AP Chemistry Unit 2 AP Classroom Questions
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
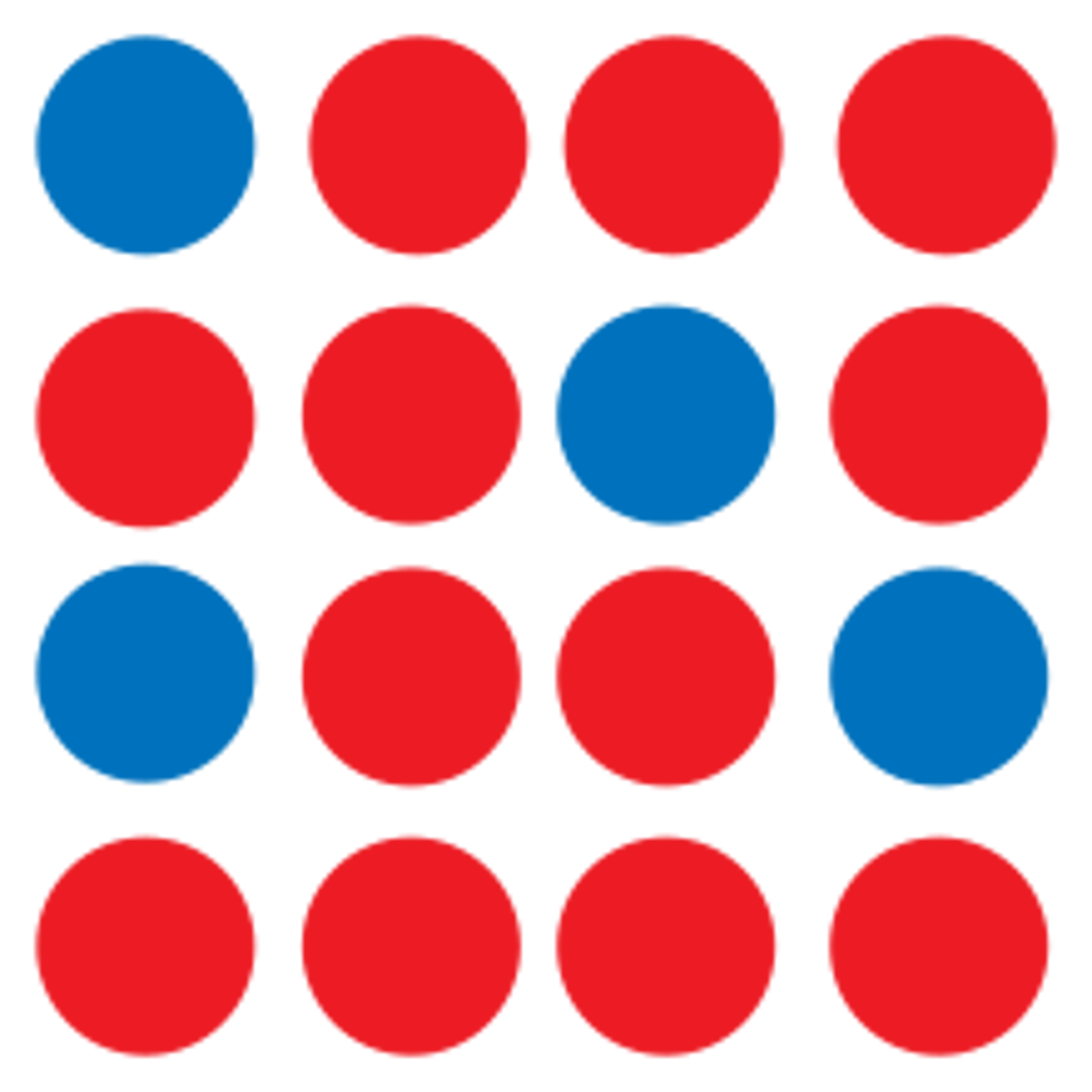
Copper atoms and zinc atoms have the same atomic radius, 135 picometers. Based on this information, which of the following diagrams best represents an alloy containing only copper and zinc atoms?
On the basis of the information above, which of the following arranges the binary compounds in order of increasing bond polarity?
H - 2.1
C - 2.5
S - 2.5
F - 4.0
Cl - 3.0
Si - 1.8
A: CH4 < SiCl4 < SF4
B: CH4 < SF4 < SiCl4
C: SF4 < CH4 < SiCl4
D: SiCl4 < SF4 < CH4
A
Which of the following has the bonds arranged in order of decreasing polarity?
A
H−F > N−F > F−F
B
H−I > H−Br > H−F
C
O−N > O−S > O−Te
D
Sb−I > Sb−Te > Sb−Cl
A
Which of the following scientific claims about the bond in the molecular compound HF is most likely to be true?
A
There is a partial negative charge on the HH atom.
B
Electrons are shared equally between the HH and FF atoms.
C
The bond is extremely weak.
D
The bond is highly polar.
D
A particle-level diagram of a metallic element is shown above. Typically, metals are both malleable and ductile. The best explanation for these properties is that the electrons involved in bonding among metal atoms are
A
unequally shared and form nondirectional bonds
B
unequally shared and form highly directional bonds
C
equally shared and form nondirectional bonds
D
equally shared and form highly directional bonds
C
Which of the following compounds contains both ionic and covalent bonds?
A
SO3
B
C2H5OH
C
MgF2
D
H2S
E
NH4Cl
E
Two pure elements react to form a compound. One element is an alkali metal, X, and the other element is a halogen, Z. Which of the following is the most valid scientific claim that can be made about the compound?
A
It has the formula XZ2XZ2.
B
It does not dissolve in water.
C
It contains ionic bonds.
D
It contains covalent bonds.
C
The elements C and Se have the same electronegativity value, 2.55. Which of the following claims about the compound that forms from C and Se is most likely to be true?
A
The carbon-to-selenium bond is unstable.
B
The carbon-to-selenium bond is nonpolar covalent.
C
The compound has the empirical formula CSe.
D
A molecule of the compound will have a partial negative charge on the carbon atom.
B
To make Au stronger and harder, it is often alloyed with other metals, such as Cu and Ag. Consider two alloys, one of Au and Cu and one of Au and Ag, each with the same mole fraction of Au. If the Au/Cu alloy is harder than the Au/Ag alloy, then which of the following is the best explanation based on the information in the table above?
A
Cu has two common oxidation states, but Ag has only one.
B
Cu has a higher melting point than Au has, but Ag has a lower melting point than Au has.
C
Cu atoms are smaller than Ag atoms, thus they interfere more with the displacement of atoms in the alloy.
D
Cu atoms are less polarizable than are Au or Ag atoms, thus Cu has weaker interparticle forces.
C
Based on the data in the tables above, which of the following statements provides the best prediction for the boiling point of NaCl?
A
NaCl will have a lower boiling point than NaF because the coulombic attractions are weaker in NaCl than in NaF.
B
NaCl will have a boiling point between that of NaF and MgO because the covalent character of the bonds in NaCl is intermediate between that of MgO and NaF.
C
NaCl will have a higher boiling point than MgO because the ions are spaced farther apart in NaCl.
D
NaCl will have a higher boiling point than MgO because the energy required to transfer electrons from the anion to the cation is larger in NaCl than in MgO.
A
The potential energy as a function of internuclear distance for three diatomic molecules, X2, Y2, and Z2, is shown in the graph above. Based on the data in the graph, which of the following correctly identifies the diatomic molecules, X2, Y2, and Z2?
X2 - H2
Y2 - N2
Z2 - O2
The energy required to dissociate an ionic solid into gaseous ions (lattice energy) for the compounds NaF and MgF2 is shown in the table above. On the basis of Coulomb's law, which of the following best helps to explain the large difference between the lattice energies of NaF and MgF2 ?
NaF lattice - 930
MgF2 lattice - 2978
A
The solubility of MgF2 is less than that of NaF.
B
The electronegativity of Mg is greater than that of Na.
C
The mass of the Mg cation is greater than that of the Na cation.
D
The charge of the Mg cation is larger than that of the Na cation.
D
The lattice energy of a salt is related to the energy required to separate the ions. For which of the following pairs of ions is the energy that is required to separate the ions largest? (Assume that the distance between the ions in each pair is equal to the sum of the ionic radii.)
A
Na+(g) and Cl−(g)
B
Cs+(g) and Br−(g)
C
Mg2+(g) and O2−(g)
D
Ca2+(g) and O2−(g)
C
The potential energy of a system of two atoms as a function of their internuclear distance is shown in the diagram above. Which of the following is true regarding the forces between the atoms when their internuclear distance is x?
A
The attractive and repulsive forces are balanced, so the atoms will maintain an average internuclear distance x.
B
There is a net repulsive force pushing the atoms apart, so the atoms will move further apart.
C
There is a net attractive force pulling the atoms together, so the atoms will move closer together.
D
It cannot be determined whether the forces between atoms are balanced, attractive, or repulsive, because the diagram shows only the potential energy
A
Of the following compounds, which is the most ionic?
A
SiCl4
B
BrCl
C
PCl3
D
Cl2O
E
CaCl2
E
Of the following single bonds, which is the LEAST polar?
A
N—H
B
H—F
C
O—F
D
I—F
E
O—H
C
The melting point of MgO is higher than that of NaF. Explanations for this observation include which of the following?
I. Mg2+ is more positively charged than Na+.
II. O2- is more negatively charged than F-.
III. The O2- ion is smaller than the F- ion.
A
II only
B
I and II only
C
I and III only
D
II and III only
E
I, II, and III
B
Which of the following best helps to explain why the value of ΔH° for the dissolving of CaF2 in water is positive?
A
CaF2(s) is insoluble in water.
B
CaF2(s) dissolves in water to form CaF2(aq) particles.
C
Ca2+ ions have very strong ion-ion interactions with F- ions in the crystal lattice.
D
Ca2+ ions have very strong ion-dipole interactions with water molecules in the solution.
C
The table above provides some information about two types of steel, both of which are alloys of iron and carbon. Which of the following best helps to explain why high-carbon steel is more rigid than low-carbon steel?
A
Elemental carbon is harder than elemental iron.
B
The additional carbon atoms within the alloy make the high-carbon steel less dense.
C
The additional carbon atoms within the alloy increase the thermal conductivity of the high-carbon steel.
D
The additional carbon atoms within the alloy make it more difficult for the iron atoms to slide past one another.
D
Lewis electron-dot diagrams for CO2 and SO2 are given above. The molecular geometry and polarity of the two substances are
A
the same because the molecular formulas are similar
B
the same because C and S have similar electronegativity values
C
different because the lone pair of electrons on the S atom make it the negative end of a dipole
D
different because S has a greater number of electron domains (regions of electron density) surrounding it than C has
D
The geometry of the SO3 molecule is best described as
A
trigonal planar
B
trigonal pyramidal
C
square pyramidal
D
bent
E
tetrahedral
A
The structural formula of the glycinium cation is shown above. Arrows indicate the pKa values for the labile protons in the molecule.
Which of the following is true about the geometry of the glycinium cation?
A
The leftmost C atom and all the atoms directly bonded to it lie in the same plane.
B
Both C atoms and both O atoms lie in the same plane.
C
The N−C−C bond angle is 180°180°.
D
The geometry around the N atom is planar.
B
The structural formula of the glycinium cation is shown above. Arrows indicate the pKa values for the labile protons in the molecule.
What is the approximate H−O−C bond angle in the glycinium cation?
A
180°
B
120°
C
105°
D
90°
C
H - C --- C - H
what is the hybridization of the carbon atoms in a molecule of ethyne, represented above?
A
sp
B
sp2
C
sp3
D
dsp2
E
d2sp
A
In the reaction represented above, what is the hybridization of the C atoms before and after the reaction occurs?
sp2 to sp3
Lewis diagrams of molecules of three different hydrocarbons are shown above. Which of the following claims about the molecules is best supported by the diagrams?
A
All the atoms in molecule 1 lie in one plane.
B
All the molecules have the same empirical formula.
C
The C-C-C bond angle in molecule 2 is close to 180°.
D
The strongest carbon-to-carbon bond occurs in molecule 3.
D
The molecule with the largest dipole moment
A
CO2
B
H2O
C
CH4
D
C2H4
E
PH3
B
The molecule with only one double bond
A
CO2
B
H2O
C
CH4
D
C2H4
E
PH3
D
The molecule that has trigonal pyramidal geometry
A
CO2
B
H2O
C
CH4
D
C2H4
E
PH3
E
Which of the following molecules contains exactly three sigma (σ) bonds and two pi (π) bonds?
A
C2H2
B
CO2
C
HCN
D
SO3
E
N2
A
Has molecules with a pyramidal shape
A
NH3(g)
B
BH3(g)
C
H2(g)
D
H2S(g)
E
HBr(g)
A
Which of the following Lewis electron-dot diagrams represents the molecule that is the most polar?
A: Cl-F
B: Br-F
C: S--C--S
D: F-B-F
|
F
B
Which of the following molecules is nonpolar but has polar covalent bonds?
A
N2
B
H2O2
C
H2O
D
CCl4
E
CH2Cl2
D
Pi (π) bonding occurs in each of the following species EXCEPT
A
CO2
B
C2H4
C
CN-
D
C6H6
E
CH4
E
Which of the following molecules has the shortest bond length?
A
N2
B
O2
C
Cl2
D
Br2
E
I2
A
According to the VSEPR model, the progressive decrease in the bond angles in the series of molecules CH4, NH3, and H2O is best accounted for by the
A
increasing strength of the bonds
B
decreasing size of the central atom
C
increasing electronegativity of the central atom
D
increasing number of unshared pairs of electrons
E
decreasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms
D
The electron-dot structure (Lewis structure) for which of the following molecules would have two unshared pairs of electrons on the central atom?
A
H2S
B
NH3
C
CH4
D
HCN
E
CO2
A
Which of the following is a nonpolar molecule that contains polar bonds?
A
F2
B
CHF3
C
CO2
D
HCl
E
NH3
C
Which of the following molecules contains only single bonds?
A
CH3COOH
B
CH3CH2COOCH3
C
C2H6
D
C6H6
E
HCN
C
Which of the molecules represented below contains carbon with sp2 hybridization?
A
CH4
B
CH2Cl2
C
C2H6
D
C2H2Cl2
E
C2H4Cl2
D
Which of the following species is NOT planar?
A
CO32-
B
NO3-
C
ClF3
D
BF3
E
PCl3
E
The BF3 molecule is nonpolar, whereas the NF3 molecule is polar. Which of the following statements accounts for the difference in polarity of the two molecules?
A
In NF3, each F is joined to N with multiple bonds, whereas in BF3 , each F is joined to B with single bonds.
B
N — F bonds are polar, whereas B — F bonds are nonpolar.
C
NF3 is an ionic compound, whereas BF3 is a molecular compound.
D
Unlike BF3, NF3 has a nonplanar geometry due to an unshared pair of electrons on the N atom.
D