Retina Anatomy 1
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Retina
The innermost layer of the eye
Neural layer
Located between the choroid and vitreous
Thin and Transparent
Thickest in the macular region and thins out as the retina goes further out in the periphery
Extends from the optic disc in both directions to the ora serrata
Reddish color of retina
combination of the retinal pigment epithelium, choroid, and choroidal vasculature
phototransduction
Photoreceptor cells (Rods/Cones) transform photons of light into a neural signal
This signal is than sent to optic nerve and finally the brain
photoreceptor cells turn photons into neural signals → bipolar cells → ganglion cells → optic nerve → brain
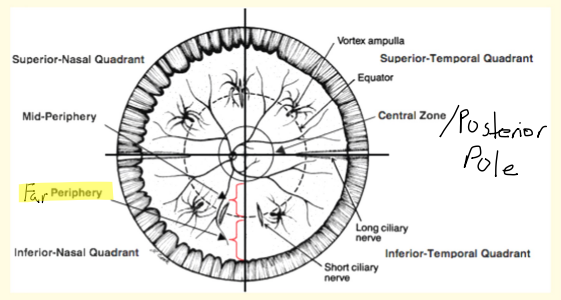
Zones in the Retina
Posterior Pole: central zone of the retina
Mid-Periphery: Extends from the posterior pole to the posterior edge of the vortex veins
Equator: Located right at the posterior edge of the ampulla of a vortex vein
Far Periphery: Extends from the anterior edge of the ampulla of the vortex vein to the ora serrata
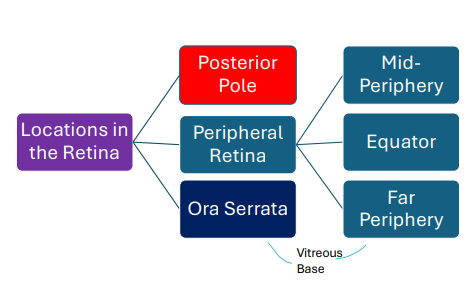
Posterior Pole (Central Retina)
Takes up very little area - optic nerve, macula, vascular arcades, and arcuate retinal nerve fibers
Majority of the cones and ganglion cells are found here
Designed for VA, detail, and color (photopic vision)
The edge of the temporal optic disc is 3.7 (3.4?) mm away from the fovea (center of macula)
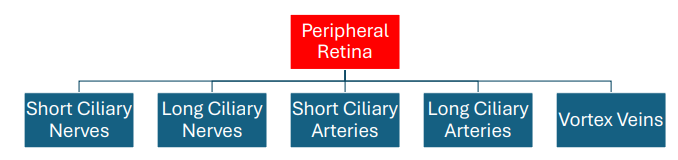
Peripheral Retina
Takes up most of the area - equator, mid-periphery, and far periphery
Majority of the rods are found here
Designed for gross form and motion, less clear but more sensitive to motion (scotopic vision)
Key Structures Found In The Peripheral Retina
Short Ciliary Nerves
Long Ciliary Nerves
Short Ciliary Arteries
Long Ciliary Arteries
Vortex Veins
Short Ciliary Nerves (peripheral retina)
About 8-10 short ciliary nerves present per eye
Seen between 10 to 2 o’clock and 4 to 8 o’clock (nasal and temporal half)
arises from ciliary ganglion
Sensory (CN V1), sympathetic, and parasympathetic (CN III & CN VII) information transmitted to Sphincter muscle in iris, ciliary body, cornea
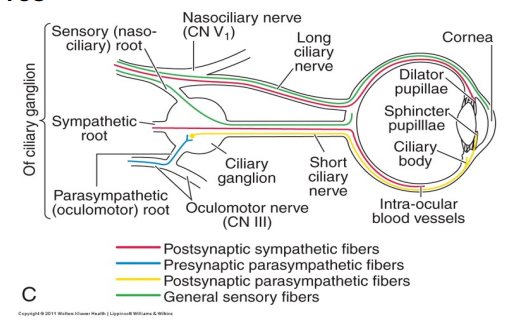
Long Ciliary Nerves (peripheral retina)
2 long ciliary nerves are present per eye
Found at 3 and 9 o’clock (superior and inferior half)
Sensory (Nasocilliary branch of CN V1) and sympathetic information to Dilator muscle in iris, ciliary body, cornea, conjunctiva
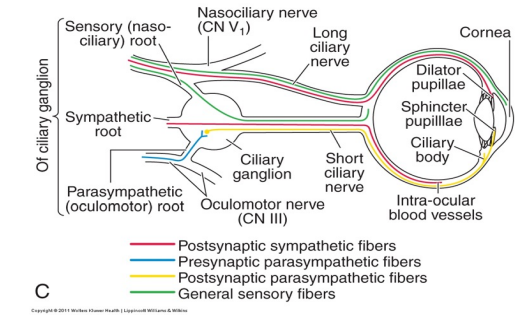
Short Ciliary Arteries (peripheral retina)
from the ophthalmic artery and divides into 10-20 branches
entwine with the short ciliary nerves
Long Ciliary Arteries (peripheral retina)
from the ophthalmic artery and divides into 2 branches
entwine with the long ciliary nerves
Vortex Veins (peripheral retina)
• Composed of tributary veins that come together at an ampulla
• Drains the vascular supply of the choroid
• About 4-8 vortex veins are present per eye (About 70% of eyes have more than 4 vortex veins)
• Are typically found in the oblique regions of the retina (IN, IT, ST, SN)
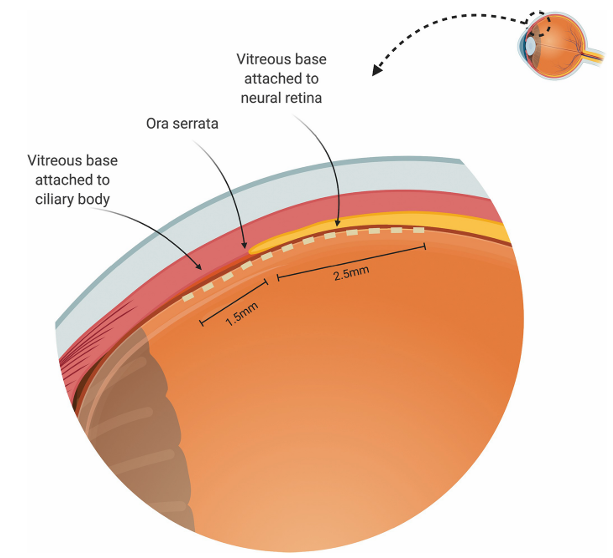
Ora Serrata
Made of dentate processes (Retina) and Bays (Pars Plana).
Serrated junction (Most serrated nasally) between the retina and ciliary body
equator region
posterior edge of the ampulla, about 2 disc diameters posterior to the vortex veins
vitreous base
Site of the strongest attachment of the vitreous to the retina
straddles the ora serrata
Anterior border: 1.5 mm anterior into the pars plana (ciliary body)
Posterior border: 2-3 mm posterior to ora serrata (2 mm temporal, 3 mm nasal)
Overall, about a 3-6mm wide zone
Right Vs. Left Eye
Optic nerve is closest to the nose
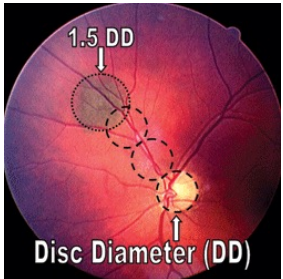
disc diameter (DD)
A disc diameter (DD) is equivalent to the size of the optic disc
• 1 Disc Diameter (DD) = 1,500 microns
• 100 microns = 0.1mm
• 1 degree = 300 microns
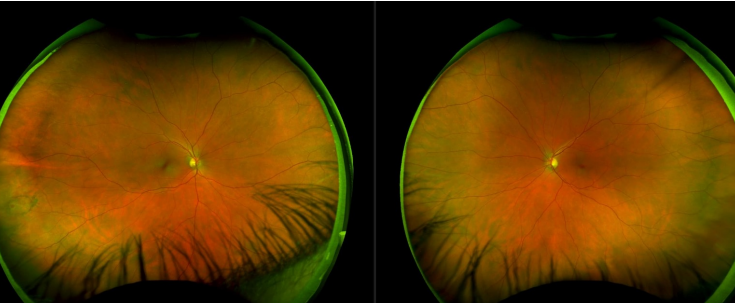
Describe The Location Of The White Without Pressure
Left eye
Superior Temporal
Zone: Far periphery
In relation to optic nerve, more anterior
In relation to ora serrata, more posterior
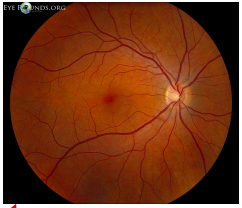
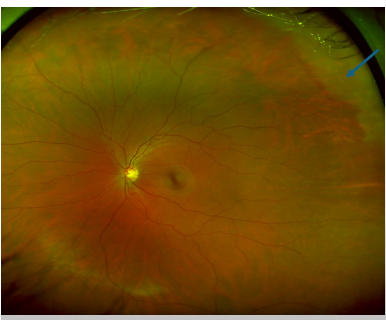
How Would You Describe The Choroidal Nevus Seen In The Retinal Photo?
1.55 DD H X 1.5 DD V (1.5 DD round)
choroidal nevus is noted about 1.75 DD superior nasal to optic nerve in the left eye
Anterior to the optic nerve head
Posterior to the equator
Fluorescein Angiography (FA)
Highlights the optic nerve, retinal, and choroidal circulation
Useful in detection of subclinical retinal/choroidal/optic nerve changes secondary to vascular conditions
Application:
• Diagnosis of retinal, choroidal, and optic nerve head vascular disorders
• Aids in treatment decisions
• Guides retinal laser therapy
Pathway: internal carotid → ophthalmic artery → choroid via short posterior ciliary arteries , retina via central retinal artery and cilioretinal artery
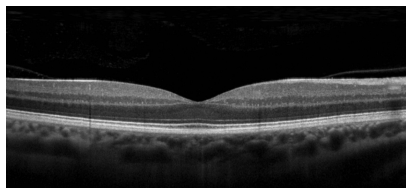
OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography)
helps visualize pathologies in each layer of the retina
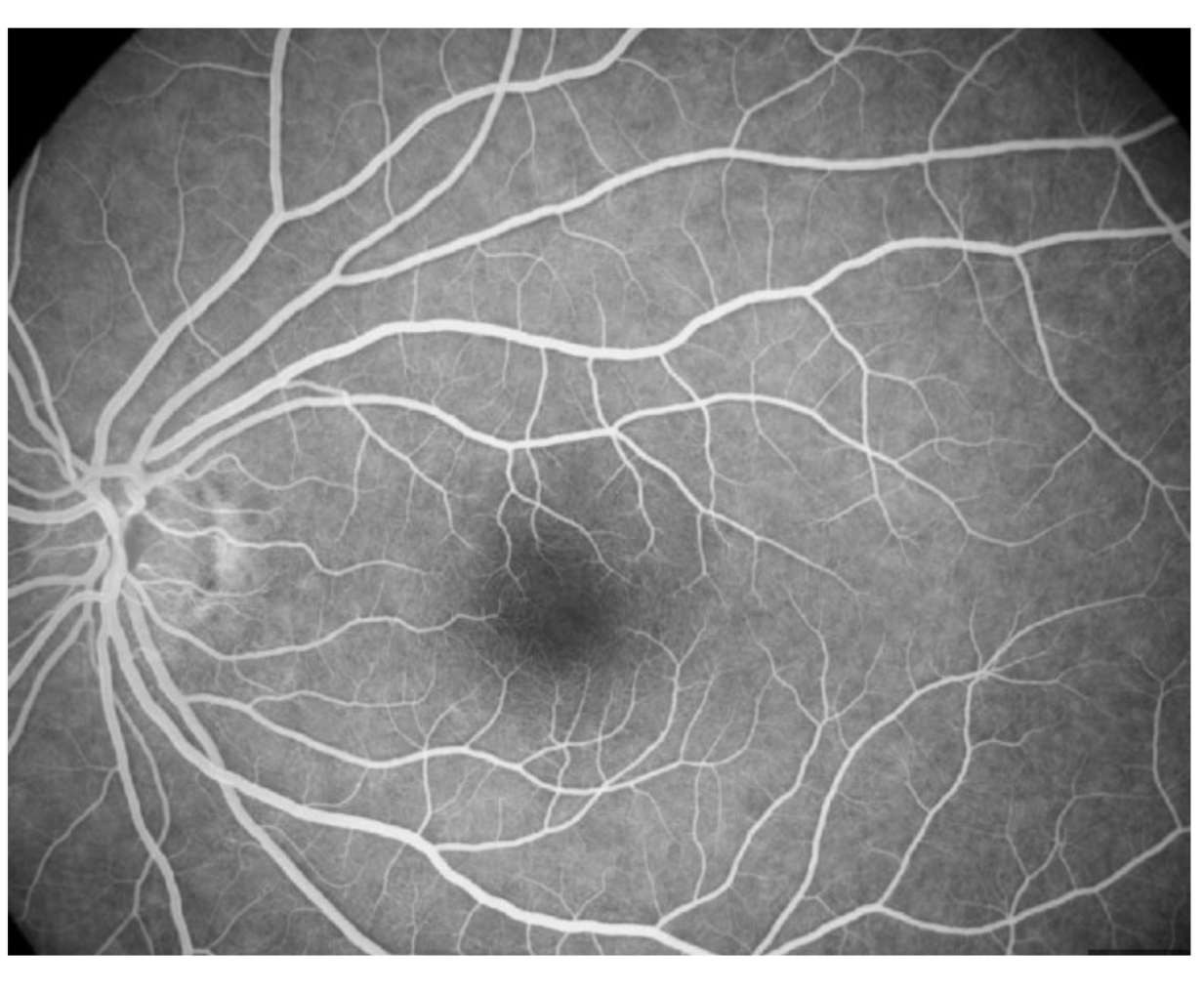
OCT-A (Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography)
visualize vessels of the retina and choroid non-invasively
Vessels are able to be visualized based on active blood flow
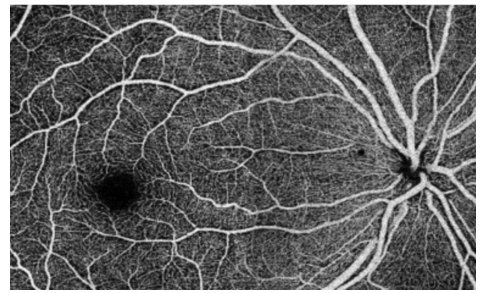

What is wrong with this OCT-A picture?
The outer retina should have no blood vessels
Wet macular degeneration
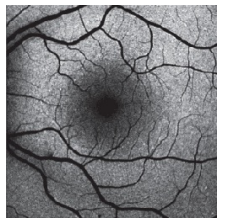
FAF (Fundus Autofluorescence)
Reflects Lipofuscin at the level of the RPE
When photoreceptors shed their outer segments, the RPE ingests these outer segments through phagocytosis.
These molecules are stored in liposomes and form lipofuscin
RPE cells are made up of 25% lipofuscin. Reason why central retina normally has a slight glow on FAF
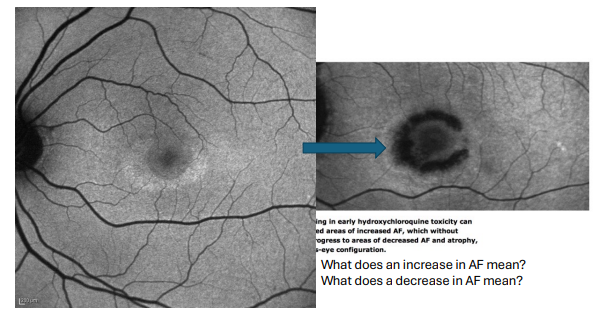
Plaquenil maculopathy on Fundus Aurofluorescence
Increased AF = excess lipofuscin accumulation
Decreased AF = loss/death of RPE cells
Bright: increase in lipofuscin (increase in break down of rods/cones) → Over time, becomes dark because photoreceptors are dead (irreversible)
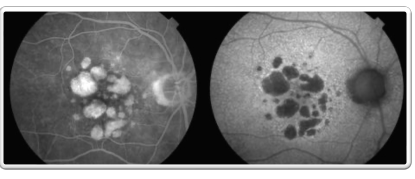
Geographic Atrophy: FA vs FAF
Fluorescein Angiography (FA): blood vessels bright
Fundus Autofluorescence (FAF): blood vessels dark
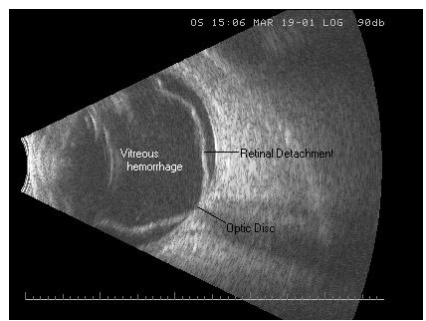
B-scan Ocular UltraSound
uses high-frequency sound waves to localize and define the shape and extension of a lesion through the eyelid
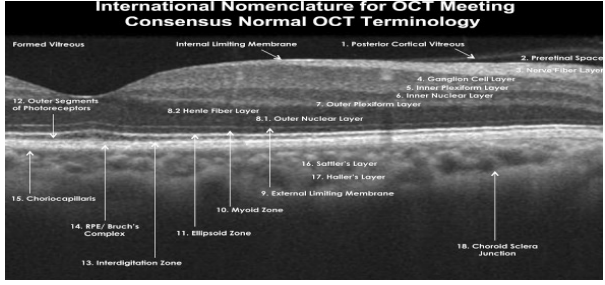
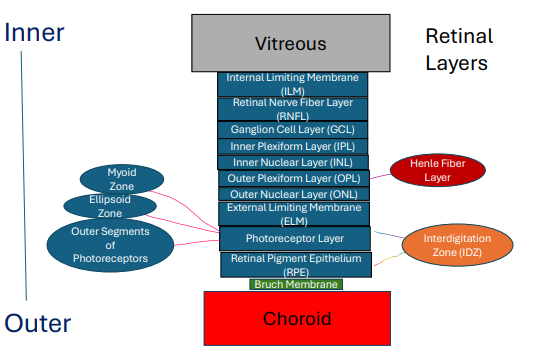
10 main layers of the retina from inner (Closest to vitreous) to outer (Closest to choroid)
• Internal limiting membrane (ILM)
• Retinal Nerve fiber layer (NFL)
• Ganglion cell layer (GCL)
• Inner plexiform layer (IPL)
• Inner nuclear layer (INL)
• Outer plexiform layer (OPL)
• Outer nuclear layer (ONL)
• External limiting membrane (ELM)
• Photoreceptor layer (Ellipsoid Zone)
• Retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)
In New Generation It Is Only Optometrists Examining Patient’s Retina
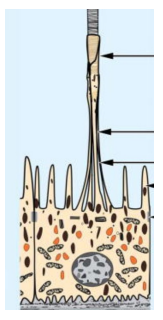
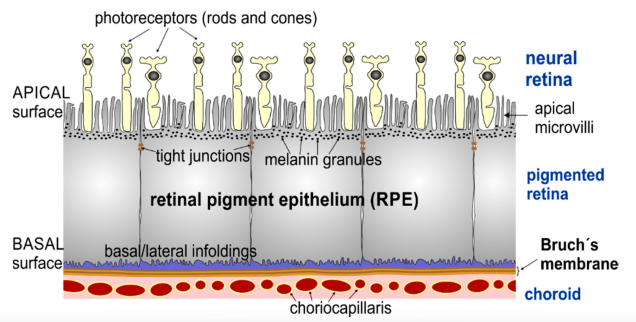
Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE)
The outermost layer of the retina
Lies between Bruch’s membrane and the photoreceptor layer
Single-cell thick, heavily pigmented hexagonal cells (cube-like when viewed as a cross section) , highly metabolic
Heavily pigmented by melanin (melanosomes and lipofuscin), densest at the macula then equator
Pigmentation may increase with age (increase in pigmented bodies, lipofuscin, and breakdown of phagocytic material)
granular appearance of macula
Within individual cells, there is unequal distribution of pigment (Most apparent at the macula since RPE cells are most dense in the macula region)
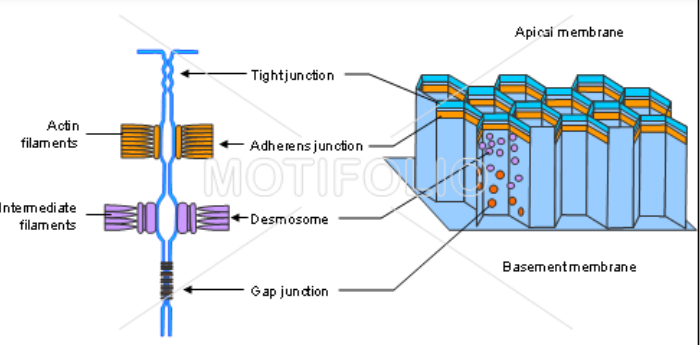
Junctions in the RPE cells
Interlocked by zonulae occludens (tight junctions) and zonulae adherens (anchoring junctions - connects actin filaments) to form an outer blood-retina barrier
Desmosomes (anchoring junctions - connects intermediate filaments) and gap junctions create a channel for ions, metabolites, and nutrients from the choroid
Appearance And Number Of Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE)
Longer, narrower at macula
Flatter, wider near ora serrata (periphery)
Most dense at the macula (Specifically at the fovea) and decrease in density further out in the periphery
Tight Junction of RPE
Zonulae occludens: Prevent passage of material in between cells. Tight seal!! Based on neural signaling, can sometimes allow ions, water soluble materials, etc to pass through
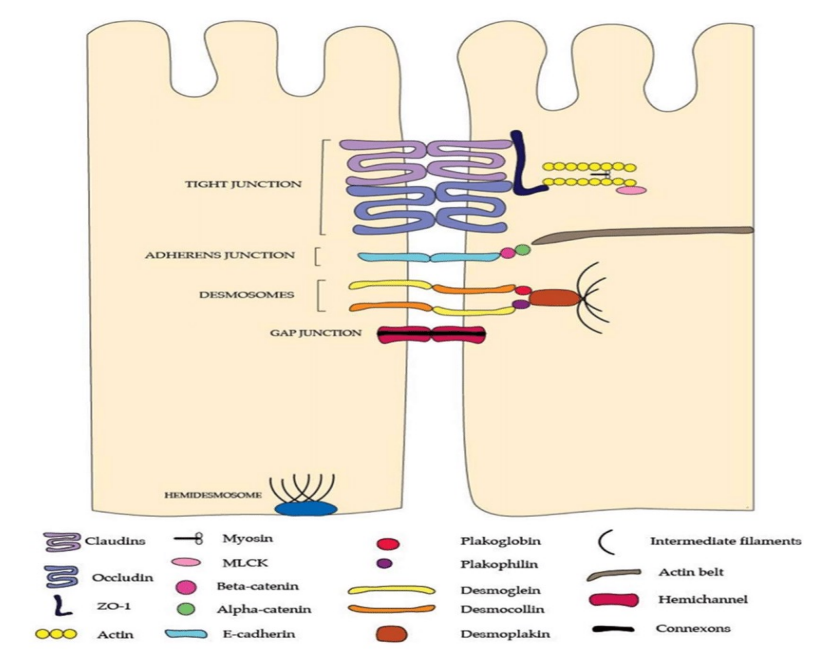
Anchoring Junction of RPE
• Zonulae Adherens: Prevents cells from sliding out of position (Specifically connects actin filaments which is more dynamic and allows for coordination of cell movement).
• Desmosomes: Provides structural support between RPE cells (Specifically connects intermediate filaments with strong adhesion).
• Hemidesmosomes: Provides structural support between an RPE cell and basement membrane (Specifically connects intermediate filaments with strong adhesion)
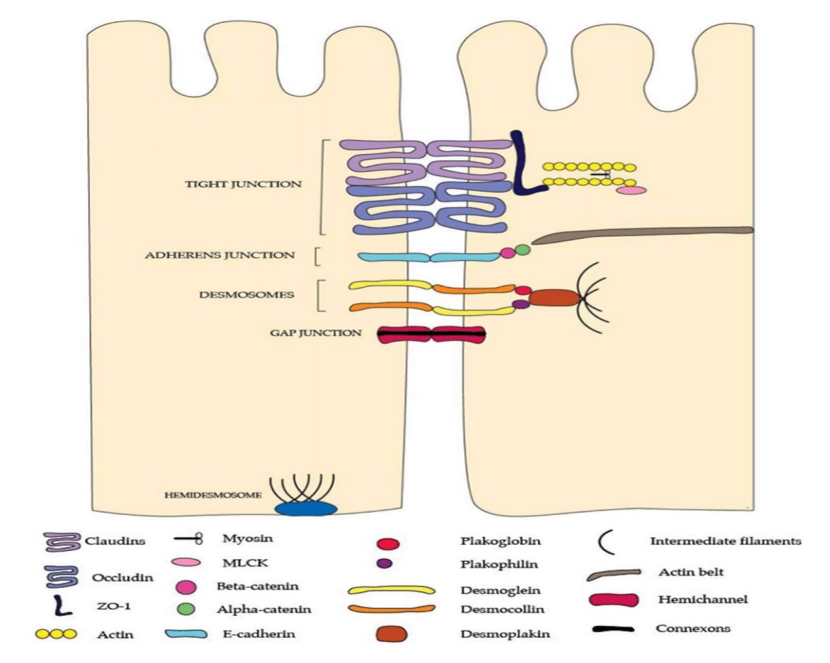
Gap Junction of RPE
Gap Junction: Channel proteins that permit electrical and chemical communication between RPE cells
3 Main Parts To A RPE Cell
Basal Component of RPE cell
majority of the mitochondria
contains infoldings to increase SA for better absorption of nutrients
very strong adhesion to Bruch’s membrane via: infoldings, extracellular matrix proteins (fibronectin, vitronectin, laminin, collagen IV)Location of the large oval nucleus, and hemidesmosomes
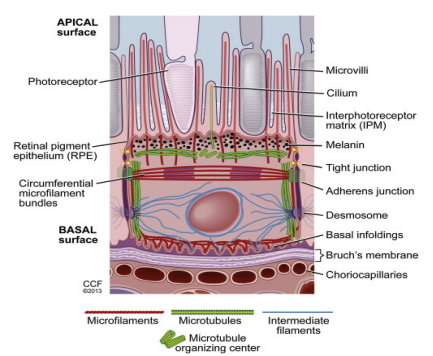
Central Component of RPE cell
Location of the large oval nucleus
Apical Component of RPE cell
closest to the photoreceptors
Microvilli, which are located at the apical portion of the RPE, extend to outer segment tips of the photoreceptors
Majority of melanin granules are found here as well which are instrumental in absorbing scattered light and stabilizing free radicals
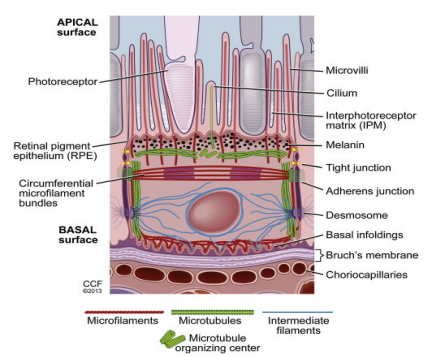
RPE-Photoreceptor Interface
potential space in between the RPE and Photoreceptors: subretinal space
potential space is absent along the peripapillary ring around the optic disc and the ora serrata which means that the neurosensory retina is strongly attached in these areas
5 Reasons For RPE-Photoreceptor Attachment
1. IOP
2. Osmotic pressure (Higher than normal)
3. Vitreous
4. Apical Microvilli of the RPE
5. Interphotoreceptor matrix (IPM)
IOP And RPE-Photoreceptor Attachment
Low IOP - risk of retinal detachment
Function Of The RPE
1. Absorption of scattered light (Decreases photo-oxidative stress to the retina)
2. Control of fluid, nutrients, and waste products
3. Visual pigment (Such as rhodopsin) regeneration and synthesis
4. Key for the visual cycle
5. Synthesis of signaling molecules
PDGF: Controls cell growth and healing
PEDF: Neuroprotectant
VEGF: Stimulates normal vascular growth and neovascularization
TGF: Controls inflammation
6. Phagocytosis of photoreceptor waste
7. Involved in regeneration and repair if there is retinal damage
8. Stores Vitamin A
9. Synthesizes IPM
10. Acts as the outer-blood retina barrier especially due to the tight junctions found in the RPE
Interdigitation Zone (IDZ)
apices of the RPE cells encase part of the cone outer segments as well as the rod outer segments
Typically only visible in the posterior pole
Part of the subretinal space
Verhoeff Membrane
Surrounds the apical portion of RPE
Composed of tight junctions between RPE cells
Found in the interdigitation zone