Supply and Demand - Chapter 3 - ECON100
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Competitive market
Has many buyers and sellers of the same good or service, none of whom can influence the price
The supply demand model
A model of how a competitive market behaves
Five key elements of the supply demand model
Demand curve
Supply curve
Factors that can shift the demand curve and factors that can shift the supply curve
Market equilibrium
changes in market equilibrium
Demand
Represents the behavior of buyers
Demand schedule
A table showing how much of a good or service consumers will want to buy at different prices
Demand curve
Shows the quantity demanded at various prices
A rightward shift means an increase in demand
A leftward shift means a decrease in demand
Quantity demanded
The quantity that buyers are willing and are able to purchase at a particular price
Law of demand
A higher price for a good leads people to demand a smaller quantity of that good
Complements (effects on demand curve)
If a decrease in the price of one good leads to an increase in demand for another good or vice verse
Consumed together
Examples: Cars and gas, shoes and socks
Normal good (changes in income; effects on demand curve)
Demand increases when income increases
Inferior good (changes in income; effects on demand curve)
Demand decreases when income increases
Example: you eat less ramen when you can afford better food
Changes in taste (effects on demand curve)
Taste and preferences are subjective and vary among consumers
Seasonal changes or fads have predictable effects on demand
Example: The demand for boots in October rises because of the season
Changes in expectations (effects on demand curve)
If consumers have a choice about the timing of a purchase, they buy according to expectations
Buyers adjust current spending in anticipation of the direction of future prices in order to obtain lowest possible price
Changes in numbers of consumers (effects on demand curve)
As the population of an economy changes, the number of buyers of a particular good also changes, therefore changing its demand
Example: When students leaves for summer, the economy on main street changes
Supply schedule
Shows how much of a good or service would be supplied at different prices
Supply curve
Shows the quantity supplied at different prices
A rightward shift shows an increase in supply
A leftward shift shows a decrease in supply
Quantity supplied
Is the quantity that producers are willing and able to sell at a particular price
Input prices (effects on supply curve)
An increase in the price of an input makes the production more costly for sellers, supply decreases
A fall in the price of an input makes the production less costly for sellers, supply increases
Changes in prices related to goods or services (effects on supply curve)
Inputs used in production have high opportunity cost, sellers will choose to use inputs with the highest profits
Sellers will supply less of a good if profitability falls and vice versa
There are substitutes and complements in production process
Technology (effects on supply curve)
New, better tech enables producers to spend less on inputs, yet still produce the same amount of output
Supply increases
Expectations (effects on supply curve)
The expectation of a higher price for a good in the future decreases current supply of the good
Example: School supplies not being sold in early summer, they start selling at a higher price later in the summer do to a higher demand
The number of producers (effects on supply curve)
Producer entry implies more sellers in the market, increasing supply
Producer exits implies fewer sellers; decreasing supply
Example: As more firms enter the solar installation market, the number of solar installations increases
Equilibrium price
When quantity supplied = quantity demanded
The amount of consumers would purchase at this price is matched exactly by the amount producers wish to sell
The price at which this takes place is ______ _____
Market price
Where consumers don’t have time to compare prices, different stores have different prices
In well established markets there is a uniform price, this is _____ ____
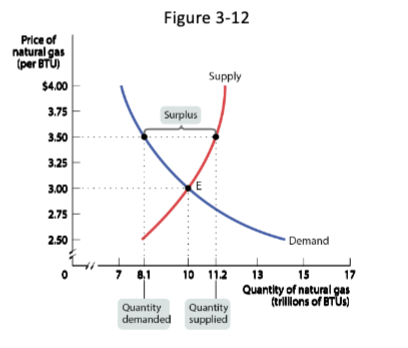
Surplus
There is a _____ of a good when the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded
occurs when the price is above its equilibrium level
Does not last: Sellers will reduce prices to get rid of the good
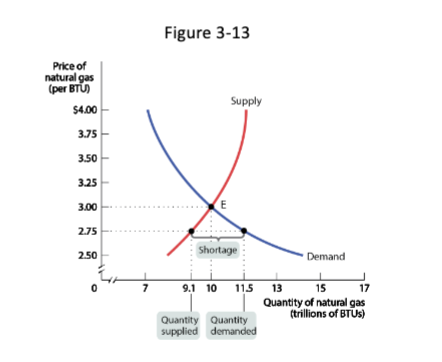
Shortage
When the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied.
Happens when the price is below equilibrium level
Does not last: Sellers will realize they can use higher prices
What happens when the demand curve shifts?
An increase in ____ leads to movement along the supply curve to a higher equilibrium price and a higher equilibrium quantity
What happens when the supply curve shifts?
An increase in ____ leads to a movement along the demand curve to a lower equilibrium price and a higher equilibrium quantity
Decrease = higher equilibrium price and lower equilibrium quantity
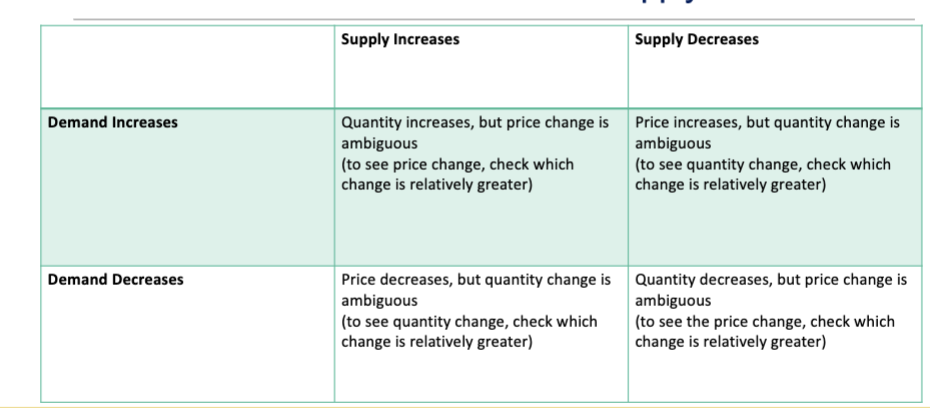
Simultaneous shifts of demand and supply curve
If the decrease in demand is larger than the decrease in supply, the equilibrium price and quantity falls
If the increase in supply is larger than the decrease in demand, the equilibrium quantity rises as the equilibrium price falls