NeuroHistology Structure & Condition
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
what are the functions of neurons
drive motor function
release hormones
regulate immune and metabolic functions
what is the junctions between neurons called
synapse
a large axon has a large cell body and a small axon has a small cell body why is that
that is because the axon must be supported by the cell body
what is the range of resting membrane potentials for a neuron
-90mv to -50mv
how is resting membrane potential established in neurons
through the sodium potassium pump and potassium leak channels
what causes neurons to utilize so much energy in the body
the use of the sodium potassium pump to reestablish the membrane potential after the action potential
what can trigger an action potential to occur
neurotransmitter binding
nociceptor response
The sudden influx of what ion allows for the action potential to begin
Sodium
What stabilizes the closed outer gate in the sodium gated channel
calcium
what direction can the action potential travel down a neuron
it can travel both directions
What are the 3 steps of repolarization
close the sodium channel
open the potassium channel
reestablish the membrane potential
How would a dog having hypoglycemia or hypoxemia affect a neuron
Neurons would not be able to run the sodium potassium pump making it hard to establish a membrane potential
how would a dog having increased extracellular potassium affect neurons
it would diminish the gradient for leak channels making it hard to establish membrane potential.
how would a dog having decreased extracellular calcium affect the neurons
it would reduce the stabilization of the outer sodium gate making it easier for an action potential to happen
Brevotoxin, tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin cause paralytic sea food poisoning. What is the target of these toxins?
Voltage gate sodium channels
Lidocaine is used to block transmission of painful stimuli along the course of sensory neurons. What is the target of this nerve block agent?
Voltage gate sodium channels
where can neurotransmitters be synthesized
axon terminus
neuron cell body
the rise of this intracellular ion causes fusion of vesicles containing neurotransmitters with the plasma membrane of the axon terminus
calcium
what are the 2 types of post synaptic receptors
ion channels
enzyme receptors
between ion and enzyme receptors which one is known as slow and which one is known as fast
ion is fast
enzyme is slow
what are the 2 general results of neurotransmitters binding
excitation
inhibition
what channels are opened in excitatory vs inhibitory responses
sodium in excitatory
potassium in inhibitory
what type of neurotransmitters bind to ion channels
small molecule rapidly acting neurotransmitters
what type of neurotransmitters bind to enzyme receptors
neuropeptides
a neuron is called a Cholinergic neurons because it produces acetylcholine why is that?
that is because a neuron can only produce one type of small molecule neurotransmitter
where are small molecule neurotransmitters synthesized
pre synaptic terminal
where are neuropeptides synthesized
cell body
what is synaptic complexity
it is where the input of various neurons may influence the activity of one postsynaptic neuron
the death of a neuron from excessive release of an excitatory neurotransmitter is called what
Excitotoxity
what is nissil substance
rough endoplasmic reticulum found in the cell body of a neuron
what are the two types of axoplasmic transport
fast antegrade
slow antegrade
the blocking of either fast antegrade or slow antegrade transport of axonal substances might cause what?
Neuroaxonal dystrophy
what structure is the result of blocking axoplasmic transport
spheroid
what is Wallerian degeneration
it is when an axon is essentially amputated
in cases of extreme hypoxemia and glycemia a cell will lose its nissel substance resulting in what
central chromatolysis
what is saltatory conduction
it is the jumping of depolarization from node to node
what are the benefits of saltatory conduction
increased action potential velocity
conserves energy
what cell produces myelin in the CNS
oligodendrocytes
what cell produces myelin in the PNS
Schwann cells
if an autoimmune disease was to target myelin what would be its difficulty
it would have to select between Schwan myelin and oligodendrocyte myelin
what special characteristic of schwann cells allows for neurons to be regrown in the peripheral nervous system
schwann cells produce collagen tissue on the side opposite of the myelin
which myelin producing cell is more efficient at covering neurons
oligodendrocytes
loss of myelination can take two forms what are they
primary demyelination
secondary demyelination
what is the cause of secondary demyelination
axon degeneration
what are causes of primary demyelination
viral infection
immune mediated
toxins
metabolic damage
if you were to find primary demyelination alongside inflammation what two causes would you suspect
viral infection
immune mediated
if you were to find primary demyelination alongside no inflammation what two causes would you suspect
toxins
metabolic damage
what are astrocytes
cells used as a replacement for the extracellular environment
what are the functions of astrocytes
metabolic support
regulate tissue water content
direct formation of the blood brain barrier
support neuronal signal transduction
in the case of injury in the CNS what cell strengthens and extends their cytoplasmic processes by increasing synthesis of cytoskeletal intermediate filaments
astrocytes
in developing neonates external granular cell layer neurons want to migrate to the internal cell layer, what cell can assist them with that
astrocytes
what are microglia
macrophages for the CNS
what two signals are microglia seeking out
damage associated molecular patterns
pathogen associated molecular patterns
interferons
what cells do microglia resemble when inactive
oligodendrocytes
what is the most abundant feature in gray matter
neuronal cell bodies
what is the most abundant feature in white matter
oligodendrocytes
in the cerebellar cortex from outside to in list of the sections of tissue
Molecular layer
purkinje cell layer
granular cell layer
white matter
in the spinal cord from outside to in name the tissue layers
white mater
dorsal gray matter
lateral gray matter
ventral gray matter
what tissue contains ascending axons
dorsal lateral gray matter
what tissue contains descending axons
ventral lateral gray matter
what cell bodies does ventral gray matter contain in the spinal cord
large motor neuron cell bodies
what cell bodies does lateral gray matter contain in the spinal cord
autonomic nervous system cell bodies
what cell bodies does dorsal gray matter contain in the spinal cord
sensory fibers
in the periphery what does ganglia mean
it is an aggregate of cell bodies
sympathetic neurons synapse with what
discrete ganglion cell neurons
parasympathetic nerons form a synapse with what
neruons embedded in the target organs
what is the synapse of a neuron located in the target organ called
plexus
from macro to micro list the connective tissue surrounding neurons in the peripheral nerves
epinerium
perinerium
endonerium
You are performing a gross post mortem examination, and you see pathological changes localized to grey matter. How do you interpret this change?
The disease is targeting neurons.
what structures form the blood brain barrier
endothelium
basement membrane
astrocyte
what areas of the brain are considered circumventricular organs
hypothalamus
pituitary glands
pineal glands
what is special about circumventricular organs
they are able to respond to systemic metabolic changes
why has axillary CSF circulatory system evolved
it addresses the needs of the cells within the center of the brain mass
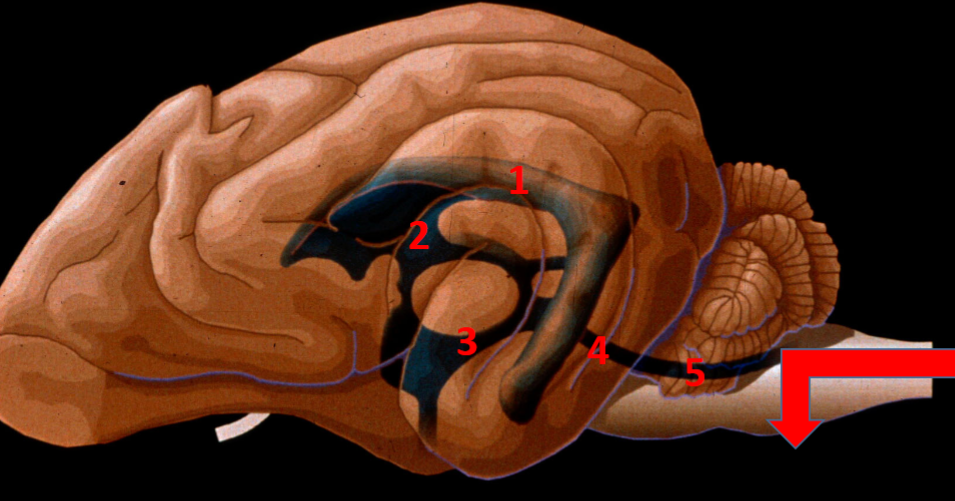
name the ventricular pathway for cerebrospinal fluid
lateral ventricle
interventricular foramen
third ventricle
mesencephalic aquaduct
fourth ventricle
after exiting the ventricles what happens to the cerebro spinal fluid
exits onto the surface of the brain
emerge onto the surface of the spinal cord
what generates the CSF
Choroid plexus
what are the parts of the choroid plexus
blood vessels
tela choroidea
plexus epithelium
in what ventricles are choroid plexi present
lateral ventricle
third ventricle
fourth ventricle
what drives circulation of the CSF
the cilia of the ependymal cell layer
True or false? The barrier between blood and CSF exists at the levels of the plexus epithelium and not the vascular endothelium.
True
what is the space called in which CSF empties into
Subarachnoid space
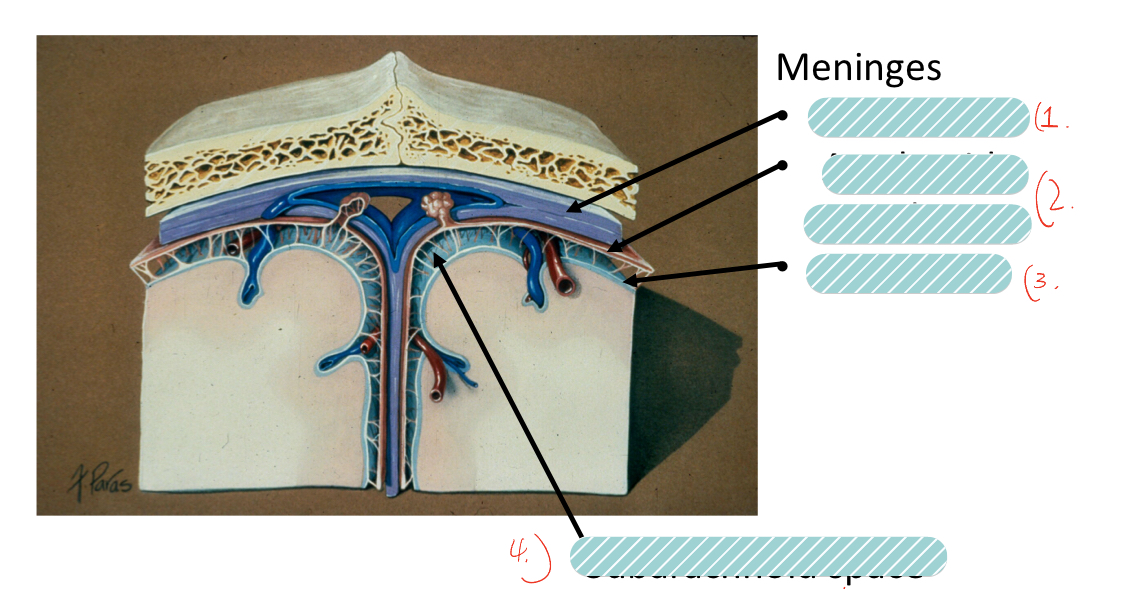
label the meninges
Dura matter
arachnoid membrane
pia matter
subarachnoid space
what structure allow for resorption of CSF into the dorsal sagittal venous sinus
Arachnoid granulation
True or false? A feedback mechanisms exists to balance CSF production with the rate of resorption.
false
what does decreased resorption of CSF cause
hydrocephalus
Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) reveals an increase in total protein and a large number of lymphocytes. How do you interpret this change?
There is inflammation, but the location cannot be determined based upon CSF analysis alone.