African Trypanpspmaiasis
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What kind of parasite is trypanasomes?
Protozoan, blood and tissue infecting
What serious disease do trypansome cause?
Sleeping sickness
What are the 2 groups of trypanasoma spp. and what are they?
Salivarian:
Life cycle stages develop in the vector FORE gut
Parasite transmitted during feeding
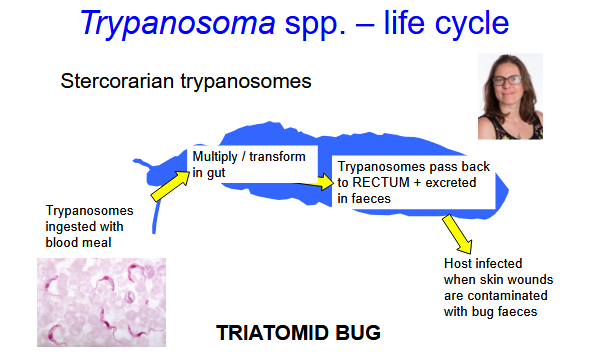
Stercorarian:
Life stages develop in the vector HIND gut
Parasite transmitted by contamination of wounds by insect faeces
Simply describe the life cycle of Salivarian trypanasomes?

Simply describe the life cycle of stercorarian trypanasomes?
Where do the tsetse flies live in various habitats?
The bushes trees,places where it can bite vertebrates
Whats the name of the vector for trypanosoma spp.?
Glossina spp, Tsetse fly
Why is it quite easy to control the flies population?
The fly only produces one big egg, so if you kill a fly that alone can really decrease the risk or decrease the flies population(control the pop)
Whats the difference between T brucei and T.vivax?
T.brucei: survive for long periods-increase the opportunity for infection of flies
T.vivax kill their host in 1-2 weeks- decreases the chnces of fly infection
Not all trypanasomes are transmitted by flies what is the animal vector that spreads T.b. evansi?
Vampire bat
What is stage 1 of Human infection by trypanasoma?
Enlarged cervivallymph node, fever and headaches
What is Stage 2 of HUman infection by trypanasoma?
Brain/cerebellum
- congestion, oedema and haemorrhage
• Behavioural and personality changes
• Confusion, fatigue, coordination loss and somnolence
• Severe immunosuppression
• Risk of secondary infection
What is trypanasoma pathogenesis?
Enlarged lymoh nodes + spleen→ eventual lymphnoid exhaustion
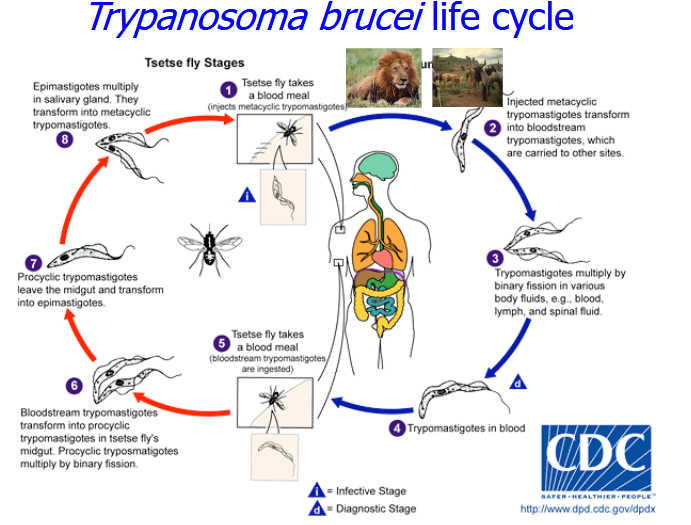
What is the human stage of T.brucei life cycle?
Tsetse fly takes a blood meal injecting metacyclic trypomastigotes
Injected metacyclic tryomatigotes transformin the blood stream trypomatigotes which are carried to other sites
Trypomastigotes multiply by binary fission in various body fluid e.g. blood, lymph and spinal fluid
Trypomastigotes in blood, tsetse fy takes blood meal

What is the tsetse fly stage life cycle ?
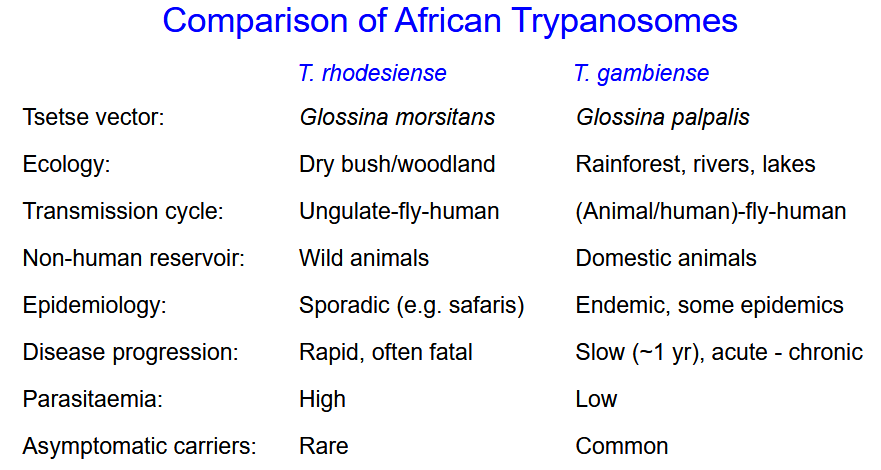
Describe the difference between T rhodesiense, and T.gambiense.
(Ecology, Transmission cycle, non human reservoir, epidemiology, disease progression, patasitaemia, asymptomatic carriers)
Whats good about Bos indicus compared to Bos taurus? But why is this bad for humans?
Bos indicus is trypano-tolerant, but remains a reservoir of infection.
What is Trypanosoma spp. Surra?
Mostly infected horse and sometimes camels, T.b. evansi, (N Africa, Asia, S.America)→ emaciation +oedema, death (days→months)
Mechanically transmitted trypanasomes (biting flies)
What is Typanosoma spp. Dourine?
Venereally-transmitted trypanasome
Horses and donkeys
Swollen penile sheath
What are the 2 Non-pathogenic species of trypanasoma?
T. theileri
T.melophagium
What are the control measures against trypanasoma spp?
Tsetse fly control : traps, nets and spraying drugs,
changing drug group reduces resistence risk
Seperate livestock from wild animals
Trypano-tolerant livestock
Therapeutic Drug treatment
Trypanasoma spp. Therapy: Pentamidine, suramin, organic arcenicals, Toxicity: if left untreated trypanasomaisis will be fatal
What are the 2 main trypano-tolerant cattle breeds?
Bos Taurus- dwarf breeds
BOS indices
What are the 2 trypano-tolerant sheep and goat breeds?
Ovis Aries: sheep
Capra hires: goat
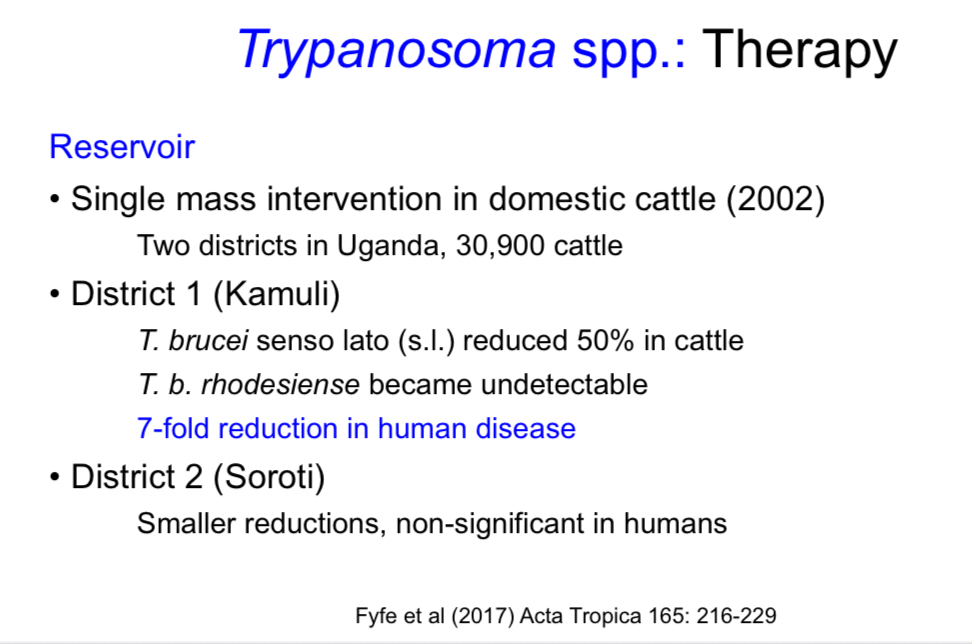
Give an example of an intervention that reduced disease?
Why is there no vaccine?
Antigenic variation/immuno-supression
How does trypanosoma spp evade the immune system?

How can we diagnose trypanosoma spp.?
Motile trypanosome fresh blood films
Giemsa-stained blood smears
Identify trypanosome-specific Ab:
ELISA, IFAT, Western blotting
Blood and cerebral fluid
Specific DNA
PCR
Quantitative PCR
LAMP
in vitro/in vivo culture