs. motor
Sensory neurons
- Cell bodies found in the dorsal root ganglia
- Sensory axons travel down the dorsal root
- receive sensory input from the external environment
Somatic motor neurons
- Cell bodies found in the ventral horn
- Axons leave via the ventral root
- Provide voluntary motor control over skeletal muscle
Spinal nerve
What is created when there is a mix of sensory and motor axons in the are just distal to the dorsal root ganglion
Epaxial muscles
-Dorsal musculature
-Makes up the intrinsic back muscles
Dorsal rami
What innervates the epaxial muscles (intrinsic back muscles)
Hypaxial muscles
Muscles that lie ventral to the vertebral column, can include limb muscles
Dermamyotome
becomes the dermis and musculature of the back, ribs, and limbs - provides motor innervation to its muscle portion and sensory innervation to its skin portion
Gray matter
Brain and spinal cord tissue that appears gray with the naked eye; consists mainly of neuronal cell bodies (nuclei) and lacks myelinated axons.
White matter
Whitish nervous tissue of the CNS consisting of neurons and their myelin sheaths.
Conus medullaris
end of spinal cord that varies in legnth across mammal species
Fetuses and infants
In what point in a mammals life is the vertebral column and the spinal cord the same length
The spinal cord and vertebral column don't grow at the same rate
Why don't the spinal nerve levels and vertebral levels not match
Cauda Equina
The extension of the dorsal and ventral roots to the same numbered vertebral level
C7 and above
What part of the spinal cord has the matching spinal nerve coming out above the vertebra
Example: Spinal nerve C1 lies right above vertebra C1
T1 and down
What part of the spinal cord has the matching spinal nerve coming out below the vertebra
Example: spinal nerve T1 lies right below vertebra T1
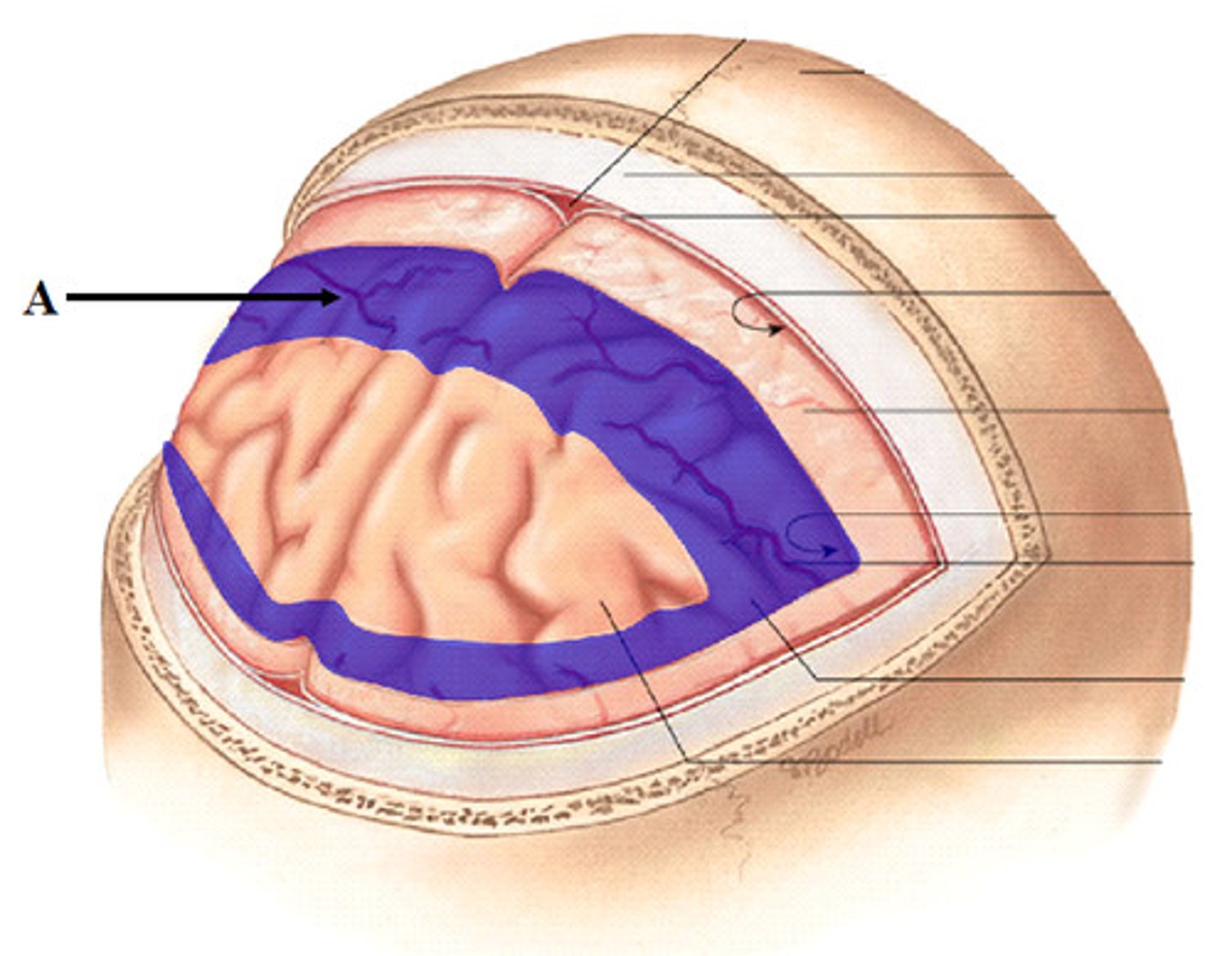
Meninges
Made up of connective tissues to support and protect
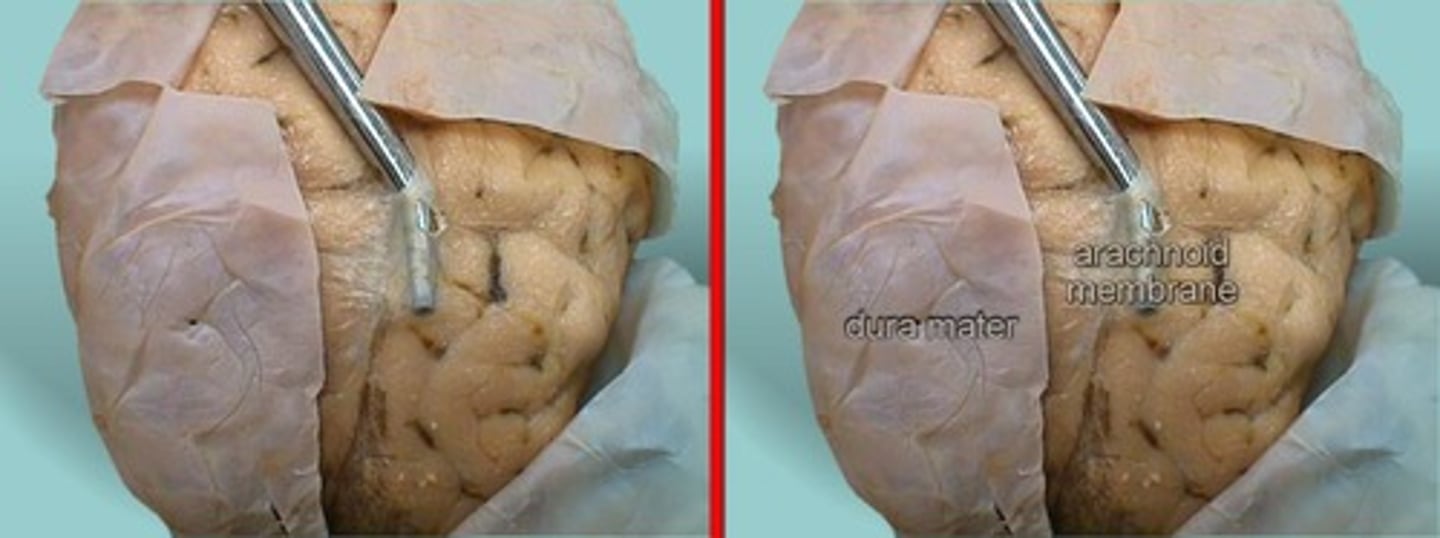
Dura mater
- thick external meningeal layer
- Tough and thick
- Continuous with the dura of the brain
- Surrounded by extradural fat in the epidural space
- Extends laterally onto the proximal spinal nerves
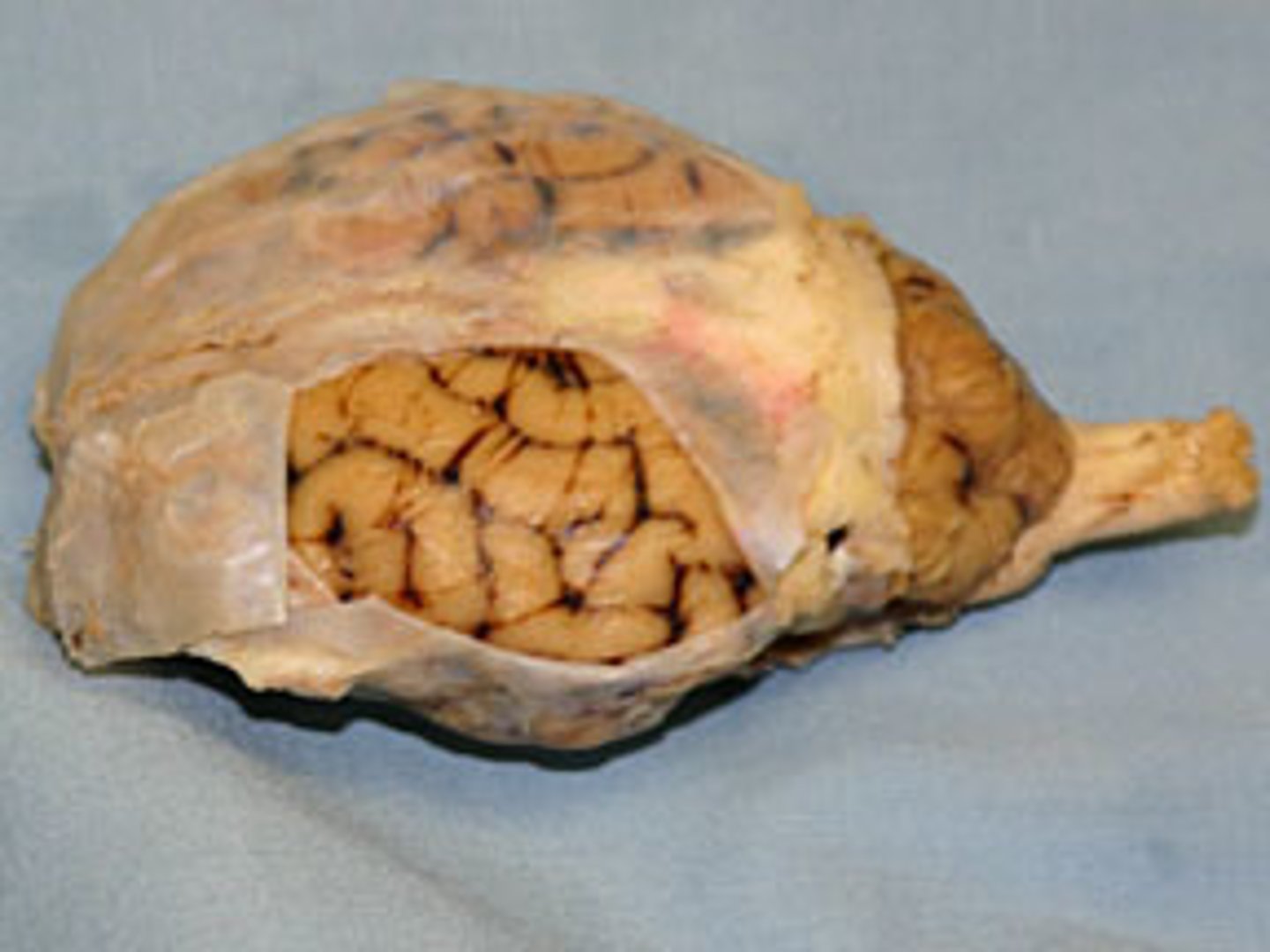
Arachnoid mater
- Just deep to the dura mater
- Thin and delicate
- Encloses the subarachnoid spaces
- continuous with the subarachnoid space around the brain
Pia mater
- innermost meningeal layer
- Completely adherent to the spinal cord
- Creates denticulate ligaments that anchor the the spinal cord to the dura
Smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and glands
What does the autonomic nervous system innervate
sympathetic nervous system
active during moments of great effort, hyperarousal, and acute stress (fight or flight)
parasympathetic nervous
active during moments of energy intake and relates to aspects of everyday life (rest and digest)
Body wall
Where are parasympathetics not present in the body
Lateral horn
In the sympathetic nervous system, what houses the pre-ganglionic sympathetic cell bodies
T1-L4
What spinal cord levels are pre-ganglionic cell bodies found in
paravertebral ganglion
What holds the post-ganglionic cell bodies in the sympathetic nervous system
prevertebral ganglia
The paravertebral ganglion typically holds the post-ganglionic cell bodies in the sympathetic nervous system
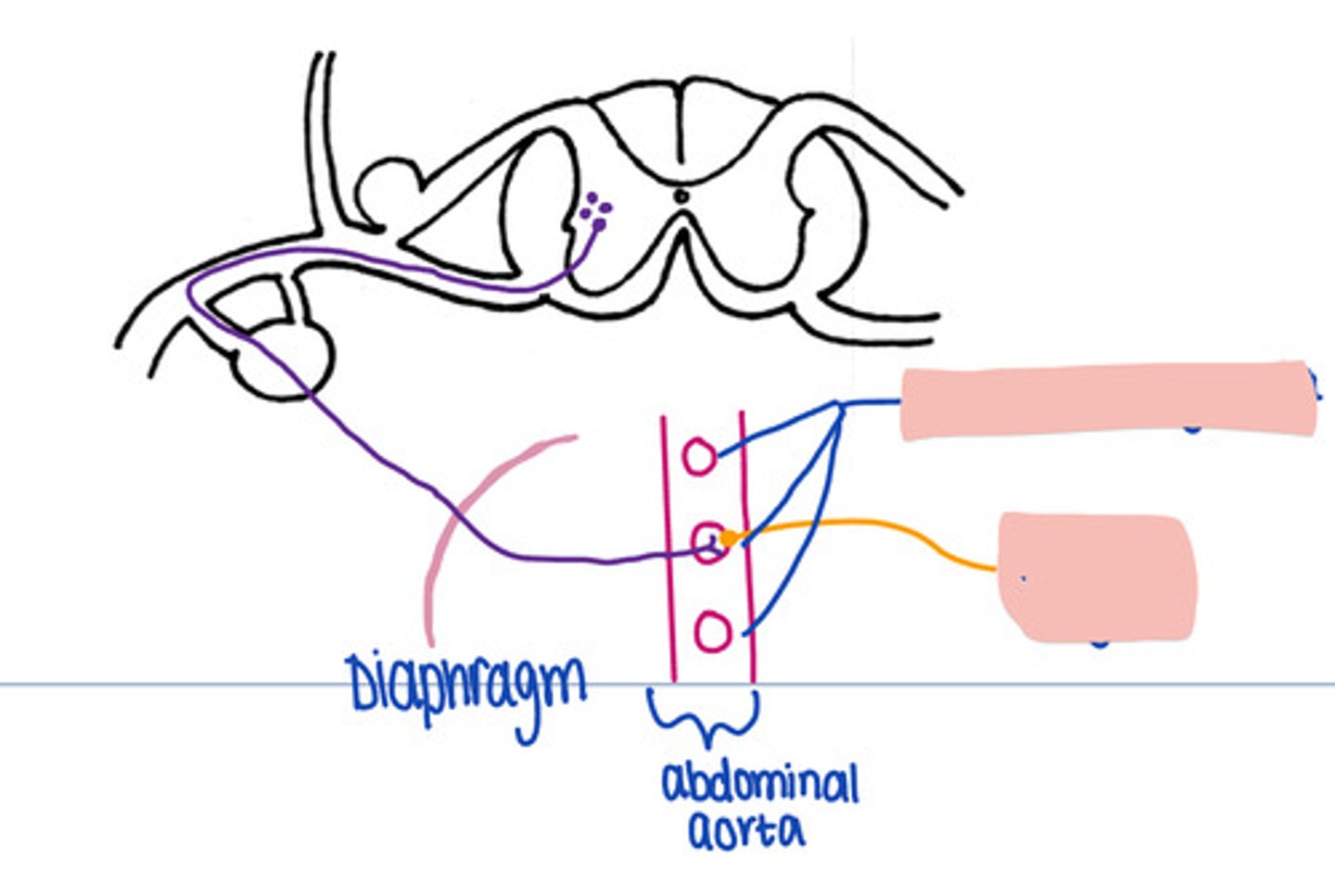
BUT what is the exception that holds the post-ganglionic cell bodies whenever they are going to the body cavity caudal to the diaphragm
Sympathetic chain
the lineup of paravertebral ganglia
Sympathetic pathways
Which nervous system have these pathways:
- To the body wall and limbs
- To the body cavity cranial to the abdominal diaphragm
- To the body cavity caudal to the abdominal diaphragm
Parasympathetic pathways
Which nervous system have these pathways:
- Head and neck
- Body caudal to the neck including ONLY the thorax, foregut, and midgut
- Body caudal to the neck including ONLY the hindgut and pelvic viscera
White ramus communicons
Since the preganglionic sympathetic axons only enter from T1-L4, what connects the spinal nerves tot he sympathetic trunk
At all levels
What level can these be found on:
- Somatic motor cell bodies in the ventral horn
- Autonomic and somatic sensory cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglion
- A postganglionic sympathetic cell body in the paravertebral ganglion
- A gray ramus communicon
- A connection to the paravertebral ganglion above and below
From T1-L4
What levels can this be found on:
- preganglionic sympathetic cell bodies in the lateral horn
- White ramus communicons
Cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves
All para vertebral ganglia that are from the superior cervical ganglion to T5 are attached to what nerve?
Brain stem
Where are the preganglionic parasympathetic cell bodies found
Vagus nerve X
In parasympathetic pathways, how do the preganglionic parasympathetic axons travel to the body
middle cervical ganglion (C5-C6)
The vagus nerve and the sympathetic chain travel together for a short period of time in pathways , where do they separate in the parasympathetic nerve pathway
in the wall of the organ
In parasympathetic nerve pathways, where are the postganglionic cell bodies found
Pain
The damage of the visceral structure, poorly localized
Non-pain
Sensations such as fullness, bloating, and cramping
Sympathetic
Which pathway does pain follow
Parasympathetic
Which pathway does non-pain follow
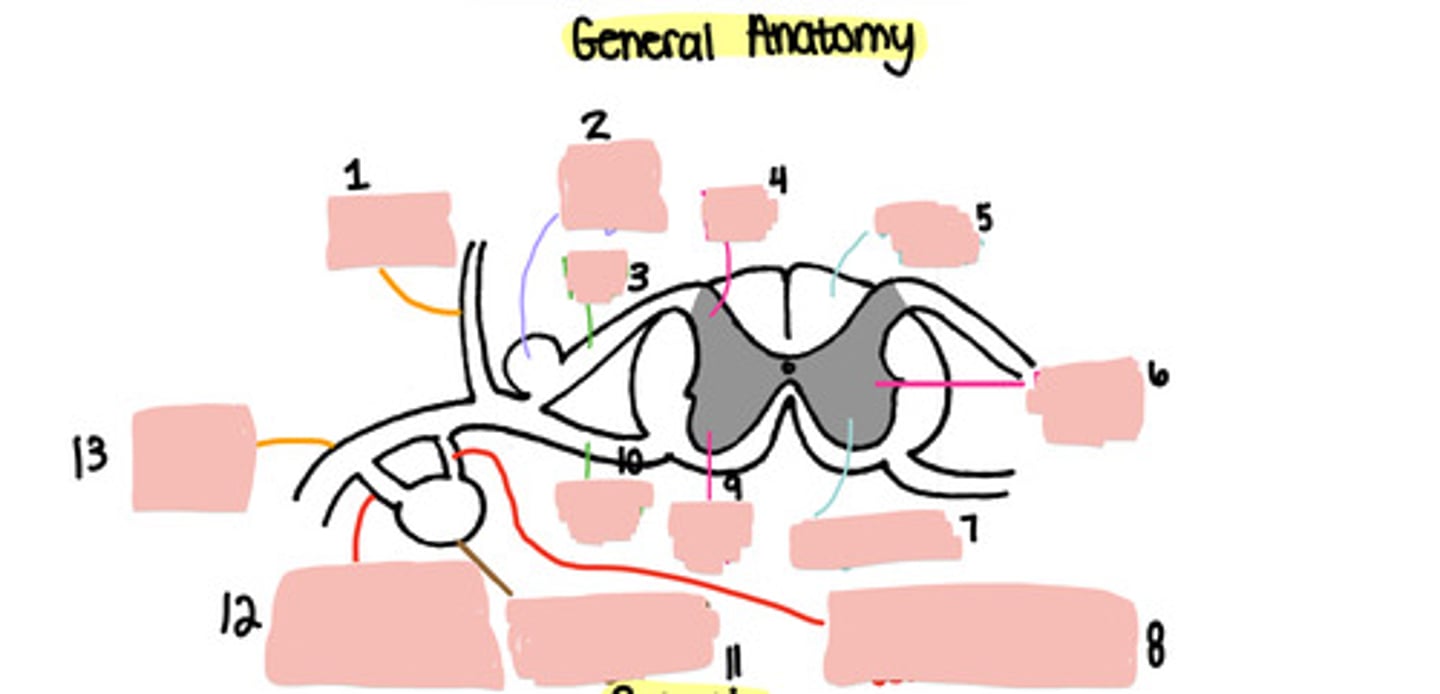
Dorsal ramus
1
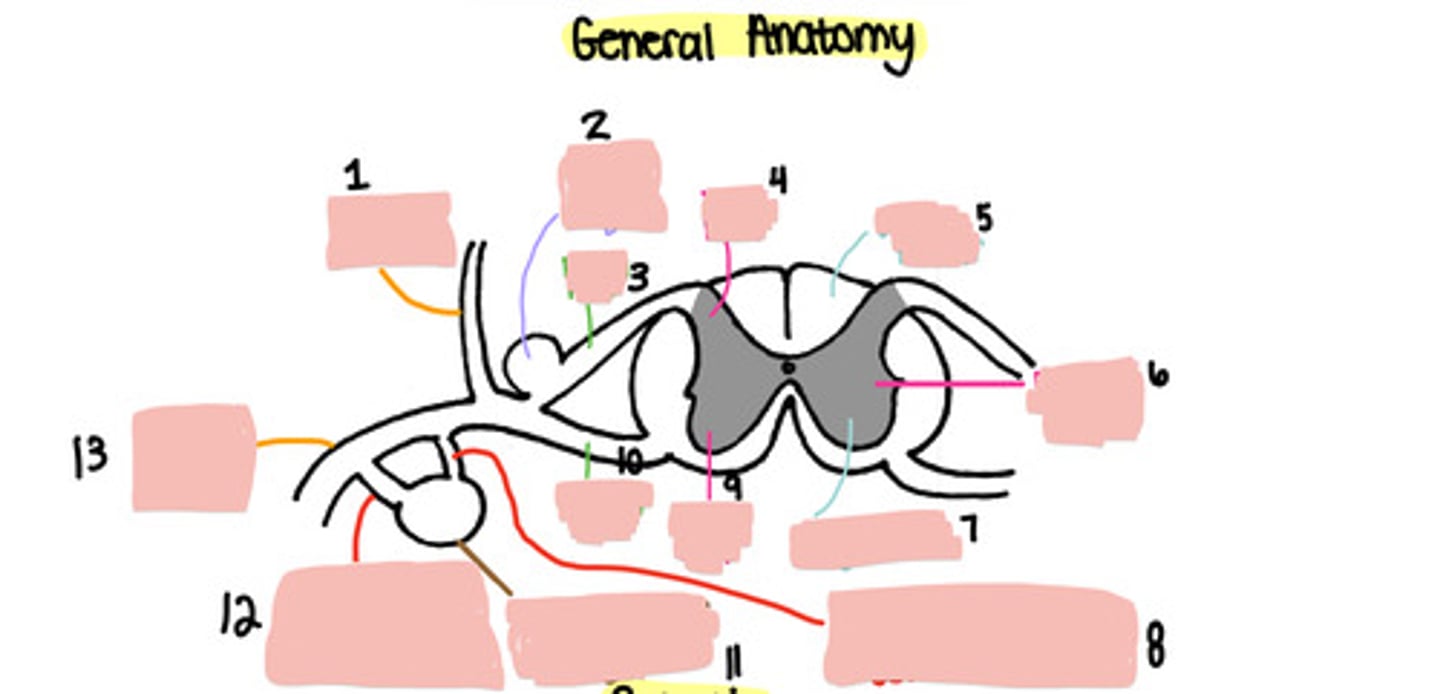
Dorsal root ganglion
2
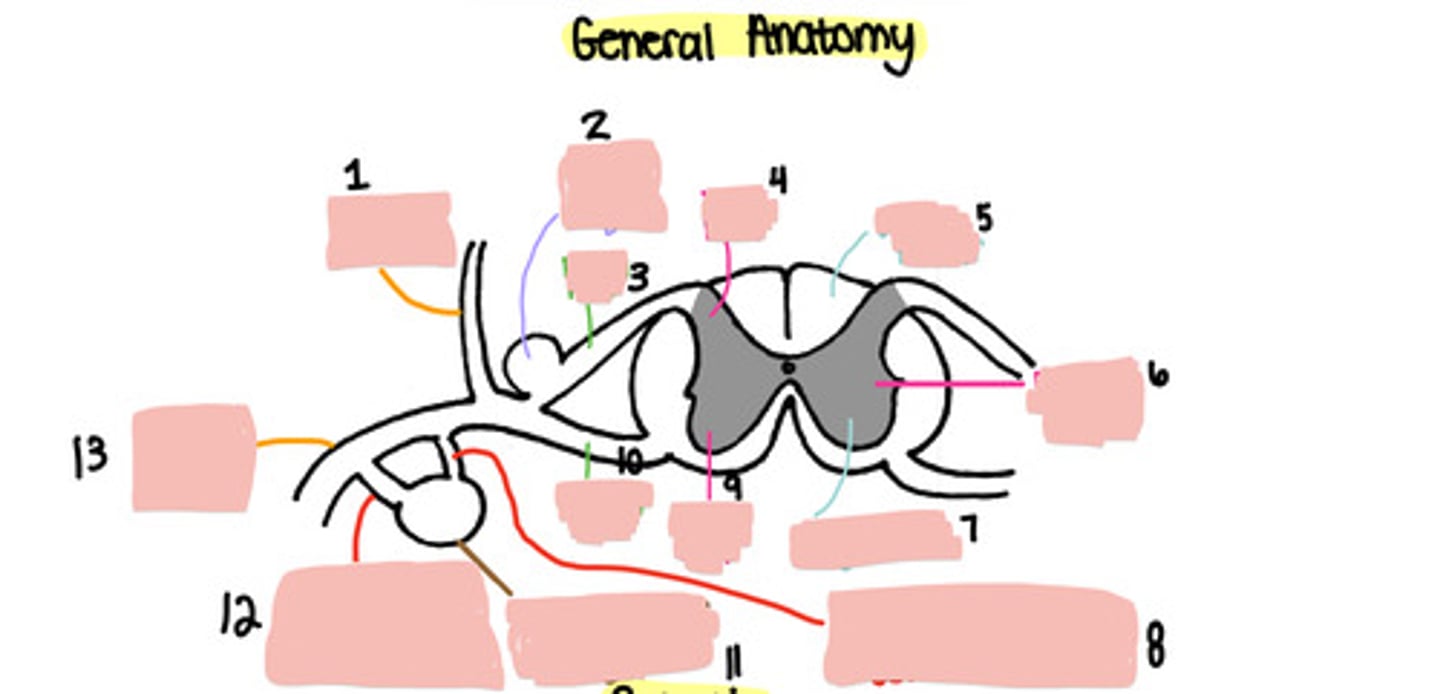
Dorsal root
3
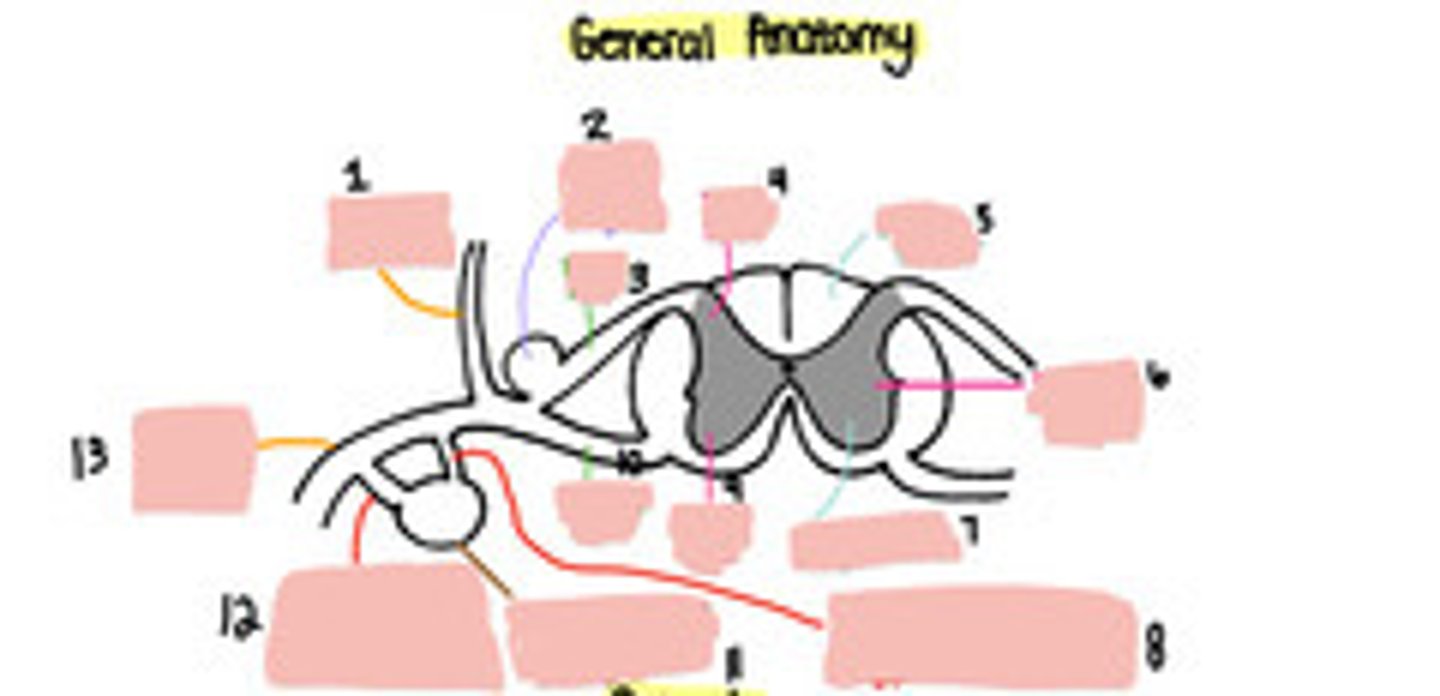
Dorsal horn
4
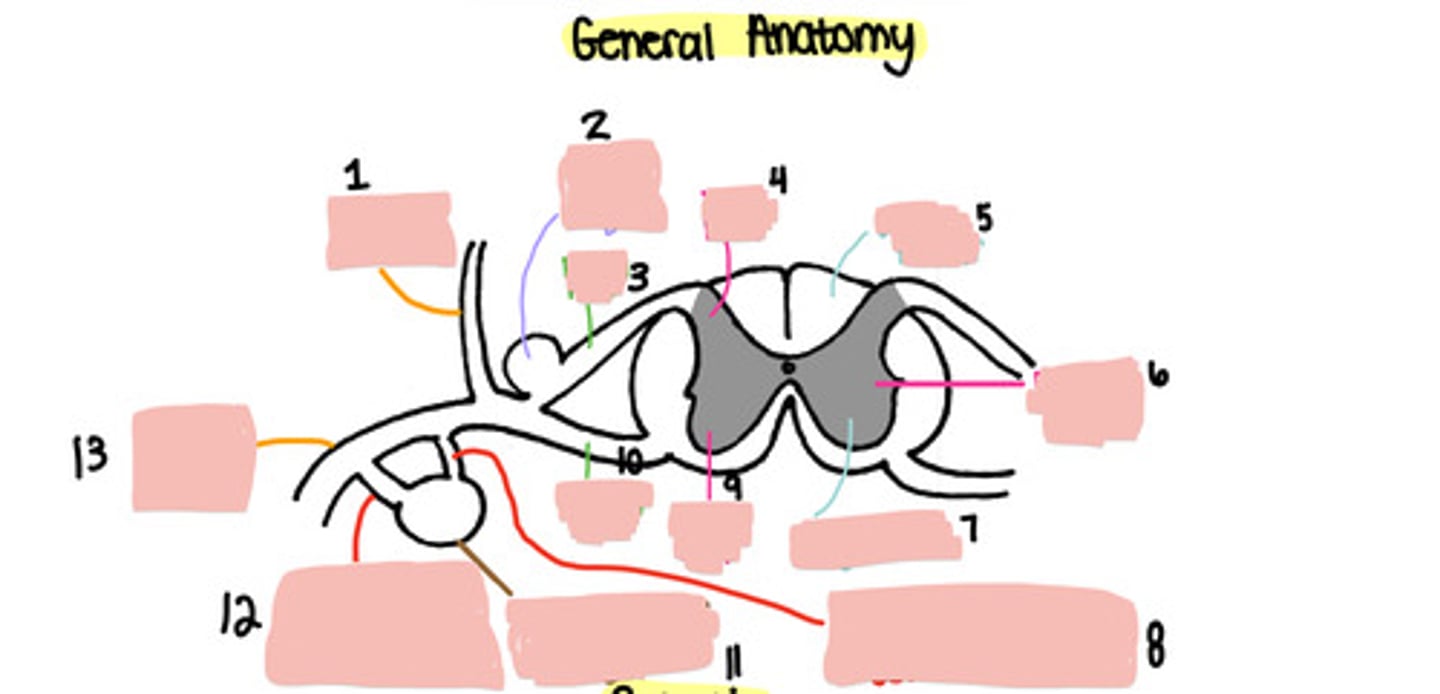
White matter
5
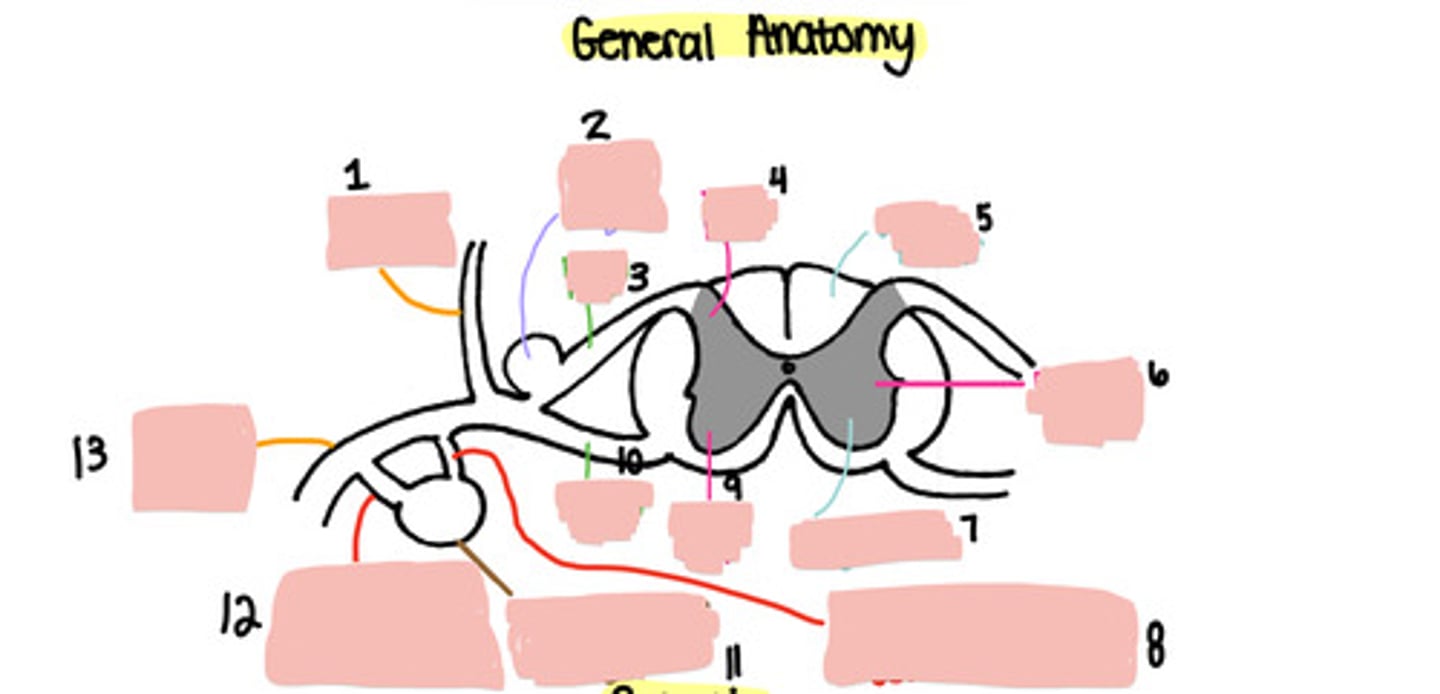
Lateral horn
6
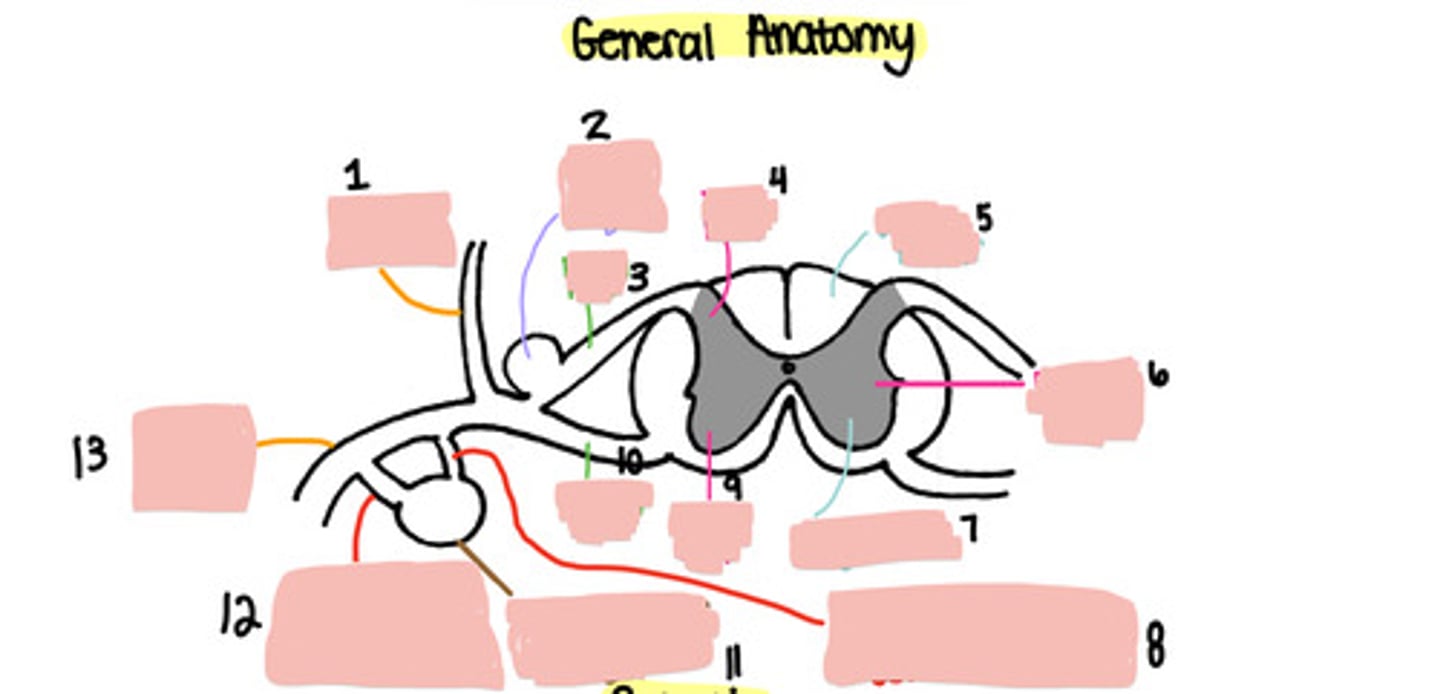
Grey matter
7
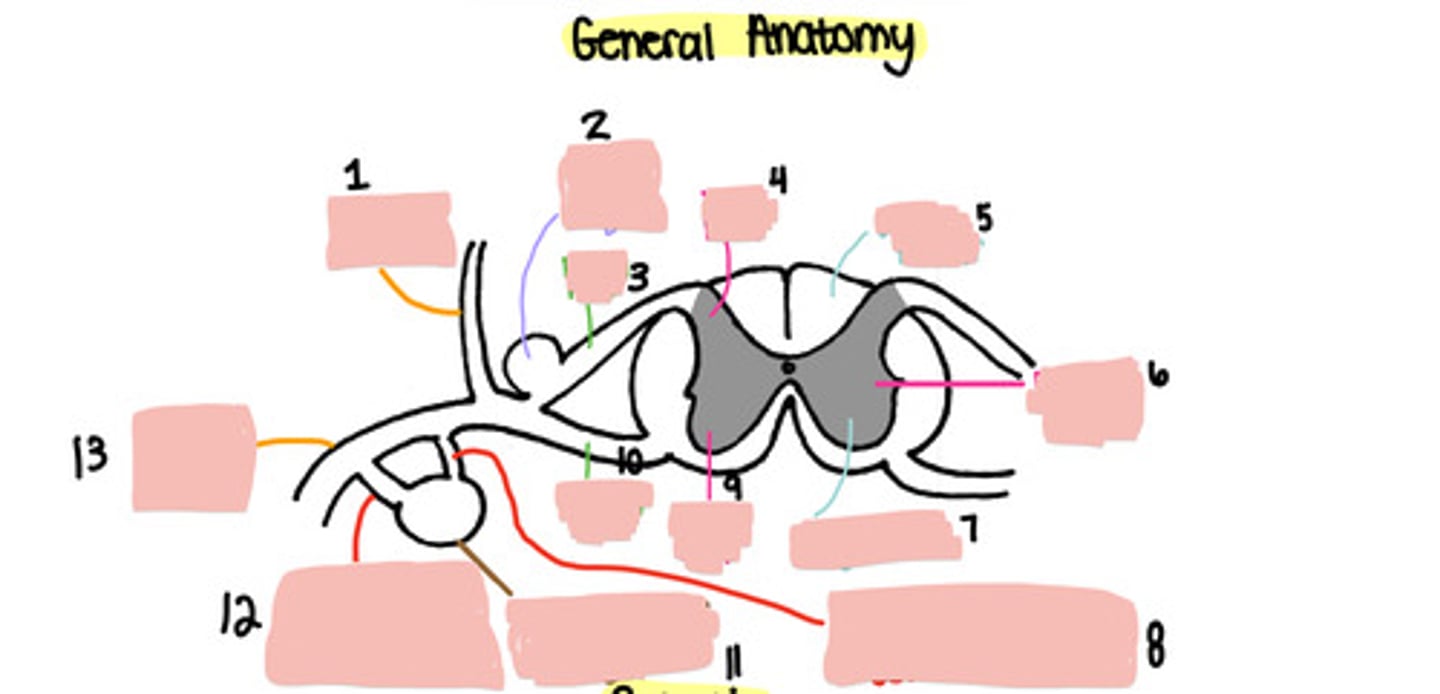
Grey ramus communicons
8
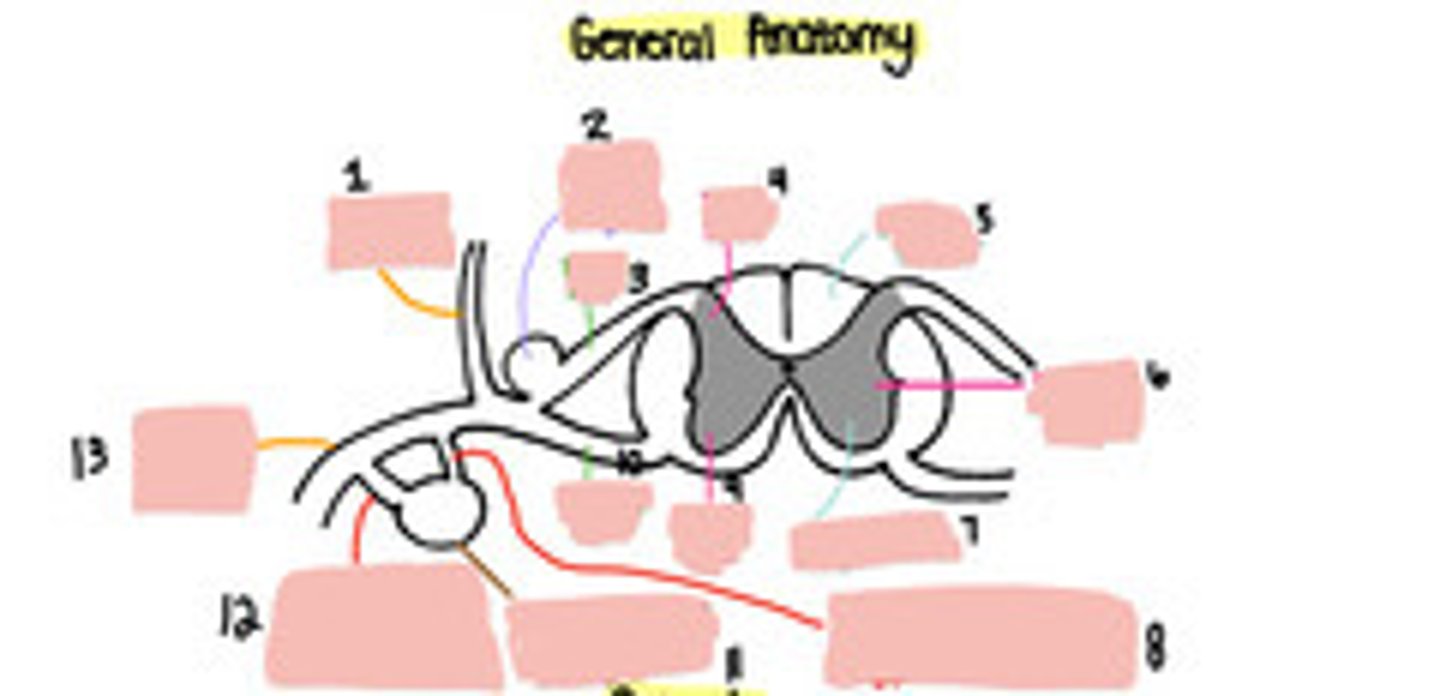
Ventral horn
9
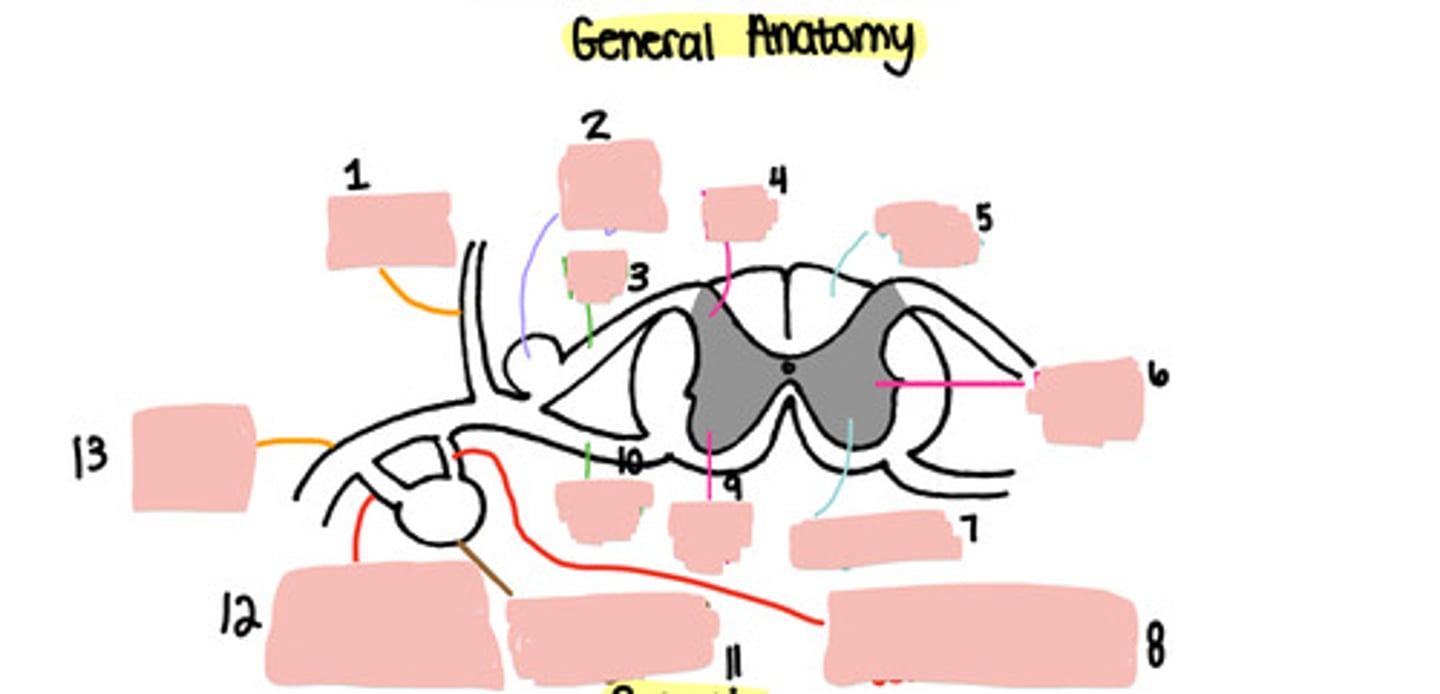
Ventral root
10
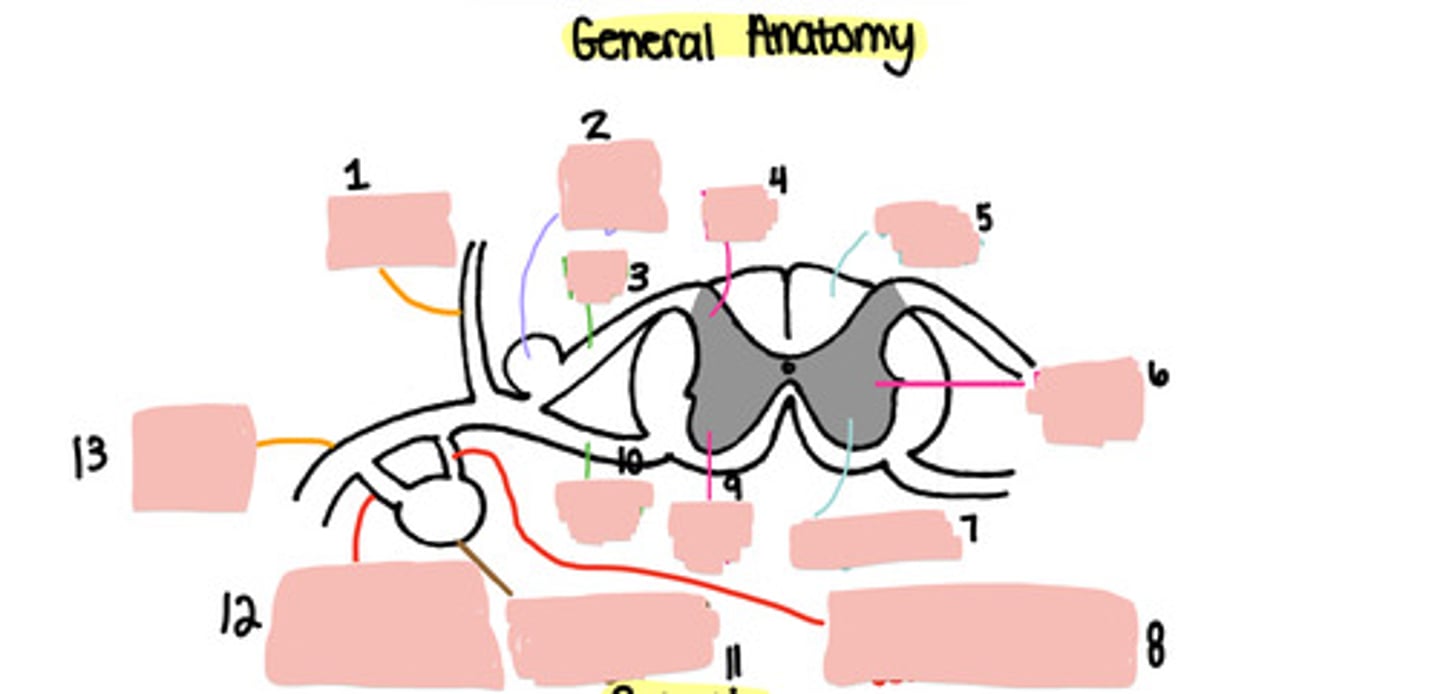
Paravertebral ganglion
11
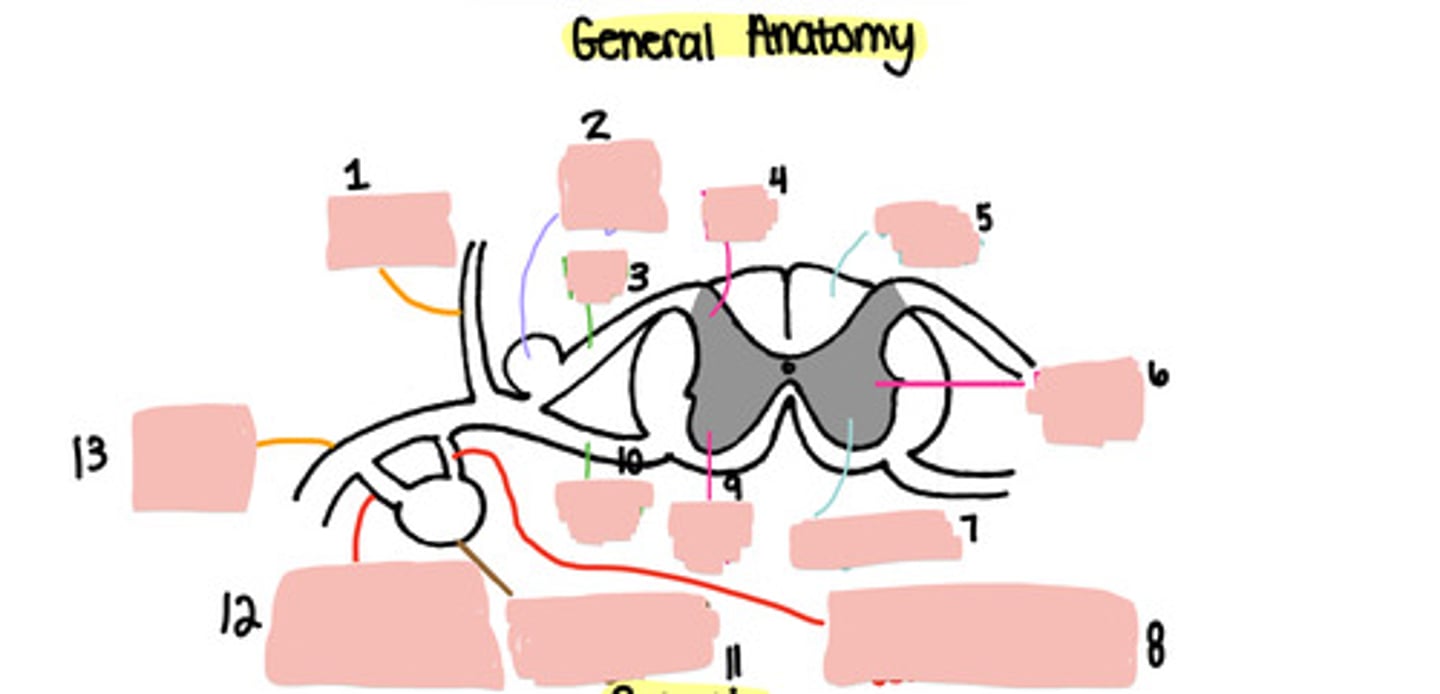
White ramus communicons
12
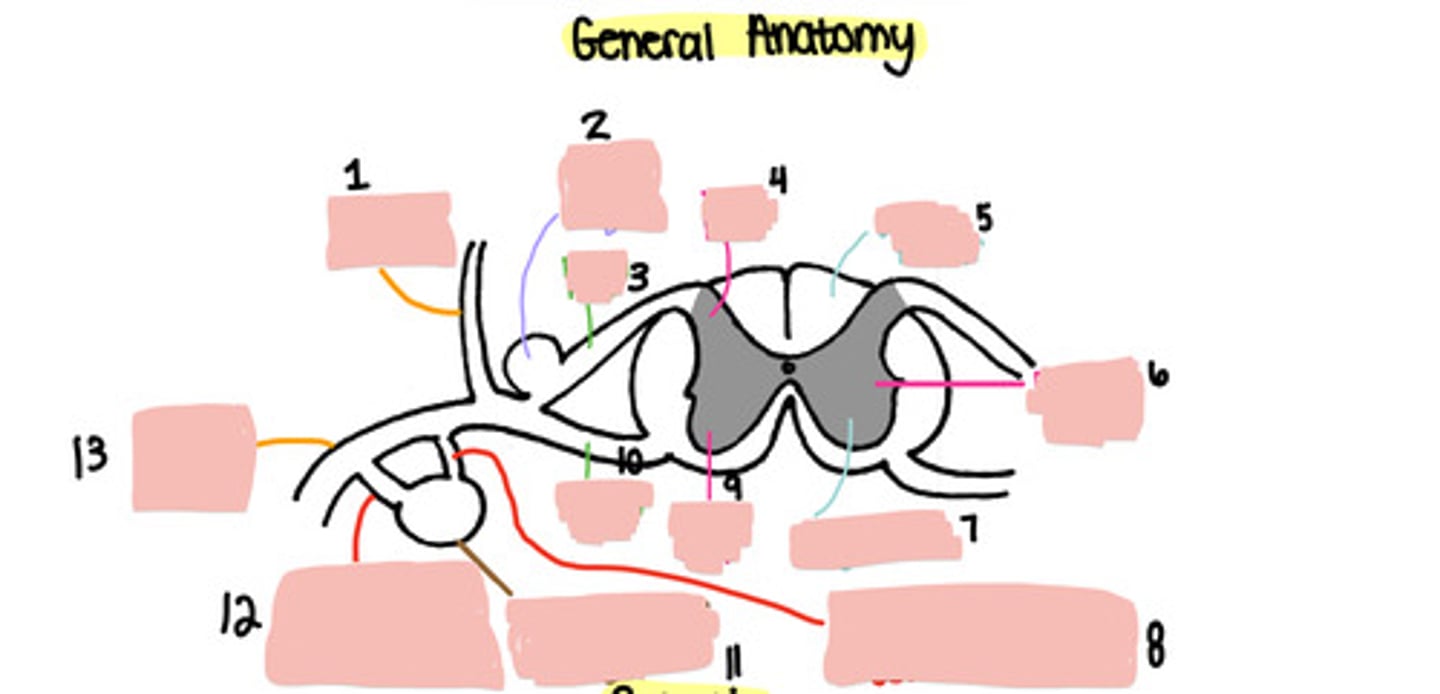
Ventral ramus
13
Sensory
Is this an example of a sensory of motor neuron
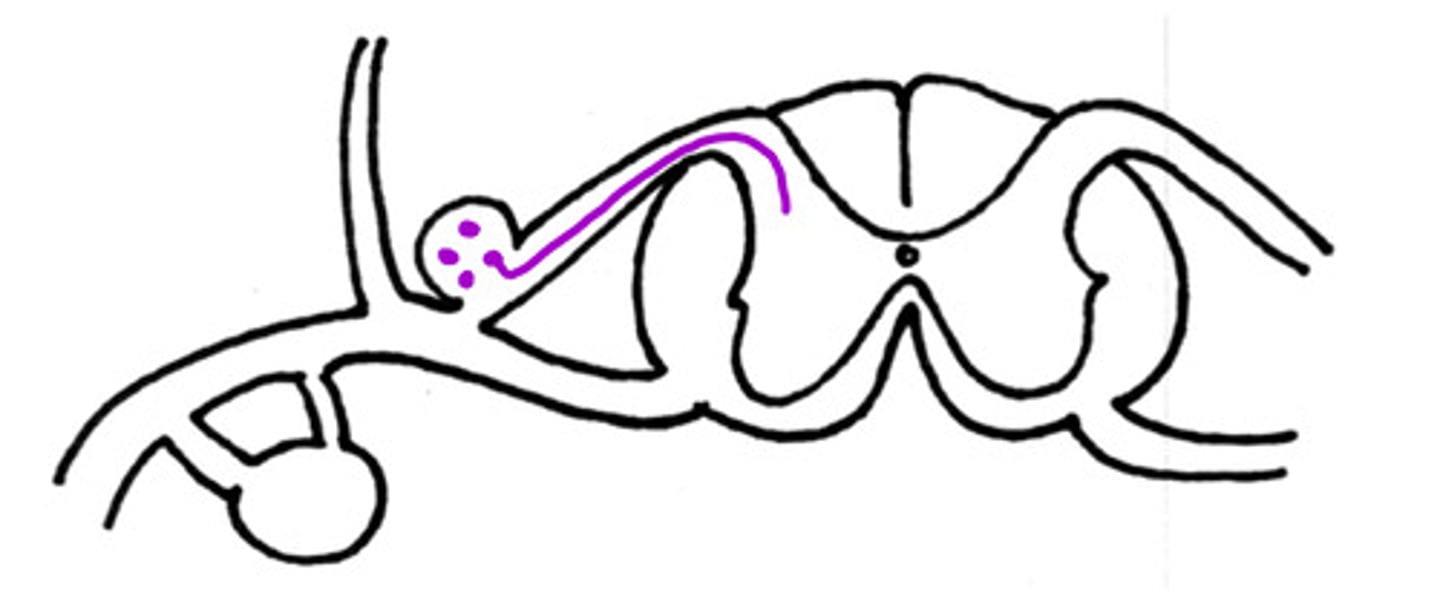
Sensory
What neuron is on the dorsal aspect
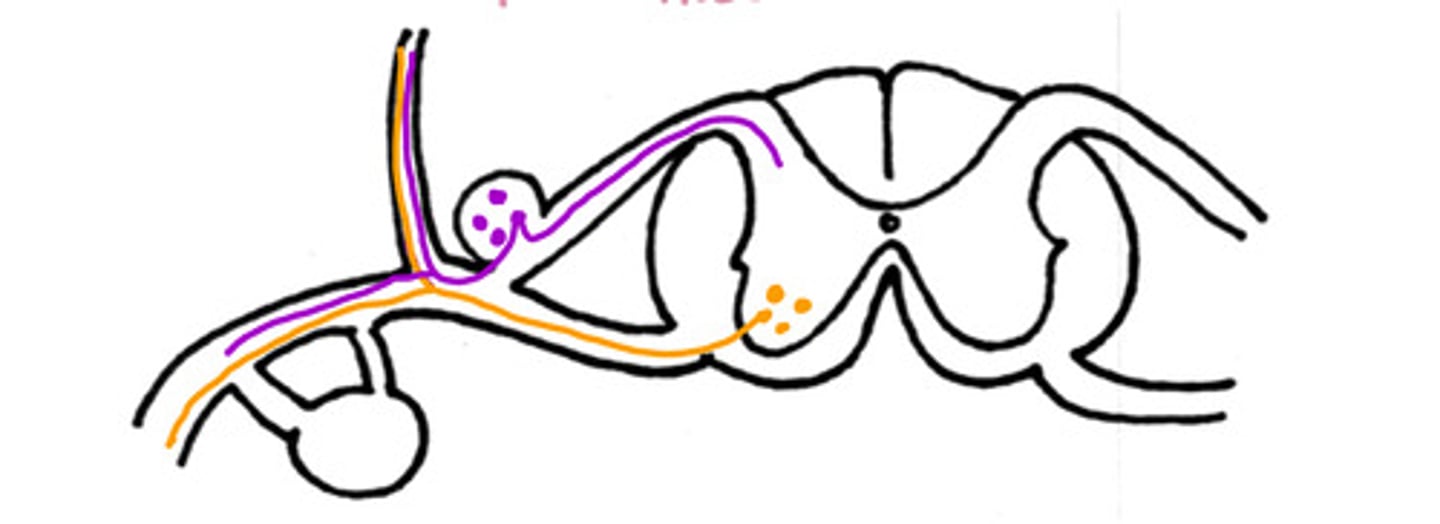
Motor
What neuron is on the ventral aspect
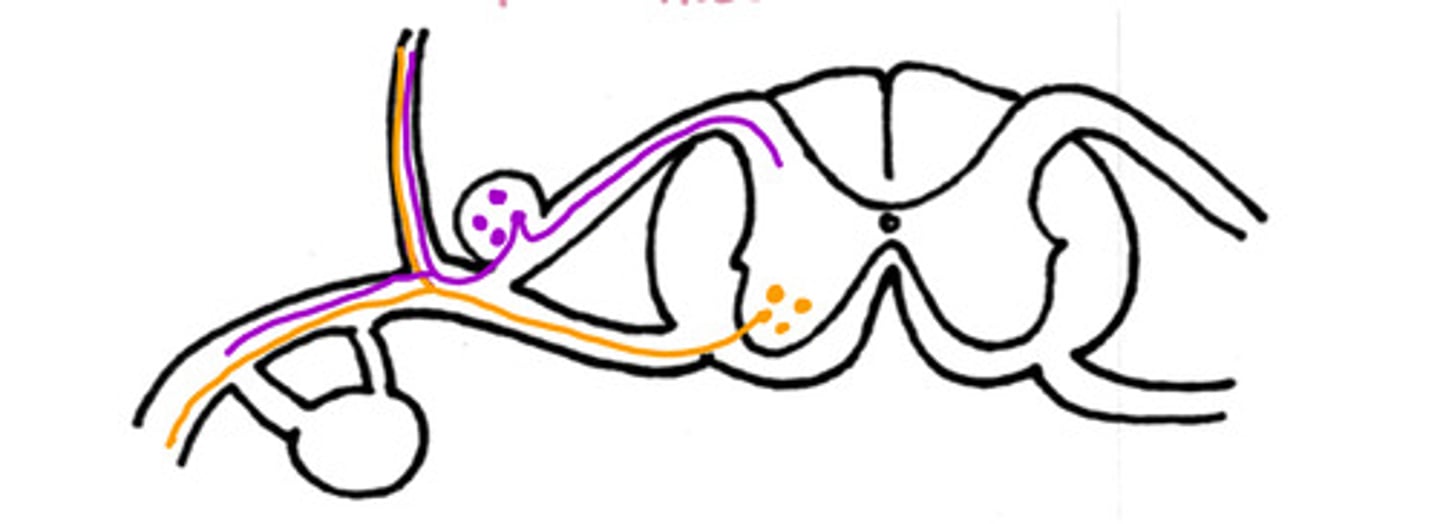
Epaxial muscles
What are the dorsal nerves innervating (general)
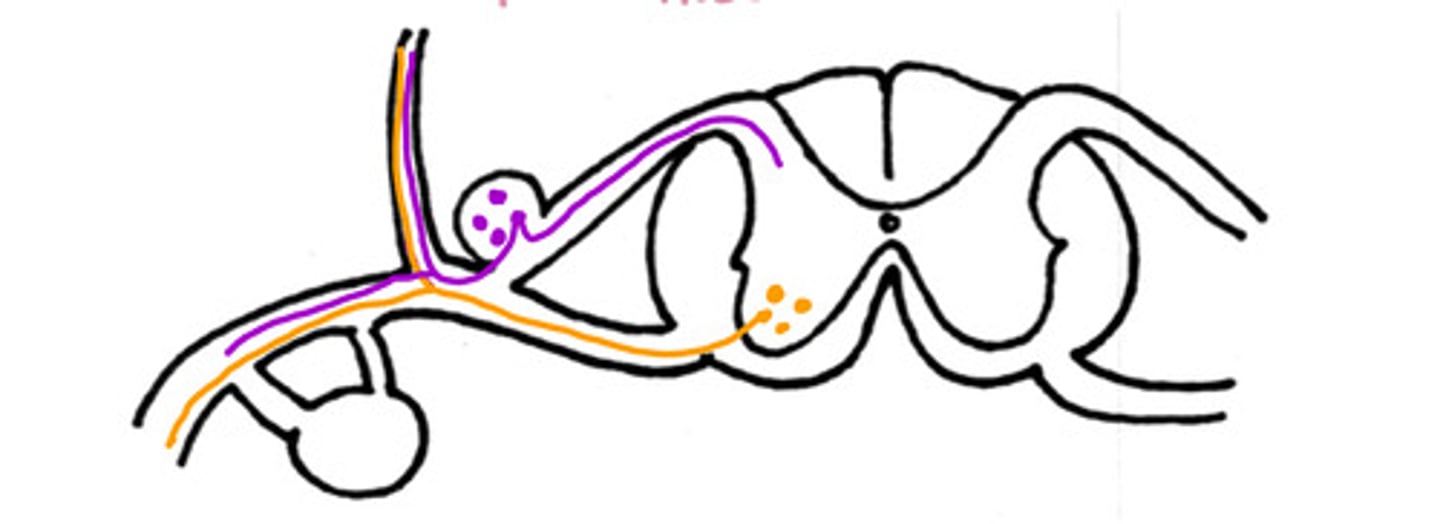
Hypaxial muscles
What are the ventral nerves innervating (general)
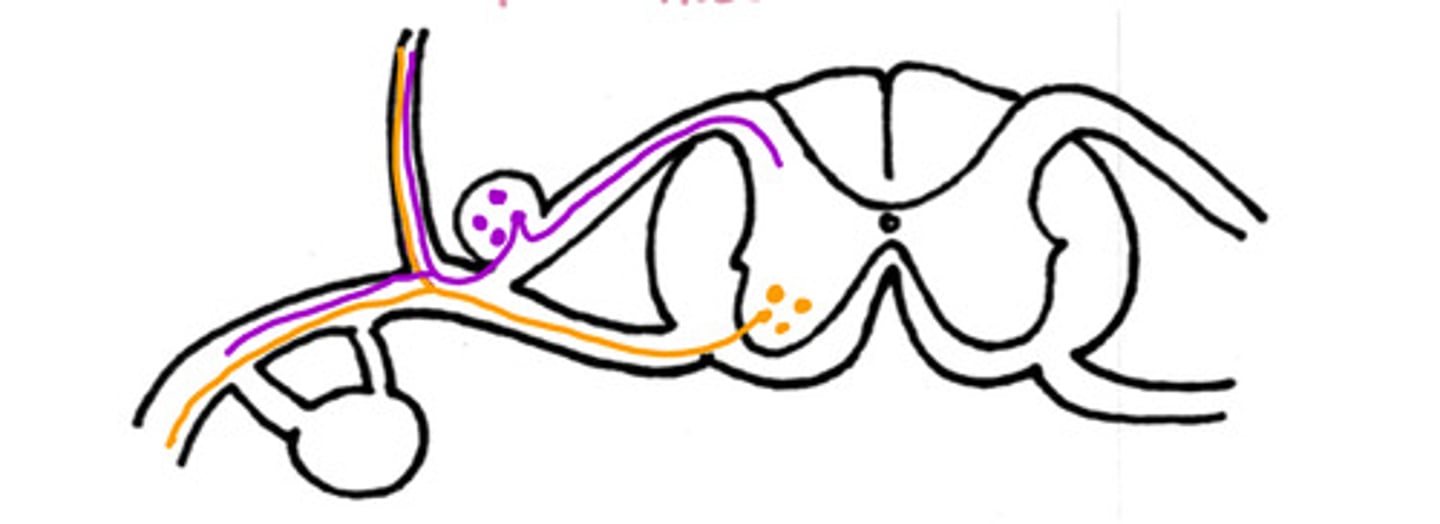
False
T/F - this could be a nerve pathway of a motor neuron to the intrinsic back muscles
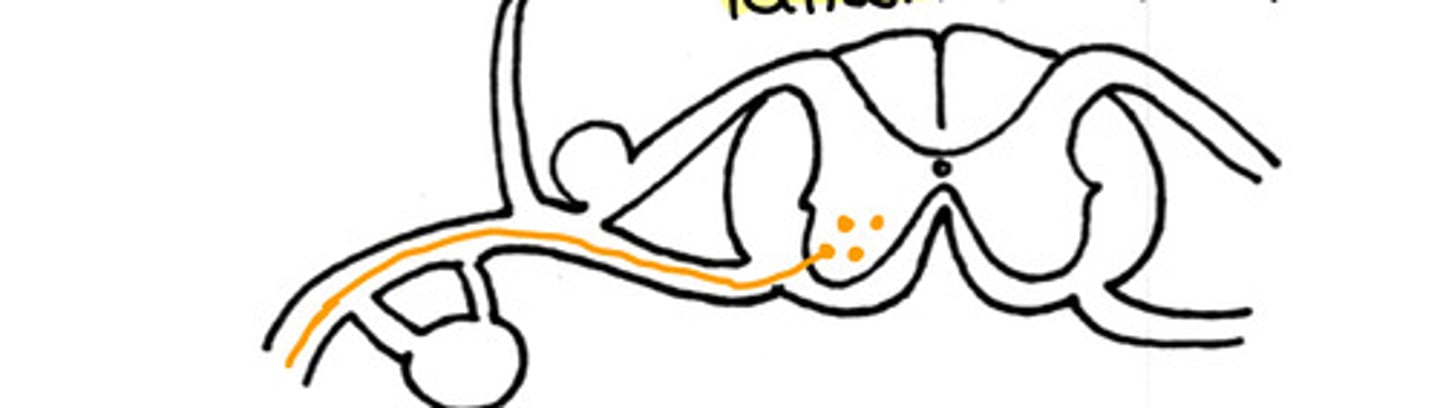
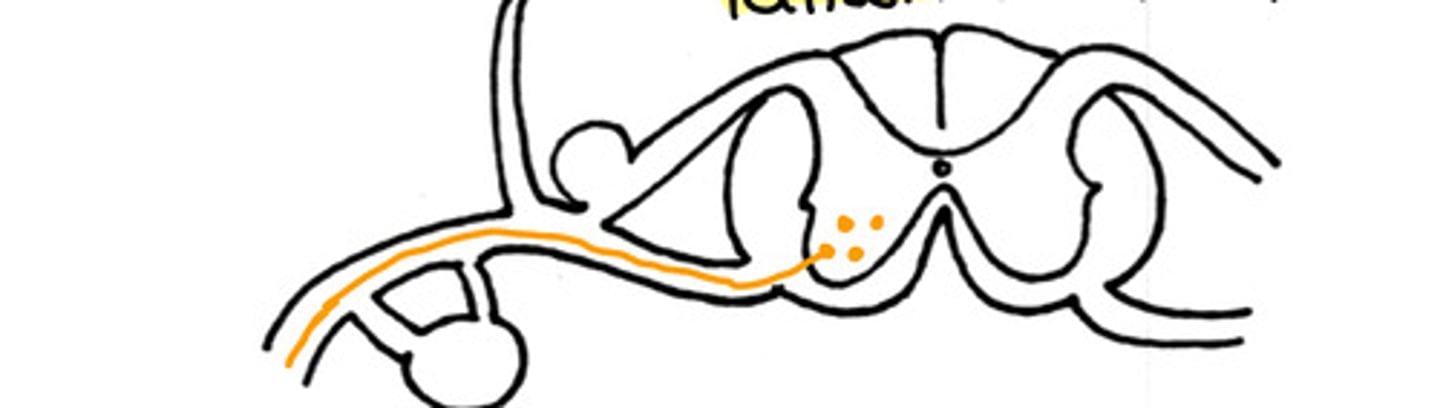
somatic motor innervation
What type of innervation is this
Somatic sensory innervation
What type of innervation is this
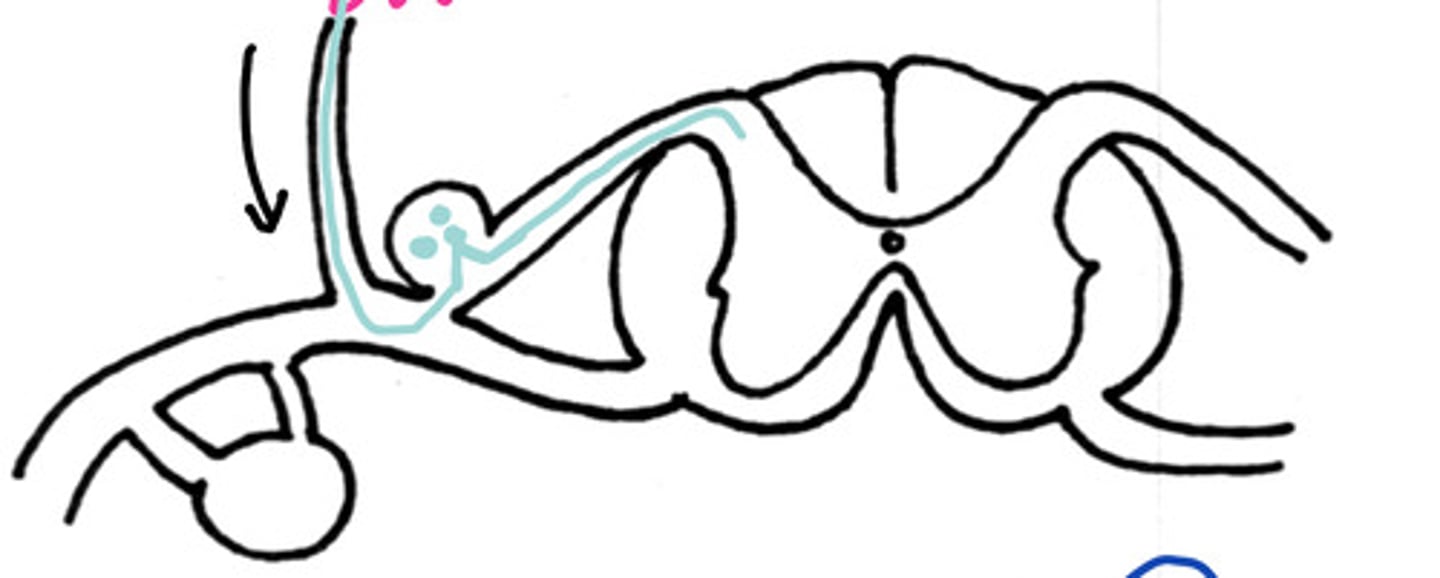
A
Would this be a somatic sensory signal from the skin on the:
A - back
B - paw
C - tail
D - Belly
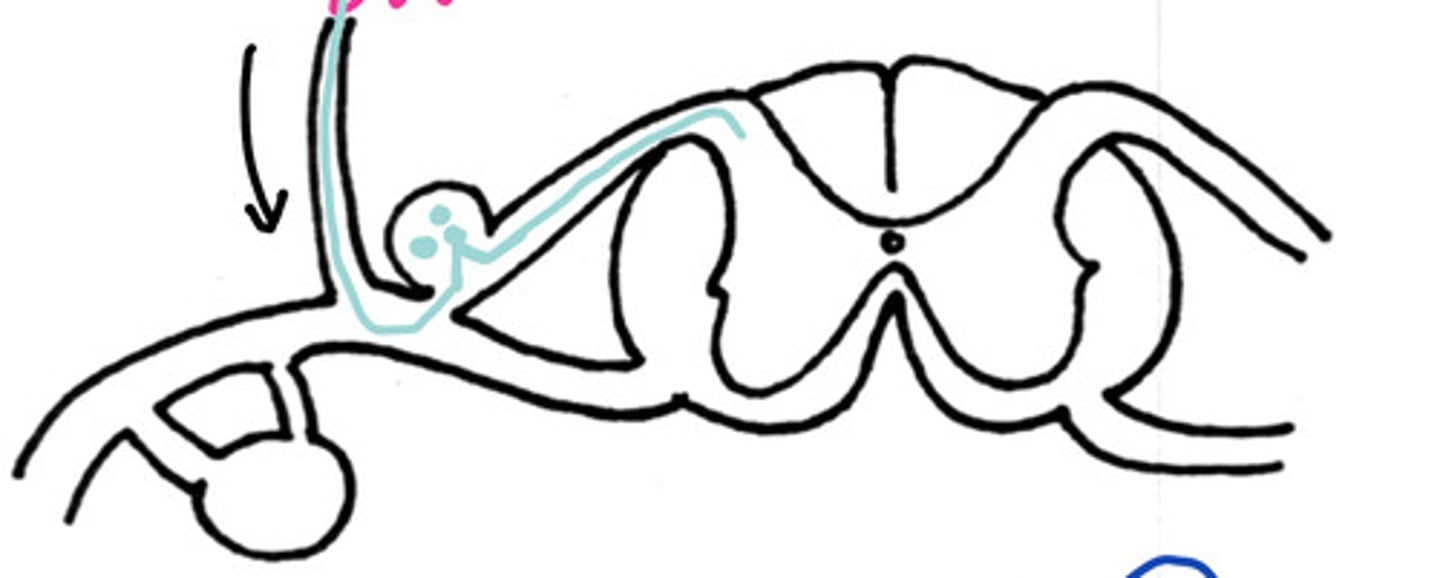
Pre-ganglionic
Is this a pre-ganglionic or post-ganglionic sympathetic pathway
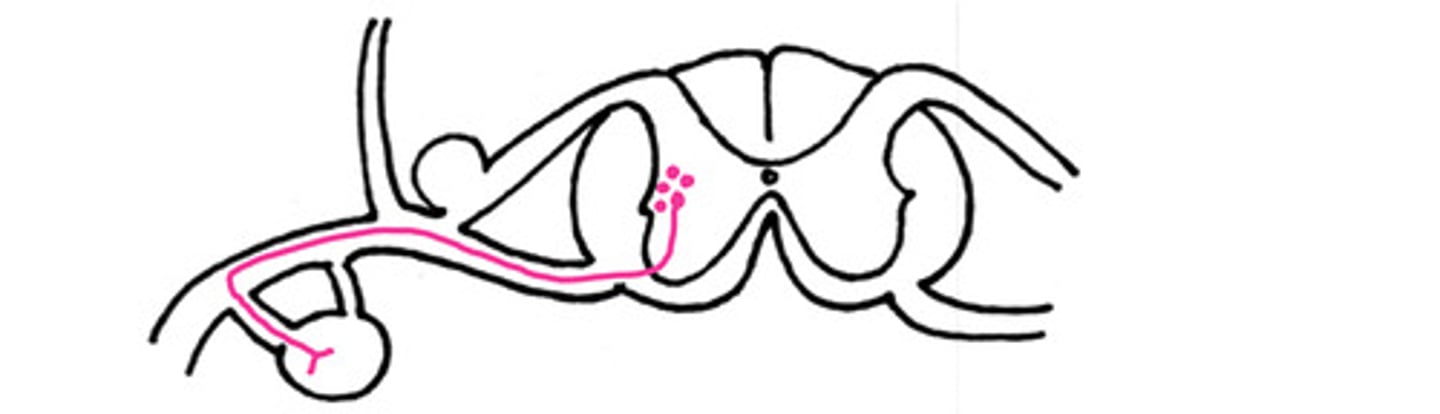
True
T/F - this could be an example of a nerve pathway that is a sympathetic pathway to the body wall
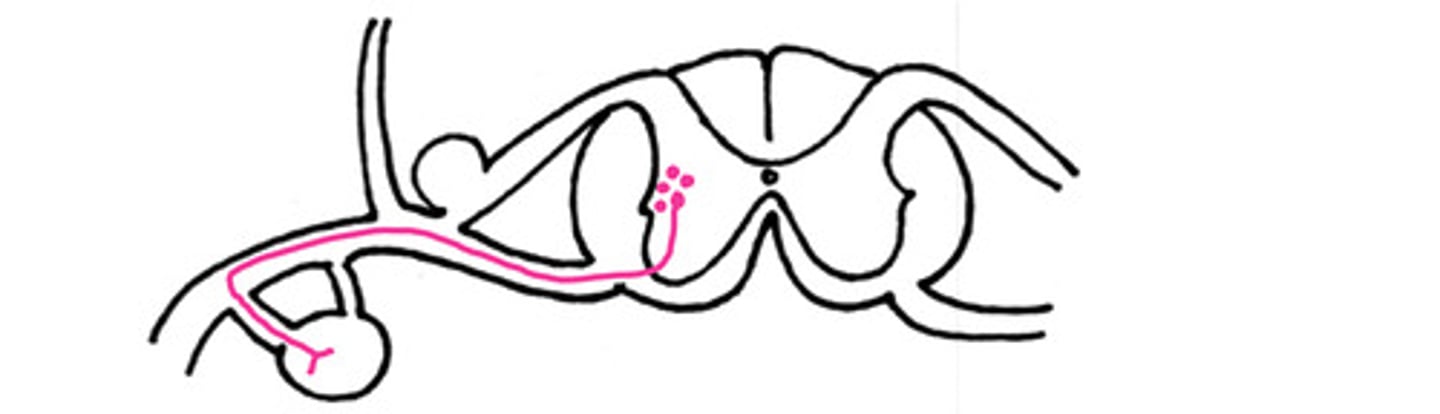
Cranial to the diaphragm
Is this a sympathetic pathway cranial or caudal to the diaphragm
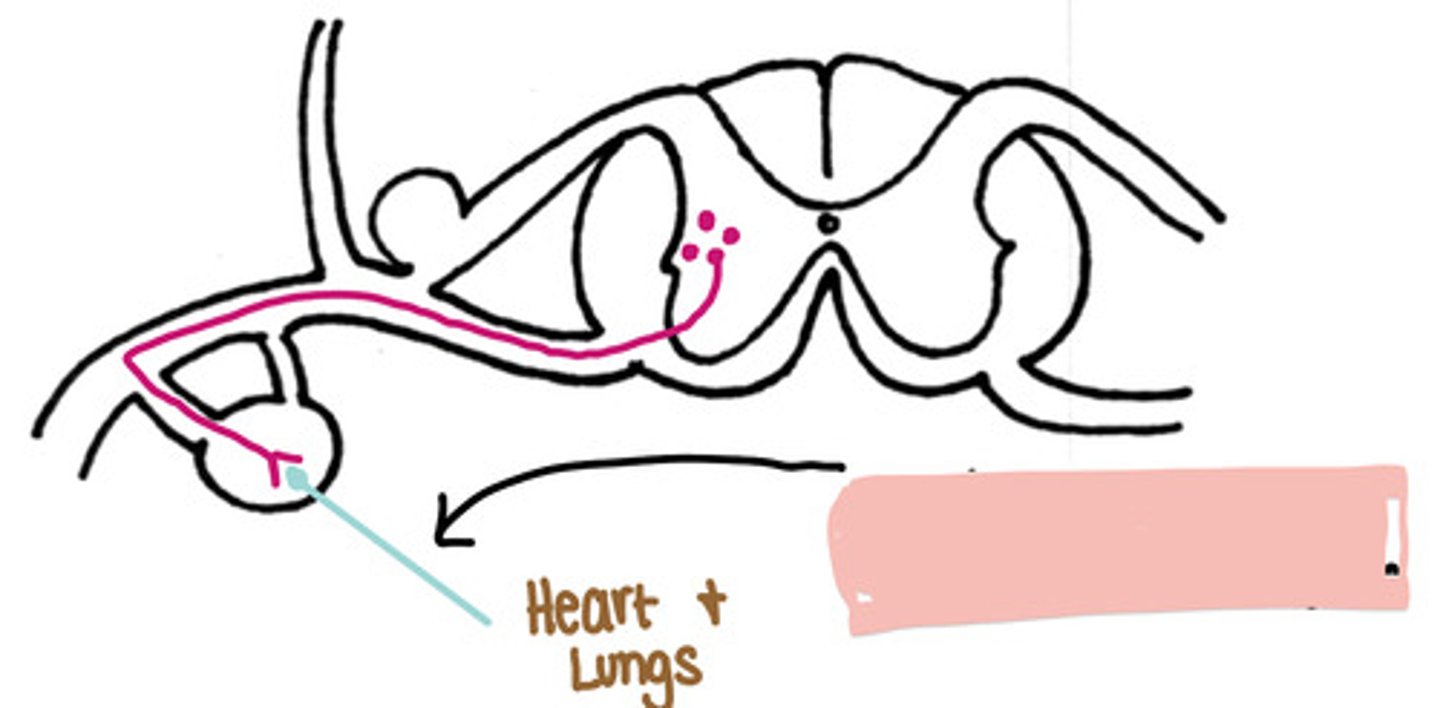
Cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerve
If this is a sympathetic pathway to cranial to the diaphragm, what is the nerve indicated by the black arrow
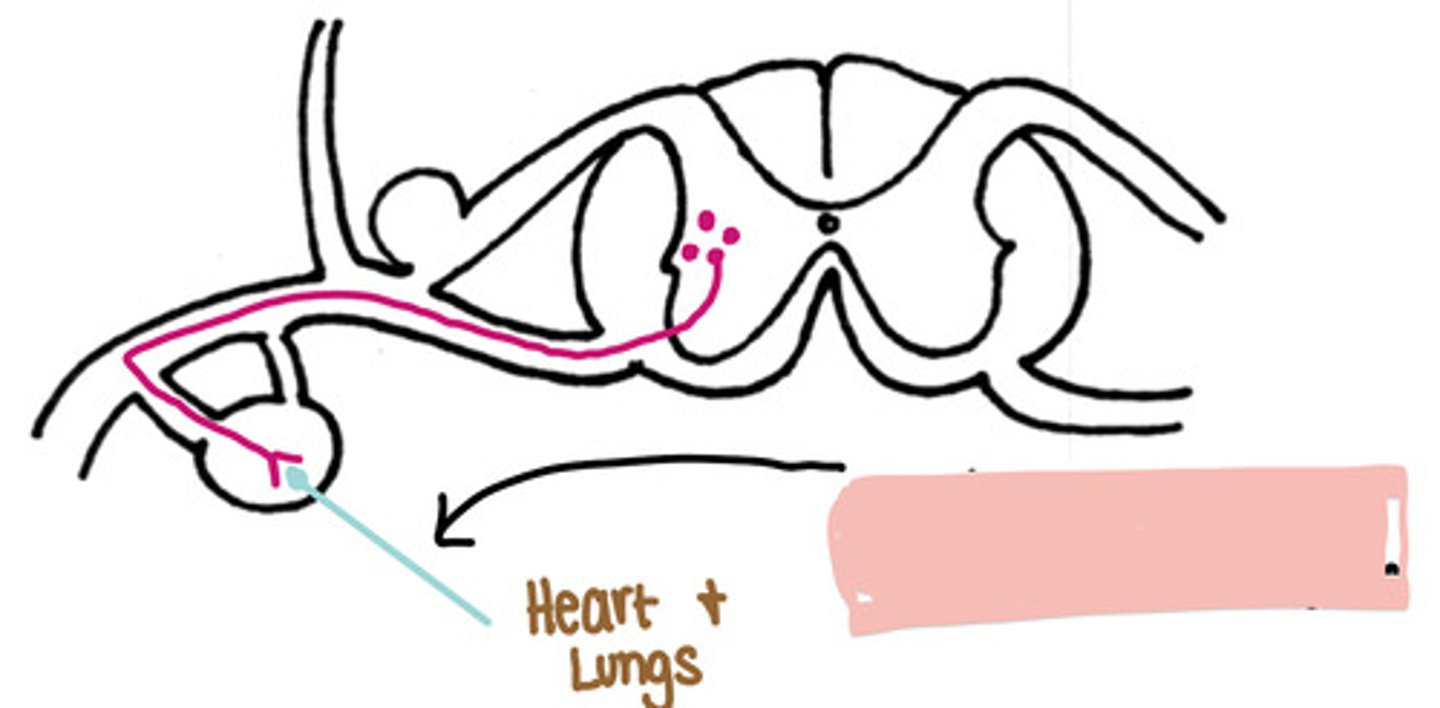
Caudal to the diaphragm
Is this a sympathetic pathway cranial or caudal to the diaphragm
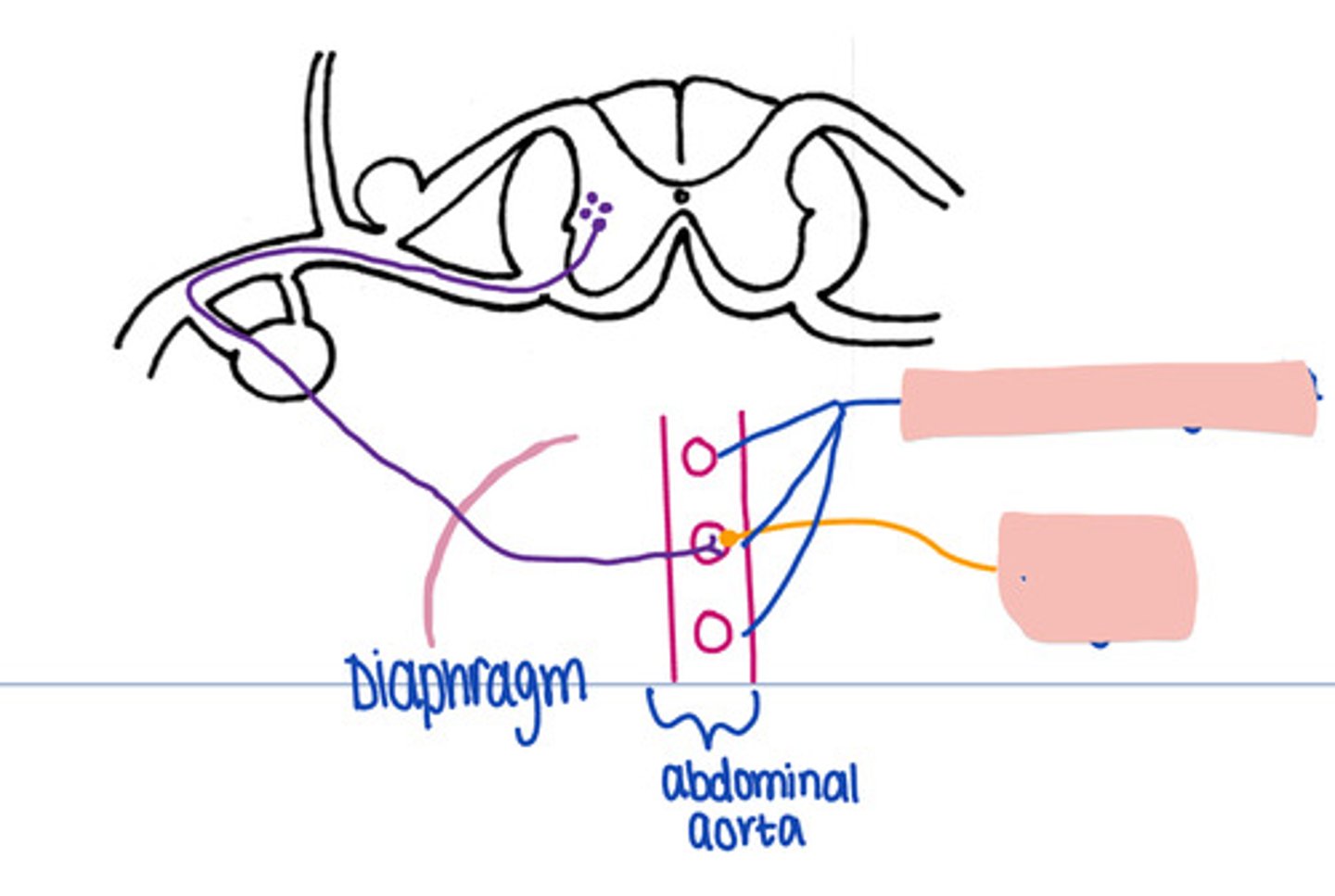
No
In a sympathetic pathways Caudal to the diaphragm, does the synapse occur in the paravertebral ganglion
prevertebral ganglia
In this pathway, where is synapse occuring
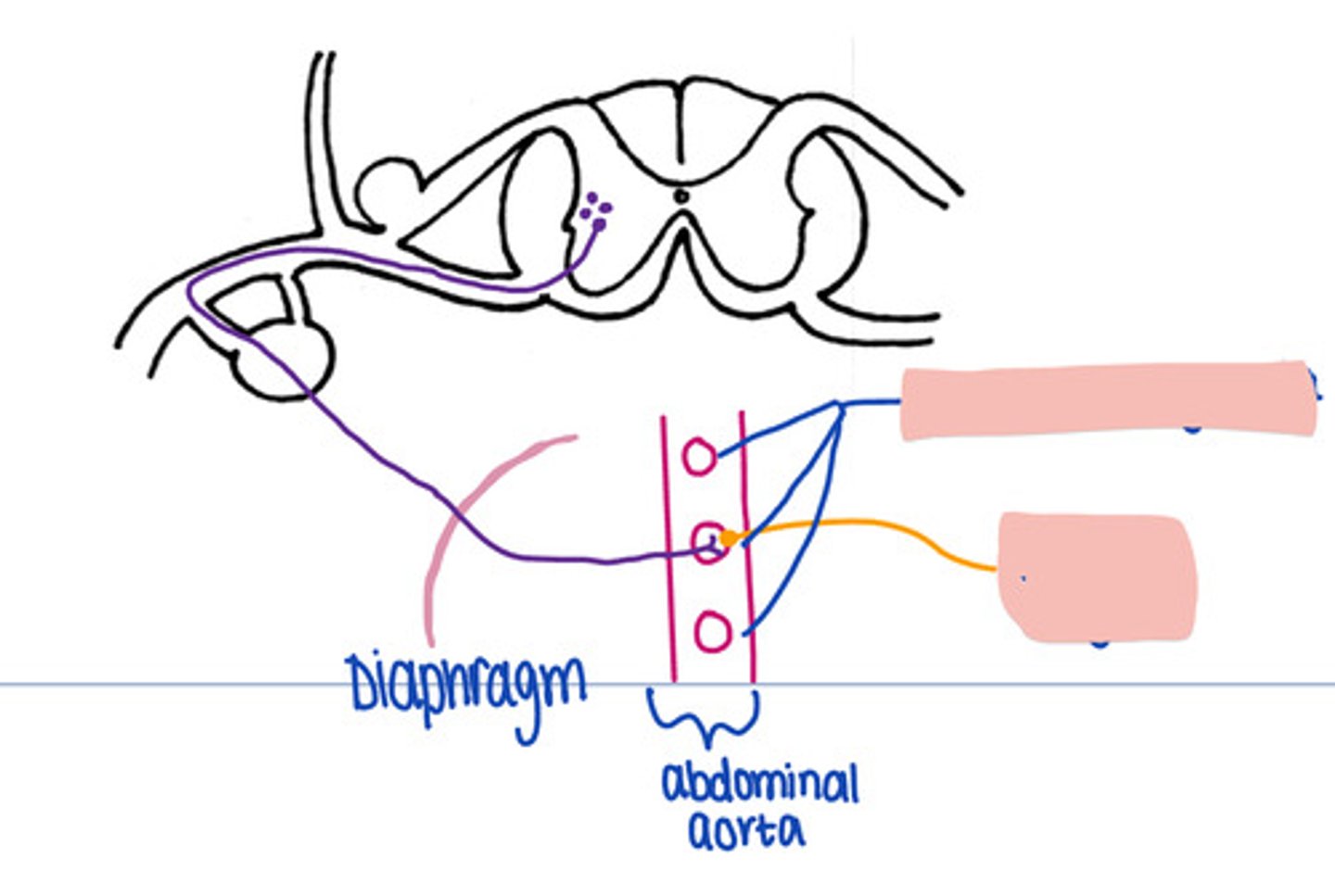
Effector organ
In this pathway, where does the impulse travel after synapse in the prevertebral ganglion.