Class 3 - Right Hemisphere Disorder
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
(History of RHD) Left hemisphere:
Broca & Wernicke discovery in 1800s led to a century of exploration of left hemisphere abilities
(History of RHD) Right hemisphere:
Considered “subordinate, minor, unconscious”
Largely ignored until advent of corpus commisurotomy in 1960s
Allowed the study of each cerebral hemisphere’s indepedent functions
Sperry won the Nobel prize in 1981 for his work on brain lateralization in split brain patients
What is RHD?
group of deficits or changes that may occur following insult to a person’s right cerebral hemisphere
communicative defects of RHD have been collectively called “Pragmatic aphasia,” “Cognitive-Communicative Disorder”
Are communication problems in RHD patients language based?
NO, rather a result of impaired cognition
if you pull out WAB & other language assessments, all those language processes would likely be intact
What is the etiology of RHDs?
any etiology that damages right hemisphere:
Stroke
Disease
Trauma
Seizure disorders
Infection
Toxicity
Level of deficit or disorder depends on the location & extent of damage (e.g., a small focal stroke may produce isolated deficits while a large stroke may produce deficits across all areas of cognition)
What are the Cognitive Behaviors present in RHD?
Hemi spatial Neglect (Left Neglect)
Agnosia types
Topographical disability
Constructional impairments
Emotions
Fundamental cognitive processes
Hemi spatial Neglect or Left Neglect or Unilateral Neglect:
Fail to report, respond to, or orient towards stimuli contralateral to their brain lesions
Can follow LHD, but occurs more frequently, lasts longer, & is generally more severe after RHD
Visual neglect has been documented most & studied most extensively
What are the 3 types of Unilateral Neglect?
Personal space
Peri-personal space
Extra-personal space
Personal space:
one’s own body
somatophrenia is inability to perceive their own body parts as being part of themselves
Neglect to shave, comb, dress on left side of body
might accompany neglect piece, but not always. Person may be so unaware of left arm, that they might bump into things. Reveals that they may have difficulty perceiving their own body
Peri-personal space:
within reaching distance
Neglect of items in drawing/copying/reading tasks
Neglect of items on left-side of table/tray
Extra-personal space:
beyond arm’s reach
Neglect of people standing on left side
Neglect of items (TV, window) on left side of room
Peri-personal Neglect Types:
Viewer-centered (Egocentric)
Object-centered (Allocentric)
Combination Viewer- & Object-centered
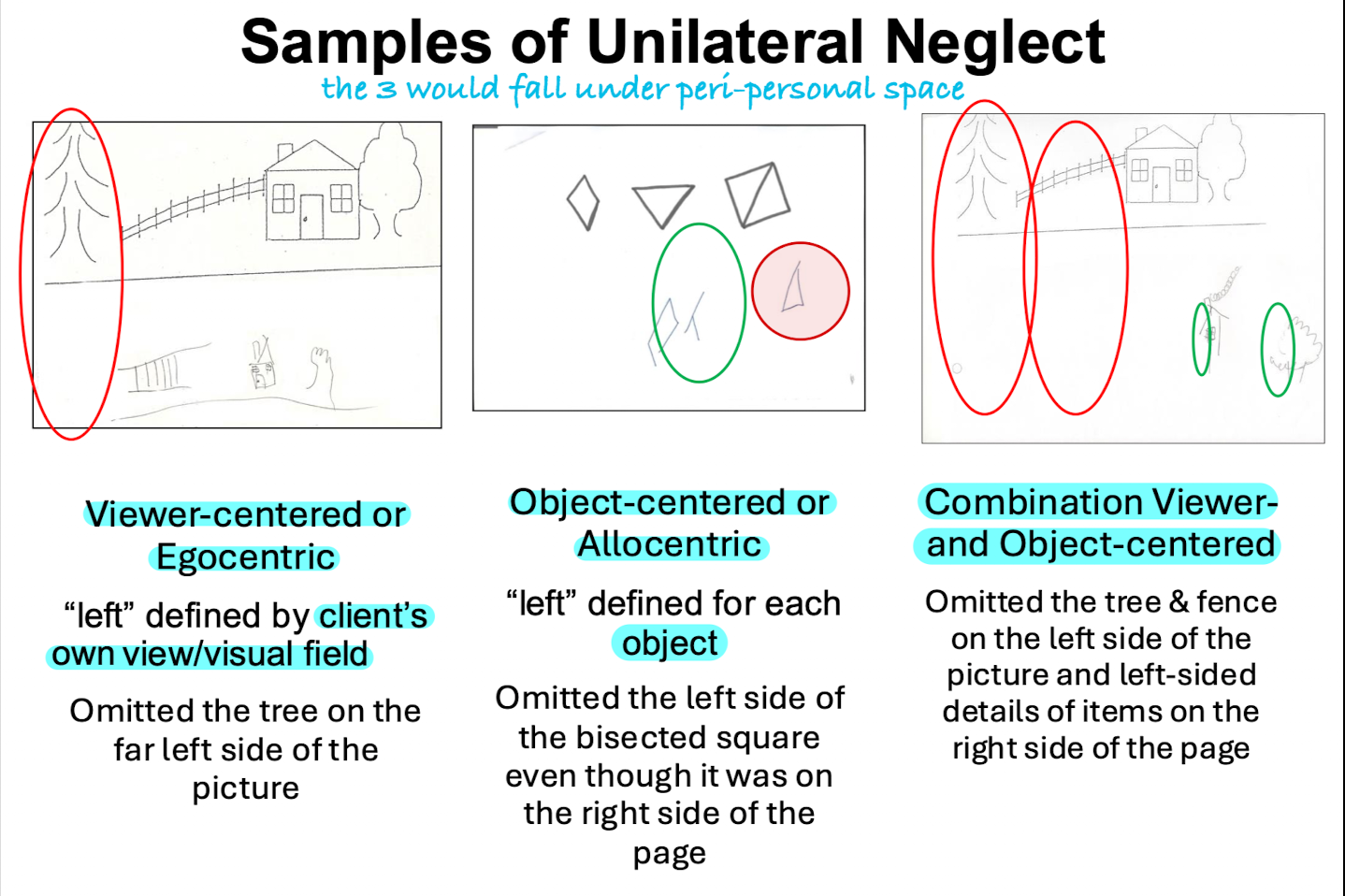
Left Neglect:
Impairment in attention
Able to see but not notice (can see when pointed to)
Unaware of problem
Can learn to compensate
Left hemianopia:
Sensory impairment affecting the ability to see the left visual fields
Aware of the problem
Compensate w/ eye or head movement
(Neglect & Language) Neglect dyslexia:
Can affect reading & writing
Omit, substitute letters on left side of words/sentences
(Neglect & Language) Neglect dysgraphia:
Begin writing in middle or on right side of page
Letter & line perseverations
May not write left to right, may start from the middle instead
(2. Agnosias) What is Anosognosia?
denies having impairment!
Lack of knowledge of a disease or imperception of disease
May deny the need for treatment, or “disown” his own affected side
_____ & neglect often co-occur
_____ affects awareness of neglect, physical communication, & cognitive deficits
Impacts Rehab & post-rehab: Poorer compliance & participation, poorer outcome
(2. Agnosias) What is Prosopagnosia?
Ability to recognize faces is important in discriminating familiar/non-familiar faces
Visual agnosia is the inability to perceive visual stimuli d/t damage to the CNS NOT damage to the optic nerve or eyes
Prosopagnosia is the inability to recognize faces in the absence of other visual agnosia
Damage to visual association areas in occipital lobe that are used to process/interpret visual info from the eyes
Individuals w/ prosopagnosia may not recognize others visually by their face, but they may recognize them by voice, smell, clothing, or other distinctive features
Prosopagnosia - Comprehending & Producing Facial Expressions:
Right hemisphere allows us to evaluate facial expressions
Problems interpreting facial expressions & emotions conveyed on faces (challenging for them to associate meanings w/ expressions)
Inability to process emotions expressed by facial expressions lead to more literal interpretation (patient would not get sarcasm, embedded meanings that involve facial expressions)
Damage to right hemisphere limits expressivity on the left side of the face, the most expressive portion of the face
Due to this, they display a flat affect & reduced facial expression
(2. Agnosias) Amusia or Music Agnosia:
Impairment in the recognition, production, & reproduction of melodies
Pitch & Melody:
RHD: Pitch perception impaired; Speech perception intact
LHD: Pitch perception intact; Speech perception impaired
Recognizing music w/o lyrics → difficult in RHD!
Topographical disorientation:
Confusion about a location in space
Difficulty describing how to travel from one place to another or getting lost
Disorientation to immediate environment
Constructional impairments:
Difficulty in assembling components to form an object or a drawing
Also called visuo-constructional deficits
Constructional deficits in RHD & LHD:
RHD: Disturbances of spatial relationships, whole picture is distorted (e.g., fragmented or rotated drawing)
LHD: Produce generally simpler drawings w/ fewer lines & fewer details
Emotions:
Difficulty reccognizing & using facial expressions
Poor emotional language
“I passed the test!” vs. “He passed away”
Hypo-affectivity: reduced ability to experience or express emotions, may appear flat, blunted, less animations in facial expressions
Hyper-affectivity: excessive emotional responses, including emotional outbursts & excessive animations in facial expressions
These presentations* may be similar to depression, PTSD, etc.
RHD: Laugh excessively
LHD: Mostly depressive
Fundamental Cognitive Processes
Orientation
Attention
Memory
Executive functions
Organization
Problem solving
Reasoning
(6. Fundamental Cognitive Processes) Orientation & Arousal:
Hypoaroused or less attentive to external stimuli
Disorientation to date, time, &/or place
Disorientation to self
Cannot recall personal info, such as birth date, age, or family members’ names - A&O(x3)
Arousal: when someone is interacting with patient, are they responding appropriately? Typically, they're not responding as well as they should
(6. Fundamental Cognitive Processes) Attention:
Sustained, selective, and divided attention
May cause individuals w/ RHD to miss relevant info, be distracted by irrelevant stimuli, & further lose track of what is being spoken of
(6. Fundamental Cognitive Processes) Memory:
Working memory
Long term memory
Problems recalling street names or important dates or faces (Prosopagnosia), & learning new info
ST & LT recall for verbal & non-verbal material is affected (Auditory WM task)
(6. Fundamental Cognitive Processes - Executive Functions) Problem solving:
Difficulty responding appropriately to common events, such as car breakdown or overflowing sink
• may need to provide cues for patient to discuss process of solving an issue, e.g., car breaking down, fire. Patient may provide bizarre answers that are not the main picture or solves problem as it typically should
Unable to initiate, or may act too quickly (impulsive) w/o first organizing info & identifying the best solutions
important for SLPs to train patient on inhibition
Cause injury to self, or others
(6. Fundamental Cognitive Processes - Executive Functions) Organization:
Trouble telling a story in order, giving directions, or planning an event
patient may be missing appointments & actually experiencing problems, but to everyday people it comes off as disorganized & messy.
(6. Fundamental Cognitive Processes - Executive Functions) Reasoning:
Difficulty in thinking rationally or finding logical answers
“Why cant you touch fire?”
What are the Communicative Behaviors present in RHD?
Aprosodia
Pragmatics
Non-literal interpretation (Humor, sarcasm, etc.)
Discourse
Conversation
Aprosodia:
Reduced use of pitch, duration, loudness & pause time to convey (production) or interpret (comprehension) meaning
Expressive: RHDs speak w/ a flat contour or monotone
Receptive: Poor identification of emotions in sentences
RHD: Affective prosody
Attitudes of speaker (e.g., politeness, rudeness)
Emotional sentences (e.g., happy, sad)
Facial expressions
LHD: Linguistic prosody
sentences w/ declarative/interrogrative contours

Pragmatics:
Non-literal interpretation
RHD - “extreme literalness”
Difficulty understanding idioms
Metaphors
Sarcasm
Indirect requests
Ironies
Focus on unimportant details & miss the main point
anything they have to interpret beyond what is being said w/ words
Ask "Can you please shut the door?" patient would say "Yes I can" & not shut door, despite implication. You deal w/ pragmatics everyday, social media, music, media
Inferences:
Difficulty making inferences (e.g., About characters’ attitudes/motives)
John-“I am searching for a new place to live”
Greg-“Oh, I don’t have a roommate!”
What is Greg implying?
Discourse comprehension:
Poor coherence (cannot apply/connect meanings from one paragraph to another)
Macrostructure deficits: Overall theme, central message of narratives, pictured scenes or discourse.
Discourse production:
Verbose, literal, focused on detail and empty
Cookie theft picture- “Well, its on a 8x11 inch paper covered with plastic, done with drawing pens..on a white paper…”
Disorganized, tangential, overly-personalized discourse production
Reduced eye contact, turn-taking
Reduced use of emotionally-laden words
Lack of sensitivity to shared knowledge
Difficulty extracting story morals or giving titles to story contents
Conversation:
Deficient Theory of Mind (ToM)
Ability to infer another person’s mental states
Difficulty interpreting jokes, sarcasm (require understanding another’s perspective or intent)
Poor coherence (don’t clarify pronouns or provide explicit references to avoid confusion)
Difficulty in lengthy conversations
Poor topic maintenance
Abrupt termination of conversation topics
Introducing unrelated tangential topics
Conversation breakdowns occur frequently
Repair strategies typically used by partners