First Civilizations Test
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Turning Point
An event that leads to lasting change.
Hunting & Gathering
The act of getting one's food by hunting for it and collecting wild fruit, vegetables, and nuts.
Agriculture
Farming.
Neolithic Era
A period in human history that came after the start of agriculture and before the development of the first civilizations.
Bronze Age
The period during which people started creating and using metal tools.
Ocean
A large body of saltwater that covers nearly three fourths of the surface of the Earth.
Civilization
A complex society that has cities, a well organized government, and workers with specialized job skills.
Cities
Early cities emerge near farming centers as populations grew due to a food surplus from farming.
Government
A group of people who make the laws for a certain area.
Religion
Often linked to government, as many rulers claimed their right to rule came from the gods.
Job Specialization
Due to a surplus of food, not everyone needed to work the farm, allowing people to specialize in other fields.
Social Classes
Groups of people who occupy different ranks or levels in society.
Public Works
Large scale projects organized by governments, such as roads, water systems, and city walls for protection.
Art & Architecture
Early people built and decorated temples, tombs, and palaces, with music and literature becoming important.
System of Writing
Each civilization had their own form of writing used to preserve information such as laws and prayers to the gods.
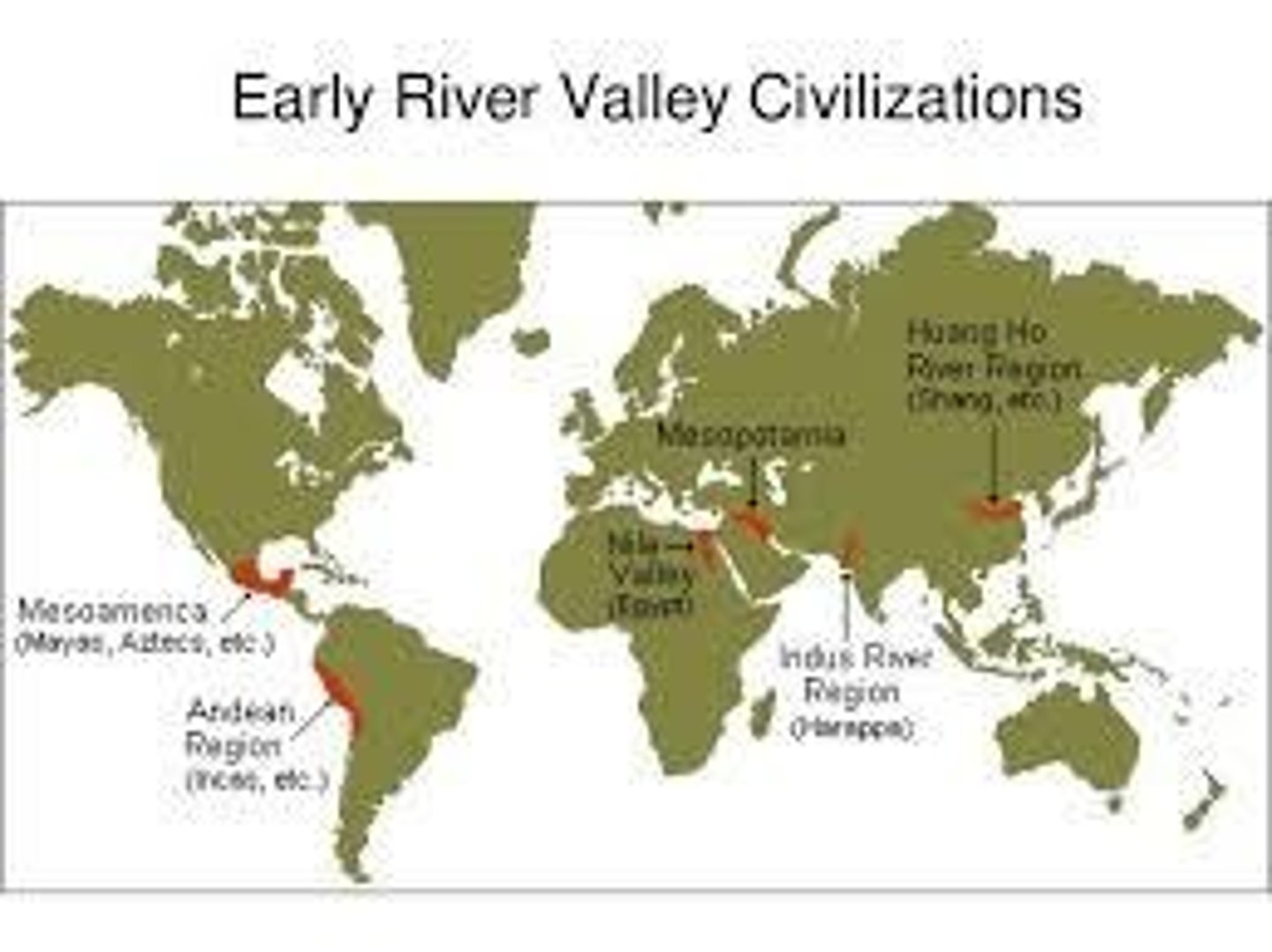
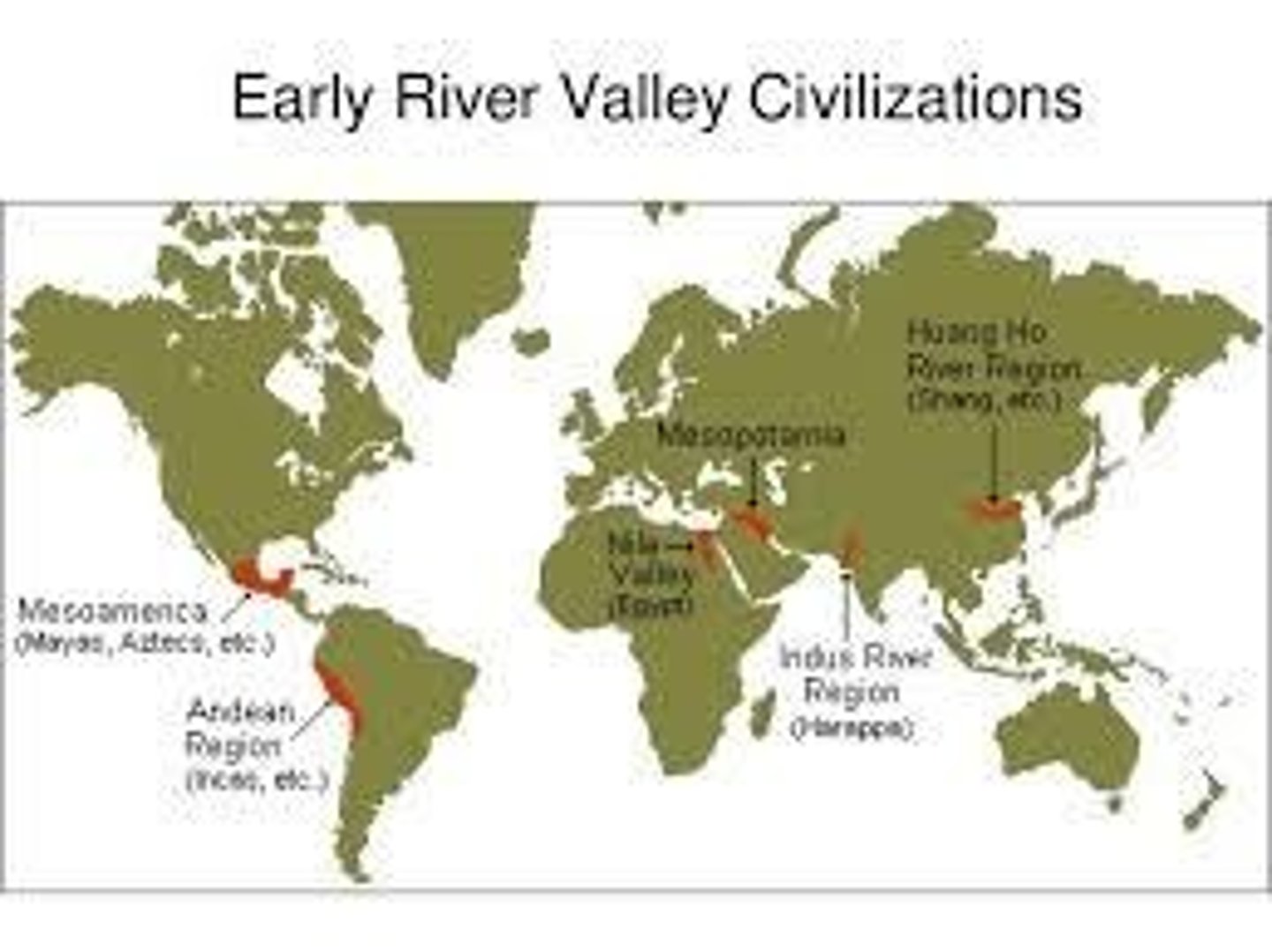
Geographic Context
The historical development shown on the map related to places where growing crops and raising domesticated animals developed before 3000 BCE.
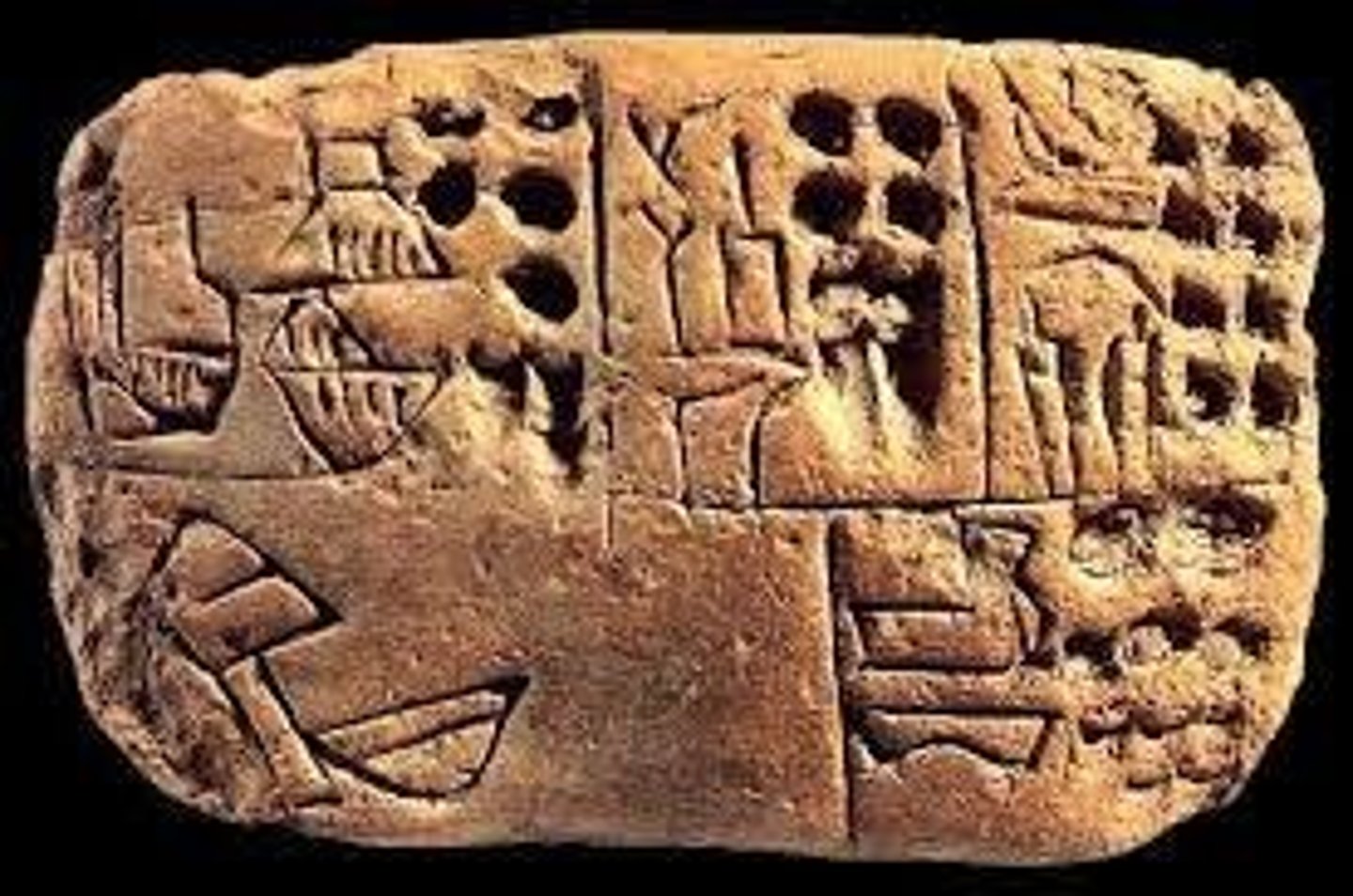
Cuneiform
A system of writing created in Mesopotamia around 3,000 BCE, initially used for tracking business transactions.
Mohenjo-daro
A city in the Indus Valley Civilization built around 2600 B.C.E., known for its sophisticated urban planning and advanced design.
Indus Valley Civilization
An ancient civilization located in present-day Pakistan, known for its advanced urban centers like Mohenjo-daro.
Granary ducts
Structures in Mohenjo-daro designed to circulate air beneath stored grain to aid in drying.
Public bath
An elaborate bathing area in Mohenjo-daro, featuring a brick-lined pool measuring 12m x 7m and 2.4m deep.
Urban sanitation systems
The world's first systems for managing wastewater within a city, as seen in Mohenjo-daro.
Egyptian Book of the Dead
A collection of hymns, spells, and instructions to guide the dead through the afterlife, placed in burial chambers.
Code of Hammurabi
A set of laws written around 1780 BCE, containing 282 laws inscribed on stone monuments for public visibility.
Shaduf
A device used by ancient Egyptians to transfer water from the Nile to their fields.
Domesticate
To tame animals or cultivate plants for human use.
Fertile
Land that is capable of producing abundant vegetation or crops.
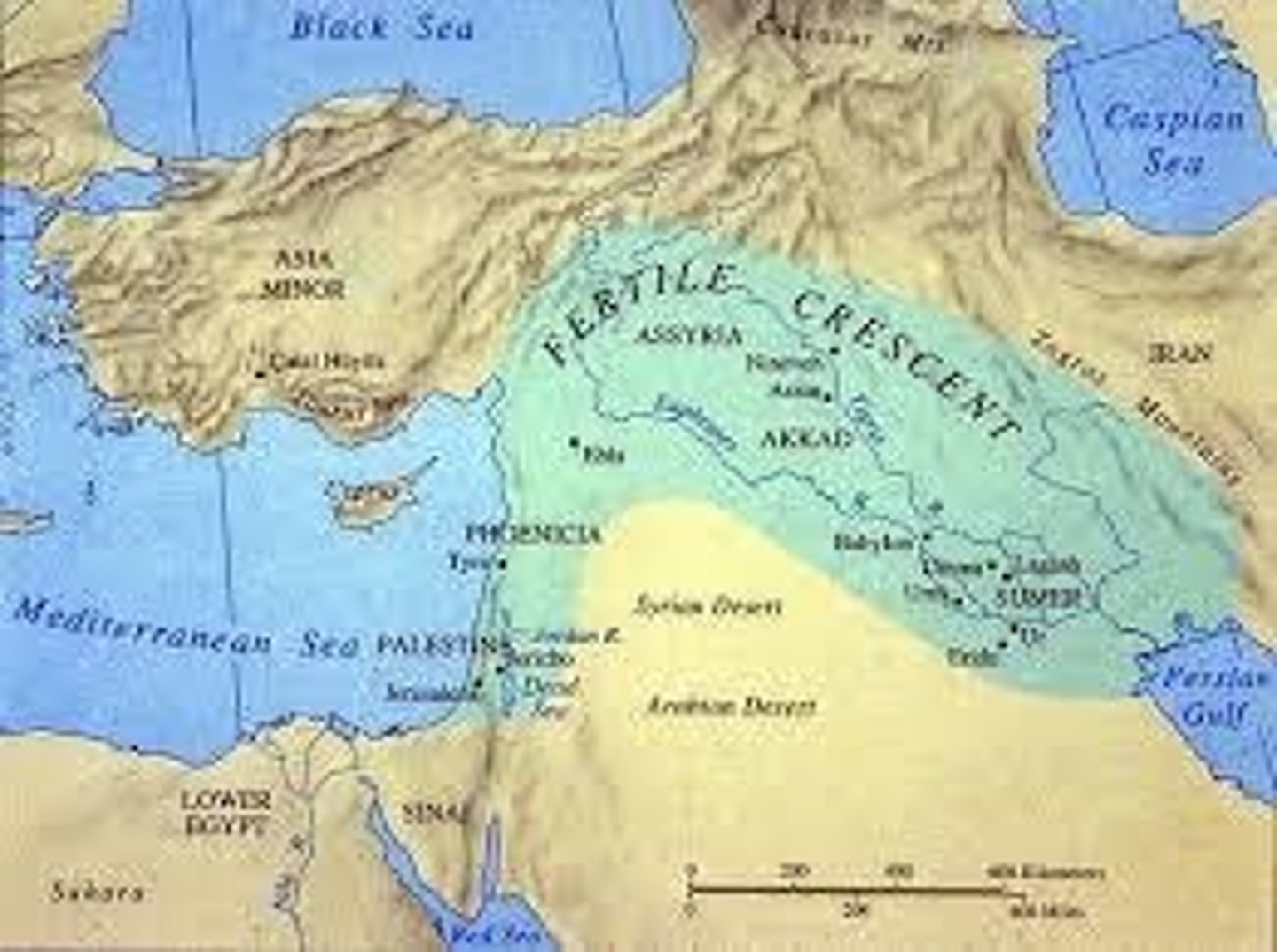
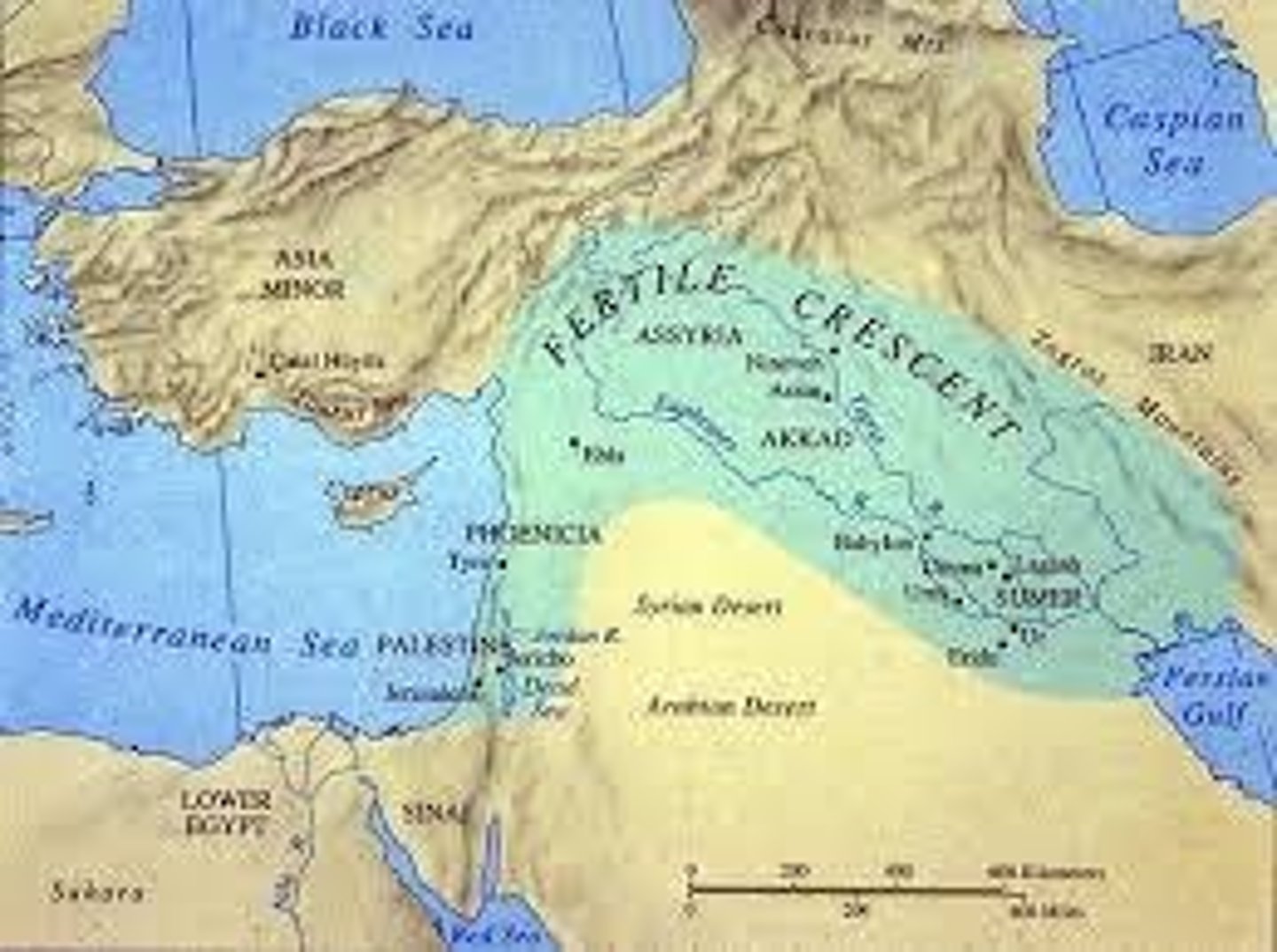
Fertile Crescent
A region in the Middle East known for its rich soils and early agricultural development.
Neolithic Revolution
The transition from nomadic hunting and gathering to settled agricultural societies.
Nomads
People who move from place to place rather than settling permanently in one location.
Paleolithic
The earliest era of human history, characterized by the use of stone tools and a hunter-gatherer lifestyle.
Settlements
Permanent communities where people live, often associated with the development of agriculture.
Technology
The application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes, especially in industry.
Babylonian Empire
An ancient empire centered in the city of Babylon, known for its contributions to law and culture.
Civilizations
Complex societies characterized by urban development, social stratification, and cultural achievements.
Irrigation
The artificial application of water to land to assist in the growing of crops.
Law Code
A systematic collection of laws and regulations governing a society.
Mesopotamia
An ancient region located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, known as the cradle of civilization.
River Valleys
Low-lying areas adjacent to rivers, often fertile and conducive to agriculture, where early civilizations developed.
Paleolithic Era
A period in human history characterized by the use of stone tools and a nomadic lifestyle.
Neolithic Revolution
A significant turning point in human history marked by the transition from hunting and gathering to agriculture.
Turning Point
An event that leads to lasting change.
Hunting & Gathering
The act of getting one's food by hunting for it and collecting wild fruit, vegetables, and nuts.
Agriculture
Farming.
Neolithic Era
A period in human history that came after the start of agriculture and before the development of the first civilizations.
Bronze Age
The period during which people started creating and using metal tools, following the Neolithic Era.
Ocean
A large body of saltwater that covers nearly three fourths of the surface of the Earth.
Pacific Ocean
One of the five world oceans.
Atlantic Ocean
One of the five world oceans.
Indian Ocean
One of the five world oceans.
Arctic Ocean
One of the five world oceans.
Antarctic Ocean
Also known as The Southern Ocean, one of the five world oceans.
Historical Circumstances
Refers to the historical events that led to a specific event, idea, or historical development.
Geographic Context
Where a historical event took place and why it took place there, considering location and geographic features.
Bias
A strong opinion that is based more on emotion than on evidence.
Point of View
An opinion or claim.
Audience
The person or group of people that a message is for.
Purpose
The reason a record, document, or source was produced.
Cause
refers to something that contributes to the occurrence of an event, the rise of an idea, or the bringing about of a development
Effect
refers to what happens as a consequence (result, impact, outcome) of an event, an idea, or a development
Similarity
tells how something is alike or the same as something else
Difference
tells how something is not alike or not the same as something else
Civilization
a complex society that has cities, a well organized government, and workers with specialized job skills
Eight Features of Civilizations
civilizations all have EIGHT things in common
Cities
Early cities emerge near farming centers. As populations grew due to a food surplus from farming, small villages grew into cities
Governments
a group of people who make the laws for a certain area
Religion
often linked to government, because many rulers claimed that their right to rule came from the gods
Job Specialization
Due to a surplus of food, not everyone needed to work the farm; people would specialize in other fields
Social Classes
groups of people who occupy different ranks or levels in society
Public Works
Governments would organize workers to build large scale projects such as roads, water systems, and city walls for protections
Art & Architecture
Early people built and decorated temples, tombs, and palaces, with music and literature becoming important parts of civilization.
System of Writing
Each civilization had their own form of writing used to preserve information such as laws and prayers to the gods.
Cuneiform
A system of writing created in Mesopotamia around 3,000 BCE.

Mohenjo-daro
A city in the Indus Valley Civilization built around 2600 B.C.E., located in present-day Pakistan, known for its advanced urban planning.
Indus Valley Civilization
An ancient civilization located in present-day Pakistan, known for its sophisticated cities like Mohenjo-daro.
Population of Mohenjo-daro
At its height, the city probably had around 35,000 residents.
Urban sanitation systems
The world's first urban sanitation systems were included in the city of Mohenjo-daro, with wastewater diverted to covered drains.
Egyptian Book of the Dead
A collection of hymns, spells, and instructions to guide the dead through the afterlife challenges, printed on papyrus.
Code of Hammurabi
A set of laws written around 1780 BCE, containing 282 laws inscribed on stone monuments for public visibility.

Hammurabi
The ruler of Babylon who created the Code of Hammurabi, a significant legal document in ancient history.
Shaduf
A device used by Egyptians to transfer water from the Nile to their fields.
Paleolithic
The era characterized by the use of stone tools and a hunter-gatherer lifestyle.
Settlements
Permanent communities established by people, often associated with agriculture.
Fertile Crescent
A region in the Middle East known for its rich soils and early agricultural development.
Irrigation
The artificial application of water to land to assist in the growing of crops.
Civilizations
Complex societies characterized by urban development, social stratification, and cultural achievements.
Nomads
People who move from place to place rather than settling permanently in one location.
Fertile
Soil that is capable of producing abundant vegetation or crops.
Crops
Plants cultivated for food, fiber, or other products.
Domesticate
To tame animals or cultivate plants for human use.
River Valleys
Geographical areas near rivers that were crucial for the development of early civilizations.