AP Psychology Midterm - Units 0 - 3
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
Critical Thinking
thinking that does not automatically accept arguments and conclusions. Examines assumptions. Discover hidden biases, asses conclusions, evaluate evidence and its source.
Hindsight Bias
the tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that you foresaw it. “I knew it all along” phenomenon. Ex: Findings from something turn out in a way, you think that you foresaw that outcome.
Overconfidence
Overconfidence - can impede critical thinking. Humans tend to think we knew more than we actually do. Ex: Psychologists found out predictions about world events were only 40% true however they thought it would be 80%.
Perceiving order in random events
Random acts don’t seem random. Humans tend to see patterns where they aren’t any to help us with daily lives. Flipping a coin, equal chance for heads or tails. Patterns in the results might seem indicative of an order.
Scientific Method
Self-correcting procedure to evaluate ideas through observation and analysis. Psychologists use it to think critically, observe behaviors, test variables, and draw conclusions.
Peer Reviewers
Scientific experts who evaluate a research article’s theory, originality, and accuracy.
Theory
Explanation using integrated set of principles that organizes observations and predicts behaviors or events. Ex: Sleep affects memory.
Hypothesis
Testable prediction often implied by a theory. Can support or disconfirm theories.
Falisifiable
possibility that an idea, hypothesis, or theory can be disproven by observation or experiment.
Operational Definition
carefully worded statement of the exact procedures (operations) used in a research study. Ex: sleep deprivation can be defined as getting 2 hours less than a person’s natural sleep requirement.
Replication
repeating the essence of the research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the initial finding can be reproduced.
Case Study
descriptive technique in which hope individual or group is studied in depth in the hope of revealing principles. Case studies can only lead to ideas.
Naturalistic Observation
Technique of observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate and control the situation.
Survey
Technique for obtaining the self-reporting attitudes or behaviors of a particular group, usually by questioning a representative, random sample in the group.
Sampling Bias
Flawed sampling process that makes an unrepresentative sample.
Random Sample
Fairy represents a population, because each member has an equal chance of being included, also called random selection.
Population
All those in a group being studied, from which random samples may be drawn. This doesn’t refer to the entire country’s population.
Correlation
a measure of the extent to which two factors vary together, and thus of how well either factor predicts the other.
Variables
any factors that can vary, and are feasible and ethical to measure.
Correlation Coefficient
statistical index of the relationship between two variables. (-1.00 to +1.00) Positive coefficients (0-1.00) indicate variables moving in same direction, increasing or decreasing together. Negative coefficients (0 to -1.00) indicate whether variables have an inverse relationship.
Scatterplot
graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the values of two variables. Suggests the strength of the correlation.
Illusory correlation
perceives a relationship where none exists, or perceives a relationship as stronger than it actually is. Ex: gamblers may only recall winning bets from the past, and mistakenly attribute their behavior to the result.
Regression toward the mean
tendency for extreme or unusual scores or events to fall back toward the average. Ex: low test scores could be the result of sleep deprivation, difficult test questions, the weather, etc. Failure to recognize can create superstitious thinking, mistaking influences on changes in behaviors.
Experiment
research method in which an investigator manipulates one or more factors (independent variables) and observes the effect on a certain behavior (dependent variable) to identify a cause and effect relationship between the variables.
Experimental group
in an experiment is the group exposed to the treatment - that is, to one version of the independent variable.
Control group
group not exposed to the treatment; it contrasts with the experimental group, serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.
Random assignment
Assigns participants to experimental and control groups by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences between each group.
Single Blind Procedure
experimental procedure in which the research participants are ignorant (blind) about whether they have received the treatment or a placebo.
Double blind procedure
experimental procedure in which both the research participants and the research staff are ignorant(blind) about whether the research participants have received the treatment or a placebo.
Placebo Effect
Used to describe experimental results caused by expectations alone; any effect on behavior caused by the administration of an inert substance, which the recipient assumes is an active agent.
Confounding variable
in an experiment is a factor other than the factor being studied that might influence results.
Validity
the extent to which a test or experiment measures or predicts what it is supposed to.
Quantitative research
research method that relies on quantifiable, numerical data
Qualitative research
research method that relies on in-depth, narrative data that are not translated into numbers.
Informed consent
gives potential participants enough information about a study to enable them to choose whether they wish to participate.
Debriefing
is the post-experimental explanation of a study, including its purpose and any deceptions to its participants.
Ethics to follow for an experiment/research
1) rules to safeguard participants 2) informed consent 3) harm/discomfort limited 4) information kept confidential 5) debrief afterward 6) institutional review boards are set up to review and approve research proposals.
Descriptive Statistics
numerical data used to measure and describe characteristics of groups.
Histogram
bar graph depicting a frequency distribution
Mode
more frequently occuring score in a distribution
Mean
arithmetic average of a distribution, adding the scores then dividing by the number of scores.
Median
Middle score in a distribution, half the scores are above, half below.
Percentile Rank
percentage of scores that are lower than a given score.
Skewed distribution
describes a representation of scores that lack symmetry around their average value.
Range
describes the difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
Standard deviation
computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score. Low standard deviation = more accurate mean.
Normal curve
symmetrical, bell-shaped curve that represents the distribution of many types of data; more scores fall near the mean, fewer and fewer near the extremes. Normal distribution.
Inferential statistics
numerical data that allow one to generalize; to infer from sample data the probability of something being true to a population. Allow researchers to draw conclusions.
Meta analysis
statistical procedure for analyzing the results of multiple studies to reach an overall conclusion. Combining the findings of multiple studies enhances the validity of the conclusion.
Statistical significance
statistical statement of the likelihood that a result occurred by chance, assuming there is no difference between the populations studied.
Effect size
refers to the strength of the relationship between two variables. the larger the effect size, the more one variable can be explained by the other.
Psychology
the science of behavior and mental processes.
Nature Nurture Issue
long-standing controversy over the relative contributions that genes and experinece make to the development of psychological traits and behaviors. Today’s science views traits and behaviors arising from an interaction of nature and nurture.
Natural selection
principle that the inherited traits enabling an organism to best survive and reproduce in a particular environment will (in compeition with other trait variations) will most likely be passed on to succeeding generations
Mutation
a random error in gene replication that leads to change
Evolutionary psychology
the study of the evolution of behavior and the mind, using principles of natural selection
Behavior genetics
the study of the relative power and the limits of genetic environmental influences on behavior. To what extent does genetics vs environment influence behavior?
Nature v Nurture = ______, _______
Genetics/Genes v Environment
Heredity
the genetic transfer of charactertistics from parents to offpsirng.
Genes
Biochemical units of heredity
Genome
the complete instructions for making an organism. 23 chromosomes from mom, 23 from dad. = 46. Chromosomes are made of molecule DNA. Each DNA is made of gene.
Identical (monozygotic) twins
individuals who developed from a single, fertilized egg that split into two, creating two genetically identical organisms.
Fraternal (dyzygotic) twins
individuals who are developed from seperate fertilized eggs, they are getetically no closer than ordinary sblings, despite sharing a prenatal environment,.
Interaction
the interplay that occurs when the effect of one factor (such as the environment) depends on another factor (such as heredity).
Epigenetics
“above” or “in addition to”. the study of the molecular mechanisms by which environments can influence egnetic expression (without a DNA change).
Nervous System
the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous system.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous system (PNS)
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body
Nerves
Bundled axons form neural cables connecting the central nervous system with muscles, glands and sensory organs.
Sensory (afferent) neurons
neurons that carry incoming information from the body’s tissues and sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord.
Motor (efferent) neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands.
Interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord; they communicate internally and process information between the sensory inputs and motor outputs.
Somatic (Skeletal) nervous system
In the peripheral nervous system (other is autonomic). Enables communication from the brain and spinal cord to our muscles connected to bones.
Autonomic nervous system
2 of 2 - part of the perpheral nervous system. Has two divions of its own, each help in maintaining homeostasis in the body. sympathetic and parasympathic.
Sympathetic nervous system
part of the autonomic nervous system. Arouses the body, prepares it for fight or flight at a time when there may be danger.
Parasympathetic nervous system
part of the autonomic nervous system. calms the body down and brings it back to a normal resting state after an arousal producing effect has passed.
Reflex
simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus, such as a knee-jerk reflex. (ex: our brain feels the pain only after the spinal cord has seet a command to move our hand from the flame.sensory neurons, internous and motor neurons all working together).
Reflex arc
Controls reflexes, spinal cord pathway.
Neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
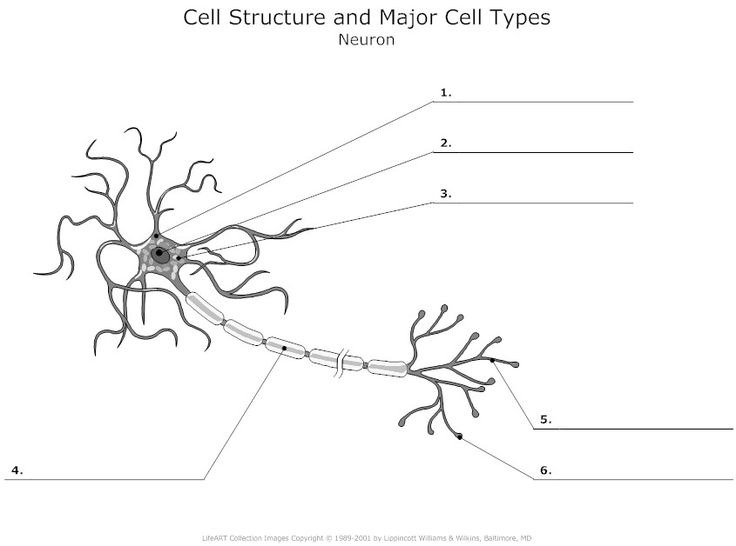
What is 3?
Cell body: the part of a neuron that contains the nucleus; the cells life support center.
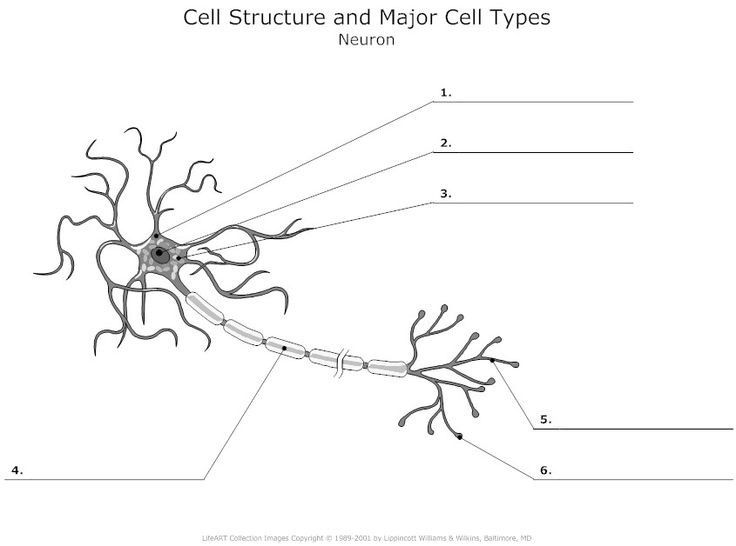
what is 2?
nucleus
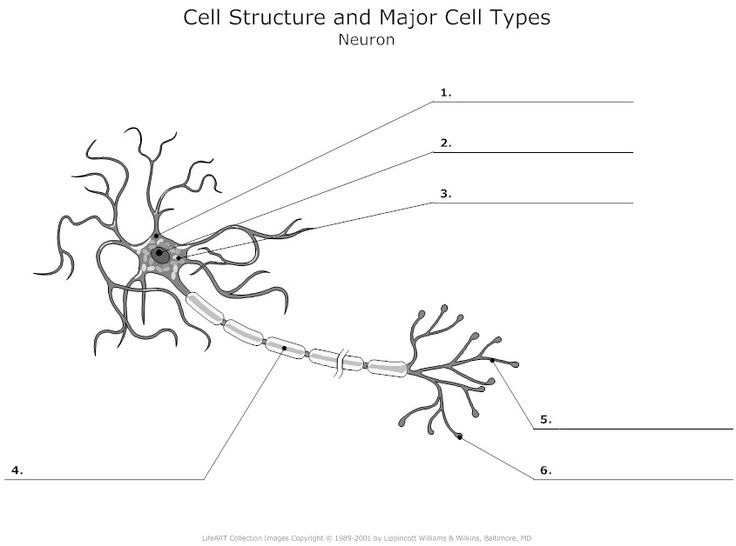
What is 1?
Dendrites, a neuron’s bushy, branching extensions that receive and integrate messages, conducting impulses toward the cell body.
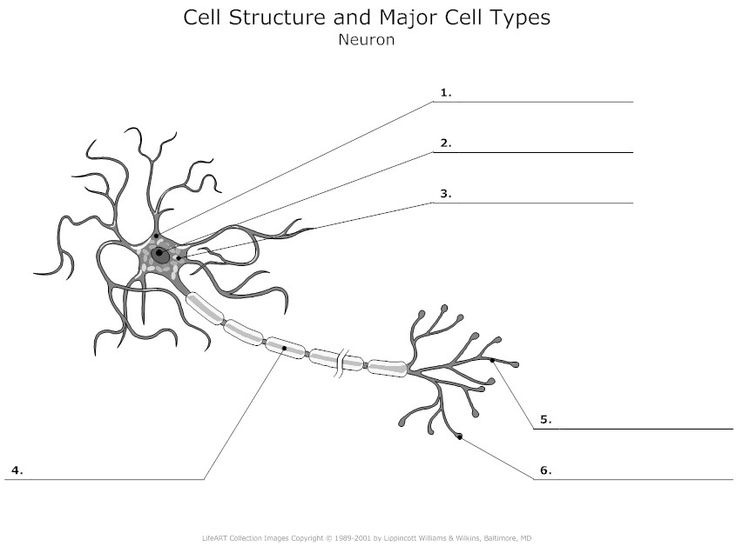
What is 4? (Two terms combined)
1) Axon - segmented neuron extension that passes messages through its branches to other neurons or to muscles or glands. 2) myelin sheath - a fatty tissue layer segmentally encasing the axons of some neurons; it enables vastly greater transmission speed as neural impulses hope from one node to the next.
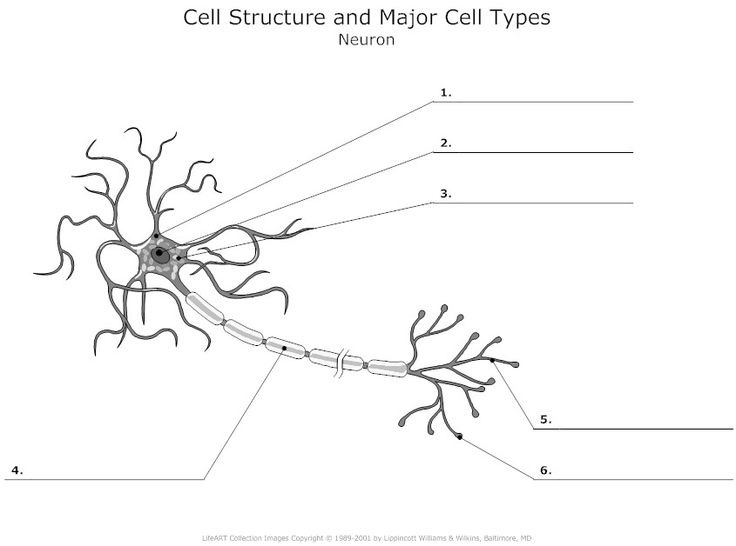
what is 5?
Terminal branches of axon
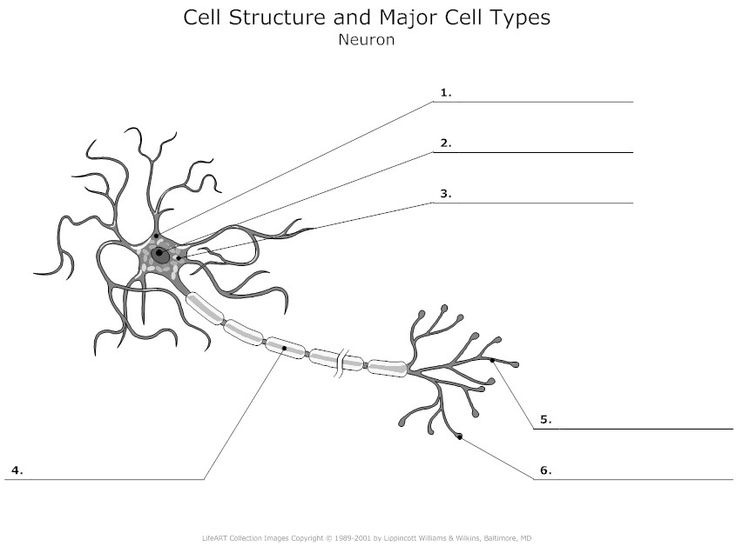
What is 6?
Axon Terminals - transmit messages to other cells via use of neurotransmitters at synapses. Doesnt receive, only transmits.
Glial Cells
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons; they also play a role in learning, thinking, and memory. Protect neurons & support. Feed them, create myelin for insulation, guide connections, clean up environment.
Action Potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon. electrochemical message - means of communication between neurons.
A brief electrical charge is created down the axon by opening a series of gates allowing positive ions to rush in ans create depolarization.
Neural impulses are mostly excitatory, telling the next neuron what its feeling. If the excitatory impulses outnumber the inhibitory ones, reaching a certain threshold, the neuron will fire the action potential.
Firing is regulated on all or nothing principle, either fire or don’t
After firing, neuron must rest during a refractory period before doing it all over again.
Threshold
level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse - excitatory outnumbers inhibitory impulses, then it will fire.
Refractory period
in neural processing, a breif resting pause that occurs after a neuron has fired; subsequent action potentials cannot occur until the axon returns to its resting state.
All or none response
a neuron’s reaction of either firing (with full-strength) or not firing.
Synapse
junction between the axon top of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. The tiny gap at this junction is the synaptic gap/synaptic cleft.
Santiago Ramon and Cajal compared close but not touching space between neurons “protoplasmic kisses”
Neurotransmitters are released into synapse just prior to the arrival of the action potential. They travel across and bind to receptor sites, either stimulating activity or blocking it in the receiving neuron
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gap between neurons. When released by sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neurons, thereby influencing whether the neuron will generate a neural impulse.
reuptake
a neurotransmitter’s reabsorption by the sending neuron
After neurotransmitters bind to receptor sites, they either stimulate activity or blocking it.
After unlocking receiving sites on dendrites, excess neurotransmitters are reabsorbed into the sending neuron in an process called reuptake.
Endorphins
our natural morphine. Natural, opiod-like neurotransmitters linked to pain control and pleasure.
oversupply with opioid drugs can suppress the body’s natural endorphin supply
Acetylcholine (ACh)
neurotransmitter that enables muscle action, learning and memory.
With Alzheimer’s disease, ACh- producing neurons deteriorate
Dopamine
neurotransmitter that influences movement, learning, attention, emotion
Oversupply linked to schizophrenia.
Undersupply linked to Parkinson’s disease & decreased mobility
Serotonin
neurotransmitter that affects mood, hunger, sleep, arousal
Undersupply linked to depression
Norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter that helps control alertness and arousal
Undersupply can depress mood
GABA (Gamma-aminobutyric acid)
Neurotransmitter that is a major inhibitory
undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, insomnia
Glutamate
neurotransmitter that is very excitatory, involved in memory.
Oversupply can overstimulate the brain, producing migraines or seizures